Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Drug Study ICU
Încărcat de
Julie NambatacDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Drug Study ICU
Încărcat de
Julie NambatacDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
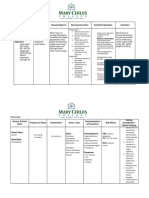
DRUG ORDER (Generic name, brand name, classification, dosage, route, frequency)
MECHANI SM OF ACTION
INDICATION
CONTRAINDICATION
ADVERSE REACTIONS
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
Generic name: isosorbide dinitrate Brand name: Coronex, IsoBid Classification: cardiovascula r agent; nitrate vasodilator Route:
IV
Relaxes vascular smooth muscle with a resultant decrease in venous return and decrease in arterial BP, which reduces left ventricular workload and decreases myocardial oxygen consumptio n.
Dinitrate: Treatm ent and prevention of angina pectoris
Contraindicated with allergy to nitrates, severe anemia, head trauma, cerebralhemorrhage,hypertrophiccardi omyopathy,narrowangleglaucoma,postduralhypotension
>CNS: Headache, apprehension, restlessness, weakness, vertigo, dizziness, faintness >CV: Tachycardia, retrosternald is comfort, palpitations, hypotension, syncope, collapse, orthostatic hypotension, angina, rebound hypertension, atrial fibrillation, postdural hypertension >Dermatologic: Rash, exfoliative dermatitis ,cutaneous vasodilation with flushing >GI: Nausea, vomiting, incontinence of urine and feces, abdominal pain, diarrhea
>Assess for pain:duration, timestarted, activitybeing performed,character,intensity >Assessorthostatichypotension, blood pressureat baseline andduring treatment
DRUG ORDER (Generic name, brand name, classification, dosage, route, frequency)
MECHANISM OF ACTION
INDICATION
CONTRAINDICATION
ADVERSE REACTIONS
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
Generic name: dopamine hydrochloride Brand name: Dopastat, Intropin, Revimine Classification: Autonomic nervous system agent; alpha and beta adrenergic agonist sympathomimitic Route: IV
Naturally occurring neurotransmitter and immediate precursor of norepinephrine. Major cardiovascular effects produced by direct action on alpha- and beta-adrenergic receptors and on specific dopaminergic receptors in mesenteric and renal vascular beds.
To correct hemodynamic imbalance in shock syndrome due to MI (cardiogenic shock), trauma, endotoxic septicemia (septic shock), open heart surgery, and CHF.
Pheochromocytoma; tachyarrhythmias or ventricular fibrillation. Safe use during pregnancy (category C), lactation, or children is not established.
CV: Hypotension, ectopic beats, tachycardia, anginal pain, palpitation, vasoconstriction, cold extremities; less frequent: bradycardia, widening of QRS complex, elevated blood pressure. GI: Nausea, vomiting. CNS: Headache. Skin: Necrosis, tissue sloughing with extravasation, gangrene, piloerection. Other: Azotemia, dyspnea, dilated pupils (high doses).
>Monitor blood pressure, pulse, peripheral pulses, and urinary output at intervals prescribed by physician. Precise measurements are essential for accurate titration of dosage. > Monitor therapeutic effectiveness
DRUG ORDER (Generic name, brand name, classification, dosage, route, frequency)
MECHANISM OF ACTION
INDICATION
CONTRAINDICATION
ADVERSE REACTIONS
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
Generic name: Mannitol Brand name: Osmitrol Drug Classification: Osmotic Diuretic Route: I.V. infusion Dosage: :0.5 to 2 g/kg I.V. infusion as 15% to 25% solution given over 30 or 60 minutes
Increases osmotic pressure of plasma in glomerular filtrate, inhibiting tubular reabsorption of water andelectrolytes (including sodium and potassium). These actions enhance water flow from various tissuesand ultimately decrease intracranial and intraocular pressures.
Test dose for marked oliguria or suspected inadequate renal function, prevent acute renal failure duringcardiovascular and other surgeries, acute renal failure, to reduce intracranial pressure and brain mass,reduce intraocular pressure, to promote dieresis in drug toxicity, irrigation during transurethralresection of prostate.
