Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Infant Mortality Rate
Încărcat de
cryobanksindiaDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Infant Mortality Rate
Încărcat de
cryobanksindiaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Infant Mortality Rate: Deconstructed
Infant mortality is the term referred to the number of infant deaths in the first 12 months of survival for every 1,000 births. Most of the deaths occur within the first 27 days after birth, known as the neonatal period in medical terms. They are often attributed to premature births, low birth weight (LBW) or other grave birth anomalies. Most common reasons for infant mortality due to LBW include respiratory distress syndrome, which may involve atelectasis (collapsed lung or lungs), hypoxemia (low oxygen absorption), and high carbon dioxide levels. Sudden Infant Death Syndrome, and lack of the essential amenities such as adequate food, warmth, shelter, and water are all crucial factors for infant mortality. However, the mortality rate is higher for male child than female child, as per the record more male births are registered as compared to females. Malnutrition is still a major cause-particularly in underdeveloped nations, while infectious diseases have been virtually eradicated through global immunization programs. However catastrophic phenomena can be brought about by rapid improvement in standards of living, medical science, sanitation, water purification, and nutrition, combined with higher education and economic conditions. Other developmental factors such as pasteurization for milk, vaccinations against childhood infectious diseases, more options in contraception, smaller families, and longer periods between the births of siblings would ensure lesser mortality rates. Out of all these factors LBW remains the highest risk to infants. The major factors for LWB include smoking while pregnancy, and teen pregnancies, and malnutrition of mother during pregnancy.The statistics shows that more than 12% of smokers give birth to LBW babies, and LBW is the infants causes neonatal infant mortality. Infant mortality rates are one of the perfect whistle blowers regarding the discrepancies in the quality of adult education and medical care available to different socioeconomic or ethnic populations in a country, state and cities. The economic boom being experienced by India masks a shameful failure to control the shocking infant mortality rate.One out of every four children in the world, who die under the age of one, is an Indian. Moreover, 46 per cent of children under three are underweight in the economically booming nation, India, and over two-thirds of infants die within the very first month of their birth. Ninety per cent of these deaths can be avoided as they occur due to easily preventable grounds like pneumonia and diarrhea. In nearly most of the cases, the infections and conditions that are the direct causes of death within the first 28 days of a childs birth and are preventable and curable with proven low-cost interventions.
Low birth weight (LBW) is the primary risk factor for infant mortality. A society's infant mortality rate is considered an important indicator of its health status, because infant mortality is associated with socioeconomic status, access to health care, and the health status of women of childbearing age. Although the current scenario seems grave, it can be easily tamed by practicing some common practices which can ensure the infant's survival. Cryobanks International India, accreted by AABB Accreditation and recently awarded with the most prestigious business award of the world THE BIZZ 2010 is a joint venture between pregnancy guide USA and RJ Corp founded in 2006. Cryobanks International is a leader in the collection, processing and banking of pregnancy weekly.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- RD Sharma Class8 SolutionsDocument2 paginiRD Sharma Class8 Solutionsncertsoluitons100% (2)
- Usp Description and SolubilityDocument1 paginăUsp Description and SolubilityvafaashkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Astract 2Document16 paginiAstract 2Sree Latha100% (1)
- Mortality RateDocument5 paginiMortality Rateamit kumar dewanganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sexuality and Contractive Use Among AdolescentsDocument35 paginiSexuality and Contractive Use Among AdolescentsUsman Ahmad TijjaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hemolytic Disease of The NewbornDocument14 paginiHemolytic Disease of The Newbornapi-441635248Încă nu există evaluări
- Principles and Practice of AsepsisDocument24 paginiPrinciples and Practice of AsepsisMuhammad AdamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rising AboveDocument123 paginiRising AboveDomingo PlomantesÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Effects of Smoking On TeenagersDocument7 paginiThe Effects of Smoking On TeenagersShireen MohdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intrauterine Growth RestrictionDocument5 paginiIntrauterine Growth RestrictionColleen MercadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pelvic Inflammatory DiseaseDocument18 paginiPelvic Inflammatory DiseaseVictorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Behavioral DisordersDocument9 paginiBehavioral DisordersAmy LalringhluaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Causes of Fetal DeathDocument3 paginiCauses of Fetal DeathRene Cordova InapanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Essential Newborn CareDocument5 paginiEssential Newborn CareElaine Iris AbastaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advantages of Breast FeedingDocument4 paginiAdvantages of Breast FeedingRollan MaulasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Low Birth WeightDocument24 paginiLow Birth WeightNabanita Tania DeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pregnancy and TBDocument24 paginiPregnancy and TBRoza MaulindraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Safe Mlotherhood Lec 2Document29 paginiSafe Mlotherhood Lec 2Isaac Nanabenyin100% (1)
