Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Chapter 11 and 12 ACC Test
Încărcat de
lkreed58Descriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Chapter 11 and 12 ACC Test
Încărcat de
lkreed58Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Name: ____________________________
Class: ____ Date: ___________________
Chapter 11 and 12 ACC Test
True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 1. Buying on margin was a method of buying stocks with mostly borrowed money. 2. The stock market crash caused the Great Depression. 3. The Hawley-Smoot Tariff dampened commerce on both sides of the Atlantic. 4. Herbert Hoover pushed Congress to provide federal government money for direct relief of impoverished families. 5. Abandoning the gold standard would increase the value of the dollar. 6. Franklin Roosevelt came to office with a clear agenda for how he was going to deal with the Depression. 7. When people lost their jobs and could no longer pay their mortgages, the Home Owners' Loan Corporation lengthened the term of their loans rather than foreclose on their property. 8. The Farm Credit Administration helped many poor farmers keep their land, but it may have slowed the overall economic recovery. 9. The Public Works Administration required its contractors to hire African Americans.
____ 10. The Supreme Court ruled unconstitutional the Wagner Act, which guaranteed certain workers' rights. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 11. Stock prices first began to decline in late 1929 because a. stockbrokers stopped margin loans. c. several companies went bankrupt. b. company earnings declined. d. investors began to sell their stock. ____ 12. In the 1920s, the Federal Reserve contributed to weaknesses in the stock market by a. keeping interest rates low. c. lending to foreign companies. b. speculating on market interest rates. d. lending to speculators. ____ 13. Farmers on the Great Plains began to lose their crops during the Depression because a. the soil lost its fertility. b. frequent rains eroded the soil. c. a fungus depleted the soil of nutrients. d. a terrible drought dried the soil.
____ 14. President Hoover hoped that public works would a. solve the budget deficit. b. spur the construction industry. c. provide jobs lost in the private sector. d. help reduce farm foreclosures. ____ 15. President Hoover opposed direct federal relief to the unemployed because he believed that a. only state and city governments should dole out relief. b. federal relief would shorten the Depression. c. charities could provide sufficient relief until the economy improved. d. individuals should be responsible for taking care of themselves. ____ 16. Thousands of World War I veterans came to Washington in 1932 to lobby Congress to a. enact a bonus for war veterans and their families. b. pass legislation giving veterans their promised bonus early. c. provide public works jobs for unemployed veterans. d. provide military jobs for unemployed veterans. During [World War I] we necessarily turned to the government to solve every difficult economic problem. . . . When the war closed . . . we were challenged with a peacetime choice between the American system of rugged individualism and a European philosophy of diametrically opposed doctrinesdoctrines of paternalism and state socialism. Herbert Hoover, campaign speech delivered October 22, 1928
____ 17.
According to the excerpt, whom did the people of the United States turn to in order to solve difficult economic problems during World War I? a. European nations c. private charities b. business leaders d. the government
____ 18. a. b. c. d.
What two philosophical positions are contrasted in this excerpt? individualism and imperialism individualism and socialism socialism and laissez-faire economics capitalism and socialism
____ 19. A major contribution to Herbert Hoovers landslide victory in the 1928 election was a. the prosperity of the 1920s. c. his promise to end Prohibition. b. his tax relief plan. d. his plan to support farm prices. ____ 20. The stock market crash weakened the nations banks because a. banks had invested their deposits in the stock market. b. banks depended on their stock for operating funds. c. investors no longer had money to deposit in banks. d. investors could no longer afford to take out loans from banks. ____ 21. In search of work or a better life during the Depression, many unemployed people a. destroyed Hoovervilles. c. became homeless. b. became farmers. d. rode the rails.
____ 22. The first feature-length animated film was a. Animal Crackers. b. The Wizard of Oz.
c. Snow White and the Seven Dwarfs. d. Mr. Smith Goes to Washington.
____ 23. The original purpose of the Reconstruction Finance Corporation was to a. regulate the stock market. b. manage public works projects. c. make loans to businesses. d. administer public assistance programs for the homeless. ____ 24. In May 1932, the Senate voted down a bill that would have a. given special tax cuts to members of the military. b. guaranteed health care for all U.S. citizens. c. authorized early payment of World War I veterans bonuses. d. provided jobs to all military veterans.