Active intracranial bleeding (except during craniotomy), anuria secondary to severe renal disease,progressive heart failure, pulmonary congestion, renal damage, or renal dysfunction after mannitoltherapy begins, severe pulmonary congestion or pulmonary edema, and severe dehydration.
CNS: dizziness, headache, seizures CV: chest pain, hypotension, hypertension, tachycardia, thrombophlebitis, heart failure, vascularoverload EENT: blurred vision, rhinitis GI: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, dry mouth GU: polyuria, urinary retention, osmotic nephrosis Metabolic: dehydration, water intoxication, hypernatremia, hyponatremia, hypovolemia, hypokalemia, hyperkalemia, metabolic acidosis Respiratory: pulmonary congestionSkin: rash, urticariaOther: chills, fever, thirst, edema, extravasation with edema and tissue necrosi
>Assesss skin turgor, mucous membranes and mental status before administration of drug. >Assess signs for electrolyte imbalance.3. >Monitor Vital signs including central venous pressure and output. >Store at room temperature. Use a filter with concentrated mannitol (15%, 20% and 25%). >Be alert for adverse reactions and drug interactions. >Monitor hepatic and renal function during therapy. >Monitor IV site carefully to avoid extravasations and tissue necrosis9.
DRUG ORDER (Generic name, brand name, classification, dosage, route, frequency)
MECHANISM OF ACTION
INDICATION
CONTRAINDICATION
ADVERSE REACTIONS
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
Generic name: atropine sulfate Brand name: AtroPen, Minims (CAN), SalTropine Classification: Anticholinergic, Antimuscarinic Parasympatholytic Antiparkinsonian Antidote Route: Oral. IV Dosage: Tablets0.4 mg; injection0.05, 0.1, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.8, 1 mg/mL
Competitively blocks the effects of acetylcholine at muscarinic cholinergic receptors that mediate the effects of parasympathetic postganglionic impulses, depressing salivary and bronchial secretions, dilating the bronchi, inhibiting vagal influences on the heart, relaxing the GI and GU tracts, inhibiting gastric acid secretion (high doses), relaxing the pupil of the eye (mydriatic effect),
Antisialagogue for preanesthetic medication to prevent or reduce respiratory tract secretions Treatment of parkinsonism; relieves tremor and rigidity Restoration of cardiac rate and arterial pressure during anesthesia when vagal stimulation produced by intra-abdominal traction causes a decrease in pulse rate, lessening the degree of AV block when increased vagal tone is a factor (eg, some cases due to digitalis) Relief of bradycardia and syncope due to hyperactive carotid sinus reflex
Contraindicated with hypersensitivity to anticholinergic drugs Contraindicated with glaucoma; adhesions between iris and lens; stenosing peptic ulcer; pyloroduodenal obstruction; paralytic ileus; intestinal atony; severe ulcerative colitis; toxic megacolon; symptomatic prostatic hypertrophy; bladder neck obstruction; bronchial asthma; COPD; cardiac arrhythmias; tachycardia; myocardial ischemia; impaired metabolic, liver, or kidney function; myasthenia gravis. Use cautiously with Down syndrome, brain damage, spasticity, hypertension, hyperthyroidism, lactation.
CNS: Blurred vision, mydriasis, cycloplegia, photophobia, increased IOP, headache, flushing, nervousness, weakness, dizziness, insomnia, mental confusion or excitement (after even small doses in the elderly), nasal congestion C V:Palpitations, bradycardia (low doses), tachycardia (higher doses) GI: Dry mouth, altered taste perception, nausea, vomiting, dysphagia, heartburn, constipation, bloated feeling, paralytic ileus, gastroesophageal reflux
>Ensure adequate hydration; provide environmental control (temperature) to prevent hyperpyrexia. >Have patient void before taking medication if urinary retention is a problem
DRUG ORDER (Generic name, brand name, classification, dosage, route, frequency)
MECHANISM OF ACTION
INDICATION
CONTRAINDICATION
ADVERSE REACTIONS
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
Generic name: nicardipinehydrochloride Brand name: cardene Classification: Calcium channel blocker (dihydropyridine) Route: Dosage: 20mg, 30mg; caps
Nicardipine inhibits the transmembrane influx of calcium ions into cardiac muscle and smooth muscle without changing serum calcium concentrations. The contractile processes of cardiac muscle and vascular smooth muscle are dependent upon the movement of extracellular calcium ions into these cells through specific ion channels. The effects of nicardipine are more selective to vascular smooth muscle than cardiac muscle. In animal models, nicardipine produced relaxation of coronary vascular smooth muscle at drug levels which cause little or no negative inotropic effect.
