Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Exhaust Hoods
Încărcat de
Mohammed MustafaDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Exhaust Hoods
Încărcat de
Mohammed MustafaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Design calculation sheet
Project no: Subject: Date:
4/13/2012 Sheet no.:
Computed by: Checked by: Approved by:
Exhaust hoods
Exhaust hoods are essential in kitchens, laboratories and many industrial application for removing fumes, mists, vapors, aerosols, particulates, hazardous substances, polluting contaminants
In general, for an exhaust hood to be efficient the height - y - should not exceed 1.20 m (4 ft) the distance - x - should not be less than 1/3 y the capture velocity - v 1 - should not be less than 0.15 - 0.20 m/s (30 - 40 ft/min) Note! Potential hazardous and polluting applications requires special solutions. Always check local regulations. The capture velocity - v 1 - of the exhaust hood can be estimated with the empirical equation v1 = q / 2 y2 c (1) where v 1 = capture velocity (m/s) q = air volume flow (m 3 /s) y = distance between table and exhaust hood (m) c = circumference of the hood (m) (1) can be modified to calculate required air volume q = 2 v1 y2 c (1a)
Exhaust Hood Calculator
The air flow volume in the exhaust hood can be calculated below 0.2 1.2 3 1.728 3661 capture velocity - v1 - (m/s) vertical distance from table to hood - y - (m) circumference exhaust hood - c - (m) Air Volume Flow (m3/s) Air Volume Flow (CFM)
Exhaust Hood with internal Plate
The efficiency of an exhaust hood can be improved by adding an internal plate.
The required air volume for an exhaust hood with a plate can in general be reduced to approximately 80% compared to an exhaust hood without a plate.
Exhaust Hood with Side Walls
The exhaust hood efficiency can be further improved by adding side walls.
Design calculation sheet
Project no: Subject:
09-15-1
Date:
######## Sheet no.:
of
Computed by: Checked by: Approved by:
Smoke Evacuation Fan
Pressurisation Fan
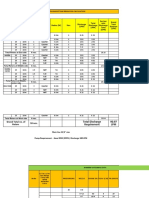
30" x 30" 12600 CFM capture velocity - v1 - (m/s)
Roof
30" x 30" 10200 CFM 30" x 18" 6800 CFM 22"x18" 3400 CFM
Grille Sizing based on 1000 fpm face velocity 4 grilles =>
Second
P.D =
First
Fan Selected : Woods
Model :.. Ground
SR 750x500
380/3/60
###### HP
DESIGN CALCULATION
Data
Building Height (m) 0 5 25 50 100 150
Fire Pressure (Pa) 8.5 8.5 8.5 8.5 8.5 8.5
Wind Stack Effect (Pa) 8 8 10.5 13 19.5 29.5
Design Pressure (Pa) 25 25 25 50 50 50
Size Single Leaf Doors in Frame Opening into Pressurized Space Single Leaf Doors in Frame Opening Outwards Double Leaf Doors with or without Central Rebate Lift Door
Crack Leakage Length (m) Area (m2) 5.6 5.6 9.2 8.0 0.01 0.02 0.03 0.06
2 m x 800 mm 3 m x 800 mm 2 m x 1.6 m 2 m High x 2 m Wide
Double Leaf Doors with or without Central Rebate
7.2.3.9 Stair Pressurization. 7.2.3.9.1 Smokeproof enclosures using stair pressurization shall use an approved engineered system with a design pressure difference across the barrier of not less than 0.05 in. water column (12.5 Pa) in sprinklered buildings, or 0.10 in. water column (25 Pa) in nonsprinklered buildings, and shall be capable of maintaining these pressure differences under likely conditions of stack effect or wind. The pressure difference across doors shall exceed that which allows the door to begin to be opened by a force of 30 lbf (133 N) in accordance with 7.2.1.4.5. 7.2.1.4.5 The forces required to fully open any door manually in a means of egress shall not exceed 15 lbf (67 N) to release the latch, 30 lbf (133 N) to set the door in motion, and 15 lbf (67 N) to open the door to the minimum required width. Opening forces for interior side-hinged or pivoted-swinging doors without closers shall not exceed 5 lbf (22 N). These forces shall be applied at the latch stile.
