Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
317 Care Plan
Încărcat de
Sandra HaggertyDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
317 Care Plan
Încărcat de
Sandra HaggertyDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
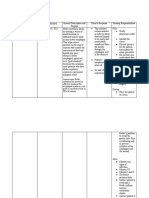
Utilizing all of the above data you have collected, create a plan of care for this woman/family using
2-3 separate priority issues. Be very specific in the interventions. ASSESSMENT/NURSING DIAGNOSIS Nursing Diagnosis Diagnosis #1 Acute pain r/t uterine contractions during labor Subjective data: Mother requests epidural, increasingly loud as contractions progress. Outcome/Goal Intervention/ Implementation Assessed mothers level of pain Encouraged spouse to encourage her, Gave water, fanned mother, applied damp cloth to her forehead. Allowed mother to change position when needed. Rationale & Source Pain is a highly subjective state assessment of pain experience is the first step in planning pain management strategies (Gulanick, M & Meyers, J. (2006) pg 144) Support measures are often more effective when delivered by a familiar person (Perry, Evaluation Intervention was successful as evidenced by mother showed increased ability to cope with the pain.
Mother exhibits signs of ability to cope with discomfort
S.E., Hockenberry, M.J., Lowdermilk, D.L., & Wilson, D. (2005) pg 514)
Comfort measures to relieve diaphoresis, change in position helps relieve stiffness and helps avoid cramping. (Perry et al. (2005) pg514)
Objective data: Facial grimacing, clenched fists, diaphoresis, moaning
Nursing Diagnosis
Outcome/Go al
Intervention/ Implementation
Rationale & Source
Evaluation
Diagnosis #2
Fatigue r/t increased energy expenditure secondary to labor and birth.
Subjective data:
Mothers energy level restored following birth.
Talked to mother about and emphasized need for rest after the birth. Monitor mothers level of fatigue
Pt states exhaustion, wishes to sleep immediatel y after birth.
Objective data:
Fatigue is common in the postpartum period and involves both physiologic components associated with long labors, cesarean birth, anemia, and breastfeed and psychologic components related to depression and anxiety. The excitement and exhileration experienced after the birth of the infant may make rest difficult. Arranging specific periods for rest and sleep will ensure that the mother can restore depleted energy levels. (Perry et al. (2005) pg 614,
514) Monitoring mothers level of fatigue allows us to ensure mothers restoration of energy (Perry et al. (2005) pg 514)
Interventions effective as evidenced by mothers energy level increasing and increased movement following birth.
Pt exhibits visible lack of energy, very tired, limited concentrati on at times
Diagnosis #3
Fear r/t loss of control and unpredictab le outcome secondary to newborn distress at birth
Subjective data
Patient verbalizes or manifests a reduction or absence of fear.
Encourage patient to verbalize problems and concerns. Answer questions and concerns of patient if able to do so. (Doctor and translator did this) Maintain calm manner while interacting with mother. Encourage spouse to stay with mother until more information is provided about infant condition.