Chronic Advanced aortic stable angina stenosis Cardiac failure. Acute cerebral infarction or hemorrhage. Hepatic or renal impairment. Measure blood pressure 12 hrs and 8 hrs after dosing. Pregnancy (Cat.C). Nursing mothers: not recommended.
Increased angina, hypotension, flushing, headache, pedal edema, asthenia, dizziness, tachycardia, somnolence, GI upset, and insomnia.
>Monitor BP carefully >Monitor cardiac rhythm regularly >Advise patient to have a frequent meal if GI upset occurs
DRUG ORDER (Generic name, brand name, classification, dosage, route, frequency)
MECHANISM OF ACTION
INDICATION
CONTRAINDICATION
ADVERSE REACTIONS
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
Generic name: Dobutamine hydrochloride Brand name: Dobutrex Classification: autonomic nervous system agent; betaadrenergic agonist; catecholamine Route: IV Dosage: ampule
Stimulates heats beta1receptors to increase myocardial contractility and stroke volume. At therapeutic dosages, drug increases cardiac output by decreasing peripheral vascular resistance, reducing ventricular filling pressure, and facilitating AV node conduction
Increase cardiac output in shortterm treatment of cardiac decompensation cause by depressed contractility, such as during refractory heart failure; adjunctive therapy in cardiac surgery
Contraindicated n patients hypersensitive to drug or its components and in those w/idiopathic hypertrophic subaortic stenosis
CNS: headache CV: hypertension, increased heart rate
>Before starting therapy, give a plasma volume to correct hypovolemia an a cardiac glycoside >Continuously monitor ECG, blood pressure, pulmonary artery wedge pressure, cardiac output and urine output
DRUG ORDER (Generic name, brand name, classification, dosage, route, frequency)
MECHANISM OF ACTION
INDICATION
CONTRAINDICATION
ADVERSE REACTIONS
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
Generic name: amiodarone Brand name: Cordarone Classification: Antiarrhythmic Route: IV, Oral Dosage: Ventricular arrhythmias { adults} loading dose 300mg IVP,
Slows sinus rate, increases PR and QT intervals, decreases peripheral vascular resistance, increases refractory period of the AV node
Prophylaxis of frequently recurring VF and hemodynamically unstable VT in patients refractory to other therapy, indicated for patients who have been prescribed oral cordarone, but are unable to take oral medications.
Hypersensitivity to the Hypotension, tremors, drug, cardiogenic shock, fatigue, N/V, dyspnea marked sinus bradycardia, 2nd or 3rd degree AV block { unless a functioning pacemaker is available}
>Monitor BP carefully during infusion and slow the infusion if significant hypotension occurs >Monitor for elevations of AST and ALT. If elevations persist or if they are 23 times above normal baseline readings, reduce dosage or withdraw drug promptly to prevent hepatotoxicity and liver damage. > Auscultate chest periodically for respiratory symptoms.
DRUG ORDER (Generic name, brand name, classification, dosage, route, frequency)
MECHANISM OF ACTION
INDICATION
CONTRAINDICATION
ADVERSE REACTIONS
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
Generic name: potassium chloride Brand name: Kaylixir, Kay Ciel, Klorvess, Klotrix Classification: Electrolyte Route: IV, Oral
Principal intracellular cation of most body tissues, participates in a number of physiologic processes maintaining intracellular tonicity; transmission of nerveimpulses; contraction of cardiac, skeletal, and smooth muscle; maintenance of normal renal function; also plays a role in carbohydrate metabolism
Prevention and correction of potassium deficiency, when associated withalkalosis, use potassium chloride; when associated with acidosis, usepotassium acetate, bicarbonate, citrate, or gluconate.
Hyperchloraemia, severe renal or adrenal insufficiency.
