Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Cardiac Pacemakers
Încărcat de
Dhruv SridharDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Cardiac Pacemakers
Încărcat de
Dhruv SridharDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
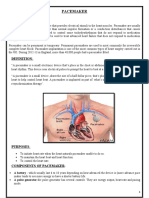
CARDIAC PACEMAKERS..
What is a PACEMAKER..??
The contraction of heart muscle in all animals with hearts is initiated by chemical impulses. The rate at which these impulses fire controls the heart rate. The cells that create these rhythmical impulses are called pacemaker cells, and they directly control the heart rate.
Where is a PACEMAKER located..??
The pacemaker is located in the wall of the right atrium.
Primary (SA node)
The sinoatrial node (SA node) is a group of cells positioned on the wall of the right atrium, near the entrance of the superior vena cava. These cells are modified cardiomyocyte. The cells in this node possess the ability of producing electrical impulses.
Secondary (AV junction and Bundle of His)
If the SA node does not function, a group of cells further down the heart will become the heart's pacemaker, this is known as an ectopic pacemaker. These cells form the atrioventricular node (AV node), which is an area between the left atria and the right ventricles, within the atrial septum. These are called the secondary pacemaker.
Generation of Action Potentials..
There are three main stages in the generation of an action potential in a pacemaker cell. There is no phase one or two, just phases zero, three and four. The key to the rhythmic firing of pacemaker cells is that, unlike muscle and neurons, these cells will slowly depolarize by themselves.
Phase 4 - Pacemaker potential Phase 0 - Upstroke Phase-3 Repolarization
For the heart to beat properly, the signal must travel down a specific path to reach the ventricles, the heart's lower (pumping) chambers. The natural pacemaker may be defective, causing the heartbeat to be too fast,too slow or irregular. The heart's electrical pathways also may be blocked. Hence , after a period, artificial pacemakers are used.
What is an ARTIFICIAL PACEMAKER..??
Cardiac pacemakers are generally used to manage a slow or irregular heart rate. The pacemaker system applies precisely timed electrical signals to induce heart muscle contraction and cause the heart to beat in a manner very similar to a naturally occurring heart rhythm
Components of an Artificial Pacemaker..
Pulse Generator At Least One Electrode One Or Two Pacing Leads Connecting The Pacemaker To The Heart
Where is it placed..??
It is usually implanted between the skin and pectoral muscle. The sealed lithium iodine battery provides electrical energy to the pacemaker. This battery replaced the mercury-zinc battery in 1975, extending the life of some pacemaker models by over 10 yr.The circuitry converts the electrical energy to small electrical signals.
Block Diagram Of A Pacemaker..
Recent Trends in Pacemakers..
Nuclear powered pacemakers
Various Power Sources Have Been Used For Pacemakers, Including A Radioactive Material Called Plutonium-238. There Are Still A Number Of People In The U.S. Who Have Nuclear Powered Pacemakers, Which Need To Be Disposed Of Properly Upon Removal.
Battery-free pacemakers
Now there are so many researches going under this topic and there are evolving methods. One such method is combining the implanted device with a microgenerator producing electricity every time the patient moves, effectively eliminating the need for an internal battery.
Wireless Pacemakers
These are the pacemakers that communicate wirelessly with a monitoring service, which is in turn accessed daily by the doctor.The device can be reprogrammed using wireless signals.This method reduces the no of surgeries that the patient has to undergo.
Laser Pacemakers
Biomedical engineers have used a laser beam with a 1.875-micrometer wavelength to force the quail embryo's heartbeat to speed up, The engineers also hope that this work might one day lead to an optical pacemaker for humans, but several obstacles remain.
SMS-capable pacemakers
The latest application is an SMS-enabled pacemaker that can automatically send messages to a cardiologist's cellphone, allowing the doctor to monitor a patient's condition. The unit was developed by Dutch manufacturer Biotronik, and the first implant was performed at VU University Medical Center in Amsterdam.
