Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Grammar
Încărcat de
Kang SlametDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Grammar
Încărcat de
Kang SlametDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
GRAMMAR
Adjectives What are adjectives? Adjectives are word that are used to clarify a noun. Adjectives can me one word or a group of words. Adjectives are sometimes used with certain verbs (such as the verb "to be"). Adjectives are used to clarify the subject that is doing the action. Adjectives are used to describe color, material, shape, size, amount, price, quality, origin, personality, weight, temperature, weight, age, direction, etc.
Adjectives usage
Adjectives are placed before the noun. Adjectives can be used with all forms of nouns (see nouns).
Examples: Adjectives with nouns:
My teacher is really nice. I was teaching in a really big high school, while I was going working on my master's degree. The university that my oldest brother is going to is really nice. The English teacher gave us a hard project.
Adjective with verbs:
The teacher is tall and thin. Our professor is a really nice man. Adjectives With Verbs
How are adjectives used with verbs? There are times when an adjective is placed after the verb. This is more common when the verb being used is a "linking verb". In this case it is common that an adjective is used with with the "linking verb", but the adjective doesn't describe the verb. The adjective descrives the subject that is performing the action. Adjectives are not used to describe the verb. Examples:
The cake looks good. Your hair looks great. Where did you get your hair cut. My mother lost her keys. The boys play ball all the time.
When using a adjectives and verb together, the adjectives comes after the verb. There are times when one adjective is not enough to describe the noun or the subject that is performing the action. When 2 or more adjectives are used together then there is a specific order of the adjectives that is usually followed. Please see multiple adjectives. It is importatnt is understand if an adjective is need or if a adverb is needed. There is an easy way to tell. Do I need to define the verb of the sentnece or do I need to define the subject that is performing the action. Example:
Your hair grew slowly. The dog grew angry. The boys talk loudly. My brother talks big. Adjectives Order
The order of more then 2 adjectives in a sentence.
1.
2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7.
In most cases the adjective is placed before the noun. There is an order that is used when using more then 2 adjectives together. The order in some cases can be changed, but it is a good guidlines for ESL and EFL students that are learning English. It is not common to used more then 3 adjectives together, but it is possible and can be grammatically correct. When there are 2 or more adjectives that are from the same group* "and" is placed between the 2 adjectives. When there are 3 or more adjectives from the same adjective group, then a comma is placed between the are from the same group.*. A comma is not placed between an adjective and a noun. When an article is used such as "a", "an" or "the" the articles are placed before the adverb. The article must agree with the noun grammatically. The adjectives must agree with the noun grammatically.
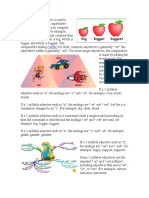
*The 9 different adjective groups are listed below. The order of the adjectives is as followed: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Determiner - a, an, her, five, many, much several etc. Opinion - pretty, ugly, smart, cheap, etc. Size - big, fat, thin, tall, large, small etc. Shape - circle, square, tall, short etc. Age - old, young 10 years, a year, a week, new etc. Color - yellow, green, pink etc. Origin - American, English, Asian, Middle Eastern, African, European, Chinese etc. Material - cotton, wood, plastic, cloth, glass, gold etc. Purpose/Qualifier hat box, sleeping bag, computer table,safe island, football field. (The words in green are the purpose/qualifer words.)
Examples: 1. 2. 3. 4. The big black dog ate my food. I like that pretty green sofa. I want to go to a big, quit, safe. We sleep in a small, pink and green room. Adjectives with Nouns It is very common to use adjectives with nouns. Adjectives are used to describe the noun. There are different groups of adjectives: Option - this group of adjectives are used to describe an option of someone or something. It is not a fact. It can't be proven to be correct or incorrect. Examples:
I think that the store is great. We like good books. The girls like children's programs on the T.V.
Facts - this group of adjectives are used to describe. Comparative Adjectives
What are comparative adjectives? Comparative adjectives are used to clerify the difference between 2 objects/nouns. .
Comparative adjectives are used to compare 2 nouns. To state that one noun has more of something then the 2nd noun.
Note: Superlative adjectives are used to compare 3 or more nouns. Examples:
The black dog is older than the white dog. My house is bigger than my sister's house. The yellow hat is more expansive than the green hat.
The Rules for using Comparative Adjectives How to Use Comparative Adjectives "Than" is usually usually used after the comparative adjective. How to Use Comparative Adjectives "Than" is usually usually used after the comparative adjective.
-er is added to the end of a 1-syllable adjective
cold colder small smaller
The winter is colder than the summer. The green hat is smaller than the yellow hat. Most basketball players are taller than me.
tall - taller
-er is added to the end of an adjective with 2 syllables, if the word ends in -y.
early earlier happy happier
I came home earlier than my sister. I am happier now than 1 year ago. My friend is crazier than me.
crazy crazier
"more" is used for words that have 2 syllables, if the word doesn't end in -y. adjectives that end in -y, change the -y to i and add -ed "more" is used for words that have 3 or more syllables
honest more honest difficultmore difficult modern more modern
The policeman are more honest than criminals. The last test was more difficult than the test today. Our generation is more modern, than our parents generation
expensive - more expensive difficult more difficult
comfortabl
e - more comfortable adjectives that end in -e, only -r is added to end of the adjective adjective that end in a consonant, vowel, consonant the last consonant is doubled
nice -nicer safe -safer big -bigger fat- fatter hot -hotter
My house is bigger than, my sisters house. My sister is fatter than me. The summer is hotter than the winter.
The Structure of Comparative Adjectives The structure of a comparative usually consists of the root of the adjective root of the adjective plus the suffix -est or "more" or "less" is added before the adjective in it's root form. The amount of syllables the adjectives contain determents if -er is added to the end of the adjective or if "more" or "less" is added before the adjective. Note: "Than" is usually usually used after the comparative adjective. Short words - words with 1 syllable or words with 2 syllables if the word ends in -y. -er is added to the end of the word. Notes: Adjectives ending in -y; change the -y to -i and add -er. Adjectives that end with a consonant, vowel, consonant - the last consonant is doubled and -er is added to the end of the adjective.
Examples
cold - colder small - smaller tall - taller
early - earlier happy - happier crazy - crazier
big -bigger fat- fatter hot -hotter
Long words - words with 3 more syllables, and words with 2 syllables that don't end in -y. The word "more" is placed before the adjective. Note: Adjectives that end in -e, only -r is added to end of the adjective. Examples
Examples honest - more honest difficult- more difficult modern - more modern Superlative Adjective
expensive - more expensive difficult - more difficult comfortable - more comfortable
What are superlative adjectives?
