Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Wool Merino Sheep
Încărcat de
bub_33Descriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Wool Merino Sheep
Încărcat de
bub_33Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
WOOL
MERINO SHEEP
ANGORA GOAT
BACTRIAN CAMEL
ANGORA RABBIT
YAK
SHEEP SHEARING
SCOURING
SORTING
GRADING
TIMBER Lumber or timber is wood in any of its stages from felling through readiness for use as structural material for construction, or wood pulp for paper production. (The distinction between the two terms is discussed below.) Lumber is supplied either rough or finished. Besides pulpwood, rough lumber is the raw material for furniture-making and other items requiring additional cutting and shaping. It is available in many species, usually hardwoods. Finished lumber is supplied in standard sizes, mostly for the construction industry, primarily softwood from coniferous species including pine, fir and spruce (collectively known as Sprucepine-fir), cedar, and hemlock, but also some hardwood, for high-grade flooring. There are over 150 species of timber which are produced in India.
FRUIT TREE A fruit tree is a tree which bears fruit that is consumed or used by people all trees that are flowering plants produce fruit, which are the ripened ovaries of flowers containing one or more seeds. In horticultural
usage, the term 'fruit tree' is limited to those that provide fruit for human food. Types of fruits are described and defined elsewhere , but would include "fruit" in a culinary sense, as well as some nut-bearing trees, such as walnuts.
MEDICINAL PLANTS Medicinal plants are various plants used in herbalism and thought by some to have medicinal properties. Few plants or their phytochemical constituents have been proven to have medicinal effects by rigorous science or have been approved by regulatory agencies such as the United States Food and Drug Administration or European Food Safety Authority. Pharmacognosy is the study of medicines derived from natural sources, including plants. The American Society of Pharmacognosy as "the study of the physical, chemical, biochemical and biological properties of drugs, drug substances or potential drugs or drug substances of natural origin as well as the search for new drugs from natural sources."
FIBER PLANT
Fiber crops are field crops grown for their fibers, which are traditionally used to make paper, cloth, or rope. The fibers may be chemically modified, like in viscose or cellophane. In recent years materials scientists have begun exploring further use of these fibers in composite materials. Fiber crops are generally harvestable after a single growing season, as distinct from trees, which are typically grown for many years before being harvested for wood pulp fiber. In specific circumstances, fiber crops can be superior to wood pulp fiber in terms of technical performance, environmental impact or cost. Botanically, the fibers harvested from many of these plants are bast fibers; the fibers come from the phloem tissue of the plant. The other fiber crop fibers are seed padding, leaf fiber, or other parts of the plant.
OIL PLANT Oils, oleoresins & extracts from plants are used in a wide variety of ways in food, as medicine, in cosmetics & toiletry, as ingredients for industrial products, as fuel, and more. We present web resources for the various plant oils and their applications. By the term plant oils, we refer to oils that are derived from one or more parts of a plant, shrub or tree. Hence the oil could be from the root, stem/bark, leaves, flowers, seeds, fruits and whatever else could be a part of the plant! Plant-derived oils can be broadly classified into two: Essential Oils & Fixed Oils. Essential oils are volatile, and are usually derived from the non-seed parts of the plants. Most fixed oils are the so-called fatty oils, and a majority of the fatty oils are derived from the seeds hence the term oilseeds, meaning oil-bearing seeds. Some of the fixed oils are derived from vegetables & nuts.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Gardeners' Guide To Botany: Gardener's Guide Series, #4De la EverandGardeners' Guide To Botany: Gardener's Guide Series, #4Încă nu există evaluări
- Useful Products From PlantsDocument2 paginiUseful Products From PlantsAmanda Noemí NuñezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Economic BotanyDocument4 paginiEconomic BotanyMujtaba Abubakar83% (6)
- Kerson Chapter IIDocument7 paginiKerson Chapter IIHazelÎncă nu există evaluări
- BiologyDocument12 paginiBiologysakadynamites041Încă nu există evaluări
- Botany: Chapter GoalsDocument50 paginiBotany: Chapter GoalsYoukha Suta WiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antifungi Activity On PlantsDocument23 paginiAntifungi Activity On PlantsBAYODE MAYOWAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thesis NamuDocument39 paginiThesis NamuEmily Sadernas AwaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3.classification of Crop PlantsDocument48 pagini3.classification of Crop PlantsAmìt Ķ MäzùmdérÎncă nu există evaluări
- Go Shu PPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPDocument7 paginiGo Shu PPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPfasil ewunetie gedamuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bio ProjectDocument68 paginiBio ProjectShalini Jain100% (1)
