Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Anxiety Disorders Review
Încărcat de
Tatiana SaenzDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Anxiety Disorders Review
Încărcat de
Tatiana SaenzDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
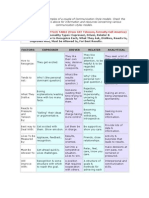
Anxiety Disorder Panic Disorder with Agorophobia
Curious things to know Phobias begin early in life and are experienced as often by as men as by women. The two peak times for the onset are between ages 15-20 yrs and then again between 30-40 yrs.
Cause Triggered by stress.
Assessment/sympto ms Recurrent and persistent thoughts that causes anxiety or distress. Recurrent episodes panic attacks.
Nursing Intervention Reassure client you will stay and panic attacks will subside. Loosen any tight clothing. Instruct and demonstrate deep, slow breathing. Decrease environmental stimuli and interactions with other people.
Treatment Individual/ group therapy: Individual: therapists helps client identify current life situations that set off anxiety. Group: Can lead to greater understanding and resolutions of important issues. Clients prepare themselves to focus on the present rather than the past. Cognitive behavioral therapy: (best option) Teaches practical thoughtmanagement techniques and prevention. Learn to cope with anxiety. Anger management. Alcohol or drug relapse prevention. Relaxation techniques Transcedetal meditation. Progressive muscle
Preferred Drugs/Medications Anxiety agents: BusPar (buspirone): GAD, panic disorder, agoraphobia,PTSD MAOIs Phenelzine (Nardil) Social phobia, agoraphobia Tricyclic Antidepressant: Imipramine (Tofranil) GAD, agoraphobia SSIRs (first line of medication to treat panic disorders) Citalopram(Celexa) Escitalopram(Lexap ro) Fluoxetine(Prozac) Fluvoxamine(Luvox ) Paroxetine(Paxil) Sertraline(Zoloft) Panic disorder, OCD,GAD, dysmorphic disorder, social phobia, PTSD
The person recognizes that the obessions are product of his/her mind. A person with agoraphobia will avoid groups of people. At least one of the panic episodes has been followed by 1 month or more of: (a)Worry about the implications of the panic attack e.g losing control, going crazy.(b) significant changes in behavior related to attacks. (c) persistent concerns of having additional
attacks.
They may become housebound.
relaxation. Yoga. Exercise. Hobbies/arts/crafts. Prayer. Assertiveness Helps people resolve conflicts without resorting to manipulative or aggressive behavior. Training/Communi cation skill trainings.
Panic Disorder w/o Agoraphobia
Phobias begin early in life and are experienced as often by as men as by women. The two peak times for the onset are between ages 15-20 yrs and then again between 30-40 yrs.
Triggered by stress. Recurrent unexpected panic attacks At least one of the panic episodes has been followed by 1 month or more of: (a)Worry about the implications of the panic attack e.g losing control, going crazy.(b) significant changes in behavior related to attacks. (c) persistent concerns of having additional attacks.
Reassure client you will stay and panic attacks will subside. Loosen any tight clothing. Instruct and demonstrate deep, slow breathing. Decrease environmental stimuli and interactions with other people.
Individual/ group therapy: Individual: therapists helps client identify current life situations that set off anxiety. Group: Can lead to greater understanding and resolutions of important issues. Clients prepare themselves to focus on the present rather than the past. Cognitive behavioral therapy: (best option)
Anxiety agents: BusPar (buspirone): GAD, panic disorder, agoraphobia,PTSD MAOIs Phenelzine (Nardil) Social phobia, agoraphobia Tricyclic Antidepressant: Imipramine (Tofranil) GAD, agoraphobia SSIRs (first line of medication to treat panic disorders) Citalopram(Celexa)
Specific Phobia The client has a fear of specific objects, such as spiders, snakes, strangers. The client has a fear of specific experiences, such as flying, being in the dark, riding in an
Marked and persistent fear that is excessive or unreasonable, cue by the presence or anticipation of a specific object or situation. The person recognizes the fear
Avoid implying that symtoms are imaginary. Teach the use of positive energy such as sitting quietly on a beach. Teach calming techniques such as
Teaches practical thoughtmanagement techniques and prevention. Learn to cope with anxiety. Anger management. Alcohol or drug relapse prevention. Relaxation techniques Transcedetal meditation. Progressive muscle relaxation. Yoga. Exercise. Hobbies/arts/crafts. Prayer. Assertiveness Helps people resolve conflicts without resorting to manipulative or aggressive behavior. Training/Communi cation skill trainings. Individual/ group therapy: Individual: therapists helps client identify current life situations that set off anxiety. Group: Can lead to greater
Escitalopram(Lexap ro) Fluoxetine(Prozac) Fluvoxamine(Luvox ) Paroxetine(Paxil) Sertraline(Zoloft) Panic disorder, OCD,GAD, dysmorphic disorder, social phobia, PTSD
SSIRs (first line of medication to treat panic disorders) Citalopram(Celexa) Escitalopram(Lexap ro) Fluoxetine(Prozac) Fluvoxamine(Luvox ) Paroxetine(Paxil)
elevator, being in an enclosed space.