Page 4
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- General Introduction: Need To Determine Pollutant Concentration at Stack Discharge Conditions (CD)Document8 paginiGeneral Introduction: Need To Determine Pollutant Concentration at Stack Discharge Conditions (CD)Shailin Shah100% (1)
- Consulting Service Report: Comments ActionDocument4 paginiConsulting Service Report: Comments ActionVijayakumar KarunanidhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Receiver SizingDocument7 paginiReceiver SizingjsaulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cerexen Nitrogen 200 Bar Calculation v2-2Document29 paginiCerexen Nitrogen 200 Bar Calculation v2-2Nghia Huynh NgocÎncă nu există evaluări
- RTS Heating and Cooling Loads GDS - SI Units Rev 2010-01-20Document1 paginăRTS Heating and Cooling Loads GDS - SI Units Rev 2010-01-20alvinchuanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Excel Fire Calc F Mowrer Templates REV 2.0Document39 paginiExcel Fire Calc F Mowrer Templates REV 2.0Argile-assholeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Foam CalculationsDocument8 paginiFoam Calculationsahmed salemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Equipment Selection & Design - 2Document5 paginiEquipment Selection & Design - 2Nabeel SiddiqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- PWP03 Fire System Pre-Comm PDFDocument3 paginiPWP03 Fire System Pre-Comm PDFJaldoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Smoke Ventilation CalculationDocument4 paginiSmoke Ventilation CalculationJunaid MateenÎncă nu există evaluări
- AED Design Requirements - Hydro-Pneumatic Tanks - Sep09Document5 paginiAED Design Requirements - Hydro-Pneumatic Tanks - Sep09mojeebmashalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Draft: The Calculation of Exhaust Gas DraftDocument2 paginiDraft: The Calculation of Exhaust Gas Draftmvbm31Încă nu există evaluări
- Design CalculationDocument1 paginăDesign Calculationapi-3728508Încă nu există evaluări
- Light Hazard Design Criteria (Guide) : Check Highest Expected Ceiling TemperatureDocument13 paginiLight Hazard Design Criteria (Guide) : Check Highest Expected Ceiling Temperatureمحمد الامينÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fire Protection-Sprinkler Sys (With Min Press 7psi) & Water Supply Sys (042114)Document2 paginiFire Protection-Sprinkler Sys (With Min Press 7psi) & Water Supply Sys (042114)Edwin TorilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3) Sme & Makeup Air CalculationDocument33 pagini3) Sme & Makeup Air CalculationAshiq NishmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pipes. Colebrook-White Equation Solved With Newton-Raphson MethodDocument23 paginiPipes. Colebrook-White Equation Solved With Newton-Raphson MethodJMVÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mr. Unnikrishnan Sprinkler Irrigation Design CalculationDocument32 paginiMr. Unnikrishnan Sprinkler Irrigation Design CalculationsabummathewÎncă nu există evaluări
- Underground Steam & Condensate Piping PDFDocument26 paginiUnderground Steam & Condensate Piping PDFZacky JoeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heat Load EstimationDocument5 paginiHeat Load EstimationSultan FirassuddinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Total Feed Water Through BFW PumpsDocument7 paginiTotal Feed Water Through BFW PumpslightsonsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Integration - H VAC Fans and Smoke Control - Control EngineeringDocument5 paginiIntegration - H VAC Fans and Smoke Control - Control EngineeringMohamedAhmedFawzyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design Calculation Sheet: 1-AbbreviationsDocument2 paginiDesign Calculation Sheet: 1-AbbreviationsOltun KAYAÎncă nu există evaluări