Superlative adjectives are used to define the highest degree of a noun. Superlative adjectives are used only if 3 or more things or people are being compared. Examples:
The black dog is the biggest. The house at the end of the street is the nicest. My mother's pizza is the best. Superlative Adjective Structure
The structure of a superlative usually consists of the root of the adjective root of the adjective plus the suffix -est or "most" or "least" is added before the adjective in it's root form. The amount of syllables the adjectives contain determines if -est is added to the end of the adjective or if "most" or "least" is added before the adjective. The chart below is a guide to help you understand the correct structure of superlative adjectives. English Superlative Adjectives Rules -est is added to the end of an adjective 1syllable word Change the y to an -i.and add -est to the end of an adjective with 2 syllables, if the word ends in -y. "most" or "least" are used for adjectives that consist of two syllables, if the word doesn't end in -y. adjectives that end in -y, change the -y to i and add -ed "most" and "least" are used for adjectives that contain 3 or more syllables If an adjectives that ends in -e, then only -r is added to end of the adjective.
cold - coldest small - smallest tall - tallest
early - earliest happy - happiest crazy - craziest
This winter is the coldest, that I can remember. The green hat is the smallest hat in the store. I am the tallest, in my class Today is the earliest that I came home all week. She is the happiest, I have been seen her. I have the craziest dog, I have ever seen.
honest - most honest difficult- most difficult
The policeman are the most honest people that I know. The last test was the most difficult. Our generation is the most modern.
modern - more modern
expensive - most expensive difficult - most difficult
That is the most expensive dress in the store. This problem is the most difficult, that I have had to solve in my life. These shoes are the most comfortable.
comfortable most comfortable
nice -nicest safe -safest
Your family is the nicest that I have ever met. This car is the safest on the market.
Adjective that end in a consonant, vowel, consonant - the last consonant is doubled and -est is added to the end of the adjective.
big -biggest fat- fattest hot -hottest
My house is the biggest on the block. My sister is the fattest in the school. The summer is the hottest time of the year.
Adverbs What are adverbs? An adverb is a word or a group of words that are used to help define the action of the verb. Adverbs can also be used to define adjectives, or other adverbs. How to tell if a word is an adverb? A word is an adverb if it answers one of the three questions, when, where or how. Examples:
Examples of English Adverbs that state when, where and how When Where How
I have to study today.
I like to read under the trees in the park.
I should exercise carefully.
My mother always listens to Our teacher rarely gives us a lot of the radio. worksheets to do.
My brother study very hard for all his exams.
Our teacher is really good this year.
We learned to play the piano quickly. We had a really good teacher.
The students and teachers work closely on the proje
English Adverbs In most cases adverbs are created by added -ly to the end of an adjective. Some common adverbs are quietly, quickly, beautifully etc. Spelling rules of adverbs: Adjectives that end in y - change the -i to -y as easy-easily, happy-happily
1. 2.
Adjectives ending -y change to -ily; lucky-luckily Adjectives ending -ble only -y is added; present -presentably, respectable -respectably Frequency Adverbs
What are frequency adverbs? Frequency adverbs are adverbs that state how often something happens or someone does something. What is the grammatical structure frequency adverbs? In geranal requencey adverbs are used just like any other adverb. They come before the main verb, except if the main verb is the verb "to be" then adverbs comes after the verb. Below is a chart a frequency adverbs, the numbers after the adverbs will give you an idea of the how often an event would take place. Frequency Adverbs Always nearly/almost always Usually Very Often/Frequently Often Sometimes Occasionally Almost never/ever Seldom/Almost never Never 90% 80% 70% 60% 50% 40% 20% 10% 0%
Positive and Negative Sentences without the verb "to be". Frequency adverbs are used in positive sentences and negative sentences. The frequency adverbs are placed after the main verb (if the main verb is not the verb "to be). Examples:
I always walk to school My cats sometimes like to play Our teacher almost never gives us a lot of homework. The teacher doesn't always come on time. My cats don't always like to play with my socks. I don't often walk to school.
Positive and Negative Sentence with the verb "to be" Frequency Adverbs are used in positive sentences and negative sentences. The frequency adverb is placed before the main verb if the main verb is the Verb "to be".
The teacher is always on time. My sister is never lazy. Our house is sometimes a mess. My brother's house is never a mess. The sofa is always fun to sit on.
Questions without the verb "to be" as the main verb When questions use the verb "to be" as the main verb the frequency adverb is placed after the subject.
Does she always walk to work? Why does the oven always stop working after 10 minutes? Do you always clean the sofa every day?
Questions with the verb "to be" as the main verb. In question when the main verb is the verb "to be" the frequency adverb is placed after the subject.
Is the food always so bad? Are your children ever late for school? Are the clocks always broken?
Frequency Adverb Chart Usage of Frequency Adverbs: Positive Sentences With Frequency Adverb Subject I We My cats She He They Auxiliary Verb (if need) has has will Frequency Adverb always often sometimes never always never Main Verb walk eat sleep been wanted use Continue the Sentence to work. meat on Saturday night. in their beds. to China. live in Paris. the old computers in the basement.
Adverbs of frequency are used in positive sentences. The frequency adverb is placed after the main verb (if the main verb is not the verb "to be). Examples:
I always walk to school. My cats sometimes like to play. Our teacher almost never gives us a lot of homework.
Adverbs of frequency are used in positive sentences. The frequency adverb is placed before the main verb if the main verb is the Verb "to be" Positive and Negative Sentences without the verb "to be" Frequency adverbs are used in positive sentences and negative sentences. The frequency adverb is placed after the main verb (if the main verb is not the verb "to be). Examples:
I always walk to school My cats sometimes like to play Our teacher almost never gives us a lot of homework. The teacher doesn't always come on time.
My cats don't always like to play with my socks. I don't often walk to school.
Positive and Negative Sentence with the verb "to be" Frequency Adverbs are used in positive sentences and negative sentences. The frequency adverb is placed before the main verb if the main verb is the Verb "to be".
The teacher is always on time. My sister is never lazy. Our house is sometimes a mess. My brother's house is never a mess. The sofa is always comfoftable to sit on.
Questions without the verb "to be" as the main verb In question when the main verb is not "to be". the frequency adverb is placed before the main verb.
Does she always walk to work? Why does the oven always stop working after 10 minutes? Do you always clean the sofa every day?
4. In questions when the verb "to be" as the main verb. In question when the main verb is the verb "to be" the frequency adverb is placed after the subject?
Is the food always so bad? Are your children ever late for school? Are the clocks always broken? Nouns
What is a noun? The definition of a noun is a word that is used to define a person, animal or living object, place, thing or quality. There are many different kinds of nouns in English. Common Nouns - general nouns such as cat, bowl, hand, tree clock etc. Countable Nouns - nouns that can be counted, such as car-cars, child-children etc. Uncountable Nouns - nouns that can't be counted, such as water, fire, air etc. Collective Nouns - nouns that refer to a group of things or people such as family, police, worker's union etc. Proper Nouns - nouns that refer to a specific name of a person, corporation, company, product, such as IBM, Microsoft, Mr. David Green, Dr. Mary Jones. Concrete Nouns - a noun that is a physical object, something that can be touched, seen, such as an animal, window, table, computer etc. Abstract Nouns - is a noun is not a physical object, it can't be touched physically. They are ideas and feelings such as intelligence, love, hate, bravery etc. Countable Nouns What are countable nouns:
A countable noun is a type of noun that can be:
presented in both the singular form and the plural form represented by a number, such as two cats, five books Rules For Using Singular Countable Nouns Rules For Using Plural Countable Nouns 1.A determiner is optional before noun(or adverb if adjectives are used.
1. A determiner must be used before noun(or adverb if adjectives are used, such as a, the, this, one, ours, his etc. 2. The article "a" or :an" can be used. 3.Only the number one can be used to state the amount. 4. Possessive adjectives my be used such as my, his, our etc. 5. Quantifiers can't be used.
2. The articles "a" or "an" can't be used. 3. Any number bigger then two can be used to state an amount. 4.Possessive adjectives my be used such as his, our, etc. 5. Quantifiers can be used, such as some, any, many, a lot etc.