- Teenage PregnancyDocument14 paginiTeenage PregnancyFred C. MirandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- DOTS Program For TB: Department of HealthDocument11 paginiDOTS Program For TB: Department of HealthCarissa De Luzuriaga-BalariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Family Developmental TasksDocument25 paginiFamily Developmental TasksPierenne Virgil Suarez Pinlac0% (1)
- Infants Diabetic MothersDocument17 paginiInfants Diabetic MothersJaya PrabhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Icterus, HiperbilirubinemiaDocument3 paginiIcterus, HiperbilirubinemiameidyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Congenital SyphilisDocument22 paginiCongenital SyphilisJuliana MariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Artificial Family PlaningDocument252 paginiArtificial Family PlaningJonah nyachaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction and BackgroundDocument50 paginiIntroduction and Backgroundمالك مناصرة100% (1)
- Preventing Early PregnancyDocument18 paginiPreventing Early PregnancyKueh LopezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maternal and Child HealthDocument62 paginiMaternal and Child HealthAsfand KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Placenta CirculationDocument11 paginiPlacenta CirculationJason Jimmy Lee PillayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adolescent Pregnancy - Risk Factors, Outcome and PreventionDocument4 paginiAdolescent Pregnancy - Risk Factors, Outcome and PreventionSebastian IribarrenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 11 PR Proj. Teenage PregnancyDocument12 paginiGrade 11 PR Proj. Teenage PregnancyDairienne Mae MaiqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Knowledge and Practice of Postnatal Mothers Regarding Personal Hygiene and Newborn CareDocument6 paginiKnowledge and Practice of Postnatal Mothers Regarding Personal Hygiene and Newborn CareUlin Nuha JazminÎncă nu există evaluări
- HEMOLYTIC DISEASE OF THE NEWBORN - Docx PrintDocument6 paginiHEMOLYTIC DISEASE OF THE NEWBORN - Docx PrintJudy HandlyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Preterm Labour and Preterm Rupture of Membranes: by Prof - Farouk Abdel AzizDocument23 paginiPreterm Labour and Preterm Rupture of Membranes: by Prof - Farouk Abdel AziznasibdinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Illegal Mining and Its ImpactsDocument4 paginiIllegal Mining and Its ImpactsAman PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Polyhydramnios 10Document4 paginiPolyhydramnios 10hussain AltaherÎncă nu există evaluări
- Preconception Care Presentation SlidesDocument15 paginiPreconception Care Presentation SlidesLucy AsconaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fetal Development and Physiological Changes During Pregnancy by Ma. Micah BananoDocument31 paginiFetal Development and Physiological Changes During Pregnancy by Ma. Micah BananoJANE CASSANOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Principles of ImmunizationDocument4 paginiPrinciples of ImmunizationDoc Prince CaballeroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Causes: Neonatal Jaundice or Neonatal Hyperbilirubinemia, or Neonatal Icterus (From The GreekDocument7 paginiCauses: Neonatal Jaundice or Neonatal Hyperbilirubinemia, or Neonatal Icterus (From The GreekIzzah100% (1)
- Prevalence of Unwanted Pregnancy and Associated FaDocument8 paginiPrevalence of Unwanted Pregnancy and Associated Fajuanda raynaldiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acknowledging The Impact and Preventions of Teen PregnancyDocument25 paginiAcknowledging The Impact and Preventions of Teen PregnancyJhana Trisha MaravillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- First 1000 Days LawDocument2 paginiFirst 1000 Days LawalyÎncă nu există evaluări
- PMTCTDocument26 paginiPMTCTMaxwell C Jay KafwaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Expanded Program On ImmunizationDocument4 paginiThe Expanded Program On Immunizationapi-3745792100% (3)
- Erythroblastosis FetalisDocument5 paginiErythroblastosis FetalisfitriarpsÎncă nu există evaluări
- (MMUNISATIONDocument54 pagini(MMUNISATIONatharva sawantÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exclusivebreastfeeding 181003124754Document39 paginiExclusivebreastfeeding 181003124754apalanavedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Capillary Blood CollectionDocument19 paginiCapillary Blood CollectionGandimareiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Menstrual Cycle: Anna Liza F. Rabo RN, ManDocument31 paginiMenstrual Cycle: Anna Liza F. Rabo RN, ManFhei Lya Dee TioÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCNDocument12 paginiMCNIan CarodanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1 Dimensions of MCHDocument5 paginiUnit 1 Dimensions of MCHLondera BainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Immunization in New BornDocument5 paginiImmunization in New BornRose Lyn Camarista VelascoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter One 1.0 Background To The StudyDocument55 paginiChapter One 1.0 Background To The StudyAbiodun GideonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sexually Transmitted DiseaseDocument20 paginiSexually Transmitted DiseaseAyesha IqbalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 24 VirusesDocument3 paginiChapter 24 VirusesBlairÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Does A Midwife DoDocument3 paginiWhat Does A Midwife Dosuperhuman_mabzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Essentials of Newborn Care)Document4 paginiEssentials of Newborn Care)Zera Cortez100% (1)