Lead-Less Pacemakers
This is a kind of pacemaker which can be implanted directly into our heart via catheter and permanently latch itself into flesh with tiny claws. Then, doctors can wirelessly monitor and even control the device from a nearby phone.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- SBM1403 Unit1Document64 paginiSBM1403 Unit1Balasaraswathi SÎncă nu există evaluări
- PACEMAKERDocument5 paginiPACEMAKERPoonam ThakurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Artificial PacemakerDocument17 paginiArtificial PacemakerNEX456Încă nu există evaluări
- PacemakerDocument26 paginiPacemakerAswathy RCÎncă nu există evaluări
- ENGL 200 Technical Description Paper (Cardiac Pacemaker) Final DraftDocument7 paginiENGL 200 Technical Description Paper (Cardiac Pacemaker) Final DraftSara FarheenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study On PacemakersDocument6 paginiCase Study On PacemakersBalamuruganÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Heart'S Conduction System and "Natural Pacemaker "Document8 paginiThe Heart'S Conduction System and "Natural Pacemaker "merin sunilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Implantable PacemakerDocument33 paginiImplantable PacemakerShifa Fauzia AfrianneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Artificial PacemakerDocument3 paginiArtificial PacemakerChristian Bartl - bartlweb.netÎncă nu există evaluări
- Q: Characterize The Different Types of Pacemaker. Explain The Various Steps of PacingDocument4 paginiQ: Characterize The Different Types of Pacemaker. Explain The Various Steps of PacingKRUPALITHAKKAR100% (1)
- Artificial Cardiac PacemakersDocument25 paginiArtificial Cardiac Pacemakersanimesh pandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Investegatory Project: Artificial PacemakerDocument18 paginiBiology Investegatory Project: Artificial PacemakerNirupama DesaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pacemaker InformatiiDocument4 paginiPacemaker InformatiiAndreea MitranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1 - Cardiac Care UnitsDocument29 paginiUnit 1 - Cardiac Care UnitssitalekshmiÎncă nu există evaluări
- PacemakersDocument22 paginiPacemakersapi-3757838Încă nu există evaluări
- Pacemaker Physics Research - High SchoolDocument7 paginiPacemaker Physics Research - High SchoolJose Rene BerliozÎncă nu există evaluări
- Setting The Pace: Pacemaker Principles: AcknowledgementsDocument40 paginiSetting The Pace: Pacemaker Principles: AcknowledgementsbenypermadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pacemaker: Presented byDocument16 paginiPacemaker: Presented bynivethitha priyadharshiniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pacemaker Physics ResearchDocument6 paginiPacemaker Physics ResearchJose Rene BerliozÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understanding The Heart's Electrical System: Cardiac PacemakerDocument5 paginiUnderstanding The Heart's Electrical System: Cardiac PacemakerDitaMaryaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- EKG/ECG Interpretation Made Easy: A Practical Approach to Passing the ECG/EKG Portion of NCLEXDe la EverandEKG/ECG Interpretation Made Easy: A Practical Approach to Passing the ECG/EKG Portion of NCLEXEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (2)
- Cardiac Pacemaker: BY E.DeepikaDocument17 paginiCardiac Pacemaker: BY E.Deepikadeepika_164Încă nu există evaluări
- Recent Trends in Medical Imaging by Using VLSIDocument4 paginiRecent Trends in Medical Imaging by Using VLSIinventyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Converts: That Energy From One Form To AnotherDocument2 paginiConverts: That Energy From One Form To AnotherSalim EchbarbiÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Ultrasonic Implant For Fighting Heart Failure: Guided byDocument19 paginiAn Ultrasonic Implant For Fighting Heart Failure: Guided byANJU KOLLAKKARAN ThomasÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is A Pacemaker?Document4 paginiWhat Is A Pacemaker?Abhishek MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pacemaker Learning Package: Paula Nekic CNE Liverpool Hospital ICU January 2016Document46 paginiPacemaker Learning Package: Paula Nekic CNE Liverpool Hospital ICU January 2016Deepak BhatÎncă nu există evaluări
