Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
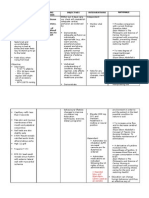
Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term Goal: Independent
Încărcat de
NinaDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term Goal: Independent
Încărcat de
NinaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Assessment Subjective: Kinakabahan ako, safe ba yan? as verbalized by the patient.
Objective: Patient frequently asks questions about the procedure Looks worried Poor eye contact Increased BP, RR, PR
Diagnosis Anxiety r/t fear of interventional treatment process, outcomes and potential complications.
Planning Short term goal: Within 30 minutes of nursing interventions, the patient will verbalize understanding of the procedure. Long term goal: Within an hour of nursing interventions, the patients anxiety will decrease as evidenced by relaxed state and effective coping skills.
Intervention Independent: Monitor vital signs and observe patients behaviour. Assess patients level of anxiety. Determine past coping skills used. Acknowledge patients anxiety; do not reassure that everything will be alright. Allow the patient to verbalize his feelings and concerns. Be available to the patient for listening and talking. Explain to the patient the procedure (preoperative, intraoperative, and postoperative) by giving accurate information and using clear and understandable words. Use therapeutic communication; allow the patient to ask questions. Teach and provide patient comfort measures such as: modifying environment, back rub, guided imagery, listening to music, focussed breathing. Encourage patient to develop positive thinking. Encourage relatives to provide support and positive feedback to the patient.
Rationale To identify physical responses associated with the situation. To determine the severity and factors causing anxiety. To identify appropriate strategies that might be helpful in the situation. To avoid giving false hopes. To assure patient that the nurse is well aware to what hes experiencing; giving emotional support. To establish therapeutic relationship. Increased knowledge about the procedure will help decrease patients anxiety and promote what is reality. To promote effective communication with the patient. To deviate patients anxiety and promote a relaxed state.
Evaluation Goals are met.
Dependent: Administer sedative and pulse oximeter as ordered. Collaborative: Introduce the staff who will assist in the procedure.
To help patient to be relaxed. To decrease patients anxiety.
Assessment Subjective: Sumisikip dibdib ko as verbalized by the patient. Objective: Increased BP, RR, PR Shortness of breath Pain lasts less than 20 minutes in ischemic events
Diagnosis Acute chest pain r/t coronary artery occlusion secondary to procedure.
Planning Short term goal: During the procedure, the patient will be able to tolerate procedure verbalizing decreased in chest pain episodes. Long term goal: During and after the procedure, further complications of chest pain will be prevented and vital signs are within normal range.
Intervention Independent: Strictly monitor patients vital signs and neurologic status. Record nature, type, location, intensity and duration of chest pain. Remind patient that pain can be felt once balloon is inflated.
Rationale To have a baseline data and to identify significant alterations that can contribute to chest pain. This is normally felt during the procedure because the balloon briefly blocks blood supply to heart; however it should disappear when blockage is compressed. These may suggest that coronary artery is reclosing.
Evaluation Goals are met.
Encourage patient to report episodes of chest pain or other symptoms such as back pain, shortness of breath, tight squeeze in the chest, dizziness or change in vision. Encourage patient to keep calm. Advise patient to do deep breathing and coughing exercises. Monitor laboratory results such as cardiac enzymes.
Pain and anxiety increase pulse rate, oxygen consumption and cardiac workload To stabilize vital signs within normal ranges. Elevation in cardiac enzymes may indicate myocardial ischemia.
Continuously monitor patients condition until absence of chest pain or other discomfort is reported. Dependent: Administer analgesics as ordered. Administer IV medications as ordered. Administer oxygen as ordered.
To detect complications for early interventions.
To promote rest, decrease oxygen consumption caused by pain, and aids patient in performing deep breathing and coughing exercises. To monitor ECG changes, especially arrhythmias accompanying pain.
Collaborative: Perform ECG by cardiologists.
