Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Drug Study Ossam
Încărcat de
Charmaine IdologDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Drug Study Ossam
Încărcat de
Charmaine IdologDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
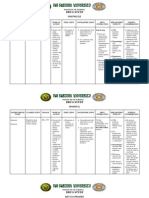
Drug study
Drug name
Indication and Classification
Antiulcer, proton pump inhibitor Short-term treatment of active duodenal cancer Shortterm treatment of active benign gastric ulcer Eradication of Helicobacter Pylori First-line therapy for treatment of heartburn or symptoms of GERD
Action
Side effects
contraindication
Nursing Responsibilities
Assessment: 1. History: hypersensitivity to omeprazole or any of its components. 2. Physical: skin lesions; reflexes; urinary output; abdominal examination; respiratory auscultation Interventions: 1. Administer before meals. 2. Administer antacids with, if needed .3. Have regular medical follow-upvisits. 4. Report severe headache, worseningof symptoms, fever,chills.
Omeprazole
Gastric-acid pump inhibitor: suppresses gastric acid secretion by specific inhibition of the hydrogen- potassium ATPase enzyme system at the secretory surface of the gastric parietal cells; blocks the final step of acid production
CNS; headache, dizziness, asthenia, vertigo, insomnia, apathy, anxiety, paresthesis, dream abnormalities Dermatologic: rash, inflammation, urticaria, pruritus, alopecia, dry skin GI: diarrhea, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, constipation,dry mouth, tongue atrophy Respiratory :URI symptoms, cough, epistaxis
Contraindicated with hypersensitivity to omeprazole or its components. Use cautiously with pregnancy, lactation.
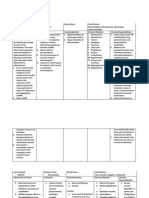
Tranexamic acid
Anti-fibrinolytic, antihemorrhagic Tranexamic acid is used for the prompt and effective control of hemorrhage in various surgical and clinical areas: Treating heavy menstrual bleeding Surgical: General surgical cases but most especially operative procedures on the prostate, uterus, thyroid, lungs, heart, ovaries, adrenals, kidneys, brain, tonsils, lymph nodes and soft tissues. promoting hemostasis in traumatic injuries. Preventing hemorrhage after
Tranexamic acid is a synthetic derivative of the amino acid lysine. It exerts its antifibrinolytic effect through the reversible blockade of lysine-binding sites on plasminogen molecules. Anti-fibrinolytic drug inhibits endometrial plasminogen activator and thus prevents fibrinolysis and the breakdown of blood clots. The plasminogenplasmin enzyme system is known to cause coagulation defects through lytic activity on fibrinogen, fibrin and other clotting factors. By inhibiting the action of plasmin (finronolysin) the anti-fibrinolytic agents reduce excessive breakdown of fibrin and
Back pain; headache; Allergic reaction to the 1. Unusual change in joint pain; muscle pain, bleeding pattern spasms, or cramps; nasal drug or hypersensitivity should be or sinus congestion; Presence of blood immediately reported stomach pain; tiredness. to the physician. Severe allergic reactions clots (eg, in the leg, lung, eye, brain), have a history 2. The medication can (rash; hives; itching; of blood clots, or are at be taken with or difficulty breathing; risk for blood clots without meals. tightness in the chest or 3. If you miss a dose of throat; swelling of the Current administration of Tranexamic Acid, mouth, face, lips, or factor IX complex take it when you tongue; flushing of the concentrates or antiremember, then take face); calf or leg pain, inhibitor coagulant your next dose at least swelling, or tenderness; concentrates 6 hours later. Do not chest pain; confusion; take 2 doses at once. coughing up blood; 4. Inform the client that decreased urination or he/she should inform difficulty urinating; eye the physician problems; fainting; immediately if the numbness of an arm or following severe side leg; seizures; persistent effects occur: dizziness or lightheadedness; shortness of breath; slurred speech; sudden headache or vomiting; vision changes
orthopedic surgeries.
effect physiological hemostasis.