- What is plant production method The plant production system encompasses the basic genetic and physiological regulations on plant growth, the impact on growth of soil, water, nutrients, disease and pests and the infDocument40 paginiWhat is plant production method The plant production system encompasses the basic genetic and physiological regulations on plant growth, the impact on growth of soil, water, nutrients, disease and pests and the infjohnabeth jamonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Asexually From Their Bulb and Sexually Through Seed ProductionDocument1 paginăAsexually From Their Bulb and Sexually Through Seed ProductionRealyn Delos Santos TañecaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Null 1Document31 paginiNull 1Sajid IqbalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 7Document14 paginiUnit 7Dr. Shriram KunjamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Principles of Crop Production CRPT 102: BS Agriculture 1 A.Y. 2021-2022 Second SemesterDocument49 paginiPrinciples of Crop Production CRPT 102: BS Agriculture 1 A.Y. 2021-2022 Second SemesterAllena VillarinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction of Non-Timber Forest ProductsDocument16 paginiIntroduction of Non-Timber Forest ProductsSumanSahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Plant Production SystemDocument12 paginiThe Plant Production SystemDane VincentÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parts of The Plants and Its UsesDocument1 paginăParts of The Plants and Its UsesJulibel GanzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plants ClassificationDocument11 paginiPlants ClassificationLeslie GandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neem, Pesticide and Medicinal ApplicationDocument60 paginiNeem, Pesticide and Medicinal Applicationlok8Încă nu există evaluări
- Herbal and Complementary Medicine Dr. Denise K. DaleyDocument92 paginiHerbal and Complementary Medicine Dr. Denise K. DaleyMarquel CulmerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gymnosperms PinusDocument15 paginiGymnosperms Pinusrajan.11proÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toxicology... 2nd LectureDocument23 paginiToxicology... 2nd LectureBushra MalikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Botany Tuber Crops Final - CompressedDocument18 paginiBotany Tuber Crops Final - CompressedAyisha PSÎncă nu există evaluări
- FPPS 128 ReviewerDocument22 paginiFPPS 128 ReviewerIring CattòÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To PharmacognosyDocument19 paginiIntroduction To PharmacognosytmleeaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6 HerbivoryDocument38 pagini6 Herbivoryangel mae estanolÎncă nu există evaluări
- Classification of Crop DetailedDocument11 paginiClassification of Crop DetailedRahulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adv Sci G7Document22 paginiAdv Sci G7Ezequiel ManluluÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To BotanyDocument25 paginiIntroduction To BotanyJenniferÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Botany: Botany Is The Branch of Biology Concerned With The Scientific Study of PlantsDocument39 paginiIntroduction To Botany: Botany Is The Branch of Biology Concerned With The Scientific Study of PlantsHazelClaveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carmela VergaraDocument3 paginiCarmela Vergaracarmela vergaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- PhanerogamsDocument3 paginiPhanerogamsKrishna JaiswalÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 SelectingBestPlants2007Document26 pagini4 SelectingBestPlants2007MarceloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plants Grade 3Document12 paginiPlants Grade 3Bryan James Aguirre DalawampuÎncă nu există evaluări
- CropSci101 Module 2Document11 paginiCropSci101 Module 2Jetro Neil GapasinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flowers and Pine Trees Are Both Seed-Producing Plants.: How Does The Plant Reproduce and Make New Plants?Document4 paginiFlowers and Pine Trees Are Both Seed-Producing Plants.: How Does The Plant Reproduce and Make New Plants?Anchal ChadhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plant Physiology:: How Plants WorkDocument70 paginiPlant Physiology:: How Plants WorkSusana DiazÎncă nu există evaluări
- AmulyaDocument6 paginiAmulyaJaya ChandranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Different Systems of Classification of Crude DrugsDocument5 paginiDifferent Systems of Classification of Crude Drugsministore kmcÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To BotanyDocument4 paginiIntroduction To BotanyEmanuel LacedaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medicine and Materials: AazzqqDocument3 paginiMedicine and Materials: Aazzqqterran2020Încă nu există evaluări
- Plant Fibre ApplicationDocument2 paginiPlant Fibre ApplicationNisa KhoirunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter TwoDocument7 paginiChapter TwoStephen LonewolfÎncă nu există evaluări
- B5-Plant & Animal ClassificationDocument11 paginiB5-Plant & Animal ClassificationHarshaWakodkar100% (1)
