Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Ge330fall09 Dijkstra l19
Încărcat de
HasrulMa'rufDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Ge330fall09 Dijkstra l19
Încărcat de
HasrulMa'rufDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
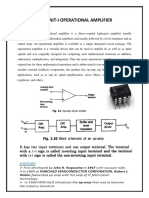
Lecture 19 Shortest Path vs Spanning Tree Max-Flow Problem
October 25, 2009
Lecture 19
Outline
Undirected Network Illustration of the dierence between the shortest path tree and the spanning tree Modeling Dilemma: Shortest path or Spanning tree? Max-Flow Problem
Operations Research Methods
Lecture 19
One-To-All Shortest Path Problem in UNDIRECTED NETWORK
We are given a weighted undirected network (V, E, C) with node set V , edge set E , and the weight set C specifying weights cij for the edges {i, j} E . We are also given a starting node s V . The problem is to determine the shortest path from s to any other node in the network.
In the gure, we have s = 1
Operations Research Methods 2
Lecture 19
Solution obtained by Dijkstras algorithm
Shortest path Length 12 7 13 9 134 20 1365 20 1346 11 The tree of the shortest paths from node 1a
a By pure chance it happen to be the same as in the directed version discussed in Lecture 18
The table has paths sorted by the index of the destination node
Operations Research Methods
Lecture 19
How is the Shortest Path tree related to the Minimal Spanning Tree? These trees are NOT the same!
Reason: The tree of shortest paths depends on the starting node
Operations Research Methods
Lecture 19
The tree of the shortest paths for a traveler starting a trip at node 1 The tree cost is 38
The tree of the shortest paths for a traveler starting a trip at node 3 The tree cost is 41
Operations Research Methods
Lecture 19
Spanning tree problem over the same network
In the spanning tree problem, there is no starting node
In the spanning tree problem: The cost is incurred by one who builds the links
The minimal spanning tree The tree cost is 33
One who builds the links sees the network with the whole structure One who travels in the network from an origin to a destination sees only the links that lead from the origin to the destination
Operations Research Methods 6
Lecture 19
Model Dilemma: Spanning Tree or Shortest Path
Confusion may arise when the problem is given in words To identify the problem type, ask yourself a question: Who incurs the cost? A user or the owner of the network? If it is a user of the network, then shortest path is the right model If it is the one who builds or owns the network, then spanning tree is the right model This helps in most of the situations BUT need not work all the time
Operations Research Methods
Lecture 19
Problem Sample
The TM mobile phone company services six geographical areas. The satellite distances in thousands of miles are given in the gure below. TM needs to determine the best quality message routes that should be established between each two areas in the network
QUESTION: What type of the problem are we facing here?
Operations Research Methods 8
Lecture 19
Max-Flow Problem: Single-Source Single-Sink
We are given a directed capacitated network (V, E, C) connecting a source (origin) node with a sink (destination) node. The set V is the set of nodes in the network. The set E is the set of directed links (i, j) The set C is the set of capacities cij 0 of the links (i, j) E . The problem is to determine the maximum amount of ow that can be sent from the source node to the sink node.
This is Max-Flow Problem for single-source and single-sink
Operations Research Methods 9
Lecture 19
Max-Flow Problem: Multiple-Sources Multiple-Sinks
We are given a directed capacitated network (V, E, C) connecting multiple source nodes with multiple sink nodes. The set V is the set of nodes and the set E is the set of directed links (i, j) The set C is the set of capacities cij 0 of the links (i, j) E The problem is to determine the maximum amount of ow that can be sent from the source nodes to the sink nodes.