6. A demonstrative adjectives can be used such as 6. A demonstrative adjectives can be used such as this, those etc. this, those etc. Examples of Countable Nouns: Nouns dog boy car window Nouns In The Singular Form The dog is big. The boy is tall. Our car is green. The window is big. Nouns In The Plural Form The dogs are big. The boys are tall. All the cars at work are white. The windows are clean. Nouns Represented By A Number There are six dogs in the room. There are three tall boys in my class. There are six cars parked on my street. The room has three window.
English Pronouns "I vs. Me" Which is correct "You vs. I" or "You and Me"? I "I" is used as the sentence's subject. "I" must be used with a verb. "I" is the subject of the verb. Examples: Me "Me" is used as the object of the sentence. "Me" is usually not followed by a verb. "Me" is the object of the sentence.
You You You The
and I are always together on the weekends. and I are going to win the science award. and I are always going to be friends. award was given to you and me.
Which is correct "You vs. I" or "You and Me"? I "I" is used as the sentence's subject. "I" must be used with a verb. Me "Me" is used as the object of the sentence. "Me" is usually not followed by a verb.
"I" is the subject of the verb. Examples:
"Me" is the object of the sentence.
You You You The
and I are always together on the weekends. and I are going to win the science award. and I are always going to be friends. award was given to you and me. Uncountable Nouns
What are Uncountable nouns? Uncountable nouns are: Nouns that can not be represented in the singular form or the plural form, such as water, air, coffee, tea are some examples of nouns that can only be represented in the singular form. Nouns that can not be represented by a number are called uncountable nouns. It is not possible to say I need 4 air, or 6 sugar. Uncountable nouns are nouns that can not be counted. Examples of uncountable nouns are: water, air, grass, paint, oil etc. Rules for Using Uncountable Nouns: Uncountable nouns only used in the singular tense. A or an can not be used with uncountable nouns. "The" can be used with uncountable nouns. Certain quantifiers can be used with uncountable nouns, such as some, any, much, a lot are some examples of the quantifiers that can be used with uncountable nouns. Quaintly of uncountable nouns is expressed by the expression "a. ....of......". (Examples: a bag of sugar, a bottle of oil. Collective Nouns What is a collective noun? Collective nouns are nouns that refer to things or people as a unit. Examples: family, police, class, team, crew etc. Collective nouns can be used in both the singular form and the plural form. Rules for Using Collective Nouns: Singular Collective Noun 1. Singular collective nouns refer to one unit of people or things. 2. Singular collective nouns are used like singular nouns. Plural Collective Nouns 1. Plural collective nouns refer to two or more units of people or things. 2. Plural collective nouns are used like plural nouns.
Common Nouns What are common nouns?
A common noun is a noun that refers to a person, thing and place. Examples: dog, house, picture, computer.
Common nouns are represented in the singular and plural form. Common nouns are represented by lower case letters.
Examples of the usage of common nouns: (The common nouns are highlighted in blue)
The red book is on the table. The black dog is in my yard. The computers are new. Proper Nouns What are proper nouns? A proper noun is a specific name of a place , a person, or a thing. The first letter of a proper noun is always represented by a capital letter. Proper Nouns in English 1.Name of the Month and Day 2. Names of Company's 3. Names of People 4. Names of Places 5. Titles of People 6. Names's of Books, Newspapers, Plays etc. January, February, April etc. Microsoft, Amazon, Nike, etc. John, Mary, Bill, Mr. Brown, Mr. Lee, Mr. Tom Jones Greentown Hospital, Town House Hotel, City Park etc. Dr. Kenny White, President Jimmy Ayusso, Ms. Miri Thomas etc. The New York Times, War and Peace, Midnight Summer Dream
Concrete Nouns What is a concrete noun? Concrete nouns are: Concrete nouns can be touched, felt, held, something visible, smelt, taste, or be heard. Concrete nouns are something physical. Concrete nouns can be countable nouns or uncountable nouns, and singular nouns or plural nouns. Concrete nouns can also be a common noun, proper nouns and collective nouns. Examples of Concrete Nouns Common Concrete Nouns Countable Concrete Nouns dog, cat, girl, plate air, water etc. singular -chair, computer, song, window plural - chairs, computers, songs, windows
Uncountable Concrete Nouns Proper Nouns
water, air, oil, sugar, salt, rice, cheese etc. Mr. Mike Jones, Tom Brown, Audrey Ryan
Abstract Nouns What is an abstract noun? There are diffrent types of nouns. All types of nouns follow the same grammar rules. When most people think of nouns, they think of people, places and things but abstract nouns are the opposite. Abstract nouns is something that can't be sensed by our five senses (smell, touth, hear, see or taste). Abstract nouns are nouns that:
Abstract Abstract Abstract Abstract
nouns nouns nouns nouns
are any nouns that can't be touched, tasted, seen, heard or smelt or felt. usually represent feeling, ideas and qualities. can be singular nouns and plural nouns. can be countable or uncountable.
Examples of abstract nouns: love, hate, violence, culture, taste Pronouns How to use pronouns? Pronouns replace the noun. A pronoun can be used as the sentences subject or the object. Most of the time a pronoun refers to something already mentioned or understood by the listener or reader. The different kinds of pronouns are:
personal pronouns indefinite pronoun demonstrative reflexive pronoun interrogative pronouns
Personal Pronouns What are Personal Pronouns? Personal Pronouns in English are used to replace nouns that refer to people. Personal Pronouns can be used as the sentences subject or objective. English doesn't have singular and plural forms of "you". "You" is used for both male and female and singular and plural. Example of Personal Pronouns Subject Personal Subject I - I went to the store. Objective Personal Pronouns Me -Is Mary going to come with me to the doctor. You - Did you & Mary eat all the cookies. Him - John is going to give him the books soon. Her - Mary is going to give her the The pronouns are used to replace the name of the people or person
You - You went to store. He - He went to the store. She - She went to the store
books soon. We - We went to the store. They - They went to the store. It - It was a good cake Reflexive Pronouns What are reflexive pronouns? Us - When is Tom going to give us the books. Them - Mary went to see them this morning. It - I am glad it worked out in the end.
Reflexive pronouns are pronouns that are used to state the subject is performing the action. The reflexive pronoun can be used to emphasize the object or the subject. Reflexive Pronouns
Myself Ourselves Themselves Yourselves Herself Himself Examples:
I We Them You She He
I lived myself while I was studying for my bachelors degree. My sister paid for university herself. Our father didn't help her out. We wanted to travel to Europe by yourself after we finished university. Are you going to drive yourselves to school today? Intensive Pronouns
What are Intensive pronouns? Intensive pronouns are:
Pronouns that refer to the noun or pronouns. Intensive pronouns are used to emphasize the subject. Intensive pronouns are used when the subject isn't performing the action. It is common for intensive pronouns are usually next to the subject. The intensive pronouns are not the subject. Intensive Pronouns
Myself Ourselves Themselves Yourselves Herself
I We Them You She
Himself Examples:
He
My sister herself is going to teach the undergraduate class. I myself have two bachelors degrees. We ourselves studied for the test. Relative Pronouns
What are relative pronouns? A defining relative clause states defining information about a person or a thing. It is used to define one object/thing or a person from another. Without this information the sentence would not be clear. Note: The relative pronoun replaces the noun. Examples:
Who is that man in there street? Whose husband is that waiting in the car? Is that cake good? When are you going to call her? Why are you so tired? Which house is yours? Relative Pronouns
Subject Object Possessive
Time -When Whose
Reason -Why -
Person Who, That Who/Whom/That Whose
Place Where -
Thing That, Which That, Which Whose
Determiners That are determiners in English? Determiners are words that are used with nouns to clarify the noun. They can clarify:
to to to to to to to
define something or someone state the amount of people, things or other nouns state possessives state something or someone is specific state how things or people are distributed state the difference between nouns state someone or something is not specific
There are different types of determiners. There type of determiner depends on the type of noun. Singular nouns always need a determiner. Plural nouns the determiner is optional. Uncountable nouns the determiner is also optional. There are about 50 different determiners in the English language they include:
Articles: a, an, the
Demonstratives: this, that, these, those, which etc. Possessives: my, your, our, their, his, hers, whose, my friend's, our friends', etc. Quantifiers:few, a few, many, much, each, every, some, any etc. Numbers: one, two, three, twenty, forty Ordinals: first, second, 1st 2nd, 3rd, last, next, etc.