is excessive or unreasonable. Disabling. Nursing assessments: What are your greatest fears in life? What situations or objects do you try to avoid in your life? Are your social or work activities limited to a geographic area? How often and in what circumstances are you able to leave home?
muscle relaxation. Help them focus on relaxing specific muscle groups: while taking a deep breath through the nose, inhaling to the count of 5.
understanding and resolutions of important issues. Clients prepare themselves to focus on the present rather than the past. Cognitive behavioral therapy: (best option) Teaches practical thoughtmanagement techniques and prevention. Learn to cope with anxiety. Anger management. Alcohol or drug relapse prevention. Relaxation techniques Transcedetal meditation. Progressive muscle relaxation. Yoga. Exercise. Hobbies/arts/crafts. Prayer. Assertiveness Helps people resolve conflicts without resorting to manipulative or aggressive behavior. Training/Communi cation skill
Sertraline(Zoloft) Panic disorder, OCD,GAD, dysmorphic disorder, social phobia, PTSD MAOIs Phenelzine (Nardil) Social phobia, agoraphobia Tricyclic Antidepressant: Imipramine (Tofranil) GAD, agoraphobia
trainings. ObsessiveCompulsive Disorder OCD It is unclear, but usually people who have OCD start at a young age. Affects 3% of the population. Males develop this disorder at a younger age (6 to 15 yrs) than females (20-29yrs) 20% of individuals with OCD have hoarding convulsions. Women w/ OCD 90% are compuslvie cleaners. Men w/ OCD are compulsive checking. Genetics Obsessivecompulsive thoughts and behaviors dominate a persons life. Thoughts are just not about the real life problems. The person recognizes that the thoughts, impulses or images are a product of his own mind. Clients who engage in constant ritualistic behaviors may have difficulty meeting self-care needs, such as personal hygiene, grooming, nutrition, fluid intake, elimination, sleep. Nursing assessments: What kinds of things do you feel a need to check or recheck frequently? How much during Point out that time spent worrying often has no impact on actual outcomes. Identify situations that trigger worries such as interpersonal conflict or uncertainty at work. Individual/ group therapy: Individual: therapists helps client identify current life situations that set off anxiety. Group: Can lead to greater understanding and resolutions of important issues. Clients prepare themselves to focus on the present rather than the past. Cognitive behavioral therapy: (not effective for hoarding symptoms.) Teaches practical thoughtmanagement techniques and prevention. Learn to cope with anxiety. Anger management. Alcohol or drug relapse prevention. Relaxation techniques Transcedetal SSRIs: Reduces symptoms by increasing serotonin Fluoxetine (Prozac) Sertraline (Zoloft), Fluvoxamine (Luvox), Citalopram (Celexa), Paroxetine (Paxil). 70% to 80% respond to these medications. Riluzole (Rilutek) may be used if SSRIs do not work. Compulsive hoarding does not respond to any medication.
the day do you spend on checking activities? Describe any movements youre forced to repeat? What kind of things do you count outloud? How much time a day do you spend doubting what you have done? If rituals include constant handwashing or cleaning, skin damage and infection may occur. Post Traumatic Stress Disorder The onset of symptoms is delayed at least 3 months from the precipitating event, and onset may not occur until years afterward. the client witnesses or experiences an actual event that threatens severe injury or death to the client or others. The client responds with fear, helplessness, or horror to the event. Symptoms of increased arousal, such as irritability, difficulty with concentration, sleep disturbance Avoidance of stimuli associated with trauma, such as avoiding people, inability to show feelings A structured environment for physical safety and predictability Monitoring for, and protection from, self-harm Daily activities that encourage the client to share and be cooperative Use of therapeutic communication
meditation. Progressive muscle relaxation. Yoga. Exercise. Hobbies/arts/crafts. Prayer. Assertiveness Helps people resolve conflicts without resorting to manipulative or aggressive behavior. Training/Communi cation skill trainings.