Dermatologic: Rash GI: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal discomfort, GI obstruction, GIbleeding, GI ulceration or perforation Hematologic: Hyperkalemia increased serum potassium, ECG changes(peaking of T waves, loss of P waves, depression of ST segment, prolongation of QTc interval) Local: Tissue sloughing, local necrosis, local phlebitis, and venospasm withinjection
Warning: Do not administer undiluted. Dilute in dextrose solution to 4080mEq/L Arrange for serial serum potassium levels before and during therapy. Administer liquid form to any patient with delayed GI emptying. Administer oral drug after meals or with food and a full glass of water to decreaseGI upset. Caution patient not to chew or crush tablets; have patient swallow tablet whole.
DRUG ORDER (Generic name, brand name, classification, dosage, route, frequency)
MECHANISM OF ACTION
INDICATION
CONTRAINDICATION
ADVERSE REACTIONS
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
Generic name: nitroglycerin Brand name: Sublingual NitroQuick, Nitrostat Transdermal: Deponit, Minitran, Nitrek, Nitro-Dur, Nitrodisc, Transderm-Nitro Translingual: Nitrolingual Classification: Antianginal Nitrate
Relaxes vascular smooth muscle with a resultant decrease in venous return and decrease in arterial BP, which reduces left ventricular workload and decreases myocardial oxygen consumption.
Sublingual, translingual preparations: Acute angina, Oral SR, sublingual, topical, transdermal, translingual, transmucosal preparations: Prophylaxis of angina, IV: Angina unresponsive to recommended doses of organic nitrates or betablockers, IV: Perioperative hypertension
Contraindicated with allergy to nitrates, severe anemia, early MI, head trauma, cerebral hemorrhage, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, pregnancy, lactation.
CNS: Headache, apprehension, restlessness, weakness, vertigo, dizziness, faintness C V: Tachycardia, retrosternal discomfort, palpitations, hypotension, syncope, collapse, orthostatic hypotension, angina Dermatologic: Rash, exfoliative dermatitis, cutaneous vasodilation with flushing, pallor, perspiration, cold sweat, contact dermatitistransdermal preparations, topical allergic reactionstopical nitroglycerin ointment GU: incontinence of urine and feces, abdominal pain
>Give sublingual preparations under the tongue or in the buccal pouch. Encourage patient not to swallow. Ask patient if the tablet "fizzles" or burns. Always check the expiration date on the bottle; store at room temperature, protected from light. >Administer transdermal systems to skin site free of hair and not subject to much movement.
DRUG ORDER (Generic name, brand name, classification, dosage, route, frequency)
MECHANISM OF ACTION
INDICATION
CONTRAINDICATION
ADVERSE REACTIONS
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
Generic name: epinephrine Brand name: epinephrine bitartrate Classification: Sympathomimetic drug Alpha-adrenergic agonist Beta1- and beta2adrenergic agonist Cardiac stimulant Vasopressor Bronchodilator Antasthmatic Nasal decongestant Mydriatic Antiglaucoma drug Route: Inhalation, injection, ophthalmic
Naturally occurring neurotransmitter, the effects of which are mediated by alpha or beta receptors in target organs. Effects on alpha receptors include vasoconstriction, contraction of dilator muscles of iris. Effects on beta receptors include positive chronotropic and inotropic effects on the heart (beta1 receptors); bronchodilation, vasodilation, and uterine relaxation (beta2 receptors); decreased production of aqueous humo
Relief from respiratory distress of bronchial asthma, chronic bronchitis, emphysema, other COPDs
Contraindicated with allergy or hypersensitivity to epinephrine or components of preparation, narrow-angle glaucoma; shock other than anaphylactic shock; hypovolemia; general anesthesia with halogenated hydrocarbons or cyclopropane; organic brain damage, cerebral arteriosclerosis; cardiac dilation and coronary insufficiency; tachyarrhythmias; ischemic heart disease; hypertension; renal dysfunction (drug may initially decrease renal blood flow); COPD patients who have developed degenerative heart disease; diabetes mellitus; hyperthyroidism; lactation. Opthalmic preparations are contraindicated for those wearing contact lenses (drug may discolor the contact lens), aphakic patients (maculopathy with decreased visual acuity may occur).
