Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Paper 1sc Ub1
Încărcat de
Khatijah Abdul RahmanDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Paper 1sc Ub1
Încărcat de
Khatijah Abdul RahmanDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
NAME :_____________________________________ Sulit 55 Science Mac 2010 1 jam
CLASS : _______________
UNIT PEPERIKSAAN DAN PENILAIAN SMK PANTAI SEPANG PUTRA 43950 SUNGAI PELEK, SEPANG
UJIAN PRESTASI 1 2010 SCIENCE FORM 2 1 Hour Prepared by: __________ (PN. NUR SHUHADA BT ABD RAZAK) Checked by : ______________
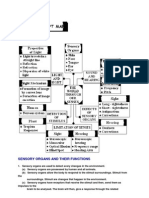
SECTION A: Instructions: Answer all questions. Each question has multiple choices answer. Choose the best answer and blacken on OMR sheets. 1. What is the organ to help to taste chemical substances? A B C D 2. The eye The skin The nose The tongue
How many sensory organs does a human have? A B C D Two Three Four Five
3.
Which of the following is a sense organ? A B C D The leg The brain The kidney The eye
4.
The table below shows the sensory organ and its respective stimulus. Which pair is matched incorrectly? Sensory organ Eye Ear Nose Tongue Stimulus Light Pressure Smell Taste
A B C D 5.
Which of the following receptors is not found under the skin? A B C D Pain Cold Dermis Pressure
6.
The diagram below shows the structure of the human skin. P, Q, R and S are receptors that are matched with their individual senses.
Which of the following pair is incorrectly matched? Receptor P Q R S Sense Touch Cold Heat Pressure
A B C D
7.
The diagram below shows the structures of the human nose.
Name the structure labelled W. A B C D 8. Nerve fibres Sensory nerves Epithelium cells Olfactory nerves
The diagram below shows areas of a human tongue.
The area labelled with L is sensitive to A B C D 9. Sour Salty Bitter Sweet
The three bones in the middle ear are called A B C D Octave Ossicles Oscillations oscilloscope
10
The table below shows that P, Q, R, S and T represent the routes taken by sound waves from the ear flap (pinna) to the inner ear. P Q R S T Transforms the energy or compressional wave into nerve impulses. Collect and channel sound to the middle ear. Transforms vibrations into a compressional wave. Nerve impulses transmitted to the brain. Transforms the energy of sound waves into vibrations.
Arrange the routes taken in the right sequence. A B C D 11 QPSRT QTRPS RQTSP PQSPT
The diagram below shows the cross section of the human eye.
The part labelled K is A B C D 12. Iris lens holder ciliary muscles suspensory ligament
A person uses concave lens spectacles to correct A B C D presbiopia astigmatism short-sightedness (myopia) long-sightedness (hypermetropia)
13.
A submerged object appears to be nearer to the surface than its actual position. This is an example of an illusion caused by A B C D optical illusion reflection of light refraction of light total internal reflection
14.
The diagram below shows the front part of the eye.
If the part labelled Z is exposed to bright sunlight it will A B C D 15. change colour become bigger become smaller remain the same size
The eye works like a A B C D camera computer laser printer mobile phone
16.
Which of the following statements is incorrect? A A positive tropism is movement growth towards the stimuli. B Hydrotropism is movement growth towards water or moisture. C Geotropism is the response of plants towards water or moisture. D A negative tropism is movement growth away from the stimuli.
17.
Phototropism is the response of plants to A B C D light water touch gravity
18.
Plants shy away at the touch of a hand. This is an illustration of
A B C D 19.
tropism thigmotropism spontaneous response seismonastic response
Which part of the plant response positively to the pull of gravity and water? A B C D Root Stem Shoot Flower
20.
The diagram below shows shoots are seen growing towards the light.
What inference can you make from the experiment? A B C D 21. The shoots response to light stimuli. The seedlings grow towards the damp soil. The shoots response to the touch stimuli. The shoots response to the pull of gravity.
______ is important because it helps to transport digested, undigested food and gas in our body. A B C D Water Vitamins Fibre Mineral salts
22.
The diagram below shows the classification of vitamins.
Deficiency of this vitamin will result in night-blindness. A B C D 23. Vitamin A Vitamin B Vitamin C Vitamin D
The following are simple sugars except A B C D rice lactose fructose table sugar
24.
________ is a component of haemoglobin in the blood cells. A B C D Iron Calcium Fluorine Magnesium
25.
The main function of the following help in the formation of strong bones and teeth except A B C D iron calcium vitamin D phosphorous
26.
The main function of carbohydrates is to A B C D prevent blood clotting. repair cells in the body. provide energy to the body. transport digested food to all parts of the body.
27.
The diagram below shows examples of a class of food.
Which class does it belong? A B C D 28. Fats Proteins Vitamins Carbohydrate
The diagram below shows a patient suffering from an illness.
The patient suffering from an illness called ________. A B C D 29. goiter anemia pellagra conjunctivas
The following are functions of protein except it A B C D insulates the body. helps in cell repair. aids in enzyme production. helps the body to grow and maintain it.
30.
The diagram below shows that the boy is obese.
