Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
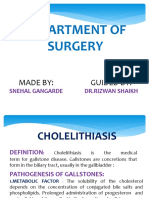
Biliary Dyskinesia
Încărcat de
Yolotl Hilario Sanchez Carrillo0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
92 vizualizări1 paginăBiliary dyskinesia or acalculous gallbladder disease occurs without gallstones. Like gallstone disease, it is much more common in women than men. The most common test to confirm clinically suspected function is a cck-hida scan.
Descriere originală:
Titlu original
Biliary_Dyskinesia
Drepturi de autor
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentBiliary dyskinesia or acalculous gallbladder disease occurs without gallstones. Like gallstone disease, it is much more common in women than men. The most common test to confirm clinically suspected function is a cck-hida scan.
Drepturi de autor:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
92 vizualizări1 paginăBiliary Dyskinesia
Încărcat de
Yolotl Hilario Sanchez CarrilloBiliary dyskinesia or acalculous gallbladder disease occurs without gallstones. Like gallstone disease, it is much more common in women than men. The most common test to confirm clinically suspected function is a cck-hida scan.
Drepturi de autor:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 1
Timothy M. Burandt, D.O., FACOS Craig A. Duncan, D.O., FACOS Eric Miller, D.O.
810 South Main Street, Suite 1, Cheboygan, MI 49721 231-627-4364 Facsimile 231-627-7758 www.cheboygansurgical.com
Biliary Dyskinesia What is biliary dyskinesia?
Gallbladder disease that occurs without gallstones is called biliary dyskinesia or acalculous gallbladder disease. It can be acute (arising suddenly, often as a one-time occurrence) or chronic (persistent, recurrent). Acute acalculous gallbladder disease usually occurs in patients who are very ill from other disorders. Chronic acalculous gallbladder disease may be caused by dysfunctional muscle or valve defects that impair the gallbladders ability to contract and release bile. The term biliary dyskinesia refers to abnormal gallbladder function characterized by right upper quadrant abdominal pain (sometimes radiating to the upper back or shoulder blades) after eating fatty or fried foods, heavy meals with nausea/vomiting or bloating, followed by loosening of stools. The excess build up of pressure in the bile ducts is thought to be responsible for these typical gallbladder symptoms. Like gallstone disease, biliary dyskinesia is much more common in women than men.
How does your physician diagnose biliary dyskinesia/acalculous gallbladder disease?
The history and physical examination of a patient with biliary dyskinesia is very similar to patients with gallstone disease. Chronic acalculous gallbladder disease is usually diagnosed when a patient complains of gallbladder symptoms but there is no evidence of stones using standard imaging techniques like ultrasound. The most common test to confirm clinically suspected functional gallbladder disease is a CCK-HIDA (cholecystokinin dimethyl iminodiacetic acid) scan. The patients blood is drawn and mixed with a low level radioactive substance and reinjected back into the blood stream where it collects in the liver and bile ducts. The patient is then given a hormone cholecystokinin octapeptide (CCK), which induces gallbladder contractions. A nuclear medicine camera captures pictures of the gallbladder emptying and determines if the gallbladder is functioning correctly. If the gallbladder demonstrates impaired emptying and/or the patient experiences a reproduction of the gallbladder symptoms, the diagnosis of biliary dyskinesia is confirmed. CCK- HIDA scanning is felt to be an objective and reproducible measure of gallbladder dysfunction, and can help predict which patients will have the best chance for symptomatic relief after cholecystectomy (gallbladder removal).
What is the treatment for biliary dyskinesia?
Most patients (75% - 95%) diagnosed with biliary dyskinesia (chronic acalculous gallbladder disease) experience partial or complete relief of their symptoms after cholecystectomy (surgical removal of the gallbladder using laparoscopic or open techniques). The CCK-HIDA scan helps predict which patients will benefit from gallbladder removal. Cholecystectomy for biliary dyskinesia provides relief of symptoms that are similar to those associated with treatment of symptomatic gallstones.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Cholecystitis Litiasis EctomyDocument23 paginiCholecystitis Litiasis EctomyTimothy WilliamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gastric Outlet Obstruction, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDe la EverandGastric Outlet Obstruction, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Warfarin Mechanism of ActionDocument7 paginiWarfarin Mechanism of ActionIna GrigorasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tube FeedingDocument47 paginiTube FeedingArlyn Mendenilla0% (1)
- Enzymes-Lactose 20intoleranceDocument2 paginiEnzymes-Lactose 20intoleranceapi-323374257Încă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Process NUTRITIONDocument82 paginiNursing Process NUTRITIONNoci M. FrenkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adult Enteral FormulasDocument2 paginiAdult Enteral FormulasMaulidatul Khasanah New100% (1)