Group and family therapy, for clients with PTSD.
Antidepressants: It improves sleep and suppress intrusive thoughts, jumpingness and explosive anger. Sertraline (Zoloft) Parozetine (Paxil) are only FDA approved for PTSD.
Duration is more than a month. Exaggerated startle response. Hyperalertness May resort to abusing alcohol or drugs Guilt is common with PTSD Distress when reminded of the event Dreams or images Reliving through flashbacks . Dissociative symptoms, such as amnesia of the trauma event, absent emotional response, decreased awareness of surroundings, depersonalization Symptoms of severe anxiety,
skills, such as openended questions, to help the client express feelings of anxiety, and to validate and acknowledge those feelings Client participation in decision making regarding care
Acute stress disorder
Symptoms occur within 4 weeks of the traumatic event. Symptoms last from 2 days to 4 weeks.
People who experience or witness an extreme traumatic stressor.
Provide a structured interview to keep the client focused on the present. Provide safety and comfort to the client during the crisis period of these disorders, as clients in severe- to panic-level anxiety are unable to problem solve and focus. Remain with the client during the worst of the anxiety to provide reassurance.
Antidepressants: It improves sleep and suppress intrusive thoughts, jumpingness and explosive anger. Sertraline (Zoloft) Parozetine (Paxil) are only FDA approved for PTSD.
such as irritability, sleep disturbance Standardized Screening Tools
Provide a safe environment for other clients and staff. Provide milieu therapy that employs the following: A structured environment for physical safety and predictability Monitoring for, and protection from, self-harm Daily activities that encourage the client to share and be cooperative Use of therapeutic communication skills, such as openended questions, to help the client express feelings of anxiety, and to validate and acknowledge those feelings Client participation in decision making regarding care
I Generalized Anxiety Disorder Generalized anxiety disorder is characterized by worry of long duration and without cause. Excessive anxiety for more days than not for at least six months about a number of events or activities Person finds it difficult to control the worry. The anxiety is associated with 3 or more of the following: restlessness, fatigue, difficulty concentrating, muscle tension, insomnia. Use relaxation techniques with the client as needed for symptoms of pain, muscle tension, and feelings of anxiety. n GAD, therapeutic goal of antianxiety agents is to limit the unpleasant symtoms to help the person return to a high level of functioning. Venlafacine (Effexor) (SNRI) Escitalopram (Lexapro) (Antidepressant) Have FDA approval for treatment of GAD Buspirone (BuSpar) is also used for non addictive and non CNS depressant. Takes time to take effect. Imioramine (Tofranil) ________________ Administer Alprozolam: drug of choice for agoraphobia.
________________ ________________ ________________ Social Phobia ________________ Fear of: Speaking in public Eating in public Using public bathrooms ________________ A marked and persistent fear of one or more social or performance cituations in which a person is exposed to unfamiliar people or Discuss feelings of fear. Listen to clients concern. Provide opportunity for questions and answers honestly.
________________ Support system enhacement Emotional Support Family integration promotion Security enhacement Support system enhacement Spiritual support
Making phone calls Writing in front of others Performing specific tasks in front of other.
to possible scrutiny by others. The individual fears that he may act in a way that will be humiliating or embarrassing. Exposure to feared situation results in anxiety/panic attack.
Agoraphobia: most common and serious phobic disorder. Triggered by severe stress. 20% to 45% of the general population has some mild form of phobic behavior. Actual phobic disorders occur in only 5% to 10% of the population Stress stimulated the hypothalamus. Stress increases glucose levels, ADH, prolactin and endorphins are increased. Blood preassure increases. Blood viscosity increases. Calcium resorption increases and leads to loss of bone mass. Mobilization of store energy results in loss of muscle.