Causes of the Great Depression
Overproduction and low demand lead to employee layoffs Low wages reduce consumer buying power High tariffs restrict foreign demand for American goods Unemployment reduces buying power
____ 25.
According to the chart, high tariffs restricted foreign demand for American manufactured goods. Why were these tariffs in place? a. Hoover refused to allow any foreign imports into the country. b. They were mandated by the Treaty of Versailles. c. They were required by the Constitution. d. They protected U.S. goods from foreign competition.
____ 26. A long period of rising stock prices is known as a a. margin call. c. foreclosure. b. bank run. d. bull market. ____ 27. The group of World War I veterans who marched on Washington in 1932 was called the a. Bonus Picketers. c. Bonus Army. b. Bonus Rebels. d. Bonus Veterans. ____ 28. During the Depression, many state governors declared bank holidays to a. give bank employees a break. c. reduce the value of the dollar. b. prevent bank runs. d. help the Federal Reserve. ____ 29. Roosevelts advisers who supported New Nationalism wanted government agencies to a. work with businesses. c. break up big companies. b. run key parts of the economy. d. set up welfare programs. ____ 30. To fight the Depression, the first thing Roosevelt set out to do was to a. provide direct relief to people. c. restore confidence in the banks. b. set up public works programs. d. provide relief for farmers.
____ 31. To regulate the stock market, Congress created the a. Federal Trade Commission. b. Securities and Exchange Commission. c. National Recovery Administration. d. Social Security Administration. ____ 32. The National Industrial Recovery Act allowed business, labor, and the government to cooperate in setting up a. trusts to promote competition. b. codes of fair competition. c. tax regulations for each industry. d. hiring requirements for each industry. ____ 33. One purpose of the Townsend plan was to a. free up jobs for the unemployed. b. redistribute wealth. c. nationalize the banking system. d. end public works programs.
____ 34. Framers of the Social Security Act saw it primarily as a. an insurance measure. c. a retirement pension measure. b. a welfare measure. d. a relief measure. ____ 35. Franklin Roosevelts court-packing plan was a serious mistake because a. many Americans opposed the idea of forced retirement. b. the angry judges reacted by striking down much of the New Deal legislation. c. it appeared to interfere with the Constitutions separation of powers. d. the angry judges struck down the plan as unconstitutional. This is preeminently the time to speak the truth, frankly and boldly. Nor need we shrink from honestly facing conditions in our country today. This great Nation will endure as it has endured, will revive and will prosper. So, first of all, let me assert my firm belief that the only thing we have to fear is fear itself. . . . Franklin Delano Roosevelt, first inaugural address, March 4, 1933
____ 36.
According the Roosevelt, what is it time for the people and nation to do? a. not cower from the current situation c. ignore their problems b. accept their current conditions d. follow their leader
____ 37. The Emergency Banking Relief Act helped solve the banking crisis by a. putting all banks under government operation. b. declaring that the gold standard would not be abandoned. c. issuing licenses to banks that federal examiners found to be financially sound. d. closing the banks long enough for the Federal Reserve to replenish their gold reserves. ____ 38. The Agricultural Adjustment Administration tried to help farmers by a. helping small farmers become more efficient. b. paying them not to grow crops. c. buying farm surpluses. d. making land available for farming.
____ 39. The Federal Number One program employed a. young men ages 18 to 25. b. workers in the construction industry. c. displaced tenant farmers. d. people in the arts.
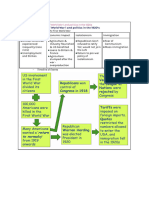
____ 40.
Which of the following choices best completes the diagram about the historic political realignment triggered by the New Deal? a. white Southerners c. business leaders b. African Americans d. progressives
____ 41. Roosevelt triggered a new economic downturn in 1937 by a. launching new programs. c. breaking up trusts. b. decreasing government spending. d. decreasing taxes. ____ 42. Senator Huey Long wanted the government to a. share the wealth of the rich. b. balance the budget. c. pay citizens over 60 a monthly pension. d. stop interfering with business. ____ 43. Franklin Roosevelts policies for ending the Depression became known as the a. fireside chats. c. gold standard. b. Glass-Steagall Act. d. New Deal. ____ 44. The period of time in 1933 when the newly elected Franklin Roosevelt sent bill after bill to Congress came to be called the a. Bank Holiday. c. Rise to Power. b. Hundred Days. d. New Deal. ____ 45. To inform and reassure citizens, Franklin Roosevelt addressed them directly by radio in what were called a. relief programs. c. safety nets. b. sit-down strikes. d. fireside chats. ____ 46. The United Auto Workers staged ________ strikes against General Motors, in which they stopped working but refused to leave the factory. a. broker c. sit-down b. violent d. mediated ____ 47. Child labor was abolished by the a. Wagner Act. b. Fair Labor Standards Act. c. Social Security Act. d. National Industrial Recovery Act.
