Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
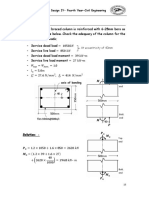
Calculation of Beam Deflection
Încărcat de
api-3848892Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Calculation of Beam Deflection
Încărcat de
api-3848892Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
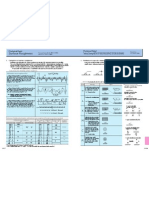
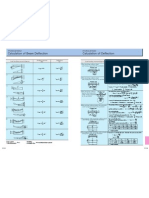
〔Technical Data〕 〔Technical Data〕
Calculation of Beam Deflection Calculation of Deflection
Bending moment Deflection
Load bending moment diagram Load bending moment diagram Maximum stress, Maximum deflection
(M) (δ)
1 r
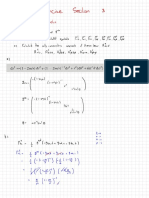
1.Disk receiving uniform load The circumferential stress σt and radial σr can be expressed as follows at the center.
W
and having supported the perimeter ( ) 2
(σt)max.=(σr)max.=± 3P 3m+12 R
δmax.
3 8mt
R
W P
(Uniform load)
R
M max.=W δmax.= Also, the central deflection δmax. can be expressed as follows:
3EI
t
3(m−1)(5m+1)
r
W δmax.= PR 4
M δmax.
(Deflection) 16Em2 t 3
R
Wherein, P:Load,R:Radius of plate,t:Plate thickness,
2 r
(Radius)
E:Young's modulus,
1
:Poisson's ratio
m
w
2.Disk receiving uniform load
The peripheral stress can be expressed as follows:
δ w
R2 w
R4 3PR2 3PR2
M max.= δmax.= and having been fixed to the perimeter σt=±
4mt 2
(σr)max.=±
4t 2
2 8EI
1 w and the central one is as follows: 3(m+1)PR
r 2 P
(Uniform load) (σt)max.=σr=±
M 2 8mt 2
The central deflectionδmax. can be expressed as follows:
t
3(m 2−l)PR 4
δmax.=
3 W δmax.
(Deflection)
16Em 2 t3
R R Wherein, P:Load,R:Radius of plate,t:Plate thickness,
δ
r
(Radius) 1
1 R
W 3 E:Young's modulus, :Poisson's ratio
m
M max.= R
W δmax.=
4 48 EI 3.Disk receiving uniform P
(Uniform load)
The central stress can be expressed as follows:
3(m+1)P R m−1 r 02
load on the concentric
1 m
M r
4 W
2r 0 p (σt)max.=(σr)max.=± +log −
2πmt 2 m+1 r 0 m+1 4R2
t
circle having supported
When the central deflection r0 is smaller than R,
to the perimeter
δmax.
R R
4 W
δmax. is expressed as follows:
3(m−1)(3m+1)PR 2
Uniform load δmax.= 2t3
δ
4πEm
2R
0
r
R3 Wherein, P:Total ただしP…同心円上の総荷重でP=π
load on the concentric circle. r 02p
2r
1 W
M max.= R
W δmax.= 1
8 192 EI R:Radius of plate, t:Plate thickness, E:Young's modulus, :Poisson's ratio
1 m
r
8 W
1 The peripheral stress can be expressed as follows:
4.Disk receiving uniform load on the concentric
M
r
8 W
3P r 0 2 σr=± 3P 1− r 0 2
circle having been fixed to the perimeter
σt =± 1− 2
2πmt 2 2R 2πt 2 2R2
5
and the central one is as follows: σt =σr=±3 m+1 2P log R + r 02
P
(Uniform load) ( ) 2
w 2πmt r 0 4R
δ 2r 0
p
1 5 wR 4 The central deflection
t
r
3(m−1)(7m+3)PR2
M max.= w
R2 δmax.= δmax. can be expressed as follows: δmax.≒
8 384EI δmax.