This may be the result of taking in too much I water. II carbohydrates. III fatty foods. A B C D I only I, II II, III I, II, III
SECTION B: Answer all the questions in the space provided. 1. The diagram below shows the areas of a human tongue that are sensitive to different tastes.
(a) Name the part of the tongue that has groups of taste receptors. [1 marks ] (b) State the tastes that stimulate area K, L, M and N.
K: L: M: N: [4 marks ] (c) (i) Name the sense that helps the sense of taste. [1 marks ] (ii) Explain how the answer in (c)(i) can help the sense of taste.
[1 marks ] 2. (a) State the composition of carbohydrate. [1 marks ] (b) (i) List three types of carbohydrate. 1. 2. 3. [3 marks ] (ii) List three examples of food which is rich in carbohydrates. 1. 2. 3. [3 marks ] (c) Explain the importance of carbohydrate to human body. [1 marks ] End of Questions
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (587)
- SEO-Optimized Title for English Exam PaperDocument18 paginiSEO-Optimized Title for English Exam PaperKhatijah Abdul RahmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- SPM Bi Trial 14 1Document4 paginiSPM Bi Trial 14 1Khatijah Abdul RahmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- English SPM ModuleDocument197 paginiEnglish SPM Moduleabdfattah100% (16)
- Sains Tingkatan 2Document63 paginiSains Tingkatan 2Sekolah Portal95% (37)
- History of Malaysia's Merdeka: Events Leading Up To IndependenceDocument18 paginiHistory of Malaysia's Merdeka: Events Leading Up To IndependenceKhatijah Abdul RahmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Pemeriksaan MataDocument39 paginiPemeriksaan MataNadilla De PutriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Visual Arts Elements)Document2 paginiVisual Arts Elements)undercoverseraph100% (2)
- Consumer Perception, RiskDocument70 paginiConsumer Perception, RiskHafis SayedÎncă nu există evaluări
- ICO Inst BK Advanced Exam 2015Document16 paginiICO Inst BK Advanced Exam 2015Edoga Chima Emmanuel0% (1)
- Hoya Eye Genius FactsheetDocument2 paginiHoya Eye Genius FactsheetMustaphaBenselkaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Method of Extending The Range of The KeratometerDocument3 paginiMethod of Extending The Range of The KeratometerDanielle SangalangÎncă nu există evaluări
- How Our Senses Detect Stimuli and Brain Produces SensesDocument6 paginiHow Our Senses Detect Stimuli and Brain Produces SensesHi hi ChanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Visual ImpairmentDocument26 paginiVisual ImpairmentMelody MejiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diabetic Eye Disease and Low VisionDocument15 paginiDiabetic Eye Disease and Low VisionYurike Natalie LengkongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Classification and Causes of Age-related CataractDocument16 paginiClassification and Causes of Age-related CataracttataÎncă nu există evaluări
- Noise and Hearing ConservationDocument25 paginiNoise and Hearing ConservationAli Mohd100% (1)
- Sensory Organs and Their FunctionsDocument48 paginiSensory Organs and Their FunctionsUsha Nanthini100% (1)
- Specialized Areas of The CerebrumDocument7 paginiSpecialized Areas of The Cerebrumapi-303067223Încă nu există evaluări
- Contact Lenses Sss 2013Document33 paginiContact Lenses Sss 2013Peter HoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Human Eye Chapter SummaryDocument3 paginiHuman Eye Chapter SummaryHarshit bhaveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy of the EarDocument12 paginiAnatomy of the EarAllene PaderangaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Color Lecture Part 1Document61 paginiColor Lecture Part 1api-270388254Încă nu există evaluări
- Part 2 - The Physiology of Hearing - Handout PDFDocument8 paginiPart 2 - The Physiology of Hearing - Handout PDFMike PosktovaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Detecting Color Vision Deficiencies Using Standardized TestsDocument4 paginiDetecting Color Vision Deficiencies Using Standardized TestsFaheem KvÎncă nu există evaluări
- Berger 1986Document3 paginiBerger 1986kameliasitorusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dizziness in The ElderlyDocument18 paginiDizziness in The ElderlyFlorencia Beatriz CadenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Health Education Library For People's Guide to Understanding DizzinessDocument2 paginiHealth Education Library For People's Guide to Understanding DizzinessNaidu VegiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Preparation: Competency Performance Checklist Assessing Ears Student: Date: - Skill Yes NoDocument2 paginiPreparation: Competency Performance Checklist Assessing Ears Student: Date: - Skill Yes NoCyril Joy N. FernandoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Handbook: Between Background andDocument1 paginăHandbook: Between Background andreacharunkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aries 28: A Large Disappointed AudienceDocument2 paginiAries 28: A Large Disappointed AudienceStarlingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Retina: Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument25 paginiRetina: Anatomy and PhysiologyRajiv DasÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Glaukoma Dan KatarakDocument1 paginăNCP Glaukoma Dan KatarakIsmi Nur KhikmahÎncă nu există evaluări
- AMBLYOPIADocument54 paginiAMBLYOPIAMolde DedekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessment of The EyesDocument32 paginiAssessment of The EyesArlyn MendenillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- HearingDocument2 paginiHearingGrace Ann LautrizoÎncă nu există evaluări