What are Demonstratives? That This These Those There are 4 demonstratives that, this, these and those. Demonstratives are used to state the distance from the speaker. The distance can be either psychological or physical. Demonstratives can be used as pronouns or adjectives. They are sometimes referred to as demonstrative adjectives or demonstrative pronouns. When they are used as adjectives they modify the noun. What is the grammatical difference between that, this, these those. The difference between the demonstratives distance (near and far) and singular and plural.
This That These Those
"This" is used for singular nouns that are close to the speaker. "That" is used for singular nouns that are far from the speaker. "These" is used for plural nouns that are close to the speaker. "Those" is used for plural nouns that are far from the speaker. Singular x x = Plural x x Close x x Far x x
Examples of English Demonstratives Demonstratives That This These Those That is the place. This is really good. These are a lot of fun. Those are really good English books Demonstrative Adjectives That restaurant is really good. This book is really good. These games are a lot of fun. Those English books are really good.
English Quantifiers What are quantifiers? Quantifiers are words that are used to state quantity or amount of something without stating the actually number. Quantifiers answer the questions "How many?" and "How much?" Quantifiers can be used with plural countable nouns and uncountable nouns. Quantifiers must agree with the noun. There are 3 main types of quantifiers. Quantifiers that are used with countable nouns, quantifiers that are used with uncountable nouns. and the 3rd type are quantifiers that are used with either countable nouns or uncountable nouns.
Countable Nouns much many few* a few** little* a little** enough plenty x x x x x
Uncountable Nouns x x x x x I don't have much money. I don't have many apples.
We know few people in the area. I would like to get to know more. We know a few people in the area. I know enough people to keep me happy. I know little English. I am going to have a problem getting around England. I know a little English, at least enough to get England. I have enough money. I have plenty of money.
** a few/a little - means that there are not a lot of something, but there is enough. There are a few apples. There are enough apples. There are a people at the meeting. There are enough people to hold a meeting. There are not a lot people, at the meeting, but there are enough I know a little English. He know enough English to manage. I have a little money.
*few/little - means that is not enough of something. There are few apples. There are not enough apples. There are few people. There are not enough people at the meeting. We can't hold a meeting, because there are not enough people. There is little money. We can't buy a lot of expensive food. If things for the holiday. I don't have enough money, then we will stay home and have a great time. They know little English. They can't get around very well. They don't know enough English to manage.
Determiners Articles What are articles? Articles are used to clarify if a noun is specific or if a noun is not specific. They are used before the nouns or adjective. There are 2 kinds of articles:
Definite articles - are used for specific nouns. Indefinite articles - are used for non specific nouns.
"A- An" are indefinite articles
It is used to refer to a noun that is not something or someone specific such as a pen, an apple, a bus). " A" or "An" is used when it is not important as to which the nounis refering to (example: an apple on the table, a pen on the table or a book from the room). It is unknown as to which the noun is referring to (example: a teacher in the hall, a letter in the mail box, a car in the street). "A" is used if the letter before the next word starts with a constenent (not a vowel a, e, i, o, u). An is used if the letter for the next word starts with a vowel (a, e, I, o, u). Examples:
I see a dog in the street. * The girls see the big black dog on the other side of the street. **
Please bring me a pen.* Please bring me the black pen that is on my desk.** I think that is a teacher from the school.* I think that is the math teacher.**
* A refers to something that is not specific, it is not clear or important as to which dog, pen or teacher. ** The refers to a specific pen "the black pen" not just any pen, "the big black dog" not just any dog, and "math teacher" not just any teacher. English Determiners Some Any When to use some and any? Some and any are used to state the quantity, amount of something. When using some or any the exact number is not stated. Some and any are quantifiers. Some and any can be used when:
The exact number is not known. The exact number is not important or relevant. Some and any are used with countable nouns and uncountable nouns.
Any - Any is used with:
Negative sentences When asking a question. Any is used when a sentence is grammatically positive, but the meaning of the sentence is negative.
Examples:
Do you have any ice cream left? I don't have any money today. I am getting paid on Friday. My brother never does any thing good.
Some - Some is used with:
Positive sentences. When asking a question, if the answer the expected answer to be positive.
Examples:
The children have so free time. Please buy some bananas. Can I have a glass of tea?
When to use some and any? Some and any are used to state the quantity, amount of something. When using some or any the exact number is not stated. Some and any are quantifiers. Some and any can be used when:
The exact number is not known. The exact number is not important or relevant. Some and any are used with countable nouns and uncountable nouns.
Any - Any is used with:
Negative sentences
When asking a question. Any is used when a sentence is grammatically positive, but the meaning of the sentence is negative.
Examples:
Do you have any ice cream left? I don't have any money today. I am getting paid on Friday. My brother never does any thing good.
Some - Some is used with:
Positive sentences. When asking a question, if the answer the expected answer to be positive.
Examples:
The children have so free time. Please buy some bananas. Can I have a glass of tea?
That & Which What is the difference between "that" and "which"? That - "That" is used with restrictive phrases. Restrictive phrases are phrase. that are essential to the sentence. Which - "Which" is used with nonrestrictive phrases. Nonrestrictive phrases are phrases that state non essential information. A phase is considered nonrestrictive phase if the phase can be omited from the sentence. Examples:
The The The The The The
shirt that you lent me is in my bag. shirt, which is red, is in my bag. house that I wanted to buy has been sold. house, which I didn't want to buy, has been sold. food store that I go to all the time is closed today. store, which is near my house, is not open today. Determiners - A , An or The
When to use A, An or The? Definite Article - "The" is a definite article, which means that it is used to specify something specific. It refers to a noun the is either understood (by the reader or listener) or has been previously referred to by the writer or speaker. Indefinite Articles - "A" and "An" are indefinite articles. The difference between "A" and "An". "An":is used is it comes after a word that starts with a vowel. "A" and "an" are used the same way grammatically. They are used before a singular noun, or before the adjective the represents the noun. They can't be used with plural nouns or uncountable nouns. Examples A/An The A/An There is a dog outside the building. We don't know which dog the writer/speaker is referring to. The black dog is outside the building. Do you know where there is a post office? It is understood to which dog the writer/speaker is referring to The writer/speaker is not referring to a specific post office
The
I am going to the post office.