CNS: Fear, anxiety, tenseness, restlessness, headache, lightheadedness, dizziness CV: Arrhythmias, hypertension resulting in intracranial hemorrhage GI: Nausea, vomiting, anorexia GU: Constriction of renal blood vessels and decreased urine Other: Pallor, respiratory difficulty, orofacial dystonia, sweating
>WARNING: Use extreme caution when calculating and preparing doses; epinephrine is a very potent drug; small errors in dosage can cause serious adverse effects. Double-check pediatric dosage.
DRUG ORDER (Generic name, brand name, classification, dosage, route, frequency)
MECHANISM OF ACTION
INDICATION
CONTRAINDICATION
ADVERSE REACTIONS
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
Generic name: norepinephrine Brand name: Levophed
Norepinephrine stimulates alpha and beta-1 adrenergic receptors in a doserelated fashion. At lower doses (less than 2 mcg Classification: per minute), stimulation autonomic of beta-1 receptors nervous system agent; alpha- and results in a positive inotropic and beta-adrenergic chronotropic effect. At agonist (sympathomimetic higher doses (greater than 4 mcg per minute), ) the alpha adrenergic Route: effect predominates, IV drip only resulting in elevated total peripheral resistance. Chronotropy diminishes as a result of baroreceptor-mediated vagal stimulation.
B/P less than 70mm Hg after other vasopressors have been unsuccessful, septic, and neurogenic shock.
Patients with heart disease or with hypovolemia.
Nausea and vomiting, headache, decreases in urinary output, hypertension, and anxiety.
> Monitor constantly while patient is receiving norepinephrine. > Adjust flow rate to maintain BP at low normal (usually 80100 mm Hg systolic) in normotensive patients. > Monitor I&O. Urinary retention and kidney shutdown are possibilities, especially in hypovolemic patients.
DRUG ORDER (Generic name, brand name, classification, dosage, route, frequency)
MECHANISM OF ACTION
INDICATION
CONTRAINDICATION
ADVERSE REACTIONS
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
Generic name: furosemide Brand name: Fumide , Furomid, Lasix, Luramide Classification: Loop diuretic Route:
Rapid-acting potent sulfonamide "loop" diuretic and antihypertensive with pharmacologic effects and uses almost identical to those of ethacrynic acid. Exact mode of action not clearly defined; decreases renal vascular resistance and may increase renal blood flow
Treatment of edema associated with CHF, cirrhosis of liver, and kidney disease, including nephrotic syndrome. May be used for management of hypertension, alone or in combination with other antihypertensive agents, and for treatment of hypercalcemia. Has been used concomitantly with mannitol for treatment of severe cerebral edema, particularly in meningitis
History of hypersensitivity to furosemide or sulfonamides; increasing oliguria, anuria, fluid and electrolyte depletion states; hepatic coma; pregnancy (category C), lactation.
CV: Postural hypotension, dizziness with excessive diuresis, acute hypotensive episodes. Metabolic: Hypovolemia, dehydration, hyponatremia hypokalemia, hypochloremia metabolic alkalosis, hypomagnesemia, hypocalcemia (tetany), hyperglycemia, glycosuria, elevated BUN, hyperuricemia. GI: Nausea, vomiting, oral and gastric burning, Hematologic: Anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenic purpura Skin: Pruritus, urticaria, exfoliative dermatitis, purpura, photosensitivity, porphyria cutanea tarde, necrotizing angiitis (vasculitis). Body as a Whole: Increased perspiration; paresthesias; activation of SLE, muscle spasms, weakness; thrombophlebitis, pain at IM injection site.
>Observe patients receiving parenteral drug carefully; closely monitor BP and vital signs. Sudden death from cardiac arrest has been reported. >Monitor BP during periods of diuresis and through period of dosage adjustment.
DRUG ORDER (Generic name, brand name, classification, dosage, route, frequency)
MECHANISM OF ACTION
INDICATION
CONTRAINDICATION
ADVERSE REACTIONS
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
Generic name: Sodium bicarbonate Brand name: Bakin Soda, Bell-Ans, Citrocarbonat e, Neut, Soda Mint Classification: antiulcer agents, alkalinizing agent Route:
Sodium Bicarbonate acts as an alkalinizing agent by releasing bicarbonate ions. Following oral administration of this medication, it releases bicarbonate which is capable of neutralizing gastric acid.
