Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
27 Aug 2011 Test Along With Answers
Încărcat de
dnagwaliorDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
27 Aug 2011 Test Along With Answers
Încărcat de
dnagwaliorDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
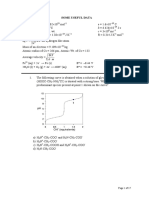
1. Which of the following transitions is the highest energy transition? (a) n to (b) n to (c) to (d) to 2.
to 2. Which of the following alkenes would have the largest max?
3. Which of the following alkenes would have the largest max?
4. What is the max for the following compound? Use the provided parameters for your calculation.
(a) (b) (c) (d)
234 nm 244 nm 273 nm 283 nm
5. Find max for the following compound. Use data given above.
(a)
229 nm
(b) (c) (d)
249 nm 254 nm 259 nm
6. Beer's Law states that; a) Absorbance is proportional to both the path length and concentration of the absorbing species b) Absorbance is proportional to the log of the concentration of the absorbing species c) Absorbance is equal to P0 / P
7. UV-Vis. Spectroscopy of organic compounds is usually concerned with which electronic transition(s)? a) * b) n* c) n* and *
8. Molar absorbtivities of compounds exhibiting charge transfer absorption are a) Small b) Moderate c) Large
9. Peaks resulting from n* transitions are shifted to shorter wavelengths (blue shift) with increasing solvent polarity.True or false? a) True b) False
10. Which of the following relationships between absorbance and %Transmittance is incorrect ? a) A = log10 100 / %T b) A = 2 - log10 %T c) A = log10 1 / %T
11.In the equation, A = bc, what quantity is represented by "" ? a) Absorbtivity b) Molar absorbtivity c) Path length
12.Why is it generally preferable to use absorbance as a measure of absorption rather than % Transmittance? a) Because %T cannot be measured as accurately as absorbance b) Because %T is dependant on the power of the incident radiation c) Because absorbance is proportional to the concentration of the analyte, whereas %T is not. 13. Does a compound with high molar absorbtivity have a higher or lower limit of detection than a compound with low molar absorbtivity? a)higher b)lower
14. Which of the following components of a monochromator is the dispersing element?
a) The collimating lens
b) The entrance slit
c) The diffraction grating
15. Why must the voltage supplied to a tungsten lamp be very stable? a) Because if it wasn't the lamp would burn out b) Because amount of energy the lamp emits is proportional to the fourth power of the operating voltage c) Because the lamp will only function at a specific voltage 16. Silicate glass is transparent to UV radiation. True or false? a) True b) False
17. Linear photodiode arrays can only detect radiation of a single wavelength. True or false? a) True b) False
18: The solvents for these determinations are often water for water soluble compounds, or ________ for organic-soluble compounds. a).Alcoholic beverage b) Ethanol c) 1,4-Butanediol d) Flumazenil 19: Ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy or ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry (UVVis or UV/Vis) involves the spectroscopy of ________ in the UV-visible region. a) Atom b) Photon c) Standard model d) Electron 20: In UV region of the electromagnetic spectrum,________ undergo electronic transitions. a) Atom b) Photon c) Molecule d) Neutron 21: The Woodward-Fieser rules are a set of empirical observations which can be used to predict max, the wavelength of the most intense UV/Vis absorption, for conjugated organic compounds such as dienes and ________. a) Alkane b) Alcohol c) Ketone d) Aldehyde 22: UV/Vis spectroscopy is routinely used in the quantitative determination of solutions of transition metal ions and highly conjugated ________. a) Carbon b) Organic Chemistry c) Biochemistry d) Organic compound
23: The most widely applicable cuvettes are made of high quality ________ or quartz glass because these are transparent throughout the UV, visible and near infrared regions. a) Fused quartz b) Optical fibre c) Silicon dioxide d) Silicon 24: The basic parts of a spectrophotometer are a light source, a holder for the sample, a ________ or monochromator to separate the different wavelengths of light, and a detector.