____ 48. In taking on a mediating role among competing interests, the New Deal established what some have called a. the relief program. c. the broker state. b. binding arbitration. d. welfare capitalism. ____ 49. Which of the following insisted that contractors not discriminate against African Americans? a. Civil Works Administration c. National Recovery Administration b. Farm Credit Administration d. Public Works Administration Completion Complete each statement. 50. ____________________ invested in stocks, betting that the market would continue to climb so that they could make a quick profit. 51. The great stock market crash occurred in the year ____________________. 52. Newly homeless people put up communities of shacks that they called "____________________," blaming the president for their plight. 53. To pay for New Deal programs, Roosevelt abandoned a balanced budget and began using _____________________ spending. Matching Match each item with the correct statement below. a. hobos f. b. Black Tuesday g. c. bank run h. d. Okies i. e. Groucho Marx j. ____ 54. migrants headed west in search of better lives ____ 55. many depositors withdrawing money at once ____ 56. investing in the stock market hoping for a quick profit ____ 57. homeless wanderers who often rode the rails ____ 58. spending more than is collected in taxes ____ 59. stock market crash Douglas MacArthur Vivien Leigh John Steinbeck speculation budget deficit
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. shantytowns f. b. Alfred E. Smith g. c. Hattie McDaniel h. d. stock market i. e. relief j. ____ 60. Democratic candidate in the 1928 election
foreclosure installment plan margin call Dust Bowl Herbert Hoover
____ 61. head of the Food Administration during World War I ____ 62. loss of property due to nonpayment of a mortgage ____ 63. buying now and making payments each month ____ 64. communities of makeshift shacks on public lands ____ 67. system for buying and selling shares of companies ____ 68. drought-related conditions in the Great Plains ____ 69. money that went directly to impoverished families ____ 70. stockbrokers demand for immediate repayment of a loan Match each item with the correct statement below. a. Civilian Conservation Corps f. b. Wagner Act g. c. Frances Perkins h. d. Committee for Industrial Organization i. e. Huey Long j. ____ 71. started the United Auto Workers (UAW) ____ 72. offered unemployed young men work planting trees, fighting forest fires, and building reservoirs ____ 73. set up a process whereby dissatisfied union members could take their complaints to binding arbitration ____ 74. urged consumers to buy goods only from companies that displayed its blue eagle symbol ____ 75. first female cabinet member ____ 76. Louisiana senator who championed the downtrodden and built a powerful and corrupt political machine ____ 75. treasury secretary who favored balancing the budget ____ 76. head of the Federal Emergency Relief Administration and, later, the Works Progress Administration ____ 77. proposed a monthly government pension for citizens over age 60 to be entirely spent each month Harry Hopkins John L. Lewis National Recovery Administration Henry Morgenthau Francis Townsend
Short Answer (worth 3 points) Walking through an American city, you might find few signs of the Depression. . . . You might notice that a great many shops were untenanted . . . ; that few factory chimneys were smoking; that the streets were not so crowded with trucks. . . . Otherwise things might seem to you to be going on much as usual. The major phenomena of the depression were mostly negative and did not assail the eye. Frederick Lewis Allen, Since Yesterday
78.
What signs of the Depression might one notice while walking through an American city, according to the excerpt?
Essay (worth 10 points each) Choose two of the four to answer. Must be a paragraph long (OVER 4 sentences) 79. Discuss three major causes of the Great Depression.
80.
Use the diagram to help you explain how banks operate and why runs on banks can result in bank failure.
81. Describe Franklin Roosevelts personality and approach to the nations problems. 82. Discuss the New Deals legacy, including its effectiveness in dealing with the Depression and its lasting effects on the role of government.