- Plants: By: Sarah Alex Teacher:Sir MushtaqDocument21 paginiPlants: By: Sarah Alex Teacher:Sir MushtaqMushtaq M.ChinoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manage Tree Assessment: Why Trees Matter?Document41 paginiManage Tree Assessment: Why Trees Matter?Aidan ChuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4th Grading Classification of PlantsDocument57 pagini4th Grading Classification of PlantsAlea DuqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medicine and Materials: AazzqqwwDocument3 paginiMedicine and Materials: Aazzqqwwterran2020Încă nu există evaluări
- Medicine and Materials: Tapping A Rubber Tree in ThailandDocument3 paginiMedicine and Materials: Tapping A Rubber Tree in Thailandterran2020Încă nu există evaluări
- PlantsDocument93 paginiPlantsnehmiryll sumaletÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medicine and Materials: AazzqqwwaaDocument3 paginiMedicine and Materials: Aazzqqwwaaterran2020Încă nu există evaluări
- Plants Cell: BY Ayaa Anthony. 2Nd Semester-Cpha I 2021/2022 Department of PharmacyDocument29 paginiPlants Cell: BY Ayaa Anthony. 2Nd Semester-Cpha I 2021/2022 Department of PharmacyAyaa AnthonyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Characterization and Potency of Kapok PlantDocument5 paginiCharacterization and Potency of Kapok PlantAnonymous KI0rMdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plant ReproductionDocument2 paginiPlant ReproductionJoniele Angelo AninÎncă nu există evaluări
- Organic Materials: Hardwoods Are Ones That Come From Broad-Leaved (Deciduous) Trees (ThoseDocument3 paginiOrganic Materials: Hardwoods Are Ones That Come From Broad-Leaved (Deciduous) Trees (ThoseJoshuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practical Lec Classification of PlantDocument3 paginiPractical Lec Classification of Plantkn kkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Review of LiteratureDocument3 paginiReview of Literaturevkumar_345287Încă nu există evaluări
- Science1Document113 paginiScience1Mary OchoaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Use of ITK in Plant ProtectionDocument4 paginiUse of ITK in Plant ProtectionmramagroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dikamali (Gardenia Resinifera Roth.) : G. Latifolia G. Resinifera G. TurgidaDocument6 paginiDikamali (Gardenia Resinifera Roth.) : G. Latifolia G. Resinifera G. TurgidaPrajakta RaneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Agris PL StudiuDocument13 paginiAgris PL Studiuradulet raduÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tipe Perkecambahan Dan SemaiDocument12 paginiTipe Perkecambahan Dan SemaiDimaz IrawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Random Plant Chart: Roll Desc Plant Name Used Part Effect Stat Buff/Debuff Type/ColorDocument2 paginiRandom Plant Chart: Roll Desc Plant Name Used Part Effect Stat Buff/Debuff Type/ColorJeffery OsvoldÎncă nu există evaluări
- US Department of Agriculture - Seeds ImportedDocument1.053 paginiUS Department of Agriculture - Seeds ImportedTaylorMooreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Riview Vanilla PDFDocument28 paginiRiview Vanilla PDFUzlifatil100% (1)
- 11th STD Botany Practical Manual English Medium - WWW - tn11th - in PDFDocument43 pagini11th STD Botany Practical Manual English Medium - WWW - tn11th - in PDFsri thamizhan80% (85)
- And Applied Manganese: Understanding Plant NutrientsDocument4 paginiAnd Applied Manganese: Understanding Plant Nutrientsanon_952599291Încă nu există evaluări
- Botafun ReviewerDocument140 paginiBotafun ReviewerYasmin Malabuyo67% (3)
- Medical Cannabis and Industrial Hemp Tissue Culture: Present Status and Future PotentialDocument22 paginiMedical Cannabis and Industrial Hemp Tissue Culture: Present Status and Future PotentialPawan MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plant Concept MapDocument2 paginiPlant Concept MapVishnu Ronaldus NarayanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Conference Stockholm Sweden Book PDFDocument524 paginiConference Stockholm Sweden Book PDFOleksandra KovalevskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guidelines For Growing BambooDocument65 paginiGuidelines For Growing BambooRaymond Katabazi86% (7)
- GR6 Tle Q1 W5 D1-D5Document10 paginiGR6 Tle Q1 W5 D1-D5Erdell BaronÎncă nu există evaluări
- Post Harvest Diseases of TomatoDocument2 paginiPost Harvest Diseases of Tomatoshyamsunder68Încă nu există evaluări
- Vojniković 2015 Rudbeckia LDocument9 paginiVojniković 2015 Rudbeckia LAnonymous dEztzVueÎncă nu există evaluări
- SteviaDocument5 paginiSteviaCbeClearÎncă nu există evaluări
- Edible Flowers Guide - Thompson & MorganDocument9 paginiEdible Flowers Guide - Thompson & MorganHoscoFoodsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Best Practices For APRICOT Production and Marketing in Afghanistan, Roots of Peace ROPDocument28 paginiBest Practices For APRICOT Production and Marketing in Afghanistan, Roots of Peace ROPMaftei MariusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Qatar Landscaping Qcs 2014Document91 paginiQatar Landscaping Qcs 2014Hemalatha Sampath89% (9)
- SorghumDocument4 paginiSorghumDr-Vijay SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 23 The Interior LandscapeDocument21 paginiUnit 23 The Interior LandscapesÎncă nu există evaluări