a) Diffraction grating b) Holography c) Dispersion(optics) d) Optics 25: This technique is complementary to ________, in that fluorescence deals with transitions from the excited state to the ground state, while absorption measures transitions from the ground state to the excited state. a) Ultraviolet b)Tryptophan c) Fluorescence spectroscopy d) Surfactant 26: The absorbance and extinction are sometimes defined in terms of the ________ instead of the base-10 logarithm. a) Natural logarithm b) Eulers formula c) Leonhard Euler d) Exponential function
27. Fluorescence occurs when... a) A molecule returns to the electronic ground state from an excited triplet state by losing it's excess energy as a photon b) A molecule returns to the electronic ground state from an excited singlet state by losing it's excess energy as a photon c) A molecule lowers its vibrational energy by losing it's excess energy as a photon 28. Internal conversion is where... a) The spin of an excited electron reverses, changing the state of the molecule (from singlet state to triplet state or vice versa) b) A molecule converts its excess energy to light, and emits a photon c) A molecule converts excess electronic energy to vibrational energy 29. Intersystem crossing is where... a) The spin of an excited electron reverses, changing the state of the molecule (from singlet state to triplet state or vice versa) b) A molecule converts its excess energy to light, and emits a photon c) A molecule converts excess electronic energy to vibrational energy 30. Phosphorescent emission of light can persist after the radiation used to excite the molecules has been turned off. True or false? a) True b) False
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Instrumental Methods of Analysis QuestionsDocument9 paginiInstrumental Methods of Analysis Questionsuvir iitm100% (1)
- AnalysisDocument14 paginiAnalysisBINDU100% (1)
- Spectroscopy (MCQ) - : YogeshDocument16 paginiSpectroscopy (MCQ) - : YogeshYUGI SINGH100% (1)
- Visible and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy-Part 2Document54 paginiVisible and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy-Part 2Amusa TikunganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phổ nghiệm (UV-Vis) đềDocument8 paginiPhổ nghiệm (UV-Vis) đềGia Hy NgôÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 3 Question bankDocument9 paginiUnit 3 Question bankprathima.dineshkumar1409Încă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry Unit 2 MCQ With AnswersDocument5 paginiChemistry Unit 2 MCQ With AnswersKaran VaswaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- MSC 2 Mcqs Analytical Chemistry MSC 2ndDocument20 paginiMSC 2 Mcqs Analytical Chemistry MSC 2ndPhoton Online Science AcademyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 3 Introduction To PhotonicsDocument14 paginiUnit 3 Introduction To PhotonicsKapil TilwaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Part 1: Choose The Best Answer From The Options Underneath EachDocument11 paginiPart 1: Choose The Best Answer From The Options Underneath EachGIRMA SELALE GELETAÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCQ Test-4, Unit 2, Engg - Chemistry, 2020-21Document10 paginiMCQ Test-4, Unit 2, Engg - Chemistry, 2020-21Dr. N. P. Tripathi100% (1)
- ITA Viva - Questions OnlyDocument4 paginiITA Viva - Questions OnlyManoj KhanalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit - 2 MCQ'sDocument5 paginiUnit - 2 MCQ'srishavr2001Încă nu există evaluări
- MCQ CharacterizationDocument18 paginiMCQ CharacterizationAmjed AL-KAHTEEB100% (2)
- Class XII 2023 2024 Prelims IDocument10 paginiClass XII 2023 2024 Prelims ITanishkha RaajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class 12 UT Set 2Document5 paginiClass 12 UT Set 2garvit1223Încă nu există evaluări
- المستندDocument12 paginiالمستندMohamed SaadallahÎncă nu există evaluări
- UV-Vis QuestionsDocument3 paginiUV-Vis QuestionsManoj MathewsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atomic and Molecular Spectroscopy-2 PDFDocument60 paginiAtomic and Molecular Spectroscopy-2 PDFHaseeb HaiderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ami MCQDocument89 paginiAmi MCQRathinavel MAMCETÎncă nu există evaluări
- Visible and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy-Part 2Document31 paginiVisible and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy-Part 2Amusa TikunganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Molecular SpectrosDocument64 paginiMolecular SpectrosShayan NavliwalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hrushikesh Organic Group 5Document10 paginiHrushikesh Organic Group 5Sarita YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- SAMPLE PAPER-09 (Unsolved)Document3 paginiSAMPLE PAPER-09 (Unsolved)ShantanuSinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- PB Xii (2022 23) Set 1Document4 paginiPB Xii (2022 23) Set 1Uday SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analysis of Samples Absorbance Susing UV-VisDocument17 paginiAnalysis of Samples Absorbance Susing UV-VisRaiwata Mertanjaya100% (2)