Chapter 11 and 12 ACC Test Answer Section
TRUE/FALSE 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: T F T F F F F T T F PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: Easy Average Challenging Average Average Easy Challenging Average Average Average REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: p. 401 p. 403 p. 405 p. 414 p. 424 p. 424 p. 427 p. 427 p. 431 p. 442
MULTIPLE CHOICE 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: D A D C A B D B A A D C C C D D C B A C B B A A C A C PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: Challenging Average Easy Average Average Average Easy Challenging Average Challenging Average Easy Average Challenging Average Average Challenging Easy Average Challenging Average Average Average Average Challenging Challenging Average REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: p. 402 p. 405 p. 407 p. 412 p. 414 p. 415 p. 401 p. 401 p. 400 p. 403 p. 406 p. 408 p. 413 p. 415 p. 405 p. 401 p. 415 p. 424 p. 424 p. 425 p. 426 p. 429 p. 436 p. 439 p. 442 p. 423 p. 425
38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49.
ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS:
B D B B A D B D C B C D
PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS:
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF:
Easy Average Easy Average Easy Easy Average Average Average Average Average Average
REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF:
p. 428 p. 436 p. 440 p. 442 p. 435 p. 423 p. 424 p. 425 p. 438 p. 445 p. 445 p. 431
COMPLETION 50. ANS: Speculators PTS: 1 51. ANS: 1929 PTS: 1 DIF: Average DIF: Average REF: p. 401 REF: p. 402 REF: p. 406 REF: p. 434 NAT: VII.H NAT: VII.H NAT: I.A| V.B| V.G NAT: VI.C| VII.D
52. ANS: Hoovervilles PTS: 1 DIF: Easy 53. ANS: deficit PTS: 1 MATCHING 54. 55. 56. 57. 58. 59. 60. 61. 62. 63. 64. 65. 66. 67. 68. 69. 70. ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: D C I A J B B J F G A D I E H D A PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 DIF: Challenging
DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF:
Average Easy Average Average Easy Average Easy Average Average Average Easy Easy Average Average Average Average Easy
REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF:
p. 407 p. 403 p. 401 p. 406 p. 413 p. 402 p. 400 p. 400 p. 415 p. 405 p. 406 p. 400 p. 407 p. 414 p. 401 p. 438 p. 430
71. 72. 73. 74. 75. 76. 77.
ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS:
B H C E I F J
PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS:
1 0 1 1 1 1 1
DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF:
Average Average Average Average Average Average Average
REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF:
p. 438 p. 429 p. 441 p. 435 p. 442 p. 431 p. 436
SHORT ANSWER 78. ANS: One might notice empty buildings and idle factories. Also, the streets might not be so crowded with trucks. PTS: 3 DIF: Average REF: p. 406 NAT: I.C| II.C| IV.E| V.B| VII.G MSC: Document Based Question NOT: Learn more about this question in The American Vision: Modern Times, page 406, and in the Reading Essentials and Note-Taking Guide, Chapter 11, Section 2, and visit this books Online Learning Center at glencoe.com. ESSAY 79. ANS: Most economists agree that overproduction was a key cause of the Depression. Increasingly efficient machinery greatly sped the production of factory and farm goods. Most Americans, however, did not earn enough to buy up the flood of goods they helped produce. As consumers bought more goods on the installment plan, the debt incurred forced some to reduce their other purchases. As sales slowed, manufacturers cut production and laid off employees. Jobless workers had to cut back purchases even more, causing business activity to spiral downward. A second cause was the loss of export sales. American banks were making loans to speculators instead of to foreign companies. This, along with the Hawley-Smoot Tariff that dampened foreign sales in the United States, caused foreign countries to buy fewer American products. A third cause was mistakes by the Federal Reserve. Instead of raising interest rates to curb excessive speculation, it kept rates low. This action encouraged banks to make risky loans and encouraged businesses to borrow more money to expand production, adding to the problem of overproduction. PTS: 10 DIF: Challenging REF: p. 404