or problem.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Histamine Intolerance Cookbook: Low-Histamine Breakfast, Snacks, Appetizers, Soups, Main Course and Dessert Recipes for Histamine IntoleranceDe la EverandHistamine Intolerance Cookbook: Low-Histamine Breakfast, Snacks, Appetizers, Soups, Main Course and Dessert Recipes for Histamine IntoleranceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nclex NotesDocument67 paginiNclex Notesjanet roosevelt94% (65)
- Drug StudyDocument3 paginiDrug StudyBheiatriz de VeraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study: OmeprazoleDocument5 paginiDrug Study: Omeprazoleclau_latojaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study TramadolDocument14 paginiDrug Study TramadolBianca Freya Porral85% (13)
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesDe la EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (2)
- Post Traumatic Stress DisorderDocument2 paginiPost Traumatic Stress Disorderapi-188978784100% (1)
- Revised List of Maharashtra HospitalsDocument16 paginiRevised List of Maharashtra Hospitalsdummy data100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument9 paginiDrug StudyShiara Ruth EdrosoloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Name of Drug Indications Action Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Side Effects Nursing ManagementDocument3 paginiName of Drug Indications Action Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Side Effects Nursing Managementjhappo31Încă nu există evaluări
- CHN Drug StudyDocument10 paginiCHN Drug StudyJoshua Cyryll ComiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drugstudy Omeprazole and Pen GDocument3 paginiDrugstudy Omeprazole and Pen GGil Joseph GodoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument6 paginiDrug StudyNajmah Saaban100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument13 paginiDrug StudyAbdullah Mascardo BarabagÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug 1Document5 paginiDrug 1Jesamine MayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study - LeptospirosisDocument19 paginiDrug Study - LeptospirosisCamille PinedaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument6 paginiDrug StudyFloramae Celine BosqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cortex Where Spread of SeizureDocument11 paginiCortex Where Spread of SeizureDustin JohnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Side Effects of AmoxicillinDocument4 paginiSide Effects of AmoxicillinAphro DhiteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Name of Drug Mechanism of Action Indications Contra-Indications Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument10 paginiName of Drug Mechanism of Action Indications Contra-Indications Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsmidskiescreamzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument7 paginiDrug StudyNatnath FernandoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study ICUDocument4 paginiDrug Study ICUArthadian De PeraltaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study 1Document4 paginiDrug Study 1bibet_martijaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drugs Study, Nursing, PreoperativeDocument9 paginiDrugs Study, Nursing, PreoperativeKevin Sam AguirreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument6 paginiDrug StudytrinaLCÎncă nu există evaluări
- DrugsDocument11 paginiDrugsClarence Lyndyll ToldingÎncă nu există evaluări
- WarfarinDocument10 paginiWarfarinMar Ordanza100% (1)
- Name of Drug Classification Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities Ampicillin Sulbactam GI: Diarrhea, NauseaDocument10 paginiName of Drug Classification Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities Ampicillin Sulbactam GI: Diarrhea, NauseaVictor BiñasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study NRMFDocument11 paginiDrug Study NRMFKristine ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ma. Patricia R. de Leon Bsn-Iv: Drug Indications Contraindicatio Ns Action Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument6 paginiMa. Patricia R. de Leon Bsn-Iv: Drug Indications Contraindicatio Ns Action Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesTricia_De_Leon_6494Încă nu există evaluări