16πEm 2 t 3
M 1
wr 2 R R Wherein, P:Total ただしP…同心円上の総荷重でP=π
load on the concentric circle. r 02p
8
(Radius) 1
R…Radius of plate, t…Plate thickness, E…Young's modulus …Poisson's ratio
m
6 5.Rectangular plate receiving uniform load The X-axis direction stress Pb2
and having supported the perimeter (σx)
at center O can be expressed as follows: max.=α 1 2
t
w
δ P
(Uniform load) The deflection
1 wR 4 Pb4
t
r
M max.= w
R2 δmax.= at the center O can be expressed as follows:δmax.=β1 Et 3
12 384 EI X
a/b 1.0 1.5 2.0 3.0 4.0 ∞
1
12
wr 2
O α1 1.150 1.950 2.440 2.850 2.960 3.000
2b
M 1
wr 2 Y
24
β1 0.709 1.350 1.770 2.140 2.240 2.280
7 2a E:Young's modulus
w
δ 6.Rectangular plate receiving uniform load and The stress to X-axis direction at the center A of the longer side can be expressed as follows:
r
M max.=
1
w
R2 δmax.=
w
R4 having been fixed to the perimeter Pb2
8 184.6EI P
(Uniform load) (σx)max.=α2
t2
1
wr 2
Pb4
8 δmax.=β2 2
9 X Et
M
128 r
w 2 A
a/b 1.0
1.5 2.0 ∞
O
2b
Y α2 1.231 1.817 1.990 2.000
Young's modulus σ ε=Deflection A
E= ε I=Cross-sectional secondary moment β2 0.221 0.384 0.443 0.454
(Vertical elastic modulus) σ=Rectangular stress
2a E:Young's modulus
1113 1114
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Calculate Moment of Inertia For Various SectionsDocument12 paginiCalculate Moment of Inertia For Various SectionsscranderiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Beam Design Formulas With Shear and MomentDocument20 paginiBeam Design Formulas With Shear and MomentMuhammad Saqib Abrar100% (8)
- Critical Thinking Skills Success in 20 Minutes A Day - Lauren StarkeyDocument182 paginiCritical Thinking Skills Success in 20 Minutes A Day - Lauren StarkeyAustin Higgins97% (61)
- PLC Basic Programme BookDocument45 paginiPLC Basic Programme Bookapi-384889275% (4)
- Retaining Wall Design Example RevisedDocument8 paginiRetaining Wall Design Example Revisedmadhes4ever100% (1)
- Example 1.1: Reinforced Concrete Design IV-Fourth Year-Civil EngineeringDocument12 paginiExample 1.1: Reinforced Concrete Design IV-Fourth Year-Civil EngineeringAhmed NasratÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 6 ConnectionDocument30 paginiChapter 6 ConnectionIvy SeahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Indice Norma: Menú Principal Indice Manual Indice VolumenDocument1 paginăIndice Norma: Menú Principal Indice Manual Indice Volumencmrn5Încă nu există evaluări
- Shear Force and Bending MomentDocument4 paginiShear Force and Bending MomentTariq HasanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Girder-Slab System Design Guide v2.0 PDFDocument20 paginiGirder-Slab System Design Guide v2.0 PDFManoj GehlodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shear and Bending MomentDocument29 paginiShear and Bending MomentLyka NaboaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Surface Roughness by Different Processing MethodsDocument1 paginăSurface Roughness by Different Processing Methodsapi-3848892100% (1)
- Surface Roughness by Different Processing MethodsDocument1 paginăSurface Roughness by Different Processing Methodsapi-3848892100% (1)
- Beam CalculationDocument43 paginiBeam CalculationjonlosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Switchgear Inspection Checklist: Section A - Customer DataDocument1 paginăSwitchgear Inspection Checklist: Section A - Customer Data20082012Încă nu există evaluări
- Bearing Capacity of Connected Parts With Slotted HolesDocument50 paginiBearing Capacity of Connected Parts With Slotted Holesaomareltayeb100% (1)
- Geopolymer Chemistry and ApplicationsDocument38 paginiGeopolymer Chemistry and Applicationsanon_203503169Încă nu există evaluări
- Standard PadeyesDocument82 paginiStandard PadeyesSeymur AkbarovÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shear StrengthDocument56 paginiShear StrengthSamuel ChristianÎncă nu există evaluări
- PTX R 410A Series NewDocument112 paginiPTX R 410A Series NewMohamed Fathi33% (15)