80. ANS: Most banks make a profit by lending out money received from depositors and collecting interest on the loans. The bank holds only a fraction of the depositors money to cover everyday business, such as occasional withdrawals. Ordinarily that reserve is enough to meet the banks needs, but if too many people withdraw their money at the same time, the reserves will not be sufficient to cover the withdrawals, and the bank will eventually collapse. PTS: 10 DIF: Challenging REF: p. 403 NAT: VII.D| VII.G
81. ANS: Americans saw in Roosevelt an energy and optimism that gave them hope despite the tough economic times. His serenity and confidence amazed many people, and his fireside chats helped reassure them. Also, many people believed that his struggle with polio had given him a better understanding of their hardships. Roosevelts confidence that he could make things better contrasted sharply with Hoovers apparent failure to do anything effective. In his campaign for president, Roosevelt revealed the approach he would take as president: Above all, try something. He implemented his campaign promise with a flurry of bills to Congress during the first Hundred Days. Unlike the public impression of Hoover, Roosevelt was doing something. PTS: 10 DIF: Challenging REF: p. 422 NAT: II.F| VI.E| X.C| VII.A
82. ANS: The New Deal had only limited success in ending the Depression. Unemployment remained high, and economic recovery was not complete until after World War II. Even so, the New Deal gave many Americans a stronger sense of security and stability. The New Deal tended to operate so that it balanced competing economic interests. Business leaders, farmers, workers, consumers, homeowners, and others now looked to government to protect their interests. This broker role in mediating among competing interests has continued under the administrations of both parties ever since. Also, the New Deal programs created a safety net that protected people against economic disaster. After the Roosevelt years, the American people felt that the government had a duty to maintain this safety net, even though it required a larger, more expensive federal government. PTS: 1 DIF: Challenging REF: p. 445
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- FDCPA Edleman CombsDocument43 paginiFDCPA Edleman CombsDarren Chaker100% (5)
- AP U.S. Unit 6 Exam + AnswersDocument8 paginiAP U.S. Unit 6 Exam + Answersdanwillametterealty100% (3)
- APUSH Unit 7 Practice TestDocument8 paginiAPUSH Unit 7 Practice TestArmando Montero100% (1)
- Great Depression and New Deal TestDocument10 paginiGreat Depression and New Deal TestLakshita SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Great Depression (1920-1940) (SparkNotes History Note)De la EverandThe Great Depression (1920-1940) (SparkNotes History Note)Încă nu există evaluări
- Ucc Financing Statement AddendumDocument3 paginiUcc Financing Statement AddendumAndre Duke CoulterÎncă nu există evaluări
- AP U.S. Unit 7 Exam + AnswersDocument8 paginiAP U.S. Unit 7 Exam + Answersdanwillametterealty60% (5)
- Apush 28-29 SampleDocument6 paginiApush 28-29 SampleJorge LopezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 26 The Great Depression PowerpointDocument39 paginiChapter 26 The Great Depression Powerpointapi-178733215Încă nu există evaluări
- Hist 1302 Exam 1 Review GMLDocument18 paginiHist 1302 Exam 1 Review GMLAnna Nguyen100% (1)
- Retainer AgreementDocument5 paginiRetainer AgreementZaira Gem GonzalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Asset Liability Management For Insurance CompaniesDocument12 paginiAsset Liability Management For Insurance Companies9848086777Încă nu există evaluări
- Lynn Szymoniac 3rd Amended PDFDocument214 paginiLynn Szymoniac 3rd Amended PDFGreg Wilder100% (3)
- Example in Tray Assessmentday PDFDocument27 paginiExample in Tray Assessmentday PDFbharathaninÎncă nu există evaluări
- Torts Fores Case DigestDocument7 paginiTorts Fores Case Digestninya09Încă nu există evaluări
- MBA Training ReportDocument69 paginiMBA Training ReportDeepak Thakur79% (14)
- Practice Test Chapters 2022 1Document13 paginiPractice Test Chapters 2022 1Jackson Van VoorenÎncă nu există evaluări
- AM HIST - New Deal - Unit TestDocument3 paginiAM HIST - New Deal - Unit TestShiloh RolleÎncă nu există evaluări
- TestDocument4 paginiTestJacob ParkerÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Great Depression: Chapter 26 Test-Open NotebookDocument5 paginiThe Great Depression: Chapter 26 Test-Open Notebookapi-178733215Încă nu există evaluări
- Crash Course 34-The New Deal-StudentsDocument3 paginiCrash Course 34-The New Deal-StudentsblakeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practice Test Chapters 1619 PDFDocument20 paginiPractice Test Chapters 1619 PDFJackson Van VoorenÎncă nu există evaluări