It is understood to which post office the speaker/writer is referring to. Prepositions
What are prepositions? Prepositions are words that specify place, direction, and time. There are three types of prepositions. Time Prepositions - Time prepositions define time. Time prepositions - In - At - On For - During - While Place Propositions - Place prepositions clarify the place someone or somebody. Place Prepositions - In - On -At Direction Prepositions - Direction prepositions are used to clarify the direction of someone or something. Examples: under, over, right, left etc. How to use a prepositions? 1. The prepositions usually comes before the noun. 2. Prepositions can be used with all forms of nouns (e.g. collective nouns, pronouns etc). 3. Prepositions can't come after a verb, but can be used before a gerund or verb in noun form. 4. The rules above do not change and there are no exceptions to the rules. Place Prepositions Prepositions of place are used to clarify a specific place. Place prepositions are used with all nouns. The preposition usually comes before the noun or the pronoun. The preposition never comes before a verb. Common Place Prepositions: aboard - She is aboard the boat. above - The picture is above the sofa. across - My house is across the street. against - The desk is against the wall. around - My house is around the block. at - Is your house at the end of the street. at the back of - We are going to sit at the back of the theater. at the bottom of - The coins are at the bottom of the lake. at the top of - The books are at the top of the shelves. between - We sit between the two boys. behind - The girls sit behind the two boys. below - The desk is below the window by - The books are by the door.
in - I live in the big green and white house. inside - I live inside the big green house. on the corner of - We live on the corner of 3rd avenue in the middle of - We live in the middle of the street. near - I don't live near the supermarket. next to - I live next to my best friend. to the left of - The blue box is to the left of the green box. to the right of - The orange box is to the right of the yellow box. on - The sun heater is on the top of the building. on the side of - There is a big sign on the side of the house. on top of - There is a man on the top of the roof. on the other side of - Do you see what is going on over there on the other side of the roof? opposite - The post office is on the opposite side of the street. outside - The car is outside the garage. under - The blanket is under the bed in a box.. underneath - The pen is underneath the box. Time Prepositions Time prepositions are used to define time. Prepositions usually come before a noun or pronoun. Prepositions never come after a verb.
after - I will be there after work. around - We will be there around 3 PM before - I will be there before I go to school. between - I will be there by - I will be there by the time that you leave for work. during - I will be there during your class. for - I will be there for your birthday. past - I wasn't there for the past 2 months. since - I didn't see her since I was 10 years old. until - I will not be home until 7:00 PM. within - I will be there within 2 hours. Time Prepositions In - On At
Time prepositions are used to clarity what time an event happened or will happen. Time prepositions are used nouns and pronouns. Prepositions usually come before nouns or pronouns. Prepositions never come before a verb. List of Time Prepositions At a specific time On days and dates In period of time - years, months, seasons
at 2:00 at lunchtime at 4:00 AM
on my birthday on the first day of the school year on 11/10/90
in a few days in a couple of months in the summer
IMPORTANT: In English we say:
in the morning -because it is considered a period of time in the afternoon in the evening at night -
Note: We say in the morning, in the afternoon, or in the evening BUT we say 'at night' Place Prepositions In - At On What are place prepositions? Place prepositions , are prepositions that are used to describe the place or position of all types of nouns. It is common for the preposition to be placed before the noun. When we refer to Place prepositions we usually refer to "in", "at" and "on". In - Is usually used to state that someone or something is in a (the boundaries can be physical or virtual place. On - Is usually used to state someone or something is on top of a surface. At - Is usually used to state something or someone is at a specific place. A list of most prepositions of place. At a specific place at the mall at the table at work IMPORTANT: In English we say: On a place that is physically on top of a place on the table on the floor on the wall In a place that is enclosed or within boundaries in the city in the box in the park
on the island in the city/country side in the mountains - except when you mean that something or someone is physically on the mountain. at the office Prepositions - For - During While
How are prepositions - for - while - during used? The 3 most common English prepositions that are used to represent time are: for - while - during. For - The preposition "for" is used to express how long something or someone is doing something. "For" is used to state a period of time and is usually used with a noun/pronoun (or any other form of nouns) .
I have been riding my bicycle for 2 hours. The dog has been barking for a long time. The traffic has been bad for the last three days.
While - The preposition "while" is used to represent the length of time an action has been happening. "While" is used when speaking about 2 actions that are happing at the same time. The length of the action is not important. "While" is used with a subject and a verb.
While I was playing with my dog, my sister was doing her homework. While we are playing cards, the radio was playing. My mother doesn't like the T. V. on while we are eating dinner.
During -The preposition "during" is used to represent the length of time of an action that is while the action is happening. "During" is used with a noun/pronoun (or any other form of nouns).
I will be really busy during the week. The kids were sleeping during the party. The lights went out during the storm. Past Verb Tenses Past Simple Tense
The past simple verb tense is used when: The action happened in the past The action/event is completed /finished at the time of speaking. The time or/and place is stated or understood. The length of the event/action is not important. Examples:
I went to the school. We did not not to the English class today. They did eat lunch at school.
Note:In English, following phrases are often used with the Past Simple Tense to define time: yesterday last year last night two years last month ago many years ago a long time ago Past Simple Verb Tense What is the structure of the past simple verb tense? Subject + Auxiliary Verb did Grammar rules for the past simple verb tense: The main verb in the sentence is: + Main Verb verb in the base form
- for regular verbs -ed is added to the verb - for irregular verbs see a irregular verb chart V2/Past Simple
Negative statements
- The auxiliary verb "did" is added after the subject. - "not" is added between the auxiliary verb "did" and the main verb - the main verb stays in it's base form, in negative sentences and questions
Questions the auxiliary verb "did" comes before the subject. - the main verb stays in it's base form. Past Simple Verb Tense Chart Subject I + We She I You He Did ? Did Did did did did I you she Auxiliary Verb not not not Main Verb live play plays live live live receive learn Clean in New york. football. outside. in New York. in London in a big house as a child. a letter in the mail? English in school? the house everyday or once a week?
Past Simple Verb Tense What is the structure of the past simple verb tense? Subject + Auxiliary Verb did Grammar rules for the past simple verb tense: The main verb in the sentence is: + Main Verb verb in the base form
- for regular verbs -ed is added to the verb - for irregular verbs see a irregular verb chart V2/Past Simple
Negative statements
- The auxiliary verb "did" is added after the subject. - "not" is added between the auxiliary verb "did" and the main verb - the main verb stays in it's base form, in negative sentences and questions
Questions the auxiliary verb "did" comes before the subject. - the main verb stays in it's base form. Past Simple Verb Tense Chart
Subject I
Auxiliary Verb
Main Verb live play plays live live live receive learn clean in New york. football. outside. in New York. in London in a big house as a child. a letter in the mail? English in school? the house everyday or once a week?
We She I did did did I you she
not not not -
You He Did
Did Did
Past Simple Verb Tense With The Verb "to be" What is the structure of the past simple verb tense with the verb "to be"? Subject + Auxiliary Verb did + Main Verb Verb in the base form -
Grammar rules for the present simple tense with the verb "to be": The main verb in the sentence is the past tense of the verb "to be" (did) When the verb "to be" (did) is used as the main verb, then no auxiliary verb is used. Negative Statements - "not" is added to make the sentence negative Questions - the verb "to be" comes before the subject Past Simple Verb Tense with the Verb "to be" Chart I + We She I You He Was ? Were Was Subject Auxiliary Verb was were was was were was I you she not not not short as a child. in New York last week. the top student in her class. tall as a child. funny last night. happy about failing the test. a lot of fun as a child? the tallest in your class? a good runner in high school? -
Past Continuous Verb Tense What is the past continuous verb tense? The past continuous verb tense, which is also know as the past progressive tense. The past continuous verb tense is one of four tenses that are used in the past. The past continuous verb tense is used in the following situations: 1. the action happened at a specific time.