Mother has increased questioning , crying,
Objective data
Interventions were successful in alleviating Verbalizing fears and concerns provides validation patient fears as of their concerns and enables evidenced by reassessment. (Gulanick et patient states reduction of fear al. (2006) pg 69) when infant condition The health care provider explained. can transmit his or her own anxiety to the client. The patients feeling of stability increases in a calm and nonthreatening atmosphere. (Gulanick et al. (2006) pg 70) The presence of significant others reinforces feelings of security for the patient in times of fear. (Gulanick et al. (2006) pg 70)
Mother tense, visually upset, trembling, crying
References (APA Format) Gulanick. M & Meyers J. (2006) Nursing Care Plans: Nursing Diagnosis and Intervention (6th ed) St. Louis: Mosby Elsevier Perry, S.E., Hockenberry, M.J., Lowdermilk, D.L., & Wilson, D. (2005). Maternal child nursing
care. (3rd ed.). St. Louis: Mosby Elsevier
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- NCP of Endometrical CancerDocument2 paginiNCP of Endometrical CancerFrando kennethÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan Format Name: - Medical Diagnosis: - DateDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan Format Name: - Medical Diagnosis: - DateSheryl Ann Barit PedinesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Family Nursing Care Plan ChapterDocument1 paginăFamily Nursing Care Plan ChapterJhe PangsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fatigue and Back Pain NCP PresentationDocument18 paginiFatigue and Back Pain NCP PresentationTine Guibao100% (1)
- NCPDocument2 paginiNCPShubhangi SarwanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Pain Related To Effects of Labor and Delivery ProcessDocument3 paginiAcute Pain Related To Effects of Labor and Delivery ProcessrlinaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Homework 1: Developing A Health Teaching Program 1. What Insights and Reflections Do You Have Based On Your Understanding of The EssentialDocument2 paginiHomework 1: Developing A Health Teaching Program 1. What Insights and Reflections Do You Have Based On Your Understanding of The EssentialRianne BaetiongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study NCPDocument4 paginiCase Study NCPKelly OstolÎncă nu există evaluări
- Actual NCPDocument2 paginiActual NCPbaki0146Încă nu există evaluări
- DR NCP InfectionDocument2 paginiDR NCP Infectionkarl montanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP For Insomnia PDFDocument2 paginiNCP For Insomnia PDFEca0% (1)
- APOLONIO, JC - Natural Theory - Thomas AquinasDocument3 paginiAPOLONIO, JC - Natural Theory - Thomas AquinasJustin ApolonioÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP For Postpartum DiscomfortsDocument3 paginiNCP For Postpartum DiscomfortsCamille Maluenda - Tan0% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 paginiNursing Care PlanJASMINE JOY BADUAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan: Provide Rest Periods To Promote Relief, Sleep, and RelaxationDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan: Provide Rest Periods To Promote Relief, Sleep, and RelaxationGrace MellaineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan: Nikolai P. Funcion, FSUU-SNDocument5 paginiNursing Care Plan: Nikolai P. Funcion, FSUU-SNNikolai FuncionÎncă nu există evaluări
- EsophagomyotomyDocument3 paginiEsophagomyotomySamVelascoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Postpartum Psychosis Parenting SupportDocument3 paginiPostpartum Psychosis Parenting SupportLyca Mae AurelioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan for Postpartum Patient with Sleep Disturbance and Risk of InfectionDocument9 paginiNursing Care Plan for Postpartum Patient with Sleep Disturbance and Risk of Infectionalaisah dimaporoÎncă nu există evaluări
- NURSING CARE PLAN Interrupted Breastfeeding: Student Nurses' CommunityDocument3 paginiNURSING CARE PLAN Interrupted Breastfeeding: Student Nurses' CommunitySaira SucgangÎncă nu există evaluări
- "My Breasts Are Sore and Tender But There Is No Milk Coming Out and Im Also in Pain Due To Uterine CrampingDocument3 pagini"My Breasts Are Sore and Tender But There Is No Milk Coming Out and Im Also in Pain Due To Uterine CrampingBAGUIO CATSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Incomplete Spinal Cord Injury Nursing CareDocument6 paginiIncomplete Spinal Cord Injury Nursing CareTherese MargaretÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Acute Pain OB Ward PDFDocument2 paginiNCP Acute Pain OB Ward PDFambiit25Încă nu există evaluări
- "Hindi Ko Kayo Masyadong Marinig Sa Kanang Tenga Ko, Pwede Bang Sa Kaliwang Side Ko Kayo Magsalita?" As Verbalized by The PatientDocument2 pagini"Hindi Ko Kayo Masyadong Marinig Sa Kanang Tenga Ko, Pwede Bang Sa Kaliwang Side Ko Kayo Magsalita?" As Verbalized by The PatientMussaib Mushtaq100% (1)