- TCVN - English VersionDocument4 paginiTCVN - English Versionambition1340cnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compressor Settle-Out CalculationDocument4 paginiCompressor Settle-Out CalculationWickyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ventilation DBRDocument16 paginiVentilation DBRVignesh GandhirajÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Design Kitchen HoodDocument2 paginiHow To Design Kitchen HoodSandeep KumawatÎncă nu există evaluări
- PEERLEES Fire Pump PDFDocument175 paginiPEERLEES Fire Pump PDFN. AndradeÎncă nu există evaluări
- M'Sia Fire Stair Pressurization SampleDocument10 paginiM'Sia Fire Stair Pressurization Samplenim_gourav1997Încă nu există evaluări
- Car Park Extract CalculationDocument5 paginiCar Park Extract CalculationShivraj SawantÎncă nu există evaluări
- ASHRAE 90 1 Kadj Calculator Revision 5Document9 paginiASHRAE 90 1 Kadj Calculator Revision 5Basil OguakaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Warning SphereDocument3 paginiWarning SphereantaryamisinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- PL 3900 Battery Room Ventilation SystemDocument2 paginiPL 3900 Battery Room Ventilation SystemcandratrikusumaÎncă nu există evaluări
- FAHUDocument4 paginiFAHUSundar DAACÎncă nu există evaluări
- Centrifugal Pump SizingDocument1 paginăCentrifugal Pump SizingVIVEKZI0Încă nu există evaluări
- SPF Stair Case FanDocument2 paginiSPF Stair Case FanAla ShakerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Expansion Tank SizingDocument1 paginăExpansion Tank Sizinghaysam0% (2)
- Air Conditioning System: Pan Humidifier Load Calculation Building Room1Document1 paginăAir Conditioning System: Pan Humidifier Load Calculation Building Room1psn_kylmÎncă nu există evaluări
- Air Change RateDocument18 paginiAir Change Ratemumbaimale20009776Încă nu există evaluări
- Pipe Size For Cooling Water SystemDocument5 paginiPipe Size For Cooling Water Systemnagu108Încă nu există evaluări
- Chimney CalculationsDocument3 paginiChimney CalculationsSteve WanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fahu 2 (Te)Document15 paginiFahu 2 (Te)Abdo RagabÎncă nu există evaluări
- EQ-502 Curve Fitting - PolynomialDocument8 paginiEQ-502 Curve Fitting - PolynomialadpanfeqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Additional Refrigerant Charge Calculation ToolDocument73 paginiAdditional Refrigerant Charge Calculation ToolStefy CarrascoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oman Hvac Component SpecificationDocument20 paginiOman Hvac Component SpecificationSalley BukhariÎncă nu există evaluări
- TCVN 5738-2001Document16 paginiTCVN 5738-2001undertaker55100% (5)
- tinh tổn thất áp lựcDocument2 paginitinh tổn thất áp lựcNghia Huynh NgocÎncă nu există evaluări
- LP Gas CalculationDocument4 paginiLP Gas Calculationlutfi awnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Duct CalculationsDocument38 paginiDuct CalculationsDilnesa EjiguÎncă nu există evaluări
- Smoke & Ventilation CalculationsDocument9 paginiSmoke & Ventilation CalculationsMarcin NowelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fire EquationsDocument148 paginiFire EquationsArgile-assholeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Apollo and Apollo ATI Natural Smoke VentilatorDocument2 paginiApollo and Apollo ATI Natural Smoke VentilatoradnanÎncă nu există evaluări
- PSYCH v10Document9 paginiPSYCH v10Daniel Puello RodeloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Smoke Management For Retails Calculation PDFDocument1 paginăSmoke Management For Retails Calculation PDFSudhir KulkarniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nitrogen IG100 Fire Supression DESIGN CALCULATION-15Document2 paginiNitrogen IG100 Fire Supression DESIGN CALCULATION-15anwerquadriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ventilation DesignDocument4 paginiVentilation DesignPhyu Mar Thein KyawÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrcial Room Ventilation System Calculation: X 1.005 X 5 Airflow (m3/hr)Document2 paginiElectrcial Room Ventilation System Calculation: X 1.005 X 5 Airflow (m3/hr)psjjoshiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Energy Balance: Hydrogen ProductionDocument7 paginiEnergy Balance: Hydrogen ProductionMohit MangalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design Guide: Hunter Rainwater SystemsDocument5 paginiDesign Guide: Hunter Rainwater SystemsTransgulfÎncă nu există evaluări
