Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Kinetic Energy and Gravitational Potential Energy
Încărcat de
Mark ProchaskaDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Kinetic Energy and Gravitational Potential Energy
Încărcat de
Mark ProchaskaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Physics First
Name
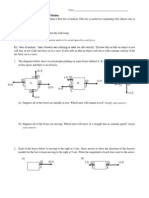
POGIL: Kinetic Energy and Gravitational Potential Energy Energy can be thought of as the capacity of an object to enact change. We have seen that energy can be transferred between different mechanisms and thus cause changes in a system. In this POGIL we will learn how to calculate the amount of energy stored in two mechanisms: kinetic energy (Ek) and gravitational potential energy (Eg). Kinetic Energy (Ek) The energy stored in kinetic energy (Ek) is associated with a systems motion. The diagrams below show several objects of different masses moving at different velocities. The energy stored in kinetic energy is calculated. Note that we use Joules as the unit of energy, abbreviated with the letter J.
15 kg
10 m/s
kinetic energy = (mass) (velocity)2 1 1 = 2 = (15 kg)(10 m/s)2 2 2 Ek = 750 Joules = 750 J kinetic energy = (mass) (velocity)2 1 1 = 2 = (15 kg)(20 m/s)2 2 2 Ek = 3000 Joules = 3000 J kinetic energy = (mass) (velocity)2 1 1 = 2 = (30 kg)(10 m/s)2 2 2 Ek = 1500 Joules = 1500 J
15 kg
20 m/s
10 m/s
30 kg
1. Calculate the energy, in Joules, stored in Ek for the following objects. (a) a 70 kg person running at 4 m/s
(b) a 1000 kg car traveling at 30 m/s
(c) a 0.05 kg ball moving at 25 m/s
(d) a 0.001 kg ant moving at a speed of 0.02 m/s
2. Can kinetic energy ever be negative? Why or why not?
Physics First
Name
3. Rank the following objects in order from LOWEST energy in Ek to HIGHEST energy in Ek. Indicate a tie with an equal sign. (a) an object of mass 1 kg traveling with a speed 1 m/s (b) an object of mass 2 kg traveling with a speed 1 m/s (c) an object of mass 1 kg traveling with a speed 2 m/s (d) an object of mass 0.5 kg traveling at speed 2 m/s (e) an object of mass 2 kg traveling at speed 0.5 m/s
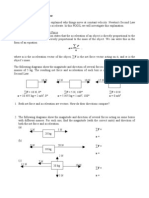
Gravitational Potential Energy (Eg) The energy stored in gravitational potential energy (Eg) is associated with an objects position relative to a planet (in most cases, the Earth) while under the influence of a gravitational force. The diagram below shows several objects of different masses at different heights above the ground. The energy stored in gravitational potential energy relative to the ground is calculated.
gravitational potential energy = mass acceleration due to gravity height = = (2 kg)(10 m/s2 )(12 m) Eg = 240 J gravitational potential energy = mass acceleration due to gravity height = = (1 kg)(10 m/s2 )(7 m) Eg = 70 J gravitational potential energy = mass acceleration due to gravity height = = (10 kg)(10 m/s2 )(3 m) Eg = 300 J gravitational potential energy = mass acceleration due to gravity height = = (15 kg)(10 m/s 2 )(0 m) Eg = 0 J
2 kg
1 kg
5m
10 kg
4m
15 kg
3m ground level, h = 0
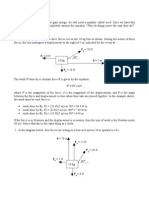
4. In the picture below, a 1000 kg car starts at point A and travels down a hill through points B, C, and D.
A B
5m 5m C 7m D
Physics First
Name
(a) Calculate the energy stored in Eg at points A, B, C, and D. Eg (point A) = Eg (point C) = Eg (point B) = Eg (point D) =
(b) Calculate the change in gravitational potential energy (Eg) when the car travels from point A to B, A to C, and A to D. Eg (A to B) = Eg (A to D) = 5. A 5 kg shotput is thrown through the air from an initial height of 1.5 m. Calculate the energy stored in Eg when the shotput is: (a) at its initial height. Eg (A to C) =
(b) 2 m above the ground.
(c) 2.5 m above the ground.
(d) 1 m above the ground.