- NCP 1 Nursing DiagnosisDocument6 paginiNCP 1 Nursing DiagnosisJosh BlasÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP On Preterm LaborDocument2 paginiNCP On Preterm LaborAngelica Malacay RevilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lonzaga Assessment PDFDocument7 paginiLonzaga Assessment PDFNiño Naryana Luke PanchoÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCPDocument2 paginiNCPCamille VirayÎncă nu există evaluări
- ASD Pathophysiology, Signs, Symptoms, and TreatmentDocument1 paginăASD Pathophysiology, Signs, Symptoms, and TreatmentMSÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP - LeprosyDocument3 paginiNCP - LeprosyKevin DareÎncă nu există evaluări
- Epidural Anesthesia Drug StudyDocument2 paginiEpidural Anesthesia Drug StudyDominic JoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- L&D Careplan 1 KarenDocument4 paginiL&D Careplan 1 KarenSimran SandhuÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP 2 LRDR For PrintDocument2 paginiNCP 2 LRDR For PrintGeorge PandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan: Determine Cause of Activity - Determining The Cause of A Disease CanDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan: Determine Cause of Activity - Determining The Cause of A Disease Canrix07Încă nu există evaluări
- NCP Impaired ComfortDocument2 paginiNCP Impaired ComfortGia P. de VeyraÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCPDocument7 paginiNCPAbbie TantengcoÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP EpisiotomyDocument1 paginăNCP EpisiotomyKaye CeprianoÎncă nu există evaluări
- High Percentage of Sleep Disturbances Can Affect The Recovery of The PatientDocument1 paginăHigh Percentage of Sleep Disturbances Can Affect The Recovery of The PatientMatt SinnungÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCPDocument3 paginiNCPTweenie DalumpinesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activity 2 - Bigleap - Immediate Care of The Newborn (Updated)Document5 paginiActivity 2 - Bigleap - Immediate Care of The Newborn (Updated)Cameron De GuzmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bukidnon State University College of NursingDocument5 paginiBukidnon State University College of NursingAIZA MAE BANGGAY100% (1)
- NCP Severe Labor PainDocument3 paginiNCP Severe Labor PainPaolo EspinosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument5 paginiAssessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationAlyssa NicoleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Corrected NCP Case 3 Intrapartum NCPDocument2 paginiCorrected NCP Case 3 Intrapartum NCPReyzel PahunaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Preeclampsia PDFDocument1 paginăNCP Preeclampsia PDFTrixy Glaire TomaseteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hernandez NCP Drug StudyDocument7 paginiHernandez NCP Drug StudyEliza Joyce HernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- HypopituitarismDocument2 paginiHypopituitarismAnne de VeraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rectal and Vaginal Suppository Insertion GuideDocument2 paginiRectal and Vaginal Suppository Insertion GuideMariah Jane TaladuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- FA5 - Contemporary WorldDocument2 paginiFA5 - Contemporary WorldGill GregorioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care PlansDocument5 paginiNursing Care PlansYannah Mae EspineliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Why Do Human Cells Rely Far More On Glucose and Fat For The Energy Than On ProteinDocument4 paginiWhy Do Human Cells Rely Far More On Glucose and Fat For The Energy Than On ProteinHamda HassanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective Data: Short Term GoalDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective Data: Short Term GoalRhos Antonette GuimbanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pot Term pregnancy-MOMANYIDocument2 paginiPot Term pregnancy-MOMANYISally Gesembe100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationJP2001100% (1)
- NCP Risk For InjuryDocument1 paginăNCP Risk For InjuryRenz Kier L. ComaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP For Parent and Child PDFDocument3 paginiNCP For Parent and Child PDFMariana Mikaela AlagarÎncă nu există evaluări