- AP Us Chaps 23 & 24 Take-Home, 14-15Document5 paginiAP Us Chaps 23 & 24 Take-Home, 14-15Takuma OkadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- GD ND NotesDocument7 paginiGD ND NotesTyshunti LevyÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Roaring Twenties: Politics, Economy, Culture and Anti-Radicalism in the 1920sDocument3 paginiThe Roaring Twenties: Politics, Economy, Culture and Anti-Radicalism in the 1920sJodie GreenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 6 Study Guide (The Great Depression and The New Deal)Document9 paginiUnit 6 Study Guide (The Great Depression and The New Deal)Morgan MunozÎncă nu există evaluări
- Great Depression TestsDocument4 paginiGreat Depression Testsapi-544553608Încă nu există evaluări
- Boom & Bust Study GuideDocument5 paginiBoom & Bust Study GuideJvonta DixonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Depression ShortDocument39 paginiDepression Shortapi-263745801Încă nu există evaluări
- Regents Prep 3Document16 paginiRegents Prep 3api-242847854Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit 2 Evaluation History 2Document8 paginiUnit 2 Evaluation History 2Safiyah KhankanÎncă nu există evaluări
- America's History Chapter 25: The New Deal, 1933-1939Document14 paginiAmerica's History Chapter 25: The New Deal, 1933-1939irregularflowers100% (2)
- How To Get Out of The GDDocument6 paginiHow To Get Out of The GDapi-281321560Încă nu există evaluări
- The Great Depression NotesDocument3 paginiThe Great Depression NotesAthena GuzmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 01-03 - Ch22: The Great DepressionDocument2 pagini01-03 - Ch22: The Great DepressionAnthony ValentinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Exam Study Guide Word 97Document20 paginiFinal Exam Study Guide Word 97Tom MarlerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chaper 25 TestDocument2 paginiChaper 25 Testapi-283772730Încă nu există evaluări
- Roosevelt and The New DealDocument8 paginiRoosevelt and The New Dealisabellamasira999Încă nu există evaluări
- Multiple Choice Quiz AssessmentDocument8 paginiMultiple Choice Quiz Assessmentdylanscharf0% (1)
- 4 FDR The New Deal 3Document5 pagini4 FDR The New Deal 3api-301854263Încă nu există evaluări
- Name: - Chapter 29 Worksheet Wilsonian Progressivism at Home and AbroadDocument4 paginiName: - Chapter 29 Worksheet Wilsonian Progressivism at Home and AbroadsamanthatnguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1920 TestDocument4 pagini1920 TestJacob ParkerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 23 OutlineDocument8 paginiChapter 23 OutlinePGDman (Dman)Încă nu există evaluări
- ReviewDocument12 paginiReviewAlex HudmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Second Quarterly Test in Hekasi 5Document4 paginiSecond Quarterly Test in Hekasi 5Lei ZelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Identify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDocument7 paginiIdentify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionJacob Parker0% (1)
- Unit 10 PacketDocument5 paginiUnit 10 Packetprissy the mf libraÎncă nu există evaluări
- PDF DocumentDocument19 paginiPDF DocumentSabrina OcampoÎncă nu există evaluări
- The USA Between The WarsDocument3 paginiThe USA Between The WarsbeujÎncă nu există evaluări
- U.S. Midterm TestsDocument4 paginiU.S. Midterm TestsJennifer JiangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Roaring 20s ExcerptDocument18 paginiRoaring 20s Excerptjdonz16Încă nu există evaluări
- CSS History of USA Online Lecture# 7: Franklin D. Roosevelt and The New DealDocument33 paginiCSS History of USA Online Lecture# 7: Franklin D. Roosevelt and The New DealJunaidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Study Guide APUSHDocument18 paginiStudy Guide APUSHmialee595Încă nu există evaluări
- American History II Great SocietyDocument4 paginiAmerican History II Great SocietyTaylor HinesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eoc Review 1920s and Great DepressionDocument7 paginiEoc Review 1920s and Great Depressionapi-252514619Încă nu există evaluări
- The New DealDocument15 paginiThe New DealRania AbunijailaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 4 - The ThirtiesDocument14 paginiCH 4 - The ThirtiesSenorita BrewsterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Great Depression Study Guide - CompletedDocument6 paginiGreat Depression Study Guide - Completedapi-234287636Încă nu există evaluări