(e) hitting the ground.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Relativistic EnergyDocument4 paginiRelativistic EnergyMark ProchaskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kinetic and Gravitational Potential EnergyDocument3 paginiKinetic and Gravitational Potential EnergyMark Prochaska50% (2)
- Newton's First LawDocument3 paginiNewton's First LawMark ProchaskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electric PowerDocument4 paginiElectric PowerMark ProchaskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electric ForcesDocument4 paginiElectric ForcesMark Prochaska100% (1)
- EnergyDocument3 paginiEnergyMark ProchaskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Temperature, Thermal Energy, and HeatingDocument3 paginiTemperature, Thermal Energy, and HeatingMark ProchaskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Work and PowerDocument3 paginiWork and PowerMark ProchaskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- POGIL: Length ContractionDocument3 paginiPOGIL: Length ContractionMark ProchaskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Em SpectrumDocument3 paginiEm SpectrumMark Prochaska100% (1)
- Newton's Third LawDocument3 paginiNewton's Third LawMark Prochaska100% (1)
- Free Body DiagramsDocument4 paginiFree Body DiagramsMark ProchaskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- AccelerationDocument4 paginiAccelerationMark Prochaska100% (1)
- 11 Phy - Gravitation - QN Bank - Only QnsDocument3 pagini11 Phy - Gravitation - QN Bank - Only QnsMohit DhaundiyalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Torque POGIL and WebquestDocument7 paginiTorque POGIL and WebquestSamuel Jay100% (1)
- Position, Displacement, VelocityDocument3 paginiPosition, Displacement, VelocityMark Prochaska0% (1)
- Chapter 9 RotationDocument7 paginiChapter 9 RotationHana Lee Jorel ZekeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ch06 ISMDocument67 paginiCh06 ISMThai-Son LeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tesla or 220 Volts of Personal - Blog ItDocument7 paginiTesla or 220 Volts of Personal - Blog ItaladinthewizardÎncă nu există evaluări
- AccelerationDocument4 paginiAccelerationMark ProchaskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Newton's Second LawDocument5 paginiNewton's Second LawMark Prochaska100% (1)
- Voltage and ResistanceDocument4 paginiVoltage and ResistanceMark ProchaskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CP Spring Scale POGIL 2012 2013Document4 paginiCP Spring Scale POGIL 2012 2013Anthony ButlerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Newton's Second LawDocument4 paginiNewton's Second LawMark ProchaskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Speed and VelocityDocument4 paginiSpeed and VelocityMark ProchaskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 11 - Work and Energy Revision Notes PDFDocument8 paginiChapter 11 - Work and Energy Revision Notes PDFShuchi MaheshwariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heating and Phase ChangesDocument4 paginiHeating and Phase ChangesMark ProchaskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Conservation of Energy: Conceptual ProblemsDocument22 paginiThe Conservation of Energy: Conceptual Problemsmukesh3021Încă nu există evaluări
- Intro Physics Instructors Guide Semester1 AppendixADocument63 paginiIntro Physics Instructors Guide Semester1 AppendixAGfour Maserati50% (2)
- Chapter No 1Document26 paginiChapter No 1Moin Khan100% (2)
- Chapter No 4Document27 paginiChapter No 4Moin KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Potential Energy Mastering PhysicsDocument23 paginiPotential Energy Mastering PhysicsLea Dominique Mangubat Fariola0% (1)
- Mass and Inertia: Dynamics 1Document11 paginiMass and Inertia: Dynamics 1Joe West100% (2)
- Class Xi Physics Annual Exam 2017 18Document3 paginiClass Xi Physics Annual Exam 2017 18Anupam TiwariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM)Document41 paginiSimple Harmonic Motion (SHM)neoeverestÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electric ForceDocument4 paginiElectric ForceMark ProchaskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bigbang PDF Final Exam PDFDocument8 paginiBigbang PDF Final Exam PDFWasyhun AsefaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chap 14Document104 paginiChap 14noscribdyoucantÎncă nu există evaluări
- Temperature and HeatingDocument4 paginiTemperature and HeatingMark ProchaskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Force of Foot On Floor (Pushing Backward) Force of Floor On Foot (Reactive Force On Foot's Push)Document4 paginiForce of Foot On Floor (Pushing Backward) Force of Floor On Foot (Reactive Force On Foot's Push)Vann Andrei PagulayanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Momentum and ImpulseDocument10 paginiMomentum and ImpulseYuniar AmaliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Formal Homework Assignment 4Document69 paginiFormal Homework Assignment 4mhm00066690% (10)