- LAS OAP 4th Quarter Produce Organic Vegetable 3Document26 paginiLAS OAP 4th Quarter Produce Organic Vegetable 3Katherene AgraveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diversified and Integrated Farming Systems (DIFS) : Philippine Experiences For Improved Livelihood and NutritionDocument16 paginiDiversified and Integrated Farming Systems (DIFS) : Philippine Experiences For Improved Livelihood and NutritionMa. Dolores MalinaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Erythrina Velutina PDFDocument2 paginiErythrina Velutina PDFRonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology: Unit: 4BI0 Paper: 2BDocument16 paginiBiology: Unit: 4BI0 Paper: 2BSajid HasanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Part 2. Overview 1Document58 paginiPart 2. Overview 1Waren LlorenÎncă nu există evaluări
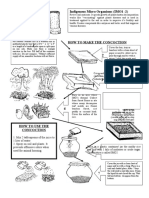
- Indigenous Micro Organisms (IMO1 - 2) : How To Make The ConcoctionDocument1 paginăIndigenous Micro Organisms (IMO1 - 2) : How To Make The ConcoctionMarycon NacitoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerDe la EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (392)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceDe la EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceEvaluare: 3 din 5 stele3/5 (18)
- The Encyclopedia of Spices & Herbs: An Essential Guide to the Flavors of the WorldDe la EverandThe Encyclopedia of Spices & Herbs: An Essential Guide to the Flavors of the WorldEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (5)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsDe la EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (6)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityDe la EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (3)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossDe la EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (6)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDe la EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2)
- Mostly Plants: 101 Delicious Flexitarian Recipes from the Pollan FamilyDe la EverandMostly Plants: 101 Delicious Flexitarian Recipes from the Pollan FamilyEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (11)
- Chicano Eats: Recipes from My Mexican-American KitchenDe la EverandChicano Eats: Recipes from My Mexican-American KitchenÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceDe la EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (516)
- Authentic Mexican: Regional Cooking from the Heart of MexicoDe la EverandAuthentic Mexican: Regional Cooking from the Heart of MexicoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pati's Mexican Table: The Secrets of Real Mexican Home CookingDe la EverandPati's Mexican Table: The Secrets of Real Mexican Home CookingEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (9)
- Instant Loss On a Budget: Super-Affordable Recipes for the Health-Conscious CookDe la EverandInstant Loss On a Budget: Super-Affordable Recipes for the Health-Conscious CookEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2)
- The Food Lover's Cleanse: 140 Delicious, Nourishing Recipes That Will Tempt You Back into Healthful EatingDe la EverandThe Food Lover's Cleanse: 140 Delicious, Nourishing Recipes That Will Tempt You Back into Healthful EatingEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (3)
- Waiter Rant: Thanks for the Tip—Confessions of a Cynical WaiterDe la EverandWaiter Rant: Thanks for the Tip—Confessions of a Cynical WaiterEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (487)
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)De la EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (378)
- Poilâne: The Secrets of the World-Famous Bread BakeryDe la EverandPoilâne: The Secrets of the World-Famous Bread BakeryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Surprise-Inside Cakes: Amazing Cakes for Every Occasion—with a Little Something Extra InsideDe la EverandSurprise-Inside Cakes: Amazing Cakes for Every Occasion—with a Little Something Extra InsideEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (6)
- Masterminds: Genius, DNA, and the Quest to Rewrite LifeDe la EverandMasterminds: Genius, DNA, and the Quest to Rewrite LifeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Instant Pot Miracle 6 Ingredients Or Less: 100 No-Fuss Recipes for Easy Meals Every DayDe la EverandInstant Pot Miracle 6 Ingredients Or Less: 100 No-Fuss Recipes for Easy Meals Every DayEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (4)
- Not That Fancy: Simple Lessons on Living, Loving, Eating, and Dusting Off Your BootsDe la EverandNot That Fancy: Simple Lessons on Living, Loving, Eating, and Dusting Off Your BootsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Saved By Soup: More Than 100 Delicious Low-Fat Soups To Eat And Enjoy Every DayDe la EverandSaved By Soup: More Than 100 Delicious Low-Fat Soups To Eat And Enjoy Every DayEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (10)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesDe la EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (397)
- Fast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperDe la EverandFast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (15)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessDe la Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (33)
- Body Love Every Day: Choose Your Life-Changing 21-Day Path to Food FreedomDe la EverandBody Love Every Day: Choose Your Life-Changing 21-Day Path to Food FreedomEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1)