- PhysicsDocument2 paginiPhysicsBIBI MOHANANÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 5 - Ultraviolet and Visible (UV-Vis) SpectrosDocument40 paginiLecture 5 - Ultraviolet and Visible (UV-Vis) SpectrosBelay HaileÎncă nu există evaluări
- BSNL Je Microwave Engineering McqsDocument18 paginiBSNL Je Microwave Engineering McqstripbrataÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exam1 04Document7 paginiExam1 04Rodney SalazarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analytical Chemistry QuestionsDocument7 paginiAnalytical Chemistry QuestionsMostafa Talaat Abu-khadraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ai Interview QuestionsDocument31 paginiAi Interview QuestionsmohanapriyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NPTEL'AC'23'Assignment 5Document5 paginiNPTEL'AC'23'Assignment 5SathishÎncă nu există evaluări
- GS2011 QP ChemistryDocument17 paginiGS2011 QP ChemistryAkash AgarwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atomic Structure MCQs & Short QuestionsDocument2 paginiAtomic Structure MCQs & Short QuestionsTajammal AminÎncă nu există evaluări
- X Ray ImagingDocument16 paginiX Ray ImagingAhmed WahiedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spectroscopy True or False MCQDocument7 paginiSpectroscopy True or False MCQmohamed arifÎncă nu există evaluări
- Instrumental Analysis Spectroscopy - ppt12Document109 paginiInstrumental Analysis Spectroscopy - ppt12kiya01Încă nu există evaluări
- PhysicsDocument28 paginiPhysicsSuleman KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCQs Nuclear Analytical Techniques MSC 4THDocument11 paginiMCQs Nuclear Analytical Techniques MSC 4THPhoton Online Science Academy100% (1)
- Visible and Ultraviolet SpectrosDocument55 paginiVisible and Ultraviolet SpectrosMarcos ShepardÎncă nu există evaluări
- Question Bank SEM I Paper 1Document7 paginiQuestion Bank SEM I Paper 1Hrishikesh SalgaonkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- FMDC 2015Document35 paginiFMDC 2015Football ManiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SKN 7 PDFDocument7 paginiSKN 7 PDFKamran AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics 203 Sample Final ExamDocument22 paginiPhysics 203 Sample Final ExamPi-ey En-jiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Colorimetry: Absorbance Is Directly Proportional To Concentration of FeDocument38 paginiColorimetry: Absorbance Is Directly Proportional To Concentration of Fedhekle_dÎncă nu există evaluări
- 102 Fundamentals of Radiology and ImagingDocument15 pagini102 Fundamentals of Radiology and ImagingShivani YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Department of Oral Medicine and Radiology MCQ 1Document14 paginiDepartment of Oral Medicine and Radiology MCQ 1Gokul RavichandranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rajesh Singh M. Pharm 1 Year: Made byDocument49 paginiRajesh Singh M. Pharm 1 Year: Made byNaman Sharma100% (1)
- Department of Oral Medicine and Radiology MCQ 1Document14 paginiDepartment of Oral Medicine and Radiology MCQ 1Gokul RavichandranÎncă nu există evaluări
- 16527Document22 pagini16527Jaikrishna SukumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- @sachin - Sir - Physics: Version 2.ODocument9 pagini@sachin - Sir - Physics: Version 2.OPrakharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 2Document59 paginiUnit 2NTGÎncă nu există evaluări
- NUCLEAR_CHEMISTRYDocument11 paginiNUCLEAR_CHEMISTRYCaleb AsharleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Visible and Ultraviolet SpectrophotometryDocument41 paginiVisible and Ultraviolet SpectrophotometryalaahamadeinÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCQ Int 2Document16 paginiMCQ Int 2abiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Project Report 2Document31 paginiFinal Project Report 2Kumar Swapnil PadhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pdf&rendition 1 1Document13 paginiPdf&rendition 1 1vijay balajiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bcs Final ReducedDocument643 paginiBcs Final Reducedkomal bandleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simulation of Transport in NanodevicesDe la EverandSimulation of Transport in NanodevicesFrançois TriozonÎncă nu există evaluări
- F.list of AbbreviationsDocument1 paginăF.list of AbbreviationsdnagwaliorÎncă nu există evaluări
- ReferencesDocument5 paginiReferencesdnagwaliorÎncă nu există evaluări