- Review Problems Semester 57Document184 paginiReview Problems Semester 57Unkabogable AkoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Energy Impulse SecretsDocument16 paginiEnergy Impulse SecretsJanaki RamanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Energy and MomentumDocument33 paginiEnergy and MomentumCK33% (6)
- Work and PowerDocument15 paginiWork and Powersujayan2005Încă nu există evaluări
- WTPDocument22 paginiWTPYogesh SarangdharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mass Defect and Binding EnergyDocument3 paginiMass Defect and Binding EnergyMark ProchaskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Newton's Second LawDocument3 paginiNewton's Second LawMark ProchaskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class 9 GravitationDocument11 paginiClass 9 GravitationShubhendu KarmakarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Magnetic Effect and MagnetismDocument12 paginiMagnetic Effect and Magnetismvishal_kalraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test - Unit 3 - Energy and MomentumDocument4 paginiTest - Unit 3 - Energy and Momentumascd_msvuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Working and PowerDocument4 paginiWorking and PowerMark ProchaskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mastering Physics CH 11 HW College Physics I LCCCDocument50 paginiMastering Physics CH 11 HW College Physics I LCCCSamuel90% (10)
- GB Atoms Pogil 2014-2015Document2 paginiGB Atoms Pogil 2014-2015api-261277442Încă nu există evaluări
- Kinetic Energy and Gravitational Potential Energy - HONORSDocument3 paginiKinetic Energy and Gravitational Potential Energy - HONORSMark ProchaskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pogil - Ke PeDocument4 paginiPogil - Ke Peapi-259781257Încă nu există evaluări
- Work Energy Power and Efficiency IB WorksheetDocument12 paginiWork Energy Power and Efficiency IB WorksheetAnonymous LZmFaXc100% (2)
- GCSE 23 WorkEnergyDocument66 paginiGCSE 23 WorkEnergyHenri OttÎncă nu există evaluări
- Energy Conversion Q&ADocument8 paginiEnergy Conversion Q&AGkid GkidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nuclear Fission and FusionDocument4 paginiNuclear Fission and FusionMark ProchaskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Work and PowerDocument3 paginiWork and PowerMark ProchaskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Time DilationDocument3 paginiTime DilationMark ProchaskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Position, Displacement, VelocityDocument3 paginiPosition, Displacement, VelocityMark Prochaska0% (1)
- Voltage and ResistanceDocument4 paginiVoltage and ResistanceMark ProchaskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Motion in Two Dimensions 1Document4 paginiMotion in Two Dimensions 1Mark ProchaskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Newton's First LawDocument3 paginiNewton's First LawMark ProchaskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Newton's Third LawDocument3 paginiNewton's Third LawMark ProchaskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vector ComponentsDocument4 paginiVector ComponentsMark ProchaskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- VectorsDocument2 paginiVectorsMark ProchaskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Working and PowerDocument4 paginiWorking and PowerMark ProchaskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Newton's Second LawDocument3 paginiNewton's Second LawMark ProchaskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Motion in Two Dimensions 2Document3 paginiMotion in Two Dimensions 2Mark ProchaskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Magnetic ForcesDocument3 paginiMagnetic ForcesMark ProchaskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mass Defect and Binding EnergyDocument3 paginiMass Defect and Binding EnergyMark ProchaskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electromagnetic InductionDocument4 paginiElectromagnetic InductionMark ProchaskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- EnergyDocument3 paginiEnergyMark ProchaskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Free Body DiagramsDocument4 paginiFree Body DiagramsMark ProchaskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electric CurrentDocument2 paginiElectric CurrentMark ProchaskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atomic NucleiDocument4 paginiAtomic NucleiMark ProchaskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- AccelerationDocument2 paginiAccelerationMark Prochaska0% (1)