We were studying English yesterday at 10:00.
the action happened at a specific time - "10:00"
there was an interruption while performing the action. I was eating dinner when the phone rang.
"eating" is the action was being performed "the phone rang" is the action that interrupted. two actions were happening at the same time. to state a change in a situation. Pas Prese Futur t nt e
the action happened at a specific time "when eating dinner". -
I was eating dinner when the phone rang. We were studying English yesterday at 10:00. The dogs were not playing in the yard when something ate your flowers. Were you sleeping when I called last night? Was your mother cooking all night?
x x x x x
What is the structure of the past continuous verb tense? Subject + Auxiliary Verb "was - were " + Main Verb verb + -ing -
Grammar rules for the past continuous verb tense:
The auxiliary verb "to be" is used. The auxiliary verb "to be" changes according to the sentence's subject. -ing is added to the main verb.
Negative Statements - "not" is add between the auxiliary verb "to be" and the subject. Questions - the order of the words is change - the auxiliary verb "to be" comes before the subject Subject I + We She I Auxiliary Verb was were was was not Main Verb going playing eating reading to the store when she called. ball yesterday morning. dinner when someone came to the door. the newspaper all day yesterday.
You He Was ? Were Was
were was I you your mother
not not -
doing sleeping going fixing sleeping
your homework when I checked on you. when I went into his room. to go to you to the store? the car while it was raining? when I called this morning?
Simple Past Perfect Verb Tense When is the simple past perfect verb tense used? The simple past perfect verb tense is used: to state "how many" to clarify the order of two past non-continuous events to state a past action was completed before an other action interchangeably with the past perfect continuous verb tense with the exact time or an unexpected time can be stated (unlike when using the simple present prefect verb tense)
The simple past perfect verb tense is used to to clarify the order of two past actions. The first action uses the simple past perfect verb tense The second action uses that past simple verb tense. Examples:
I wasn't hungry when I came home from school. I had eaten on my way home from school. We had already left for school, when I found out that the my English class was cancelled.
The simple past perfect verb tense be used to state an action that occurred in the past was completed, before a 2nd action in the past started.
I was very tired when my friends came to pick me up. I had worked all day. We slept only a few hours, when we had to wake up to go to school.
The simple past perfect tense can be used to answer the question "how many". Examples:
I had lived in in Europe, so many years ago. We had visited so many different places, before we came home.
There are many cases where the past perfect continuous verb tense can be interchangeable with the simple past perfect tense. Examples:
I I I I
had slept all night. - past perfect simple tense had been sleeping all night. - past perfect continuous verb tense have lived in this house many years. - past perfect simple tense have been living in this house for many years. - past perfect continuous verb tense
What is the structure of the simple past perfect verb tense?
Subject = -
Auxiliary Verb had
Main Verb Verb + -ed/V3-past participle
Grammar rules for the simple past perfect verb tense: The past tense of the auxiliary verb "have" is used (had). The main verb uses the verb form past participle/V3 or -ed is added to main verb.
Regular verbs add --ed to the verbs base form. Irregular verbs see verb chart past participle/V3
Negative statements - "not" is added between the auxiliary verb "have" (had) and the main verb. Questions - The verb "to be" comes first, then the subject. Using adverbs is optional. Adverbs come before the main verb in the sentence. Simple Past Perfect Verb Tense Chart Subjec t I + We She I You He Had ? Had Had Auxiliary Verb had had had had had had the dog you she not not not Main Verb stamped read played lived studied eaten gone called cleaned your letter, and then sent it for you. the books form the library, and returned them last week. outside for an hour. in New York, before, I moved to Paris. very much, that is why you failed your test. all day, so when he got home was hungry. to the vet. He was very sick for last week. your teacher. She left you a message a few days ago. the house yesterday, because we had a party.
Past Perfect Continuous Verb Tense How is the past perfect continuous verb tense used? The past perfect continuous verb tense is a one of four past tenses in English. The past perfect continuous verb tense is used to:
represent the "past in the past" repeated actions clarify the order of 2 past actions answers the question "how long" clarifies the order of two past actions states that an action was in progress, when a second action stared represents the conclusion of an event action states the duration of an event, before a past action
The past perfect continuous verb tense can be used to state that an action was still in progress when the 2nd action started. When is the past perfect continuous verb tense used? There are 6 ways the past prefect continuous verb tense is used:
The past perfect continuous verb tense is used to state the first action had been happening over a period of time, when more then one or more actions occurred. When 2 actions happened in the past, the past perfect continuous verb tense is used to clarify which action happened first.
The first action is clarified by using the past perfect continuous verb tense. The second action is clarified by using the past simple verb tense.
Examples:
Mary looked tired. I could see that she had been studying for her English test recently. The children were soaking wet. I knew they had been swimming in the lake.
The past perfect continuous verb tense is used to state actions happen repeatedly. Examples:
The bus has been coming late everyday this week. The teacher has been giving us exams every week for the past few weeks.
The past perfect continuous verb tense is used to make conclusions. Examples:
There was a leak in the pipes, that is why the water bill had been getting higher and higher each month. The teacher looks very tired. She has been marking test all day.
The past perfect continuous verb tense is also used to state a past action that occurred over a period of time. Example:
I have been playing the violin, since I was a child. We have been working in the university for many years.
There are many cases where the past perfect continuous verb tense can be interchangeable with the simple past perfect verb tense. Examples:
I I I I
had slept all night. - past perfect simple verb tense had been sleeping all night. - past perfect continuous verb tense have lived in this house many years. - - past perfect simple verb tense have been living in this house for many years. - past perfect continuous verb tense
The past perfect continuous verb tense can be used to answer the question "how long". Examples:
Tips:
How long had you been waiting for the bus to come? How many year had you been studying to be a teacher?
The past perfect continuous verb tense is also known as "past perfect progressive tense". The past perfect continuous verb tense is used in English is used to emphasize:
the action/activity the length of time
What is the structure of the past perfect continuous verb tense? Subje Auxiliary Auxiliary Main + + + ct Verb Verb Verb - had - been verb + -ing
Grammar rules for the past prefect continuous verb tense: The past tense of the auxiliary verb "have" is used. The auxiliary verb "to be" always stays in the V3/past participle form (been). -ing is added to the main verb. Negative statements - "not" is added between the auxiliary verb "have" (had) Question - the auxiliary verb "have" (had) comes before the subject Past Perfect Continuous Verb Tense Chart Subject I + We She I You He Had ? Had Had Auxiliary Verb had had had had had had I it she not not not Auxiliary Verb been been been been been been been been been studying cleaning playing sleeping studying eating making raining cleaning really all night. I was really tired. all week, before my mother came to visit. outside for hours. She needed to take a shower. for the last few days, so I went to the doctor. very much before your test, that is why you failed. for the last few day. She lost a lot of weight. a lot of noise, while you were sleeping? all night, because it is all wet outside.? the house last week, it looks really clean?