- EKG Interpretation: Making EKG/ECG Interpretation Easy!De la EverandEKG Interpretation: Making EKG/ECG Interpretation Easy!Încă nu există evaluări
- Ei 65 Unit 5Document31 paginiEi 65 Unit 5karthiha12Încă nu există evaluări
- Ekg Ecg Interpretation by DR Jason Lowe PDF Bb3 DR NotesDocument79 paginiEkg Ecg Interpretation by DR Jason Lowe PDF Bb3 DR NotesGuru RewriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pacemakers PK2 Jan2018Document16 paginiPacemakers PK2 Jan2018ItachiÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Review On Pacemakers: Device Types, Operating Modes and Pacing Pulses. Problems Related To The Pacing Pulses DetectionDocument12 paginiA Review On Pacemakers: Device Types, Operating Modes and Pacing Pulses. Problems Related To The Pacing Pulses DetectionsdekapureÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pacemaker Implantation and Follow-Up CareDocument3 paginiPacemaker Implantation and Follow-Up CareRiya BhoyarÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Hearts Conduction SystemDocument4 paginiThe Hearts Conduction System8pvz96ktd9Încă nu există evaluări
- EKG | ECG: An Ultimate Step-By-Step Guide to 12-Lead EKG | ECG Interpretation, Rhythms & Arrhythmias Including Basic Cardiac DysrhythmiasDe la EverandEKG | ECG: An Ultimate Step-By-Step Guide to 12-Lead EKG | ECG Interpretation, Rhythms & Arrhythmias Including Basic Cardiac DysrhythmiasEvaluare: 3 din 5 stele3/5 (5)
- What Is A Defibrillator?Document8 paginiWhat Is A Defibrillator?Rajib RajuÎncă nu există evaluări
- PacemakersDocument19 paginiPacemakersAswathy RCÎncă nu există evaluări
- PacemakersDocument12 paginiPacemakersNixter TurnÎncă nu există evaluări
- The HeartDocument10 paginiThe HeartNabil Magdi HasanÎncă nu există evaluări
- PacemakerDocument15 paginiPacemakermariet abraham100% (4)
- Cardiac Pacing For The SurgeonsDocument46 paginiCardiac Pacing For The SurgeonsRezwanul Hoque BulbulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adsız DokümanDocument7 paginiAdsız Dokümanomom omÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrocardiography II StudentDocument20 paginiElectrocardiography II StudentArmando Valdez ZamoranoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pacemaker Patient Information 2021 FINALDocument16 paginiPacemaker Patient Information 2021 FINALardhenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ++ 437-1692-1-PBDocument9 pagini++ 437-1692-1-PBAli TarkashvandÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pacemaker and TypesDocument7 paginiPacemaker and TypesPrathamesh ShindeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electro-Medical Applications: Physics For Medical Students - MaradiDocument31 paginiElectro-Medical Applications: Physics For Medical Students - MaradiHadassah ImbansÎncă nu există evaluări
- Major Project Phase 1 Report CloudDocument35 paginiMajor Project Phase 1 Report CloudPraj CÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interpreting AV (Heart) Blocks: Breaking Down The Mystery: 2 Contact HoursDocument29 paginiInterpreting AV (Heart) Blocks: Breaking Down The Mystery: 2 Contact HoursAsri RachmawatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECG Circuit GuideDocument24 paginiECG Circuit Guideapi-3854767100% (2)
- Medical Electronics Unit 3Document64 paginiMedical Electronics Unit 3TamilselvanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillators: Pacemakers & DefibrillatorsDocument2 paginiImplantable Cardioverter-Defibrillators: Pacemakers & DefibrillatorsGo StargÎncă nu există evaluări
- IEEEDocument5 paginiIEEESanjana GururajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Implantable CardioverterDocument5 paginiImplantable CardioverterpratonyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mount Zoin Engineering & Technology Cycle Test Ii Medical Electronic-Ec1006Document11 paginiMount Zoin Engineering & Technology Cycle Test Ii Medical Electronic-Ec1006bhagyampÎncă nu există evaluări