- HLL Resource6227Document9 paginiHLL Resource6227abhijit.salvekarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 125Document46 pagini125aditya017Încă nu există evaluări
- Sri Dwi Mutiara-Jurnal CRSS OSNE 1Document11 paginiSri Dwi Mutiara-Jurnal CRSS OSNE 1sri dwi mutiaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- DUPLICATE BILL TITLEDocument8 paginiDUPLICATE BILL TITLEMohammed AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8602 BookDocument240 pagini8602 BookSohail100% (2)
- Optimization Module For Abaqus/CAE Based On Genetic AlgorithmDocument1 paginăOptimization Module For Abaqus/CAE Based On Genetic AlgorithmSIMULIACorpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Detect and Diagnose HVAC Equipment ErrorsDocument1 paginăDetect and Diagnose HVAC Equipment ErrorsCatalin DragomirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Plan 2 Sine Rule and Cosine RuleDocument8 paginiLesson Plan 2 Sine Rule and Cosine Ruleapi-280114661Încă nu există evaluări
- Toaz - Info Interchange 2 Quiz Units 5 Ampamp 6 Revision Del Intento PRDocument5 paginiToaz - Info Interchange 2 Quiz Units 5 Ampamp 6 Revision Del Intento PRMarco Antonio Gonzalez CastilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Obeid Specialized Hospital - Riyadh: Inpatient DeptsDocument4 paginiObeid Specialized Hospital - Riyadh: Inpatient DeptsLovelydePerioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Configure NTP, OSPF, logging and SSH on routers R1, R2 and R3Document2 paginiConfigure NTP, OSPF, logging and SSH on routers R1, R2 and R3Lars Rembrandt50% (2)
- 13 Nilufer-CaliskanDocument7 pagini13 Nilufer-Caliskanab theproÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assembly Transmission Volvo A40GDocument52 paginiAssembly Transmission Volvo A40GNanang SetiawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anie Altamirano Learning For Life HandoutDocument4 paginiAnie Altamirano Learning For Life HandoutAnnapurna VÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basf Masteremaco Application GuideDocument15 paginiBasf Masteremaco Application GuideSolomon AhimbisibweÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computers and Operations Research: Yulin Sun, Simon Cong Guo, Xueping LiDocument12 paginiComputers and Operations Research: Yulin Sun, Simon Cong Guo, Xueping LiQuỳnh NguyễnÎncă nu există evaluări
- ZSL National Red List of Nepal's Birds Volume 2Document636 paginiZSL National Red List of Nepal's Birds Volume 2Tushita LamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- P2-1 - NME1106 - Gas Turbine LabworkDocument23 paginiP2-1 - NME1106 - Gas Turbine LabworkKoh JovenÎncă nu există evaluări
- LTE Interview QuestionsDocument10 paginiLTE Interview QuestionsMahesh Pratap100% (1)
- GulliverDocument8 paginiGulliverCris LuÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Introduction to Heisenberg Groups in Analysis and GeometryDocument7 paginiAn Introduction to Heisenberg Groups in Analysis and Geometrynitrosc16703Încă nu există evaluări
- Handy 2010 Case StudyDocument6 paginiHandy 2010 Case Studycancer6Încă nu există evaluări
- SECURE ROAD BLOCKERS PREVENT VEHICLE ATTACKSDocument2 paginiSECURE ROAD BLOCKERS PREVENT VEHICLE ATTACKSMuhammad Tahir QamarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Get Started On Creating Your Event Budget:: If You Decide To Build Your Own Start by Creating A Few ColumnsDocument4 paginiGet Started On Creating Your Event Budget:: If You Decide To Build Your Own Start by Creating A Few ColumnsGeomarkPaalaMortelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kompres Panas Dingin Dapat Mengurangi Nyeri Kala I Persalinan Di Rumah Sakit Pertamina Bintang AminDocument9 paginiKompres Panas Dingin Dapat Mengurangi Nyeri Kala I Persalinan Di Rumah Sakit Pertamina Bintang AminHendrayana RamdanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mascot LD series hydraulic motor specsDocument6 paginiMascot LD series hydraulic motor specsM S GokulÎncă nu există evaluări
- WaidhanDocument86 paginiWaidhanPatel Nitesh OadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Writing Emails Part 1 Informal British English Teacher Ver2Document7 paginiWriting Emails Part 1 Informal British English Teacher Ver2Madalina MandiucÎncă nu există evaluări
- Innovations in Drill Stem Safety Valve TechnologyDocument22 paginiInnovations in Drill Stem Safety Valve Technologymiguel mendoza0% (1)
- Exoskeleton Power Requirements Based on Human BiomechanicsDocument54 paginiExoskeleton Power Requirements Based on Human Biomechanicsja2ja1Încă nu există evaluări
- An Introduction To Pascal Programming MOD 2010Document5 paginiAn Introduction To Pascal Programming MOD 2010Johnas DalusongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Report Card of Army Public School StudentDocument2 paginiReport Card of Army Public School StudentRama KrishnaÎncă nu există evaluări