Management of metabolic acidosis Used to alkalinize urine and promote excretion of certain drugs in over dosage situations Used as an antacid
Metabolic or respiratory alkalosis, Hypocalcemia, Excessive chloride loss, It is not recommended as an antidote following ingestion of strong mineral acids, Patients on sodium restricted diet, Renal failure, Severe abdominal pain of unknown cause especially if associated with fever
Edema, Flatulence, Gastric distention, Metabolic alkalosis, Hypernatremia, Hypocalcemia, Hypokalemia, Sodium and water retention, Irritation at IV site, Tetany
>Symptoms of fluid overload should be reported such as hypertension, edema, difficulty breathing or dyspnea, rales or crackles and frothy sputum. Sigs of acidosis should be assessed such as disorientation, headache, weakness, dyspnea and hyperventilation. Hypernatremia >clinical manifestations should be Hypokalemia should also be assessed by monitoring signs and symptoms IV sites should be observed closely. >Extravasation should be avoided as tissue irritation or cellulitis may occur when taking sodium bicarbonate. >Tablets must be taken with a full glass of water. For clients taking the medication as a treatment for peptic ulcers it may be administered 1 and 3 hours after meals and at bedtime.
DRUG ORDER (Generic name, brand name, classification, dosage, route, frequency)
MECHANISM OF ACTION
INDICATION
CONTRAINDICATION
ADVERSE REACTIONS
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
Generic name: norepinephrine Brand name: Levophed
Norepinephrine stimulates alpha and beta-1 adrenergic receptors in a doserelated fashion. At lower doses (less than 2 mcg Classification: per minute), stimulation autonomic of beta-1 receptors nervous system agent; alpha- and results in a positive inotropic and beta-adrenergic chronotropic effect. At agonist (sympathomimetic higher doses (greater than 4 mcg per minute), ) the alpha adrenergic Route: effect predominates, IV drip only resulting in elevated total peripheral resistance. Chronotropy diminishes as a result of baroreceptor-mediated vagal stimulation.
B/P less than 70mm Hg after other vasopressors have been unsuccessful, septic, and neurogenic shock.
Patients with heart disease or with hypovolemia.
Nausea and vomiting, headache, decreases in urinary output, hypertension, and anxiety.
> Monitor constantly while patient is receiving norepinephrine. > Adjust flow rate to maintain BP at low normal (usually 80100 mm Hg systolic) in normotensive patients. > Monitor I&O. Urinary retention and kidney shutdown are possibilities, especially in hypovolemic patients.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Reteplase (MIRel)Document23 paginiReteplase (MIRel)Jhoann JamanilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Perioperative NursingDocument13 paginiPerioperative NursingTobiDaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudiesDocument4 paginiDrug StudiesgyantuazonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Discharge Planning PaperDocument5 paginiDischarge Planning Paperapi-283173905Încă nu există evaluări
- Water Sealed DrainageDocument2 paginiWater Sealed DrainagefairwoodsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument3 paginiDrug StudyKorina FranciscoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case StudyDocument34 paginiCase StudyBSNNursing101Încă nu există evaluări
- Central Venous Pressure (CVP)Document27 paginiCentral Venous Pressure (CVP)Danial Hassan100% (1)
- Careplan Medication ListDocument17 paginiCareplan Medication ListGiorgia ScorsoneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zaroxolyn MetolazoneDocument1 paginăZaroxolyn MetolazoneCassieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Premature Ventricular ContractionDocument17 paginiPremature Ventricular Contractiondr_jofrilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 067 Sirs ModsDocument25 paginiChapter 067 Sirs Modsapi-232466940Încă nu există evaluări
- Hypertension NclexDocument5 paginiHypertension Nclexハニファ バランギÎncă nu există evaluări
- Post Cesarean Section DeliveryDocument5 paginiPost Cesarean Section Deliveryᒙᕧᖇᕦᙏᖻ ᗴᔛᓦᗩᖆᗩÎncă nu există evaluări
- 0.9% NaCl or Plain NSSDocument13 pagini0.9% NaCl or Plain NSSJeannette Richelle DacilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of AnesthesiaDocument6 paginiTypes of AnesthesiaEnrick CastroÎncă nu există evaluări
- PNSSDocument2 paginiPNSSBianca Nicole Gacad FernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9 Ketamine Drug StudyDocument7 pagini9 Ketamine Drug Studyshadow gonzalezÎncă nu există evaluări
