Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Protozoa Revision - Toxoplasma Gondii
Încărcat de
fiena92Descriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Protozoa Revision - Toxoplasma Gondii
Încărcat de
fiena92Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
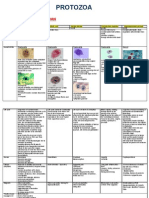
protozoa Portal of entry Final site in the host MOT
Risk groups characteristics
Toxoplasma gondii mouth All organs, esp brain and lymph node Food and water borne (cyst and oocyst) Organ transplant (zoite and cyst) Cats feces (oocyst) Blood transfusion (zoite) Laboratory accidents (zoite) Pregnant woman (zoite) Immunosuppressed patient (cyst, zoite, oocyst) Oocyst
Oval shape More resistant but destroyed in boil water, burning and contact with strong NH3 for 3 hours Tachyzoite
Life cycle
Cresent/oval shape Pseudocyst : tachyzoite + its wall Destroyed : freezing/thawing Bradyzoite Slowing dividing form Destroyed : freezong/irradiation Definitive host : cat Accidental host : human Release of oocysts in the cats feces Shedding of oocysts (infected host) Sporozoites (in intestine) Trophozoites (pseudocyst-endodyogeny) Invade macrophages (lymphatic vessels) Enter blood stream and other intestinal organs True tissue cysts Intracellularly in tissues The immunity is established in healthy host Tissue cysts (dormant bradyzoites) *when host resistant is lowered, cyst is reactivated and bradyzoites are released toxoplasmosis Congenital toxoplasmosis 1st trimester : abortion 3rd trimester : congenital abnormalities infected newborn : ocular involvement, intracerebral calcification, hydrocephalus, psychomotor disturbances and mental retardation ocular toxoplasmosis : acute retinochoroiditis, pain, photophobia, blurred vision, healed scar pale, prominent black spots of choroidal pigment, blindness acute disease fever, malaise, lymphadenopathy, sore throuat myalgia, popular rash chronic reactivated disease encephalitis myocarditis pneumonitis Isolation : animal inoculation, tissue culture Parasite detection : histological examination PCR Radiology serology Pyrimethamine + sulfadiazine Pregnant woman Spiramycin + Folate acid
disease Clinical symptoms
diagnosis
treatment
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Pharmacology of Autonomic Nervous System Cholinergic AgonistsDocument6 paginiPharmacology of Autonomic Nervous System Cholinergic Agonistsfiena920% (1)
- Journal FINAL....Document6 paginiJournal FINAL....fiena92Încă nu există evaluări
- Pharmacology of Adrenergic AgonistsDocument9 paginiPharmacology of Adrenergic Agonistsfiena92Încă nu există evaluări
- Muscarinic (M) Receptor Blockers (Antagonists) Anti Muscarinic Drugs Anti Cholinergic DrugsDocument4 paginiMuscarinic (M) Receptor Blockers (Antagonists) Anti Muscarinic Drugs Anti Cholinergic Drugsfiena92Încă nu există evaluări
- Adverse Drug ReactionDocument5 paginiAdverse Drug Reactionfiena92Încă nu există evaluări
- Adrenergic AntagonistsDocument6 paginiAdrenergic Antagonistsfiena92100% (2)
- Helminth 5Document5 paginiHelminth 5fiena92100% (2)
- Helminths - Revision IDocument1 paginăHelminths - Revision Ifiena92Încă nu există evaluări
- Opce Samples March 2006Document14 paginiOpce Samples March 2006fiena92Încă nu există evaluări
- Helminth Revision 2Document1 paginăHelminth Revision 2fiena92Încă nu există evaluări
- Helminth 4Document1 paginăHelminth 4FarlogyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 5: Chemicals For ConsumerDocument10 paginiChapter 5: Chemicals For Consumerfiena9292% (13)
- Helminth 3Document2 paginiHelminth 3Farlogy100% (5)
- Protozoa RevisionDocument6 paginiProtozoa Revisionfiena92100% (1)
- Brochur A.UDocument2 paginiBrochur A.Ufiena92Încă nu există evaluări
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)