- Diabetes Mellitus Type 2Document16 paginiDiabetes Mellitus Type 2MTs MIFDAÎncă nu există evaluări
- ATORVASTATINDocument2 paginiATORVASTATINAubrey Unique EvangelistaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 - Presentation - Management of Preclamplsia, Mild and ModerateDocument22 pagini1 - Presentation - Management of Preclamplsia, Mild and ModeratesharonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrolyte ReplacementDocument3 paginiElectrolyte ReplacementRatih Dwi OctariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- TPNDocument56 paginiTPNdenekeÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP GeDocument14 paginiNCP GeSuluhTriUtomoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 Polypharmacy Case StudyDocument6 pagini5 Polypharmacy Case Studyapi-392216729Încă nu există evaluări
- PancreatitisDocument12 paginiPancreatitismardsz100% (5)
- Gastrointestinal DrugsDocument45 paginiGastrointestinal DrugsCindy MaslagÎncă nu există evaluări
- Failure To ThriveDocument2 paginiFailure To Thrivekafosid100% (1)
- Drug Induced Renal DisorderDocument50 paginiDrug Induced Renal DisorderYv SantoshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Respiratory Distress SyndromeDocument30 paginiAcute Respiratory Distress SyndromeOya Zuraini KamalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mesalazine: Mesalazine (INN, BAN), Also Known As Mesalamine (USAN) or 5-Aminosalicylic AcidDocument4 paginiMesalazine: Mesalazine (INN, BAN), Also Known As Mesalamine (USAN) or 5-Aminosalicylic AcidAnkan PalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study 2Document4 paginiCase Study 2api-2451636590% (1)
- HyperlipidemiaDocument17 paginiHyperlipidemiabent alfay7a2Încă nu există evaluări
- Myasthenic Crisis Vs Cholinergic CrisisDocument1 paginăMyasthenic Crisis Vs Cholinergic CrisisNicole VogelsbergÎncă nu există evaluări
- BUN Blood Urea NitrogenDocument12 paginiBUN Blood Urea NitrogenGlydenne Glaire Poncardas Gayam100% (1)
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease .. Last EditDocument22 paginiInflammatory Bowel Disease .. Last EditRashed ShatnawiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study For LeukemiaDocument5 paginiCase Study For LeukemiaGabbii CincoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Enteral Feeding: Indications, Complications, and Nursing CareDocument6 paginiEnteral Feeding: Indications, Complications, and Nursing CareSheena CabrilesÎncă nu există evaluări
- 11 Nursing Management in Uterine (Endometrial) CancerDocument17 pagini11 Nursing Management in Uterine (Endometrial) Cancerclaire yowsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Discharge PlanDocument4 paginiDischarge PlanKabang MoaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Management Pancreatic CancerDocument2 paginiNursing Management Pancreatic CancerKit NameKo100% (2)
- Gallstone DiseaseDocument14 paginiGallstone DiseaseSuryaAtmajayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Adaptation Syndrome TheoriesDocument4 paginiGeneral Adaptation Syndrome TheoriesHema JothyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medications and Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument6 paginiMedications and Nursing ResponsibilitiesDarla JoyceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brand NameDocument5 paginiBrand NameJunrey AbarcaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Live Preterm Baby Delivered NSDDocument13 paginiLive Preterm Baby Delivered NSDKristine Anne SorianoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evaluation of Fetal Well BeingDocument22 paginiEvaluation of Fetal Well BeingJoanah Mae AsuncionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Immunodeficiency DisordersDocument8 paginiImmunodeficiency Disordersbpt2Încă nu există evaluări
- Renal Replacement TherapyDocument23 paginiRenal Replacement TherapyShelly Dwi SilvitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP RenalDocument22 paginiNCP Renalمحمود على ما تفرجÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument4 paginiAnatomy and PhysiologyBeRnAlieÎncă nu există evaluări
- OPHTHA Case Report Diabetic RetinopathyDocument51 paginiOPHTHA Case Report Diabetic RetinopathyJessa MeaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Community Nutrition QuizDocument3 paginiCommunity Nutrition QuizAli Aufar HutasuhutÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diabetes Mellitus, Often Simply Referred To As Diabetes, Is A Group of Metabolic Diseases inDocument28 paginiDiabetes Mellitus, Often Simply Referred To As Diabetes, Is A Group of Metabolic Diseases inKrissy GaluraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmacological Management of GIT Disorders For First Year Medicine StudentsDocument85 paginiPharmacological Management of GIT Disorders For First Year Medicine Studentsmex GbrekorkosÎncă nu există evaluări
- RevisionDocument17 paginiRevisionMatt RenaudÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nutrition Support Case StudyDocument6 paginiNutrition Support Case StudydakotaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Triamcinolone (Topical) - Drug InformationDocument5 paginiTriamcinolone (Topical) - Drug InformationMauricio Sv0% (1)