Assessment Objective: Scanty bleeding on the incision site Slightly diminished pulse on the left groin area (grading of 3) Presence of bruise on the left groin area
Diagnosis Risk for bleeding r/t the use of blood thinning medications and blood vessel injury secondary to procedure.
Planning Short term goal: Within 30 minutes of nursing interventions, patients risk for bleeding will be controlled. Long term goal: After several hours of ongoing assessment and nursing interventions, the patient will be able to demonstrate behaviours and safety measures to prevent episodes of bleeding.
Intervention Independent: Monitor vital signs.
Rationale Bleeding can cause increased in heart rate and decreased in blood pressure. Active bleeding, pain, tenderness, swelling, hematoma are all signs of bleeding. It gives information on the coagulation/clotting status of the patient. Direct pressure on the incision site promotes haemostasis. To minimize the risk of bleeding from the incision
Evaluation Goals are met.
Assess the incision site for evidence of bleeding. Monitor Partial thromboplastin time, Prothrombin time and platelet count. Provide manual pressure for 515 minutes or application of compression device on the femoral artery. Encourage patient to minimize movement of the affected
extremity and advised patient to maintain bed rest in supine position for at least 6 hours. Instruct patient to apply minimal pressure on the incision site upon sneezing and coughing. Dependent: Administer heparin via infusion pump as prescribed.
site. To minimize the risk of bleeding and to facilitate clot formation.
To ensure prescribed dosage depending on the result of partial thromboplastin time. To minimize the risk of bleeding in accordance to the use of blood thinners.
Collaborative: Consult the physician on adjusting the dose of anticoagulant agents, when possible, taking into account the patients weight, age, and kidney function.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Objective Interventions Rationale Expected Outcome Short Term: Short TermDocument4 paginiAssessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Objective Interventions Rationale Expected Outcome Short Term: Short TermGensen Cu RoxasÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Battle Against Covid-19 Filipino American Healthcare Workers on the Frontlines of the Pandemic ResponseDe la EverandThe Battle Against Covid-19 Filipino American Healthcare Workers on the Frontlines of the Pandemic ResponseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 paginiNursing Care PlanMarielle SorianoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cues Diagnosis Background Knowledge Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 paginiCues Diagnosis Background Knowledge Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationhaniehaehaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Pain SCMCDocument2 paginiAcute Pain SCMCWik Wik PantuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument1 paginăNursing Care Plan Impaired Gas ExchangeKarylle PetilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Concept Map - Abby !Document2 paginiConcept Map - Abby !Abegail Abaygar100% (3)
- Impaired Gas Exchange NCPDocument3 paginiImpaired Gas Exchange NCPRomel BaliliÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP PTBDocument6 paginiNCP PTBJay Dela VegaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PneumoniaDocument2 paginiPneumoniaPia MedinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care PlanDocument14 paginiNursing Care PlanVin Landicho100% (1)
- NCP Total Hip ReplacementDocument11 paginiNCP Total Hip ReplacementDoneva Lyn MedinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Acute PainDocument5 paginiNCP Acute PainEzra TuanÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Cad ElectiveDocument1 paginăNCP Cad ElectivejoegeÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCPDocument8 paginiNCPryzaimaliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Healthcare - Nursing Care Plan - Excess Fluid VolumeDocument4 paginiHealthcare - Nursing Care Plan - Excess Fluid VolumeBenjamin CañalitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCPDocument8 paginiNCPJoseph Anthony Benitez VerzosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plans For Activity IntoleranceDocument3 paginiNursing Care Plans For Activity Intoleranceravenshadow100% (2)