c i j
This is Max-Flow Problem for multiple-sources and multiple-sinks
Operations Research Methods 10
Lecture 19
Multiple-sources multiple-links problem can be converted to a single-source and single-sink problem by
Introducing a dummy source node that is connected to the original source nodes with innite capacity links Introducing a dummy sink node that is connected with the original sink nodes with innite capacity links
Operations Research Methods
11
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5795)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- CEC CategoryDocument4 paginiCEC CategoryQ8123Încă nu există evaluări
- 2001 Daewoo Nubira Service Manual2 PDFDocument685 pagini2001 Daewoo Nubira Service Manual2 PDFalberto 32100% (1)
- GED 7 Life and Works of Jose RizalDocument104 paginiGED 7 Life and Works of Jose RizalRheamie Fuyonan100% (1)
- Piping and Plumbing Symbols ListDocument1 paginăPiping and Plumbing Symbols Listsiddarth amaravathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 ID FansDocument43 pagini2 ID Fansshubham vermaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Black Mirror Analysis: 15 Million Merits (Due 27/04/16)Document11 paginiBlack Mirror Analysis: 15 Million Merits (Due 27/04/16)Will MunnyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Frequently Asked Questions For Revisiting Spacetrack Report #3Document2 paginiFrequently Asked Questions For Revisiting Spacetrack Report #3javiermonroycÎncă nu există evaluări
- Entire Environmental Quality - DesignDocument374 paginiEntire Environmental Quality - DesignLTE002Încă nu există evaluări
- Toyota Toyota+sienna+2013+manualDocument1 paginăToyota Toyota+sienna+2013+manualNur Cholik Widyan Sa0% (1)
- MHSIR00491976Document1 paginăMHSIR00491976Patan Rafiq KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Surveying Lab ManualDocument76 paginiSurveying Lab ManualIan Lawrence YupanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pte Apeuni 20240408 Global Monthly en Kd54Document321 paginiPte Apeuni 20240408 Global Monthly en Kd54Boyes WorldÎncă nu există evaluări
- Probability DistributionsDocument167 paginiProbability DistributionslihaiyangÎncă nu există evaluări
- SPHE8281DDocument35 paginiSPHE8281Ddiego-tÎncă nu există evaluări
- CDI1Document40 paginiCDI1Leonino Angelica Aiko S.Încă nu există evaluări
- MODEL: SC330 Industrial Range Powered by Cummins: Diesel Generating Set 400/230 V - 50 HZ - 3phaseDocument4 paginiMODEL: SC330 Industrial Range Powered by Cummins: Diesel Generating Set 400/230 V - 50 HZ - 3phaseDefly GustiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ic NotesDocument67 paginiIc NotesVijaya Kumar VadladiÎncă nu există evaluări
- En 4j2 4fDocument71 paginiEn 4j2 4fRafael HernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Citaion Style GuideDocument2 paginiCitaion Style Guideedustar330Încă nu există evaluări
- Json Out InvoiceDocument2 paginiJson Out Invoicetkpatel529Încă nu există evaluări
- Manual SomachineDocument228 paginiManual SomachineMauricio NaranjoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rele A Gas BuchholtsDocument18 paginiRele A Gas BuchholtsMarco GiraldoÎncă nu există evaluări
- THMT 3312: Research Methods For Tourism & Hospitality ManagementDocument13 paginiTHMT 3312: Research Methods For Tourism & Hospitality Managementmilrosebatilo2012Încă nu există evaluări
- Competitiveness Huawei Casestudy WebDocument40 paginiCompetitiveness Huawei Casestudy Webjameslee27Încă nu există evaluări
- Government Polytechnic, Pune: ET2107 - NODocument8 paginiGovernment Polytechnic, Pune: ET2107 - NOG012 Bhise AniketÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data Sheet 3VA2225-5HL32-0AA0: ModelDocument7 paginiData Sheet 3VA2225-5HL32-0AA0: ModelJENNYÎncă nu există evaluări
- CNC RoboticsDocument17 paginiCNC RoboticsKunal DuttÎncă nu există evaluări
- TAPCON® 240: Voltage Regulator For Regulating TransformersDocument6 paginiTAPCON® 240: Voltage Regulator For Regulating TransformerscastrojpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 4 Social Sciences-Geography Term 2 Lesson PlansDocument9 paginiGrade 4 Social Sciences-Geography Term 2 Lesson Plansgobedimalapile02Încă nu există evaluări
- Dist Census Book Latur PDFDocument770 paginiDist Census Book Latur PDFMP100% (1)