- 8 c10 MiniquizDocument1 pagină8 c10 MiniquizMÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test Bank For Empowerment Series Introduction To Social Work Social Welfare Critical Thinking Perspectives 5th EditionDocument18 paginiTest Bank For Empowerment Series Introduction To Social Work Social Welfare Critical Thinking Perspectives 5th Editionandrewgonzalesqngxwbatyr100% (27)
- 5causesofthegreatdepression PDFDocument6 pagini5causesofthegreatdepression PDFchaudhry umar farooqÎncă nu există evaluări
- AMH 2020 Worksheet Chapter 20Document5 paginiAMH 2020 Worksheet Chapter 20Imani AlvaradoÎncă nu există evaluări
- American Promise Value Edition Voulme II 6th Edition Roark Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument42 paginiAmerican Promise Value Edition Voulme II 6th Edition Roark Test Bank Full Chapter PDFaffluencevillanzn0qkr100% (13)
- USA 1919 - 1941Document14 paginiUSA 1919 - 1941maescotttÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brinkley Chap 26 OutlineDocument7 paginiBrinkley Chap 26 OutlineVictoria DieckÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture ch24Document40 paginiLecture ch24api-171412573Încă nu există evaluări
- Vasu P. Shetty vs. M - SDocument8 paginiVasu P. Shetty vs. M - SSaksham KaushikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cyanoacrylate AdhesiveDocument4 paginiCyanoacrylate AdhesivePathan Sameer KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Micro Credit For Sustainable Development: Role of NgosDocument4 paginiMicro Credit For Sustainable Development: Role of NgosSpandana AchantaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elements of a Valid Contract in MalaysiaDocument12 paginiElements of a Valid Contract in MalaysiaShar Khan0% (2)
- Application Form For Financing OF Feature FilmsDocument17 paginiApplication Form For Financing OF Feature Filmsrupeshmore145Încă nu există evaluări
- 122253-2006-Coastal Pacific Trading Inc. v. Southern20180406-1159-Jglc63Document18 pagini122253-2006-Coastal Pacific Trading Inc. v. Southern20180406-1159-Jglc63Christian VillarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Appendix-Petition 13-7280, Rule 5.1 Constitutional Challenge HECMDocument14 paginiAppendix-Petition 13-7280, Rule 5.1 Constitutional Challenge HECMNeil Gillespie0% (1)
- Boi Intership ProjectDocument58 paginiBoi Intership ProjectRishiNigamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blackbook Project On Consumer Perception About Life Insurance PoliciesDocument94 paginiBlackbook Project On Consumer Perception About Life Insurance PoliciesKáúśtúbhÇóól60% (5)
- Mortgage Digests - Zubiri To MovidoDocument4 paginiMortgage Digests - Zubiri To MovidoCelestino LawÎncă nu există evaluări
- Entrepreneurship (Woman Entrepreneurs)Document32 paginiEntrepreneurship (Woman Entrepreneurs)RuchiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multiple choice exam on pledge and mortgageDocument2 paginiMultiple choice exam on pledge and mortgageab galeÎncă nu există evaluări
- ALLAHABAD BANK BRANCH REPORT FRAUD RISK COMPLIANCEDocument2 paginiALLAHABAD BANK BRANCH REPORT FRAUD RISK COMPLIANCEprem kumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- BachrachDocument3 paginiBachrachRicky Quizzagan MaguigadÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Comparative Study Between Public and Private Housing Finance Companies (HFCS) in IndiaDocument4 paginiA Comparative Study Between Public and Private Housing Finance Companies (HFCS) in IndiaIJEMR JournalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Banking Sector Reforms - Narasimham Committee - Main RecommendationsDocument13 paginiBanking Sector Reforms - Narasimham Committee - Main RecommendationsSakthirama Vadivelu0% (1)
- Sangrador V Valderama - GR 79552Document9 paginiSangrador V Valderama - GR 79552Jeremiah ReynaldoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fabozzi Ch23 BMAS 7thedDocument63 paginiFabozzi Ch23 BMAS 7thedParina AhluwaliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Study On Performance Appraisal System Towards Employees in APSFCDocument69 paginiA Study On Performance Appraisal System Towards Employees in APSFCkavya_repala100% (1)
- REP V V. LIMDocument2 paginiREP V V. LIMJossa ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Be A Property MillionaireDocument4 paginiBe A Property Millionairengsw9999Încă nu există evaluări
- Charrie Mae MDocument2 paginiCharrie Mae MRaymond GanÎncă nu există evaluări