Hamilton Rating Scale for Anxiety The Hamilton Anxiety Scale (HAMA) is a rating scale developed to quantify the severity of anxiety symptomatology, often used in psychotropic drug evaluation. It consists of 14 items, each defined by a series of symptoms. Each item is rated on a 5-point scale, ranging from 0 (not present) to 4 (severe)
Modified Speilberger State Anxiety Scale Scores range from 20 to 80, with higher scores correlating with greater anxiety
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Jim Keith - Mass ControlDocument212 paginiJim Keith - Mass ControlChronosGod93% (15)
- 966baf PDFDocument86 pagini966baf PDFkaw gd100% (2)
- Understanding Anxiety and Panic Attacks 2012Document20 paginiUnderstanding Anxiety and Panic Attacks 2012yemresimsekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Emotionally - Focused - Therapy - WikipediaDocument26 paginiEmotionally - Focused - Therapy - WikipediaBojan KlapčićÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cognitive RestructuringDocument2 paginiCognitive Restructuringapi-252192010Încă nu există evaluări
- Self Harm Work BookDocument78 paginiSelf Harm Work BookRyan PetersonÎncă nu există evaluări
- CBTDocument13 paginiCBTAmit TamboliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Relaxation Technique 1: Breathing Meditation For Stress ReliefDocument5 paginiRelaxation Technique 1: Breathing Meditation For Stress Relieflcom freeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Habits and AddictionsDocument37 paginiHabits and AddictionsBogdan DitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- AngerDocument17 paginiAngerAamir Faiz100% (1)
- 10 Best-Ever Anxiety-Management TechniquesDocument12 pagini10 Best-Ever Anxiety-Management TechniquesManuel HerreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control Your Emotion With Positive AffirmationDocument2 paginiControl Your Emotion With Positive AffirmationNhor Halil Quibel100% (1)
- AnxietyDocument48 paginiAnxietyGira HirparaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anxiety Disorder and Its TypesDocument32 paginiAnxiety Disorder and Its TypesWiwi Wulandani AbÎncă nu există evaluări
- Athletes Use of Exercise Imagery During Weight Training 2007Document6 paginiAthletes Use of Exercise Imagery During Weight Training 2007Carlos López NoriegaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Body Scan MindfulnessDocument3 paginiBody Scan MindfulnessLaura LouÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Techniques Are Used With CBTDocument13 paginiWhat Techniques Are Used With CBTZymarl Abigail Fernandez100% (1)
- Written Report On Mental Health PDFDocument7 paginiWritten Report On Mental Health PDFLovelene ChrizzeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psychopharmacology Basics and Beyond Tolisano 2019Document109 paginiPsychopharmacology Basics and Beyond Tolisano 2019Anil Kumar100% (1)
- Sensory Modulation in Acute Mental Health Wards PDFDocument64 paginiSensory Modulation in Acute Mental Health Wards PDFSoniaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Autism and OcdDocument8 paginiAutism and OcdTaha MohamedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Axis I Clinical Psychiatric Disorders - LMM-1Document11 paginiAxis I Clinical Psychiatric Disorders - LMM-1richhuangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mental Illness in Third World Countries - An Overview.Document20 paginiMental Illness in Third World Countries - An Overview.Cherif100% (1)
- Learning and Emotions PDFDocument2 paginiLearning and Emotions PDFdebanikgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Healthy MindDocument3 paginiHealthy MindKropok LekorÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Following Are Examples of A Couple of Communication Style ModelsDocument2 paginiThe Following Are Examples of A Couple of Communication Style ModelsyaenyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Supporting Patients Who Are BereavedDocument5 paginiSupporting Patients Who Are BereavedVictoria AlmeidaÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Overcome Fear and Anxiety: What Makes You Afraid?Document5 paginiHow To Overcome Fear and Anxiety: What Makes You Afraid?Boda Tanvi100% (1)
- Psychiatric Study GuideDocument18 paginiPsychiatric Study Guiderebeccacampbell100% (1)