- Pharmacology ReviewDocument64 paginiPharmacology ReviewRichard BakerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument11 paginiDrug StudyNedemar OcampoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gastrointestinal AgentsDocument40 paginiGastrointestinal Agentse_sagadÎncă nu există evaluări
- DrugsDocument11 paginiDrugsElisa Libo-onÎncă nu există evaluări
- Emergency Room DrugsDocument20 paginiEmergency Room DrugstsikiÎncă nu există evaluări
- AmoxicillinDocument2 paginiAmoxicillindheng05Încă nu există evaluări
- MedicationsDocument11 paginiMedicationsHussein MohsenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nclex NotesDocument121 paginiNclex NotesJaira Ardales97% (29)
- Indications For Ferrous Sulfate: Mechanism of ActionDocument4 paginiIndications For Ferrous Sulfate: Mechanism of ActionErelle John Vasquez EscaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument8 paginiDrug Studysarah1217Încă nu există evaluări
- Drug Name Mode of Action Indications Adverse Effects of The Drug Contraindications: Nursing ConsiderationDocument2 paginiDrug Name Mode of Action Indications Adverse Effects of The Drug Contraindications: Nursing ConsiderationKatrina PonceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Considerations Assessment: History: Infections Kidney Disease Liver Disease, Hypothyroidism UlcerativeDocument5 paginiNursing Considerations Assessment: History: Infections Kidney Disease Liver Disease, Hypothyroidism UlcerativeSophia limÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument9 paginiDrug StudyShane Arroyo100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument3 paginiDrug StudyGail SantosÎncă nu există evaluări
- MedSurg Medication Study Guide Test 1Document12 paginiMedSurg Medication Study Guide Test 1Sarah PlunkettÎncă nu există evaluări
- DrugsDocument5 paginiDrugsVal Ian Palmes SumampongÎncă nu există evaluări
- CefuroximeDocument11 paginiCefuroximeAlmira Ballesteros CestonaÎncă nu există evaluări
- WEEK2 Course Task (ALFEREZ, DINIELA)Document4 paginiWEEK2 Course Task (ALFEREZ, DINIELA)DINIELA ALLAINE ALFEREZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drugstudy and SoapieDocument17 paginiDrugstudy and SoapieYasi EcheniqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Legaspi Course Task 2Document7 paginiLegaspi Course Task 2FATIMA AIRA LEGASPIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument5 paginiDrug StudyDick Morgan FerrerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study (Pedia)Document7 paginiDrug Study (Pedia)Caurrine Monsalud100% (1)
- Ward6 Drug StudyDocument6 paginiWard6 Drug StudyMichael Lloyd T. SabijonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drusadg Study For Paracetamol Omeprazole and Vitamin B ComplexDocument3 paginiDrusadg Study For Paracetamol Omeprazole and Vitamin B ComplexzerpthederpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument10 paginiDrug StudyFritzie Beatrice NomusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chlorpheniramine Maleate: (klor-fen-AIR-uh-meen MAL-ee-ate)Document4 paginiChlorpheniramine Maleate: (klor-fen-AIR-uh-meen MAL-ee-ate)Nurginayah RusliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Pharmacology And Drug Calculations [Practice Questions And Answers]De la EverandBasic Pharmacology And Drug Calculations [Practice Questions And Answers]Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1)
- Overcoming Histamine Intolerance: Complete Guide on How to Diagnose and Treat Histamine Intolerance and Effectively Lower Histamine LevelsDe la EverandOvercoming Histamine Intolerance: Complete Guide on How to Diagnose and Treat Histamine Intolerance and Effectively Lower Histamine LevelsEvaluare: 2.5 din 5 stele2.5/5 (7)
- Winning against Prostatitis in the Elderly. Insider’s View of a Medical Worker.De la EverandWinning against Prostatitis in the Elderly. Insider’s View of a Medical Worker.Încă nu există evaluări
- A Simple Guide to Gastritis and Related ConditionsDe la EverandA Simple Guide to Gastritis and Related ConditionsEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (3)
- Gastro-Esophageal Reflux Disease-A Self Help GuideDe la EverandGastro-Esophageal Reflux Disease-A Self Help GuideÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Superhero LifestyleDocument9 paginiThe Superhero LifestyleDerp Blood0% (3)