Present Tenses Present Simple Verb Tense How is the present simple tense used? The present simple is the tense used to describe actions that are timeless. If the time of the action can be defined, then the present simple tense is used. The time and/or place is stated or understood. The Present Simple Tense is used in the following situations:
permanent actions actions that happen on a regular basis facts statements that are always true to state existence
to state feeling static verbs general actions Past Present x x x x x x x x x x Future
I go to school everyday I live in New York. Water boils at 100 degrees Celsius I love to go to my English class. This is a pen.
x x x x x
Note: The x prepresents the time of the action. Note: the present simple tense is also used in other parts of English grammar, such as conditional statements and the future tense. What is the structure of the Present Simple Tense? Subject + Auxiliary Verb do - does Grammar rules for the present simple tense: In positive sentences the auxiliary verb is not used. In positive sentence the main verb changes form according to the subject. In negative statements the auxiliary verb "do-does" is added after the subject. In negative statements and questions the main verb stays in its base form. In negative statements and questions but the auxiliary verb changes form according to the subject. Present Simple Tense Chart + Subject I We She I You He Do ? Do Does do do does I you she Auxiliary Verb not not not Main Verb live play plays live live live make learn clean in New york. football. outside. in New York. in London in a big house. a lot of money? English in school? the house everyday or once a week? + Main Verb Verb in the base form (-s/-es -
What is the structure of the present simple tense with the verb "to be"? Subject -+ Auxiliary Verb do - does + Main Verb Verb in the base form (-s/-es --
Grammar rules for the present simple tense with the verb "to be": The verb "to be" is the main verb used in the sentence. When the verb "to be" is used as the main verb, no auxiliary verb is used. The main verb "to be" changes forms according to the subject. In order to form negative statements "not" is added between the the verb "to be" and the main verb. In order to form questions the verb "to be" before the subject. Present Simple Tense with the Verb "to be" Chart Subject I + We She I You He Am ? Are Is Auxiliary Verb am are is am are is I you she Present Continuous Verb Tense How is the present continuous tense used? The present continuous tense is used describe an action is happening at the time of speaking/writing or temporary actions. The present continuous tense is also called the present progressive tense. When using the present continuous tense the verb "to be" is used with the main verb. - ing is added to the main verb. The present continuous tense is used in the following situations: The actions is temporary. The actions is going to happen in the near future. The term "near future" is relative to the situation. Actions that are happening at the time of speaking/writing. Future actions that are planned. The verb "going to" is used when used with words that state the future such as tomorrow, soon, later next week etc. not not not tall. from New York. a nice girl. tall. funny. happy. tall or short? tall? a good runner?
Example I am eating dinner. We are playing a game. My sister is going to Paris next week. The girls are not doing their homework. Are you coming with us to the store?
Past -
Present x x x x x
Future -
What is the structure of the Present Continuous Verb Tense? Subject + Auxiliary Verb "to be" + Main Verb verb + -ing -
Grammar rules for the preset perfect tense: The auxiliary verb "to be" changes according to the sentence's subject. Add -ing to base form the verb of the main verb Negative Statements -: "not" is added beween the verb "to be" and the main verb Questions - the order for questions is reversed. The verb "to be" comes before the subject. Present Continuous Tense Chart Subject I + We She I You He Am ? Are Is Auxuilly Verb am are is am are is I you she not not not Main Verb going playing eating reading cooking watching going fixing cleaning to the store. ball. dinner. the newpaper. dinner. the movie. to the store with you? the car? the house today?
Present Perfect Tense When is the present perfect tense used? The present perfect tense is used to describe an action that happened in the past, but has a connection to the present. The present perfect tense is also sometimes called the present perfect simple tense. The auxillary verb "have" is always used with the present perfect tense. The present prefect tense is used in the following situations:
There is a connection with the past. The exact time of the action is not known. "For" and "since" can be used to state the time of the action. The action is not completed at the time of speaking/writing The action happened before you expect.
The action has been repeated numerous time, and is expected to be repeated in the future. Past x x x x Present x x x x Future -
Example I am not hungry. I have eaten at the school cafeteria. I have learned English since 1956. We have not known her for very long. Have you been to China? Has she finished college?
What is the structure of the Preent Perfect Tense? Subject + Auxiliary Verb have + Main Verb Verb + --ed/V3-past participle -
Grammar rules for the present perfect tense: The auxiliary verb "have" changes according to the sentences subject. The main verb uses the verb form past participle/V3. - Regular verbs add -ed to the verbs base form. - Irregular verbs see verb chart past participle/V3. Negative sentences - "not" is added between the Auxiliary Verb and the main verb Questions - the auxiliary verb comes before the subject Present Perfect Tense Chart Subject I + We She I You He Have ? Have Has Auxiliary Verb have have has have have has I you she not not not Main Verb lived played played lived lived lived gotten learned cleaned in that house for 2 years. football for 2 years. outside for an hour. here for a long time. with my parents for over 10 years. here for many years. any mail today? English for a long time? the house for a long time?
Present Perfect Continuous Verb Tense Chart How is the present perfect continuous tense used? The present perfect continuous tense is a tense that is a tense that is sometimes confusing. It refers to an action that started in the past, but has continued to the present or has just finished.The present perfect continous tense uses the auxiliary verb "have - has" and -ing added to the main verb. The present perfect continuous tense is used when:
The action started in the past. The action continued at the time of speaking/writing or the action just finished at the time of speaking/writing The statement answers "how long" an action has been happening. The action has happened continuously with stopping. Past Present x x x x x x Future --
I have been waiting for my teacher for 1 hour. We have been learning English since the age of three. They have not been playing basketball for a long time. My sister has not been living in China for many years. Has your house been racing for a long time? Have you been living in that has since you have been married? How is the present perfect continuous tense used?
x x x x x x
The present perfect continuous tense is a tense that is a tense that is sometimes confusing. It refers to an action that started in the past, but has continued to the present or has just finished.The present perfect continous tense uses the auxiliary verb "have - has" and -ing added to the main verb. The present perfect continuous tense is used when:
The action started in the past. The action continued at the time of speaking/writing or the action just finished at the time of speaking/writing The statement answers "how long" an action has been happening. The action has happened continuously with stopping. Past Present x x x x x x Future --
I have been waiting for my teacher for 1 hour. We have been learning English since the age of three. They have not been playing basketball for a long time. My sister has not been living in China for many years. Has your house been racing for a long time? Have you been living in that has since you have been married? Present Perfect Continuous Tense What is the structure of the Present Perfect Continuous Tense? Subject + Auxiliary Verb have + Auxiliary Verb been
x x x x x x
Main Verb verb + -ing
Grammar rules for the present prefect continuous tense: The auxiliary verb "have" changes according to the subject (have -has). The auxiliary verb "to be" always stays in the V3/past participle form (been).
- ing to added to the base form the main verb. Negative statements - add "not" between the auxiliary verb "have" and the the auxiliary verb "been". Questions - the order is change the order the auxiliary verb "have" comes before the subject. Present Perfect Continuous Tense Chart Subject Auxiliary Verb have have has have have has I you she not not not Auxiliary Verb been been been been been been been been been Main Verb living playing playing living living living making learning cleaning in this house since I was a baby. football for 2 years. outside for an hour. here for a long time. in with my parents for over 10 years. here for many years. a lot of noise? English for a long time? the house for a long time?