- NCP BronchopneumoniaDocument8 paginiNCP BronchopneumoniaCrisantaCasliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objective Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objective Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveFreisanChenMandumotanÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCPDocument10 paginiNCPNefre Dayap DarrocaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activity IntoleranceDocument1 paginăActivity IntoleranceAndrea Francesca SantosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Growth and DevelopmentDocument5 paginiGrowth and DevelopmentGabrielLopezÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP CSDocument4 paginiNCP CSJM UncianoÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP PainDocument2 paginiNCP PainApril_Ivy_Raga_3835Încă nu există evaluări
- Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion Related ToDocument7 paginiIneffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion Related TohannahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plans For Activity IntoleranceDocument4 paginiNursing Care Plans For Activity IntolerancethebigtwirpÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Impaired Skin IntegrityDocument4 paginiNCP Impaired Skin IntegrityElgie SantosÎncă nu există evaluări
- MGH 8 - Ihd - NCPDocument12 paginiMGH 8 - Ihd - NCPSesinando Niez Quilao Jr.100% (1)
- ASTHMADocument9 paginiASTHMAmildred alidonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute PainDocument3 paginiAcute PainJayr ChinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Impaired Gas Exchange NCPDocument3 paginiImpaired Gas Exchange NCPRomel BaliliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scribd 020922 Case Study-Oncology A&kDocument2 paginiScribd 020922 Case Study-Oncology A&kKellie DÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fistula NCPDocument1 paginăFistula NCPHasna LisnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ineffective Airway Clearance CareplanDocument6 paginiIneffective Airway Clearance CareplanderreshaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chest Pain Care PlanDocument2 paginiChest Pain Care Planapi-545292605Încă nu există evaluări
- Nusing CareplanDocument3 paginiNusing Careplanardec_143Încă nu există evaluări
- Wk2 NCP Edited2012Document6 paginiWk2 NCP Edited2012Jessely Caling SalasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)Document3 paginiAttention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)Hazzel Mea OberoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 paginiNursing Care Planapi-309251523Încă nu există evaluări
- NCP Proper CholecystectomyDocument2 paginiNCP Proper CholecystectomyGail Lian SantosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Surgical NCPDocument6 paginiSurgical NCPAreeya SushmitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Student Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 paginiStudent Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluationgreyciee은Încă nu există evaluări
- NCP Copd AirwayDocument2 paginiNCP Copd AirwaySugar Capule - ManuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care PlanDocument26 paginiNursing Care PlanPrincessLienMondejarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nueva Ecija University of Science and TechnologyDocument7 paginiNueva Ecija University of Science and TechnologyKym RonquilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Self CaRE DeficitDocument1 paginăNCP Self CaRE Deficitnicole pageÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Cavernous Sinus ThrombosisDocument3 paginiNCP Cavernous Sinus ThrombosisVencel Mae Famas Villahermosa50% (2)
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument4 paginiDecreased Cardiac OutputAdnan Khan100% (1)
- NCPDocument9 paginiNCPHendy Hency YunusÎncă nu există evaluări
- ISBAR DocumentationDocument1 paginăISBAR DocumentationFrancorussÎncă nu există evaluări
- Asthma Care PlanDocument3 paginiAsthma Care PlanSam ParkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Angel Therisse B. Ramelb BSN Ii-C Nursing DiagnosisDocument2 paginiAngel Therisse B. Ramelb BSN Ii-C Nursing DiagnosisSalvaje CaballeroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Impaired Physical Mobility R/T Neuromuscular ImpairmentDocument3 paginiImpaired Physical Mobility R/T Neuromuscular ImpairmentjisooÎncă nu există evaluări