- Lecture Three - Welded ConnectionsDocument30 paginiLecture Three - Welded ConnectionsAhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solid Works Drawing and DetailingDocument69 paginiSolid Works Drawing and Detailingapi-3848892100% (1)
- 1-Piping Manual-Pdms12Document413 pagini1-Piping Manual-Pdms12MOHSEN2005IBÎncă nu există evaluări
- Australian Castolin Eutectic: Flame Spray Equipment and PowdersDocument18 paginiAustralian Castolin Eutectic: Flame Spray Equipment and PowdersАлмаз КенжетаевÎncă nu există evaluări
- Env 1996-1-1-1996Document129 paginiEnv 1996-1-1-1996nvh202148Încă nu există evaluări
- Pile FoundationDocument17 paginiPile Foundationritam1991Încă nu există evaluări
- Service Handleiding Hisense LC VloermodelDocument204 paginiService Handleiding Hisense LC VloermodelMichel ZreikÎncă nu există evaluări
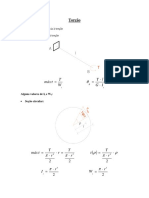
- Torsion 03 PDFDocument17 paginiTorsion 03 PDFAnonymous yyjpEsydasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Surface RoughnessDocument1 paginăSurface Roughnessapi-3848892100% (2)
- Surface RoughnessDocument1 paginăSurface Roughnessapi-3848892100% (2)
- Surface RoughnessDocument1 paginăSurface Roughnessapi-3848892100% (2)
- Socket Head Cap ScrewsDocument1 paginăSocket Head Cap Screwsapi-3848892100% (5)
- Socket Head Cap ScrewsDocument1 paginăSocket Head Cap Screwsapi-3848892100% (5)
- Design ProblemsDocument30 paginiDesign ProblemsNelson Naval Cabingas67% (3)
- Connections-Bolted 1Document46 paginiConnections-Bolted 1sachin.meenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Column DesignDocument32 paginiColumn DesignBaskar KannaiahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shape Factor For Various Sections I - T - CDocument2 paginiShape Factor For Various Sections I - T - CTapabrata2013Încă nu există evaluări
- Structural SteelDocument4 paginiStructural SteelSyed IrfanuddinÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 1 (Compression Members)Document30 pagini5 1 (Compression Members)yugoingÎncă nu există evaluări
- W Flange Beams and Allowable Uniform LoadDocument2 paginiW Flange Beams and Allowable Uniform LoadHorace Prophetic DavisÎncă nu există evaluări
- FLRPLATEDocument3 paginiFLRPLATEcravikumar1971Încă nu există evaluări
- Second Moment of AreaDocument9 paginiSecond Moment of AreaPham Cao ThanhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Corbel DesignDocument12 paginiCorbel DesignprsscribdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shear Force and Bending Moment Diagrams PDFDocument18 paginiShear Force and Bending Moment Diagrams PDFCholan PillaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Weld PDFDocument7 paginiWeld PDFGÎncă nu există evaluări
- Formula Sheet EE-434 Power Electronics: Basic Expressions CapacitorDocument3 paginiFormula Sheet EE-434 Power Electronics: Basic Expressions CapacitorMuhammad Muzammil SaleemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simple Torsion in Beams at Circle Cross-Section and PipesDocument7 paginiSimple Torsion in Beams at Circle Cross-Section and Pipeshamza2085Încă nu există evaluări
- Mechanics of Materials II:: Thin-Walled Pressure Vessels and TorsionDocument6 paginiMechanics of Materials II:: Thin-Walled Pressure Vessels and TorsionWolf LordÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engineering Design II: Shafts - AnalysisDocument56 paginiEngineering Design II: Shafts - AnalysisSean ChanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pie-Pipette: C., (T) Foram - 2:::: - RHR 1/FDocument12 paginiPie-Pipette: C., (T) Foram - 2:::: - RHR 1/FSuchit GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- LawsDocument2 paginiLawsMohamed AbdallahÎncă nu există evaluări
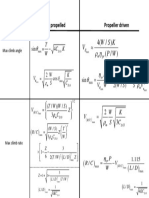
- WSK V PW: Propeller Driven Jet PropelledDocument1 paginăWSK V PW: Propeller Driven Jet Propelleddeep865Încă nu există evaluări