- DM & DI ExamsDocument11 paginiDM & DI ExamsTomzki CornelioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bupivacaine Merk 4Document2 paginiBupivacaine Merk 4PutuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study EditedDocument5 paginiDrug Study EditedfabtaciousVeelaÎncă nu există evaluări
- TahbsoDocument4 paginiTahbsomichZ_13Încă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudiesDocument16 paginiDrug Studiesvitcloud23100% (2)
- Emergency Drugs: (A Drug Study)Document13 paginiEmergency Drugs: (A Drug Study)Marichu BajadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clonidine Hydro ChlorideDocument4 paginiClonidine Hydro Chlorideapi-3797941100% (1)
- Nursing DiagnosisDocument10 paginiNursing DiagnosisZaty ChaiyOkk100% (1)
- CABGDocument32 paginiCABGأمينةأحمد100% (1)
- Chest Pain Care PlanDocument2 paginiChest Pain Care Planapi-545292605Încă nu există evaluări
- Detrol (Tolterodine)Document1 paginăDetrol (Tolterodine)EÎncă nu există evaluări
- CyclosporineDocument2 paginiCyclosporineMuhammad ArsalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- DuaventDocument9 paginiDuaventAjurs UrsabiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study On DigoxinDocument8 paginiDrug Study On DigoxinDonald BidenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parenteral Fluid TherapyDocument4 paginiParenteral Fluid TherapyPrincess PlateroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cerebral Aneurysms: Aneurysms Posterior Circulation Basilar Artery Vertebral Arteries Posterior Communicating ArteryDocument10 paginiCerebral Aneurysms: Aneurysms Posterior Circulation Basilar Artery Vertebral Arteries Posterior Communicating ArteryRani SujithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Epinephrine Drug StudyDocument7 paginiEpinephrine Drug StudyJhoy Iris SarangayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Propofol Drug Study SheetDocument3 paginiPropofol Drug Study Sheetjevon.brooks0515Încă nu există evaluări
- Atracurium BesylateDocument3 paginiAtracurium BesylateWidya WidyariniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Product Information Avil Product NamesDocument4 paginiProduct Information Avil Product Namesindyanexpress100% (1)
- ATCN Policies and ProceduresDocument40 paginiATCN Policies and ProceduresOséias AlvesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study FinalDocument6 paginiDrug Study FinalJade HemmingsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sanaani Nur Hathi M. Nso Jugular Venous Oximetry Staff Nurse 1Document7 paginiSanaani Nur Hathi M. Nso Jugular Venous Oximetry Staff Nurse 1Nur SanaaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- START / Jump START Triage: ImmediateDocument2 paginiSTART / Jump START Triage: ImmediateJerome DanielÎncă nu există evaluări
- 24 Emergency DrugsDocument7 pagini24 Emergency DrugsApple BelicanÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Self Care DeficitDocument3 paginiNCP Self Care DeficitLeizel ApolonioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Post Test Upper Gi BleedingDocument4 paginiPost Test Upper Gi BleedingMardie ArcesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study Worksheet EndocarditisDocument6 paginiCase Study Worksheet EndocarditisSharlee StoneÎncă nu există evaluări
- LOSARTANDocument3 paginiLOSARTANReinell GoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Folinic AcidDocument1 paginăFolinic AcidMuhammad ArsalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intensive Care Unit Clinical ObjectivesDocument1 paginăIntensive Care Unit Clinical ObjectivesTuTitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sotalol Drug CardDocument2 paginiSotalol Drug CardJanet SheldonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument7 paginiDrug Studykymsh_kimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study TKRDocument22 paginiCase Study TKRInspirasi KhadijahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Somera Case 1928Document68 paginiSomera Case 1928jrkalbo75% (4)