- Case Study JatDocument45 paginiCase Study JatHSEINÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmacologic Management: BleomycinDocument1 paginăPharmacologic Management: BleomycinKim ApuradoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Addison's DiseaseDocument14 paginiAddison's Diseasedivya4nirmalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bacillus Clausii Is A RodDocument9 paginiBacillus Clausii Is A RodGrax DeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHH Drug Study Week 3Document21 paginiCHH Drug Study Week 3maryxtine24Încă nu există evaluări
- PonstanDocument5 paginiPonstanYou know whoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clinical Case StudyDocument5 paginiClinical Case Studyv2wish_iÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nutritional Issues in The ICU Case FileDocument2 paginiNutritional Issues in The ICU Case Filehttps://medical-phd.blogspot.com100% (1)
- Presentation PathophysiologyDocument11 paginiPresentation PathophysiologyJade DeopidoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gastroespohageal Reflux Disease (GERD) Amp - PPT Amp - PPT LaryngopharyngealDocument16 paginiGastroespohageal Reflux Disease (GERD) Amp - PPT Amp - PPT LaryngopharyngealLestariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDe la EverandHirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gall Bladder Stones Surgical Treatment by Dr. Mohan SVSDocument5 paginiGall Bladder Stones Surgical Treatment by Dr. Mohan SVSFikri AlfarisyiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jurnal ColelitiasisDocument5 paginiJurnal ColelitiasisAnugrah WulanÎncă nu există evaluări
- BJP Will Take Bihar Out of BIMARU: Modi: Economy Shifting Gears, Results of CII Survey ShowDocument20 paginiBJP Will Take Bihar Out of BIMARU: Modi: Economy Shifting Gears, Results of CII Survey ShowAnonymous JE7uJRÎncă nu există evaluări
- Answers For Oral FinalDocument139 paginiAnswers For Oral FinalIris BakerÎncă nu există evaluări
- CholangitisDocument4 paginiCholangitisNarianne Mae Solis Bedoy100% (1)
- The Diagnosis and Management of Gallstones in The Elderly: Liver DiseasesDocument5 paginiThe Diagnosis and Management of Gallstones in The Elderly: Liver Diseasessusanto kusumaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calculous CholecystitisDocument137 paginiCalculous Cholecystitisrremonde100% (5)
- Choledocholithiasis: A Case Study ofDocument5 paginiCholedocholithiasis: A Case Study ofJanelle Kate SaleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digestive System: Yousef Ali Sazan Falah Snor Dilan KawtharDocument21 paginiDigestive System: Yousef Ali Sazan Falah Snor Dilan Kawtharkauther hassanÎncă nu există evaluări
- ENZYME by DR JoeanDocument8 paginiENZYME by DR JoeanHenry Teepoh100% (1)
- Right Upper Quadrant Pain: William MiddletonDocument14 paginiRight Upper Quadrant Pain: William MiddletonAmalia Gh,Încă nu există evaluări
- Chirurgie 1 Teste VozianDocument47 paginiChirurgie 1 Teste Voziangm hashÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cholelithiasis SneDocument12 paginiCholelithiasis SneSuhas IngaleÎncă nu există evaluări
- New Step 2 CK Free 120 Answer Explanations PDFDocument20 paginiNew Step 2 CK Free 120 Answer Explanations PDFEmad Khan67% (3)
- Hepatobiliary SystemDocument19 paginiHepatobiliary SystemKevin Jose Huamani TorresÎncă nu există evaluări
- CYL456: Chemistry of Life - An Introduction Biomolecules: LipidsDocument45 paginiCYL456: Chemistry of Life - An Introduction Biomolecules: LipidsMegraj MeenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Daftar PustakaDocument3 paginiDaftar PustakaBella Juni SafiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Calculous CholecystitisDocument25 paginiAcute Calculous CholecystitisShankar LamichhaneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Group 3 - Acute PancreatitisDocument5 paginiGroup 3 - Acute Pancreatitismelba040510Încă nu există evaluări
- Draft Case Study CholedocholithiasisDocument15 paginiDraft Case Study Choledocholithiasisapi-3828211100% (5)
- Common Symptoms of Gallbladder Disease and How To Recognize Them - Dr. Samrat JankarDocument3 paginiCommon Symptoms of Gallbladder Disease and How To Recognize Them - Dr. Samrat JankarDr. Samrat JankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- SurgeryDocument14 paginiSurgeryVinit ChoudharyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Git MRCGP 2015Document170 paginiGit MRCGP 2015AlexandraOsmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gallblader Stone Natural TreatmentDocument5 paginiGallblader Stone Natural TreatmentMuhammad KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Last Minute Revision Points SurgeryDocument45 paginiLast Minute Revision Points Surgerysrikanth harinadhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pancreatitis: David Minter, DO, FACOIDocument66 paginiPancreatitis: David Minter, DO, FACOINabeel ShahzadÎncă nu există evaluări
- 300 Essential SBAs in SurgeryDocument43 pagini300 Essential SBAs in SurgeryRicardo Uzcategui ArreguiÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHOLECYSTITIS With CHOLECYSTOLITHIASISDocument2 paginiCHOLECYSTITIS With CHOLECYSTOLITHIASISkennice_nereaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gall Bladder DiseaseDocument11 paginiGall Bladder Diseasedarellejaide100% (1)
- Ebook PDF Churchills Pocketbook of Surgery e Book 5th Edition PDFDocument30 paginiEbook PDF Churchills Pocketbook of Surgery e Book 5th Edition PDFelizabeth.mcmillion447100% (32)