- Reinforcement Design Summery Report For 1 Floor Slab Panels: em en TDocument3 paginiReinforcement Design Summery Report For 1 Floor Slab Panels: em en TKrishnasamy SanjeevanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Moment of Momentum: Inertial Control VolumeDocument6 paginiMoment of Momentum: Inertial Control VolumeEmily ShumÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Logarithmic Mean Is A MeanDocument5 paginiThe Logarithmic Mean Is A MeanluishippÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2014 2015 Midterm2Document5 pagini2014 2015 Midterm2elif sÎncă nu există evaluări
- Torção: W T Máx I G L TDocument5 paginiTorção: W T Máx I G L Tjcunha4740Încă nu există evaluări
- Wang 120.00Document10 paginiWang 120.00shachen2014Încă nu există evaluări
- Various Problems III Physics CircleDocument7 paginiVarious Problems III Physics CircleRafael FerreiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanical Design 1.2Document135 paginiMechanical Design 1.2dapp_706085Încă nu există evaluări
- Tarea 3.1Document3 paginiTarea 3.1maria pazÎncă nu există evaluări
- TorsionDocument11 paginiTorsionAakash DagarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solutions MIDocument6 paginiSolutions MIsalithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture - 08 Shaft IDocument23 paginiLecture - 08 Shaft Iwkho0007Încă nu există evaluări
- Class: GraphsDocument28 paginiClass: GraphsAlifiyah HussainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Applications of Multiple IntegralsDocument3 paginiApplications of Multiple IntegralsJaneP18Încă nu există evaluări
- Theory: English (Official)Document4 paginiTheory: English (Official)Bentley CarrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Homework Assignment (Introduction - Basic Units and Viscosity)Document11 paginiHomework Assignment (Introduction - Basic Units and Viscosity)MallikarjunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atmospheric Gravity WavesDocument20 paginiAtmospheric Gravity WavesHenry Zegarra RodriguezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adobe Scan Jul 24, 2023Document1 paginăAdobe Scan Jul 24, 2023Zaid AnsariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Handouts 2 Bending StressDocument7 paginiHandouts 2 Bending Stresssureyya.yusifovaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson No. 7 in Machine Design 1Document5 paginiLesson No. 7 in Machine Design 1Carl JavierÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tut 13Document11 paginiTut 13Onur YalçınkayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spek Alat Ti 15 (Zyb420)Document7 paginiSpek Alat Ti 15 (Zyb420)yusuf ofanantaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Beam Diagrams FormulasDocument18 paginiBeam Diagrams FormulasMiss MichiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of Beam I. Design Criteria: Total, WDocument33 paginiDesign of Beam I. Design Criteria: Total, WAJ DE CASTROÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technology LevelsDocument23 paginiTechnology LevelsAshline DsouzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exercises Section 3orlisDocument3 paginiExercises Section 3orlisDANIEL ESTEBAN GONZALEZ TAMAYOÎncă nu există evaluări
- โครงสร้างที่รับแรงบิดDocument46 paginiโครงสร้างที่รับแรงบิดMhee UtdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Table of Diameter of Screw Low Hole (Low Anchor)Document1 paginăTable of Diameter of Screw Low Hole (Low Anchor)api-3848892Încă nu există evaluări
- Greek Symblos-Atomic SymbolsDocument1 paginăGreek Symblos-Atomic Symbolsapi-3848892Încă nu există evaluări
- SI (System International D Unit's)Document1 paginăSI (System International D Unit's)api-3848892100% (1)
- Fit Selection BasicDocument1 paginăFit Selection Basicapi-3848892100% (2)
- Claculation of Area, Center of Gravity and Sectional Secondary MomentDocument1 paginăClaculation of Area, Center of Gravity and Sectional Secondary Momentapi-3848892Încă nu există evaluări
- Greek Symblos-Atomic SymbolsDocument1 paginăGreek Symblos-Atomic Symbolsapi-3848892Încă nu există evaluări
- Examples of Applicable Steels For Typical ProductsDocument1 paginăExamples of Applicable Steels For Typical Productsapi-3848892Încă nu există evaluări