- Tips For A Better Night of Sleep: in The MorningDocument5 paginiTips For A Better Night of Sleep: in The Morningphani BhushanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9.2 Panic Disorder: Etiology Biological FactorsDocument7 pagini9.2 Panic Disorder: Etiology Biological FactorsFayeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psychotherapy For Specific Phobia in Adults PDFDocument6 paginiPsychotherapy For Specific Phobia in Adults PDFdreamingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pubh 1005: Sleeps, Eats & Exercises Sleep Log Assignment Name: Date Complete in The MorningDocument3 paginiPubh 1005: Sleeps, Eats & Exercises Sleep Log Assignment Name: Date Complete in The Morningtpark101Încă nu există evaluări
- Anxiety-Control Strategies Is There Room For Neutralization in Successful Exposure TreatmentDocument46 paginiAnxiety-Control Strategies Is There Room For Neutralization in Successful Exposure TreatmentHAnaRoxanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mindful Breathing: Why Mindfulness Exercises?Document2 paginiMindful Breathing: Why Mindfulness Exercises?Alen RendakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mental Disorders WHO 2020Document6 paginiMental Disorders WHO 2020BeatrizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Selective Serotonin Reuptake InhibitorsDocument38 paginiSelective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitorsfaisalnadeem100% (1)
- Relaxation TechniquesDocument3 paginiRelaxation TechniquesKannanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bipolar Disorder: Download PDF Download Epub Order A Free Hardcopy en EspañolDocument50 paginiBipolar Disorder: Download PDF Download Epub Order A Free Hardcopy en EspañolMark Anthony Bueno AsuncionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sleeping Difficulties: Harrow Mental Health Information Directory FactsheetDocument4 paginiSleeping Difficulties: Harrow Mental Health Information Directory FactsheetjmaurpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Panic Attacks and Panic DisorderDocument5 paginiPanic Attacks and Panic DisorderBook ReaderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Notes On Cognitive Therapy PDFDocument3 paginiNotes On Cognitive Therapy PDFpsychonomyÎncă nu există evaluări
- PsychotherapyDocument47 paginiPsychotherapyanisha batraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Emotions and MoodsDocument22 paginiEmotions and MoodsAreej xÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument11 paginiDrug StudyHennah Reblando100% (3)
- Why Use Reflective Listening Skills HandoutDocument2 paginiWhy Use Reflective Listening Skills HandoutSSCÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mood DisorderDocument42 paginiMood DisorderAbdul Razak OthmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- DIALECTICAL BEHAVIOR THERAPY: Mastering DBT Skills for Emotional Resilience and Balanced Living (2024 Beginner Guide)De la EverandDIALECTICAL BEHAVIOR THERAPY: Mastering DBT Skills for Emotional Resilience and Balanced Living (2024 Beginner Guide)Încă nu există evaluări
- PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGYDocument2 paginiPSYCHOPHARMACOLOGYJulia Rae Delos SantosÎncă nu există evaluări
- AbPsych Unit 5 PPT ComerDocument72 paginiAbPsych Unit 5 PPT ComerGreg PoulinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Surg LT Oo For WNCNMDocument29 paginiSurg LT Oo For WNCNMSola SokeyeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder: OCD Was Classified As An Anxiety Disorder Due To The SometimesDocument23 paginiObsessive-Compulsive Disorder: OCD Was Classified As An Anxiety Disorder Due To The SometimesAlessandra Dominique MarianoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understanding Depression PowerPointDocument17 paginiUnderstanding Depression PowerPointNikko Edoloverio NaduaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Emotional SchemaDocument4 paginiEmotional Schemaerkankalem3783Încă nu există evaluări
- Meditation Therapy For Anxiety DisordersDocument23 paginiMeditation Therapy For Anxiety DisordersJosé AntônioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder in Children and Adolescents: Georgina Krebs, Isobel HeymanDocument5 paginiObsessive-Compulsive Disorder in Children and Adolescents: Georgina Krebs, Isobel HeymanRidwan AdiansyahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anger Management Intro and ObjectivesDocument3 paginiAnger Management Intro and ObjectivesAllyson DraytonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Teaching The Turtle Technique 5Document2 paginiTeaching The Turtle Technique 5api-327377615Încă nu există evaluări