- EKG | ECG Interpretation. Everything You Need to Know about 12-Lead ECG/EKG InterpretationDe la EverandEKG | ECG Interpretation. Everything You Need to Know about 12-Lead ECG/EKG InterpretationEvaluare: 3 din 5 stele3/5 (1)
- Rohini 13809826106Document7 paginiRohini 13809826106shivalishivali590Încă nu există evaluări
- 4 2 3 A Ekg Student Response Sheet (Revised 2 23 15)Document8 pagini4 2 3 A Ekg Student Response Sheet (Revised 2 23 15)api-281824634100% (1)
- Data Asimilasi Untuk PemulaDocument24 paginiData Asimilasi Untuk PemulaSii Olog-olog PlonkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Seabank Statement 20220726Document4 paginiSeabank Statement 20220726Alesa WahabappÎncă nu există evaluări
- 레벨 테스트Document2 pagini레벨 테스트BÎncă nu există evaluări
- CN1111 Tutorial 4 QuestionDocument3 paginiCN1111 Tutorial 4 Questionthenewperson0% (1)
- Binary OptionsDocument24 paginiBinary Optionssamsa7Încă nu există evaluări
- Exotic DVM 11 3 CompleteDocument12 paginiExotic DVM 11 3 CompleteLuc CardÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Econometrics Questions and AnswersDocument3 paginiBasic Econometrics Questions and AnswersRutendo TarabukuÎncă nu există evaluări
- S4 HANALicensing Model External V19Document28 paginiS4 HANALicensing Model External V19Edir JuniorÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 Minute Pediatric ConsultDocument5 pagini5 Minute Pediatric Consultajescool0% (4)
- Item Analysis and Test BankingDocument23 paginiItem Analysis and Test BankingElenita-lani Aguinaldo PastorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Atomistic Simulation Through Density Functional TheoryDocument21 paginiIntroduction To Atomistic Simulation Through Density Functional TheoryTarang AgrawalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Notes On Antibodies PropertiesDocument3 paginiNotes On Antibodies PropertiesBidur Acharya100% (1)
- Open Source NetworkingDocument226 paginiOpen Source NetworkingyemenlinuxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Concrete Repair Manual (2017)Document59 paginiConcrete Repair Manual (2017)Fernando EscriváÎncă nu există evaluări
- EAC Inquiry SDCDocument9 paginiEAC Inquiry SDCThe Sustainable Development Commission (UK, 2000-2011)Încă nu există evaluări
- List of Iconic CPG Projects in SingaporeDocument2 paginiList of Iconic CPG Projects in SingaporeKS LeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- SreenuDocument2 paginiSreenuSubbareddy NvÎncă nu există evaluări
- 24 DPC-422 Maintenance ManualDocument26 pagini24 DPC-422 Maintenance ManualalternativblueÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10 Killer Tips For Transcribing Jazz Solos - Jazz AdviceDocument21 pagini10 Killer Tips For Transcribing Jazz Solos - Jazz Advicecdmb100% (2)
- Iphone and Ipad Development TU GrazDocument2 paginiIphone and Ipad Development TU GrazMartinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alternative Network Letter Vol 7 No.1-Apr 1991-EQUATIONSDocument16 paginiAlternative Network Letter Vol 7 No.1-Apr 1991-EQUATIONSEquitable Tourism Options (EQUATIONS)Încă nu există evaluări
- Organic Chemistry 1Document265 paginiOrganic Chemistry 1Israk Mustakim IslamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Battery Guide - 2021Document27 paginiBattery Guide - 2021Mario LaurieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kapinga Kamwalye Conservancy ReleaseDocument5 paginiKapinga Kamwalye Conservancy ReleaseRob ParkerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Class 3 ThirdDocument1 paginăComputer Class 3 ThirdbeakraamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Roxas City For Revision Research 7 Q1 MELC 23 Week2Document10 paginiRoxas City For Revision Research 7 Q1 MELC 23 Week2Rachele DolleteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aakriti 1Document92 paginiAakriti 1raghav bansalÎncă nu există evaluări
- National Football League FRC 2000 Sol SRGBDocument33 paginiNational Football League FRC 2000 Sol SRGBMick StukesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multimodal Essay FinalDocument8 paginiMultimodal Essay Finalapi-548929971Încă nu există evaluări
- CSE 202.04 Inspection of Concrete StructuresDocument67 paginiCSE 202.04 Inspection of Concrete StructuresJellyn BaseÎncă nu există evaluări