- Calculation of Beam DeflectionDocument1 paginăCalculation of Beam Deflectionapi-3848892100% (2)
- Conversion Table of HardnessDocument1 paginăConversion Table of Hardnessapi-3848892100% (2)
- Solidworks Tutorial 07nov06Document13 paginiSolidworks Tutorial 07nov06Robin SanjayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prepare For IELTSDocument170 paginiPrepare For IELTSevilinside_me96% (23)
- Mastercam Tutorial Surface ModelingDocument4 paginiMastercam Tutorial Surface Modelingapi-3848892100% (1)
- Cosmos SWDocument52 paginiCosmos SWRicardo Vargas GraciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- English TestDocument23 paginiEnglish Testapi-3848892100% (1)
- Solid Works AssemblyDocument46 paginiSolid Works Assemblyapi-3848892Încă nu există evaluări
- Sach Hoc Tieng AnhDocument269 paginiSach Hoc Tieng Anhapi-26623512100% (1)
- Ug Nx3 TutorialDocument235 paginiUg Nx3 TutorialAJAYKRISHNAA92% (13)
- English Test 2Document26 paginiEnglish Test 2api-3848892Încă nu există evaluări
- SI (System International D Unit's)Document1 paginăSI (System International D Unit's)api-3848892100% (1)
- Cl80 Inrow Cooler: Data SheetDocument2 paginiCl80 Inrow Cooler: Data SheetRavi ShankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- NDT PDFDocument4 paginiNDT PDFBHARANIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kelken US Metric Chart ASTM F1554 Grade 55Document1 paginăKelken US Metric Chart ASTM F1554 Grade 55muathÎncă nu există evaluări
- Midas Civil - Integral Bridge SupportsDocument7 paginiMidas Civil - Integral Bridge SupportsVũ Cao AnhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment01 PPT57Document15 paginiAssignment01 PPT57Usman AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- P.W.D Electrical SR 10-11Document60 paginiP.W.D Electrical SR 10-11uday.sachin PandithÎncă nu există evaluări
- PLA PBS Pbat: According To Established Standards & Certification SchemesDocument1 paginăPLA PBS Pbat: According To Established Standards & Certification SchemesPonglert ChanthornÎncă nu există evaluări
- INST. INST. 844-TZ For Item 40Document4 paginiINST. INST. 844-TZ For Item 40Zubab Panni100% (1)
- (PPT) Drawing 1Document29 pagini(PPT) Drawing 1AXELÎncă nu există evaluări
- Republic of The Philippines Architectural General NotesDocument1 paginăRepublic of The Philippines Architectural General NotesRosario Dela CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guidance Note Installation of Preloaded Bolts No. 7.05: ScopeDocument6 paginiGuidance Note Installation of Preloaded Bolts No. 7.05: ScopeAli ZarkaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manual Instalación Multiclin PremiumDocument70 paginiManual Instalación Multiclin PremiumnoeliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Artigo 2015 OSBDocument12 paginiArtigo 2015 OSBVania SaÎncă nu există evaluări
- BIRCOsir en 03 2017Document58 paginiBIRCOsir en 03 2017raghebomÎncă nu există evaluări
- AS 1379 - 1997 - Specification and Supply of ConcreteDocument38 paginiAS 1379 - 1997 - Specification and Supply of Concretekevin kurnia marpaungÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 Elastic Modulus and Strength of Hollow Concrete Block Masonry With Refrence To The Effect of Lateral TiesDocument10 pagini4 Elastic Modulus and Strength of Hollow Concrete Block Masonry With Refrence To The Effect of Lateral Tiessunil reddy0% (1)
- An Overview of Dual-Phase SteelsDocument43 paginiAn Overview of Dual-Phase SteelsLaura RodriguezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Loft Above Counter Sink Less Faucet Hole 0552.000Document1 paginăLoft Above Counter Sink Less Faucet Hole 0552.000Ruffa OzaetaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Material ScienceDocument810 paginiMaterial ScienceNikhil Batham67% (3)
- UNS S41000 (Type SS 410) : SS 304 Bonded To 3mm Non-Conductive Grey EPDM WasherDocument1 paginăUNS S41000 (Type SS 410) : SS 304 Bonded To 3mm Non-Conductive Grey EPDM WasherrimshadtpÎncă nu există evaluări