- BSN 215 Reflection Essay - LagoDocument2 paginiBSN 215 Reflection Essay - LagoAlliahkherzteen LagoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care PlanDocument22 paginiNursing Care PlanjamÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP BMDocument1 paginăNCP BMSourabh MehraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care PlanDocument5 paginiNursing Care PlanPaola Marie VenusÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCPDocument9 paginiNCPLeolene Grace BautistaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Analysis - The New Market Opportunity - FinalDocument10 paginiCase Analysis - The New Market Opportunity - FinalNinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- RMC No 17-2018Document6 paginiRMC No 17-2018fatmaaleahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Civ 2 Q&aDocument14 paginiCiv 2 Q&aNinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2021-083022262426 - Verified Petition (Notarized)Document3 pagini2021-083022262426 - Verified Petition (Notarized)NinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CRALaw - Labor Law Pre Week (2019)Document153 paginiCRALaw - Labor Law Pre Week (2019)freegalado88% (25)
- Career MappingDocument3 paginiCareer MappingNinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rabuya Civ Forecast PDFDocument9 paginiRabuya Civ Forecast PDFimelry10073829Încă nu există evaluări
- Digest of Bir Rulings 2002 - Taxation of FBTDocument19 paginiDigest of Bir Rulings 2002 - Taxation of FBTarrianemartinezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Urgent Motion To Resolve FormatDocument3 paginiUrgent Motion To Resolve FormatNinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Analysis - The New Market Opportunity - FinalDocument10 paginiCase Analysis - The New Market Opportunity - FinalNinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digest of Bir Rulings 2002 - Taxation of FBTDocument19 paginiDigest of Bir Rulings 2002 - Taxation of FBTarrianemartinezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Legal FormsDocument44 paginiLegal FormsDan ChowÎncă nu există evaluări
- Affidavit of Discrepancy in NameDocument1 paginăAffidavit of Discrepancy in NameRonalyn Lopez90% (31)
- Manual On Real Property Appraisal AndAssessment OperationsDocument279 paginiManual On Real Property Appraisal AndAssessment OperationsReihannah Paguital-Magno100% (3)
- RMC No 17-2018Document6 paginiRMC No 17-2018fatmaaleahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ca-Gr SP GR 93370Document11 paginiCa-Gr SP GR 93370NinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Urgent Motion To Resolve FormatDocument3 paginiUrgent Motion To Resolve FormatNinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tax Opinion Atty GuevaraDocument63 paginiTax Opinion Atty GuevaraRheneir MoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- DOF BLGF Local Treasury Operations Manual LTOMDocument608 paginiDOF BLGF Local Treasury Operations Manual LTOMResIpsa Loquitor98% (128)
- Digest of Bir Rulings 2002 - Taxation of FBTDocument19 paginiDigest of Bir Rulings 2002 - Taxation of FBTarrianemartinezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manual On Real Property Appraisal AndAssessment OperationsDocument279 paginiManual On Real Property Appraisal AndAssessment OperationsReihannah Paguital-Magno100% (3)
- RMC No 39-2014Document2 paginiRMC No 39-2014Mark OyalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Umali vs. MiclatDocument2 paginiUmali vs. MiclatNinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aleco Apec Concession AgreementDocument33 paginiAleco Apec Concession AgreementNina100% (1)
- Reviewer For Consti I - Art 6 - Sec. 1 - 17Document13 paginiReviewer For Consti I - Art 6 - Sec. 1 - 17NinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- LEGAL POSITIVISM - Notes On HartDocument5 paginiLEGAL POSITIVISM - Notes On HartNinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eclampsia Effects On The FetusDocument6 paginiEclampsia Effects On The FetusNinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reviewer For Persons - Art. V To XVDocument12 paginiReviewer For Persons - Art. V To XVNinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eclampsia Effects On The FetusDocument6 paginiEclampsia Effects On The FetusNinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reviewer For Persons - Family Code Art. 1 To 10Document7 paginiReviewer For Persons - Family Code Art. 1 To 10NinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Air Blower ManualDocument16 paginiAir Blower ManualshaiknayeemabbasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kallatam of Kallatar (In Tamil Script Tscii Format)Document78 paginiKallatam of Kallatar (In Tamil Script Tscii Format)rprabhuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Catalogo PukangDocument41 paginiCatalogo PukangClarita Muller LeigueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Corelink Mmu600ae TRM 101412 0100 00 enDocument194 paginiCorelink Mmu600ae TRM 101412 0100 00 enLv DanielÎncă nu există evaluări