- APRV - Pressure Relief VentsDocument4 paginiAPRV - Pressure Relief VentsArt JamesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Torre Sauter 0 - 5 - 320 - 025 - 4 PDFDocument27 paginiTorre Sauter 0 - 5 - 320 - 025 - 4 PDFGuiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ricoh Shotmaster ZoomDocument17 paginiRicoh Shotmaster Zoommanana mappleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pmled 6 5K 10a 66Document6 paginiPmled 6 5K 10a 66Eduardo SalgadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Specification For Construction of Concrete ReservoirsDocument18 paginiSpecification For Construction of Concrete ReservoirsKeysha ApriliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digital Joints Solutions - Sep-2016-CatalogueDocument102 paginiDigital Joints Solutions - Sep-2016-CatalogueiamlpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analysis+of+Non Symmetrical+Flapping+AirfoilsDocument18 paginiAnalysis+of+Non Symmetrical+Flapping+AirfoilsAsif HameedÎncă nu există evaluări
- HRTEMDocument5 paginiHRTEMRajathi YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technical Delivery Condition of S500MCDocument4 paginiTechnical Delivery Condition of S500MCdcevipin100% (1)
- Enzymes and Effects of PHDocument4 paginiEnzymes and Effects of PHSeph Cordova50% (2)
- Understanding IBR 1950Document7 paginiUnderstanding IBR 1950sammar_10Încă nu există evaluări
- GU Pipette Quick Check ENDocument20 paginiGU Pipette Quick Check ENCeren Alim DavutluoğluÎncă nu există evaluări
- MTK 1023-Material and ConsumableDocument13 paginiMTK 1023-Material and ConsumableGraceLamÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 16Document20 paginiCH 16Engr. Talha Riaz PersotaÎncă nu există evaluări
- E5263 - M4A87TD EVO PDFDocument76 paginiE5263 - M4A87TD EVO PDFLeandro Henrique AgostinhoÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Punjab Factory RuleDocument313 paginiThe Punjab Factory Rulesafety_rliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Metode Statement of Fabrication RebarDocument11 paginiMetode Statement of Fabrication RebararifÎncă nu există evaluări
- Servomotor WedgeDocument24 paginiServomotor WedgeAlanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Expansion Joint PDFDocument7 paginiExpansion Joint PDFPramit RajKarnikarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cabos UtpDocument7 paginiCabos UtpRoberto RmoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Revision Question Bank ME 2204Document11 paginiRevision Question Bank ME 2204Rajendra Kumar YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Licenta - Algoritmi de Rezolvare A Cubului Rubik PDFDocument46 paginiLicenta - Algoritmi de Rezolvare A Cubului Rubik PDFRazvan SavucÎncă nu există evaluări
- 82 To 88 CompleteDocument6 pagini82 To 88 CompleteUmer KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Company ProfileDocument6 paginiCompany ProfileFaidzil ChabibÎncă nu există evaluări
- Item 103 Structure ExcavationDocument3 paginiItem 103 Structure ExcavationGerry Velicaria100% (1)
- Concrete Solutions-ProgramDocument18 paginiConcrete Solutions-ProgramEfthymios TatsisÎncă nu există evaluări
- KP Sharma Estimate PDFDocument3 paginiKP Sharma Estimate PDFSudip GhimireÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amyuni PDF ConverterDocument22 paginiAmyuni PDF ConverterMikeyarnoldÎncă nu există evaluări
- Joraform JK Series Operating PrinciplesDocument6 paginiJoraform JK Series Operating Principlesapi-236782993Încă nu există evaluări
- Administration-Guide Open Bee OCSDocument7 paginiAdministration-Guide Open Bee OCSpeka76Încă nu există evaluări
- Makalah Program PDFDocument10 paginiMakalah Program PDFIvanFolkÎncă nu există evaluări