- DSM-5 Personality Disorders PDFDocument2 paginiDSM-5 Personality Disorders PDFIqbal Baryar0% (1)
- February 2019Document4 paginiFebruary 2019sagar manghwaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ifm Product Innovations PDFDocument109 paginiIfm Product Innovations PDFJC InquillayÎncă nu există evaluări
- E3sconf 2F20187307002Document4 paginiE3sconf 2F20187307002Nguyễn Thành VinhÎncă nu există evaluări
- FINALE Final Chapter1 PhoebeKatesMDelicanaPR-IIeditedphoebe 1Document67 paginiFINALE Final Chapter1 PhoebeKatesMDelicanaPR-IIeditedphoebe 1Jane ParkÎncă nu există evaluări
- ISBAR For Clear CommunicationDocument6 paginiISBAR For Clear Communicationmehara1920Încă nu există evaluări
- Vicat Apparatus PrimoDocument10 paginiVicat Apparatus PrimoMoreno, Leanne B.Încă nu există evaluări
- S:/admin/mpi/MP1169 - Amaia Skies Samat/000 - ACTIVE DOCUMENTS/09 - SPECS/2013-07-23 - Design Development/04-Plumbing/15050Document19 paginiS:/admin/mpi/MP1169 - Amaia Skies Samat/000 - ACTIVE DOCUMENTS/09 - SPECS/2013-07-23 - Design Development/04-Plumbing/15050Lui TCC BariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Laws and Regulation Related To FoodDocument33 paginiLaws and Regulation Related To FoodDr. Satish JangraÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10.0 Ms For Scaffolding WorksDocument7 pagini10.0 Ms For Scaffolding WorksilliasuddinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug AbuseDocument33 paginiDrug AbuseharshulnmimsÎncă nu există evaluări
- RCM Design and ImplementationDocument34 paginiRCM Design and ImplementationRozi YudaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Astm A712 PDFDocument3 paginiAstm A712 PDFCristian OtivoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Capstone-ModDocument25 paginiCapstone-ModMohammad Ryyan PumbagulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Photoperiodism Powerpoint EduDocument12 paginiPhotoperiodism Powerpoint EduAlabi FauziatBulalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practical Cookery 14th Edition SAMPLEDocument16 paginiPractical Cookery 14th Edition SAMPLETendaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fomula Spreadsheet (WACC and NPV)Document7 paginiFomula Spreadsheet (WACC and NPV)vaishusonu90Încă nu există evaluări
- KhanIzh - FGI Life - Offer Letter - V1 - Signed - 20220113154558Document6 paginiKhanIzh - FGI Life - Offer Letter - V1 - Signed - 20220113154558Izharul HaqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Durock Cement Board System Guide en SA932Document12 paginiDurock Cement Board System Guide en SA932Ko PhyoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technical Publication: Direction 2296441-100 Revision 06 Ge Medical Systems Lightspeed 3.X - Schematics and BoardsDocument380 paginiTechnical Publication: Direction 2296441-100 Revision 06 Ge Medical Systems Lightspeed 3.X - Schematics and BoardsJairo Manzaneda100% (2)
- Multilevel Full Mock Test 5: Telegramdagi KanalDocument20 paginiMultilevel Full Mock Test 5: Telegramdagi KanalShaxzod AxmadjonovÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optical Fiber Communication Unit 3 NotesDocument33 paginiOptical Fiber Communication Unit 3 NotesEr SarbeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Electrical Engineering Mcqs Unit 1Document13 paginiBasic Electrical Engineering Mcqs Unit 1shubha christopherÎncă nu există evaluări
- UIP ResumeDocument1 paginăUIP ResumeannabellauwinezaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technology For Teaching and Learning 2 OBE SyllabusDocument9 paginiTechnology For Teaching and Learning 2 OBE Syllabusjesreel canalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Readers Digest November 2021 PDF RD 2021 PDF EnglishDocument172 paginiReaders Digest November 2021 PDF RD 2021 PDF EnglishIslam Gold100% (1)
- Fittings: Fitting Buying GuideDocument2 paginiFittings: Fitting Buying GuideAaron FonsecaÎncă nu există evaluări





















































![Basic Pharmacology And Drug Calculations [Practice Questions And Answers]](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/475660044/149x198/2c7fc45015/1691161640?v=1)