- Worked Solution Paper5 A LevelDocument8 paginiWorked Solution Paper5 A LevelBhoosan AncharazÎncă nu există evaluări
- ABBindustrialdrives Modules en RevBDocument2 paginiABBindustrialdrives Modules en RevBMaitry ShahÎncă nu există evaluări
- TechBridge TCP ServiceNow Business Case - Group 6Document9 paginiTechBridge TCP ServiceNow Business Case - Group 6Takiyah Shealy100% (1)
- Dependent ClauseDocument28 paginiDependent ClauseAndi Febryan RamadhaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- HDO OpeationsDocument28 paginiHDO OpeationsAtif NadeemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Managing Errors and ExceptionDocument12 paginiManaging Errors and ExceptionShanmuka Sreenivas100% (1)
- Chapter1 Intro To Basic FinanceDocument28 paginiChapter1 Intro To Basic FinanceRazel GopezÎncă nu există evaluări
- DG Oil SpecificationDocument10 paginiDG Oil SpecificationafsalmohmdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Extraction of Mangiferin From Mangifera Indica L. LeavesDocument7 paginiExtraction of Mangiferin From Mangifera Indica L. LeavesDaniel BartoloÎncă nu există evaluări
- DHA - Jebel Ali Emergency Centre + RevisedDocument5 paginiDHA - Jebel Ali Emergency Centre + RevisedJam EsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case ColorscopeDocument7 paginiCase ColorscopeRatin MathurÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Problem Books in Mathematics) Antonio Caminha Muniz Neto - An Excursion Through Elementary Mathematics, Volume III - Discrete Mathematics and Polynomial Algebra (2018, Springer)Document647 pagini(Problem Books in Mathematics) Antonio Caminha Muniz Neto - An Excursion Through Elementary Mathematics, Volume III - Discrete Mathematics and Polynomial Algebra (2018, Springer)Anonymous iH6noeaX7100% (2)
- OsciloscopioDocument103 paginiOsciloscopioFredy Alberto Gómez AlcázarÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Analysis of Students' Error in Using Possesive Adjective in Their Online Writing TasksDocument19 paginiAn Analysis of Students' Error in Using Possesive Adjective in Their Online Writing TasksKartika Dwi NurandaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Music Production EngineeringDocument1 paginăMusic Production EngineeringSteffano RebolledoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pantone PDFDocument53 paginiPantone PDF2dlmediaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zero Tolerance 2010Document16 paginiZero Tolerance 2010Adrian KozelÎncă nu există evaluări
- PCM Cables: What Is PCM Cable? Why PCM Cables? Application?Document14 paginiPCM Cables: What Is PCM Cable? Why PCM Cables? Application?sidd_mgrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Writ Petition 21992 of 2019 FinalDocument22 paginiWrit Petition 21992 of 2019 FinalNANDANI kumariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit-Ii Syllabus: Basic Elements in Solid Waste ManagementDocument14 paginiUnit-Ii Syllabus: Basic Elements in Solid Waste ManagementChaitanya KadambalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1 Bearer PlantsDocument2 paginiUnit 1 Bearer PlantsEmzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Docket - CDB Batu GajahDocument1 paginăDocket - CDB Batu Gajahfatin rabiatul adawiyahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Post Renaissance Architecture in EuropeDocument10 paginiPost Renaissance Architecture in Europekali_007Încă nu există evaluări
- UG ENGLISH Honours PDFDocument59 paginiUG ENGLISH Honours PDFMR.Shantanu SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tax Havens IMF PDFDocument59 paginiTax Havens IMF PDFClassic PhyXÎncă nu există evaluări
- Agenda - 2 - Presentation - MS - IUT - Thesis Proposal PPT Muhaiminul 171051001Document13 paginiAgenda - 2 - Presentation - MS - IUT - Thesis Proposal PPT Muhaiminul 171051001Tanvir AhmadÎncă nu există evaluări