- Dalidig - Drug StudyDocument28 paginiDalidig - Drug StudyRaf DalidigÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan Date Assessed: December 11, 2017 Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Objective Nursing Intervention Scientific Explanation EvaluationDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan Date Assessed: December 11, 2017 Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Objective Nursing Intervention Scientific Explanation EvaluationCelyn Nicole Fernandez RollanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case 1Document9 paginiCase 1Joselyn M. LachicaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Discharge Plan Post SeizureDocument2 paginiDischarge Plan Post SeizureVecky TolentinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) InhibitorsDocument4 paginiAngiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) InhibitorsPutri Mulia HasibuanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Management of Tuberculosis: A guide for clinicians (eBook edition)De la EverandManagement of Tuberculosis: A guide for clinicians (eBook edition)Încă nu există evaluări
- OLFU Intesive Post Test 50 ItemsDocument5 paginiOLFU Intesive Post Test 50 ItemsmonmonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Report Workshop NQPS May 2018 (Eng)Document34 paginiReport Workshop NQPS May 2018 (Eng)JuanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- N Tees 2013Document2 paginiN Tees 2013api-2477290330% (2)
- Evis Exera Ii Duodenovideoscope Olympus TJF Type Q180VDocument94 paginiEvis Exera Ii Duodenovideoscope Olympus TJF Type Q180Vaironarg100% (1)
- Adrenergic Antagonists EditedDocument60 paginiAdrenergic Antagonists EditedJohn Benedict VocalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inverted Nipple PaperDocument7 paginiInverted Nipple PaperFarisah Dewi Batari EmsilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Glove SOP For Glove by DR Mohamed RifasDocument3 paginiGlove SOP For Glove by DR Mohamed RifasDrMohamed RifasÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Rare Huge Myxofibrosarcoma of Chest WallDocument3 paginiA Rare Huge Myxofibrosarcoma of Chest WallIOSRjournalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Short Bowel SyndromeDocument50 paginiShort Bowel SyndromeAbdul QadirÎncă nu există evaluări
- N N Burdenko Journal of Neurosurgery 2016-06Document108 paginiN N Burdenko Journal of Neurosurgery 2016-06amereÎncă nu există evaluări
- Viral HepatitisDocument26 paginiViral HepatitisNasriah MacadatoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Effects of Isotretinoin On Meibomian GlandsDocument6 paginiEffects of Isotretinoin On Meibomian GlandsTeddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- AA Effectiveness - Faith Meets ScienceDocument68 paginiAA Effectiveness - Faith Meets SciencejgogekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Primary Angle-Closure GlaucomaDocument10 paginiPrimary Angle-Closure Glaucomanisa_kartikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Euthanasia ThesisDocument11 paginiEuthanasia ThesisAyush MathurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Machine Learning in Medicine - Jeff DeanDocument12 paginiMachine Learning in Medicine - Jeff DeanArun RaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharma 2Document3 paginiPharma 2zaydeeeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antihistamines (Hayfever) and BreastfeedingDocument2 paginiAntihistamines (Hayfever) and BreastfeedingEzraGoenadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- OsteomyelitisDocument35 paginiOsteomyelitischinnnababu100% (1)
- Health CareDocument1 paginăHealth CareMikeÎncă nu există evaluări
- SoftClinic Software - PresentationDocument31 paginiSoftClinic Software - PresentationMahmoud AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- HRUK Pulse SpringSummer 2013 ScreenDocument36 paginiHRUK Pulse SpringSummer 2013 ScreenhrukcommunicationsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Self Blood Sugar MonitoringDocument8 paginiSelf Blood Sugar MonitoringAniruddh Varadarajan100% (1)
- Fibroscan LeafletDocument2 paginiFibroscan LeafletI-one SyahputraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tracheotomies Bronchoscopy: Med-Surg Final Exam Study Guide Fall 2010Document3 paginiTracheotomies Bronchoscopy: Med-Surg Final Exam Study Guide Fall 2010Lynn SueningÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medicolegal Book ContentsDocument5 paginiMedicolegal Book ContentsVirendar Pal SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medical Application FormDocument5 paginiMedical Application FormRaz De NeiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathology of Lung CancerDocument24 paginiPathology of Lung CancerWeiLinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Manual 11102016 PDFDocument239 paginiLab Manual 11102016 PDFDesyAyu DzulfaAry EomutÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anemia in HIV/AIDSDocument15 paginiAnemia in HIV/AIDSK. Vijay Ananth100% (1)