- Guided Imagery and Recovered Memory Therapy - Considerations and Cautions 2006Document12 paginiGuided Imagery and Recovered Memory Therapy - Considerations and Cautions 2006Hashem Al-attasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anger and Its Elimination Part IDocument4 paginiAnger and Its Elimination Part IAtman NityanandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Therapeutic Hotline Treatment of Prurigo Nodularis and Lichen Simplex Chronicus With GabapentinDocument6 paginiTherapeutic Hotline Treatment of Prurigo Nodularis and Lichen Simplex Chronicus With Gabapentinwilliam28asshole100% (1)
- A Neuroscience Model of Compassion - Stephanie BrownDocument17 paginiA Neuroscience Model of Compassion - Stephanie BrownccareemailÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neurotransmitters AVDocument5 paginiNeurotransmitters AVDr. Hashibu SsekweyamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- About This Article: Basics of Pain ControlDocument22 paginiAbout This Article: Basics of Pain ControlJailan IbrahimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmacotherapy For Generalized Anxiety Disorder in Adults - UpToDate V eDocument14 paginiPharmacotherapy For Generalized Anxiety Disorder in Adults - UpToDate V eMonique GloverÎncă nu există evaluări
- Meditation Report 140106Document439 paginiMeditation Report 140106Laurynas Bambalas100% (1)
- Tusita Hermitage Meditation HandbookDocument44 paginiTusita Hermitage Meditation HandbookJames BankÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Role For Mindfulness Meditation in The Treatment of Sexual Addictions Kishore ChandiramaniDocument10 paginiA Role For Mindfulness Meditation in The Treatment of Sexual Addictions Kishore ChandiramaniMeek ElÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coping With PTSD Trauma1704206530Document4 paginiCoping With PTSD Trauma1704206530phani BhushanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Content - 73 - 351 - Side Effects of Antidepressants An OverviewDocument9 paginiContent - 73 - 351 - Side Effects of Antidepressants An OverviewAbraham TheodoreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maladaptive DaydreamingDocument2 paginiMaladaptive DaydreamingSaumya SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Concept Map For Paranoid SchizzopreniaDocument4 paginiConcept Map For Paranoid SchizzopreniaJu Lie AnnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Best 5-HTP Supplements of 2020: RatingDocument22 paginiBest 5-HTP Supplements of 2020: RatingTanjil TafsirÎncă nu există evaluări
- ptj3012740 PDFDocument8 paginiptj3012740 PDFAnand VibhutiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Autism 2Document15 paginiAutism 2Pakde Putu HadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compulsive Masturbation Treated With Fluvoxamine-A Case StudyDocument3 paginiCompulsive Masturbation Treated With Fluvoxamine-A Case StudyNisha SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Social Anxiety DisorderDocument6 paginiSocial Anxiety DisorderbrokentoeÎncă nu există evaluări
- PracticeTestFullPrep by MagooshDocument41 paginiPracticeTestFullPrep by MagooshNahid MirzazadeÎncă nu există evaluări
- My Anxiety, Its Symptoms, Diagnosis and TreamentDocument7 paginiMy Anxiety, Its Symptoms, Diagnosis and TreamentKhawar Jamil RizviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study FluvoxamineDocument2 paginiDrug Study FluvoxamineAngeline de Gala0% (1)
- Ann Blake SSRI DepressionDocument17 paginiAnn Blake SSRI Depressionthings3100% (1)
- Depression OutlineDocument8 paginiDepression OutlineErica93% (15)
- Maladaptive Patterns of Behavior A. AnxietyDocument19 paginiMaladaptive Patterns of Behavior A. AnxietyTeal OtterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bokor 2014Document15 paginiBokor 2014RavennaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psychiatric RationaleDocument13 paginiPsychiatric RationaleJohn Derama SagapsapanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cannabis 051815Document31 paginiCannabis 051815Shubhrima KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psych ReportDocument80 paginiPsych ReportPaul Carlo GonzalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- NP5 Sample QuestionsDocument7 paginiNP5 Sample QuestionsIvan LouiseÎncă nu există evaluări
- PsychopharmacologyDocument1 paginăPsychopharmacologypayumoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ejercicios Verbal GREDocument23 paginiEjercicios Verbal GREElena LostaunauÎncă nu există evaluări