- POGIL: Length ContractionDocument3 paginiPOGIL: Length ContractionMark ProchaskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- WavesDocument4 paginiWavesMark ProchaskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Work and PowerDocument4 paginiWork and PowerMark Prochaska100% (1)
- Temperature and HeatingDocument4 paginiTemperature and HeatingMark ProchaskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- VelocityDocument4 paginiVelocityMark ProchaskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Universal GravitationDocument3 paginiUniversal GravitationMark ProchaskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Vehicle Dynamics: Vehicle Equation of MotionDocument16 paginiAdvanced Vehicle Dynamics: Vehicle Equation of Motionbiruk1Încă nu există evaluări
- Physics Investigatory PrijectDocument10 paginiPhysics Investigatory Prijectneevahirwar498Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 8 Matriculation STPMDocument129 paginiChapter 8 Matriculation STPMJue Saadiah100% (7)
- Kinematics of FlowDocument6 paginiKinematics of FlowDavid Kegaya100% (1)
- Ch-04 Moving Charges and Magnetism: Lect-10Document32 paginiCh-04 Moving Charges and Magnetism: Lect-10Kishan KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heat Transfer ConductionDocument29 paginiHeat Transfer ConductionDilaFirizqinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- WWW - Studyguide.pk: PhysicsDocument16 paginiWWW - Studyguide.pk: PhysicsMohammad MoosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Extented Heat Transfer Surface - FINDocument7 paginiExtented Heat Transfer Surface - FINbekkuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 24 - Intro To Turbulence Modeling in CFDDocument23 paginiChapter 24 - Intro To Turbulence Modeling in CFDprashanthreddyhÎncă nu există evaluări
- OEM - Syllabus Oct 2020 - Feb 2021Document6 paginiOEM - Syllabus Oct 2020 - Feb 2021LUIS DAVID MOROCHO POGOÎncă nu există evaluări
- BMI UNIT IV Ultrasound Blood FlowDocument3 paginiBMI UNIT IV Ultrasound Blood FlowARAVIND ELAÎncă nu există evaluări
- 08 Stationary WavesDocument10 pagini08 Stationary WavesDachou GeetuÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Earth's Atmosphere - K. Saha PDFDocument374 paginiThe Earth's Atmosphere - K. Saha PDFIvetteÎncă nu există evaluări
- METAT and TAF Weather Report 1612262538Document12 paginiMETAT and TAF Weather Report 1612262538cplowhangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stage 2 Biomechanics 2nd Ed Sample PackageDocument13 paginiStage 2 Biomechanics 2nd Ed Sample PackagegundadanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Helical NewDocument14 paginiHelical Newshiox1989Încă nu există evaluări
- Weather Elementary Eng FileDocument28 paginiWeather Elementary Eng Fileiryna myskivÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heat ExchangersDocument77 paginiHeat ExchangersMervin PerezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heat TransferDocument17 paginiHeat TransfertadesseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 8 PhysicsDocument5 paginiGrade 8 Physicsheenamehta2702Încă nu există evaluări
- The Skin Effect - Philips Technical Review Volume28Document16 paginiThe Skin Effect - Philips Technical Review Volume28shrikrisÎncă nu există evaluări
- G8 Wave PropertiesDocument4 paginiG8 Wave PropertiesCheazitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of Mooring System of Oil Storage Barges in Shallow WaterDocument10 paginiDesign of Mooring System of Oil Storage Barges in Shallow Watermrmoh3nÎncă nu există evaluări
- Homework+5 20220607Document1 paginăHomework+5 20220607許廷睿Încă nu există evaluări
- Physics - Unit 5 Other TopicsDocument4 paginiPhysics - Unit 5 Other TopicsJTBTeddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wave Behaviour of ParticlesDocument15 paginiWave Behaviour of ParticlespriyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- IrradiationDocument29 paginiIrradiationDerickPabalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Noise Pollution MCQDocument4 paginiNoise Pollution MCQ01ABHIGYAN MAJIÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Calculation of The Mean Radiant Temperature of A Subject Exposed To The Solar Radiation-A Generalised AlgorithmDocument9 paginiThe Calculation of The Mean Radiant Temperature of A Subject Exposed To The Solar Radiation-A Generalised AlgorithmGiulia SantoroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Applies A Centripetal Force To The Second Dancer's Hand. in Which Case The Centripetal Force Is Maximum?Document7 paginiApplies A Centripetal Force To The Second Dancer's Hand. in Which Case The Centripetal Force Is Maximum?abai0316Încă nu există evaluări