- M&M: Mindfulness and Meditation While On Home Quarantine: An Encounter With The Lord / A Synthesis Paper of Topics DiscussedDocument5 paginiM&M: Mindfulness and Meditation While On Home Quarantine: An Encounter With The Lord / A Synthesis Paper of Topics DiscussedpaulinaveraÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP ObDocument2 paginiNCP ObtimmyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Studi Deskriptif Pendampingan Dan Dukungan Suami Terhadap Pengurangan Rasa Nyeri Pada Ibu Bersalin Kala I Di Rs Panti Wilasa Citarum SemarangDocument9 paginiStudi Deskriptif Pendampingan Dan Dukungan Suami Terhadap Pengurangan Rasa Nyeri Pada Ibu Bersalin Kala I Di Rs Panti Wilasa Citarum SemarangAuliaAnggraeniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psychopharmacology and Pregnancy: Treatment Efficacy, Risks, and GuidelinesDe la EverandPsychopharmacology and Pregnancy: Treatment Efficacy, Risks, and GuidelinesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class III Cavity Treatment (Procedure, Materials)Document2 paginiClass III Cavity Treatment (Procedure, Materials)Manos KritikosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Symposiumbooklet CareerDocument36 paginiSymposiumbooklet Careerroh009Încă nu există evaluări
- Canadian Standards For Hospital LibrariesDocument4 paginiCanadian Standards For Hospital LibrariesFernando HernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scientific Validation of Urakka Varmam Stimulation With Special Reference To Baroreflex Activation TherapyDocument5 paginiScientific Validation of Urakka Varmam Stimulation With Special Reference To Baroreflex Activation TherapyMurali SmatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Efficacy of Transpalatal Arch As An Anchorage Rein PDFDocument7 paginiEfficacy of Transpalatal Arch As An Anchorage Rein PDFOana CostanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reliability of Anatomic Reference Planes in Establishing The Occlusal Plane in Different Jaw Relationships: A Cephalometric StudyDocument8 paginiReliability of Anatomic Reference Planes in Establishing The Occlusal Plane in Different Jaw Relationships: A Cephalometric Studyedy harahapÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quick Guide to Bandaging TechniquesDocument4 paginiQuick Guide to Bandaging TechniquesTheodore GonzaloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biochemistry For Anesthesiologists and IntensivistsDocument11 paginiBiochemistry For Anesthesiologists and IntensivistsAndi tenri sanda datuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evaluation MyocarditisDocument5 paginiEvaluation MyocarditisRaidis PangilinanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thumb Exercises ActiveDocument6 paginiThumb Exercises ActiveMichael NelsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- AlgorithmACLS Tachycardia 200612Document1 paginăAlgorithmACLS Tachycardia 200612YassarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abdominal UltrasoundDocument6 paginiAbdominal Ultrasounds0800841739100% (1)
- Endocrine Exam ReviewDocument2 paginiEndocrine Exam Reviewrockforj3susÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phobic EncounterDocument1 paginăPhobic EncounterEmanuel PeraltaÎncă nu există evaluări
- F.A.S.T.H.U.G: I W. AryabiantaraDocument35 paginiF.A.S.T.H.U.G: I W. Aryabiantaraarnawaiputu60Încă nu există evaluări
- Orthopedic Nursing. Lecture Notes at Philipine Orthopedic CenterDocument7 paginiOrthopedic Nursing. Lecture Notes at Philipine Orthopedic Centerhannjazz100% (5)
- Mental Health Personal Statement - Docx'Document2 paginiMental Health Personal Statement - Docx'delson2206Încă nu există evaluări
- MemoryDocument46 paginiMemoryMaha Al AmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lymphbuster Version 1.0 PDFDocument395 paginiLymphbuster Version 1.0 PDFDiana MariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- JC Oncology55211005Document32 paginiJC Oncology55211005Neenuch ManeenuchÎncă nu există evaluări
- PCI-DPharm Syllabus Guidelines 2020Document30 paginiPCI-DPharm Syllabus Guidelines 2020Chander PrakashÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Client With A Brain Tumor: Nursing Care PlanDocument1 paginăA Client With A Brain Tumor: Nursing Care Planshabatat2002Încă nu există evaluări
- Dengulata KosamDocument3 paginiDengulata KosamChina SaidaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Radial Club Hand TreatmentDocument4 paginiRadial Club Hand TreatmentAshu AshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cerebrospinal Fluid: Physical Characteristic and Composition of The Cerebrospinal FluidDocument5 paginiCerebrospinal Fluid: Physical Characteristic and Composition of The Cerebrospinal FluiderickÎncă nu există evaluări
- Role and Responsibilities of CROs and SponsorsDocument33 paginiRole and Responsibilities of CROs and SponsorsShilpi Paliwal100% (2)
- Martial Arts SecretsDocument4 paginiMartial Arts SecretsGustavoRodriguesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fin e 222 2018Document143 paginiFin e 222 2018Gnana SekarÎncă nu există evaluări
- HouseflyDocument16 paginiHouseflyRitu Puri50% (2)
- Aghamohammadi Et Al 2016 WEB OF SCIENCE Integrative Cancer TherapiesDocument9 paginiAghamohammadi Et Al 2016 WEB OF SCIENCE Integrative Cancer Therapiesemmanuelle leal capelliniÎncă nu există evaluări