- Physical Growth of A ChildDocument18 paginiPhysical Growth of A ChildNurul IzzatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scholarly Paper (Psychology) Reasons of High Infant Mortality Rate Submitted by Fazal Rabbi Roll No 28 Year 3 Semester 6 Faculty:-Mrs Shahla ArshadDocument9 paginiScholarly Paper (Psychology) Reasons of High Infant Mortality Rate Submitted by Fazal Rabbi Roll No 28 Year 3 Semester 6 Faculty:-Mrs Shahla ArshadSHAFIQÎncă nu există evaluări
- Infant MortalityDocument16 paginiInfant Mortalityeek.the.katÎncă nu există evaluări
- Health 634 e Portfolio 3 Literature ReviewDocument5 paginiHealth 634 e Portfolio 3 Literature Reviewapi-370740412Încă nu există evaluări
- How Is Each Pregnancy Stage DifferentDocument2 paginiHow Is Each Pregnancy Stage DifferentcryobanksindiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reasons and Signs of Fetal MortalityDocument2 paginiReasons and Signs of Fetal MortalitycryobanksindiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stem Cells TherapyDocument2 paginiStem Cells TherapycryobanksindiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Having A Baby With Cesarean Pregnancy I C - Section OperationDocument2 paginiHaving A Baby With Cesarean Pregnancy I C - Section OperationcryobanksindiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stem Cell Definition and Usage in MedicationDocument2 paginiStem Cell Definition and Usage in MedicationcryobanksindiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scholomance 1 GravitonDocument18 paginiScholomance 1 GravitonFabiano SaccolÎncă nu există evaluări
- Segmentation of Blood Vessels Using Rule-Based and Machine-Learning-Based Methods: A ReviewDocument10 paginiSegmentation of Blood Vessels Using Rule-Based and Machine-Learning-Based Methods: A ReviewRainata PutraÎncă nu există evaluări
- BIO 201 Chapter 11 LectureDocument34 paginiBIO 201 Chapter 11 LectureDrPearcyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Worksheet - 143760187HS-II, TUTORIAL ON CH-5Document14 paginiWorksheet - 143760187HS-II, TUTORIAL ON CH-5A MusaverÎncă nu există evaluări
- CulvertsDocument18 paginiCulvertsAmmar A. Ali100% (1)
- Kami Export - Subject Complements-1 PDFDocument3 paginiKami Export - Subject Complements-1 PDFkcv kfdsaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vanish Magic Magazine VANISH MAGIC MAGAZINE 58 May 2019Document118 paginiVanish Magic Magazine VANISH MAGIC MAGAZINE 58 May 2019mick byrnes100% (1)
- FebvreDocument449 paginiFebvreIan Pereira AlvesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bravo MRI II Operation ManualDocument45 paginiBravo MRI II Operation ManualLuis100% (1)
- Ict 2120 Animation NC Ii Week 11 20 by Francis Isaac 1Document14 paginiIct 2120 Animation NC Ii Week 11 20 by Francis Isaac 1Chiropractic Marketing NowÎncă nu există evaluări
- EXAMPLE 8.6 Veneer Grades and RepairsDocument2 paginiEXAMPLE 8.6 Veneer Grades and RepairsnickÎncă nu există evaluări
- Karl MarxDocument4 paginiKarl Marxeirvine noah isidroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bchem 455 - Module 3Document42 paginiBchem 455 - Module 3WilliamÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECE199R-C12 Final Document OJTDocument48 paginiECE199R-C12 Final Document OJTRigel ZabateÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rectifier 5G High Density Embedded Power (3U Power Rack, Three Phase Four Wire) E...Document4 paginiRectifier 5G High Density Embedded Power (3U Power Rack, Three Phase Four Wire) E...Lintas LtiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liftchain (LC2A) Catalog AirHoistDocument10 paginiLiftchain (LC2A) Catalog AirHoisteduardshark100% (1)
- Concrete Super Structure ReportDocument43 paginiConcrete Super Structure ReportLivian TeddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Loads Considered For Design of BridgeDocument45 paginiTypes of Loads Considered For Design of BridgeAbhishek100% (1)
- Test7 PointersDocument16 paginiTest7 PointersPratibha DwivediÎncă nu există evaluări
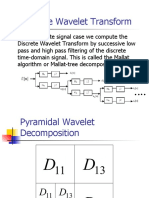
- Discrete Wavelet TransformDocument10 paginiDiscrete Wavelet TransformVigneshInfotechÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exam 3 DynamicsDocument7 paginiExam 3 DynamicsJulioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bagpipe LV 1-5Document228 paginiBagpipe LV 1-5Sathia Kdms100% (2)
- Birla MEEP Op ManualDocument43 paginiBirla MEEP Op ManualAshok ChettiyarÎncă nu există evaluări
- EXCEL For Pump DesignDocument2 paginiEXCEL For Pump Designkad-7Încă nu există evaluări
- Javanese PeopleDocument22 paginiJavanese PeopleDenisaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Valdez, Shenny RoseDocument3 paginiValdez, Shenny Roseyeng botzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carinthia Katalog DownloadDocument16 paginiCarinthia Katalog DownloadOperator_010100% (2)
- Minimalist KWL Graphic OrganizerDocument2 paginiMinimalist KWL Graphic OrganizerIrish Nicole AlanoÎncă nu există evaluări