I + We She I - You He Have ? Have Has
Present Perfect Verb Tense or Present Perfect Continuous Verb Tense What is difference between the present perfect tense and the present perfect continuous tense? The difference between the present perfect tense and the present perfect continuous tense is very small. There are many times when the two tenses can be used interchangeability. There are differences in the structure of the tenses. The two tenses use the auxiliary verb "have". The present perfect tense -ed/v3 is added to the main verb and the present perfect continuous tense -ing is added to the main verb and the verb "to be" is also used. The Present Perfect Tense vs. the Present Perfect Continuous Tense Present Perfect Tense to state an action that was not continuous or was interpreted Present Perfect Continuous Tense
to state an action that is continuations
to state the amount of times an action took place
to state the length of time or to state "how long" the action took place. to emphasize the period of time the action took place
The Verb Tense - "Have" In all the simple tenses, the verb "have" can be used as the main verb. In all the perfect tenses the verb "have" is used as an auxiliary verb. When the verb "have" is used as the main verb, it is usually used only in the simple form (static verbs). The verb "have" can be used in the progressive tense, only in the present and future. The verb have can not be used in the past progressive tenses. Have as the Main Verb in Positive Sentences Subject I We Main Verb "Have" have /had/will have have /had/will have Continue the Sentence a car. a lot of homework.
You The cars Natalie Her father
have/had/will have have/had/will have has/had/will have has/had/will have
a nice house. new tires. a great time in the States. a very good job.
*have is used in the present simple tense. *has is used in the past simple tense. *will have is used in the future simple tense. Have as the Main Verb in Negative Subject I We They The car Our teacher My father Auxiliary verb do/did/will do/did/will do/did/will does/did/will does/did/will does/did/will Not not not not not not not Main Verb "Have" have have have have have have Continue the Sentence time to visit him. to cook dinner when I got home. a lot of time to visit Mary. a new paint job. a hard time teaching us. me spent a lot of money on candy.
*Do is used in the present simple tense with the following pronouns I. you, we, they, and plural nouns. *Does is used in the Present Simple Tense with the following pronouns he, she, it and plural nouns and uncountable nouns. Question with the verb "have" as the main verb Wh - word (if needed) When Why When Does/Did/Will Why Auxiliary Verb do/did/will Do/Did/Will do/did/will does/did/will our teacher does/did/will Subject I we they the car have your father Main Verb "Have" have have have have a hard time teaching us?. have so much candy in the car?. Continue the Sentence time to visit him? to cook dinner when we got home? little homework? to get a new paint job?
http://www.english-the-easy-way.com/English_ESL/English_Verb_Usage_Have.htm Future Verb Tenses Future Simple Verb Tense Future Simple Verb Tense is used: Decisions - to make decisions that are made at the time of speaking
We will eat dinner today at 6:00PM We will clean your room this week.
Desire - Willingness - to state desire or willingness for something or someone
The girls will be happy to go on holiday for a few weeks. I will be happy to help you today.
Facts - to state a fact about the future
My teacher will be happy, the whole class passed the test. The phone bill will be very very high, my father will be very upset.
Predict - to predicate a future event or action
I think it will rain this afternoon. My sister will be a great teacher.
Formal Statements - to make a formal statement about a future action or event
The president will make a public announcement on Tuesday at 8:00PM. The school will be closed for a few days.
Suggestions - to make suggestions or state ideas
We will be happy drive you to the store. Will we go to the store tonight or tomorrow morning.
Request - to make a request
Will you come with me to the store? You will do your homework now.
The structure of the future simple verb tense is outlined in the chart: Subject + Auxiliary Verb Will + Main Verb Verb in the base form -
How to build sentences using the future simple verb tense.
1. 2. 3. 4.
The auxiliary verb "will" is used with the future simple verb tense. The base form of the main verb is always used. For negative sentences "not" is added between the auxiliary verb "will" and the main verb. See chart. For questions the auxiliary verb "will" comes before the subject. See chart.
Positive Sentences Auxiliary Verb "will"
Subject I, We, They, You, He, She, It Singular Nouns Plural Nouns Uncountable Nouns Examples:
Main Verb
Continue the Sentence
will
base form of the verb
I will be at school to today. They will go to the doctor tomorrow. My dog will come home this evening. Your coffee will be cold if you don't drink it. The girls will be home at ten.
Negative Sentences Auxiliary Verb "will" Continue the Sentence
Subject I, We, They, You, He, She, It Plural Nouns Singular Nouns Uncountable Nouns Examples:
Not
Main Verb
will
not
base form of the verb
I will not be at school to today. They will not go to the doctor tomorrow. My dog will not come home this evening. Your coffee will not be hot if you don't drink it. The girls will not be home at ten o'clock.
Questions Auxiliary Verb "will" Continue the Sentence
Subject I, we, they, you, he, she, it plural nouns singular nouns uncountable nouns
Main Verb
Will
base form of the verb
Examples:
Will Will Will Will Will
I have time to go to the store? you be home next week? your friends help you clean your room latter? there be hot water when I come home tonight? someone buy some milk and cheese?
Future Simple Verb Tense "Going to The future simple verb tense "going to" is used in the following situations: Planed Events - When a future event that has been planed before the time of speaking.
I am going to Mexico in a few days. We are not going to work next week. They are going to university next year.
Predictions - To make a future prediction based on facts.
There is going to be a really big storm in a few hours. The test next week is going to be really hard. The puppies are cute. I am sure someone is going to adapt them.
Intentions - To state the something that is intended to take place in the future, in informal conversations.
I am going to be a rich person someday. We are going to pass the test. The puppies are going to make a big mess in house.
What is the structure of the simple future verb tense "going to"? Subject + Auxiliary Verb "to be" + Main Verb going to --
How to build sentences using the future simple verb tense "going to"?
1. 2. 3. 4.
The auxiliary tense "to be"is used with the future simple verb tense "going to". The base form of the main verb is always "going to". For negative sentences "not" is added between the auxiliary verb "to be" and the main verb "going to". See chart. For questions the auxiliary tense "to be" comes before the subject. See chart.
Positive Sentence Subject I He, She, It Singular Nouns Uncountable Nouns Examples: + Auxiliary Verb "to be" + Main Verb "going to" + Continue the Sentence + am are is + + + going to going to going to + + +
We, They, You, Plural Nouns + +
I am going to be at school to today. They are going to the doctor tomorrow. My dog is going to come home this evening. Your coffee is going be cold if you don't drink it. The girls are going to be home at ten o'clock.
Negative Sentences Auxiliary Verb + "to be" am are is + + + Main Verb "going + to" going to going to going to + + + Continue the Sentence
Subject I, He, She, it We, They, You Plural Nouns Singular Nouns Uncountable Nouns Examples:
+ + + +
Not not not not
+ + + +
I am not going to be at school to today. They are not going to the doctor tomorrow. My dog is not going to come home this evening. The girls are not going to be home at ten o'clock.
Questions Auxiliary Verb "To be" Am Main Verb "going to" going to Continue the Sentence
+ +
Subject I,
+ +
+ +
Are
we, they, you, plural nouns uncountable nouns he, she, it singular nouns
going to
Is
going to
Examples:
Am I going to the hospital next week? Are you going to be home next week? Are your friends going to help you clean your room latter? Is there going to be hot water when I come home tonight? Is someone going to buy some milk and cheese?
Future Continuous Verb Tense The future continuous verb tense is used to: Emphasize - to emphasize an action or an event that will be in progress at sometime in the future. Next week we will be asking in the mountains. Tomorrow my parents are coming to visit out new house. Events - for events or activity's that are planned for a future time. Specific Time - the specific time of the future event or the future activity can be stated. Approximate Time - the approximate time of the future event or the future activity can be stated. The time of an future event or the future activity doesn't have to be stated. Unplanned Future Events - "Will" is used to state desire to do something. The difference between "will" to state desire and "will" used with the future continues tense: "Will be" is used with the future continues tense. "Will" used without "be" is used to state desire. "Will" can also be used with the present continuous tense to state an unplanned event or action. When "will" is used with the present contentious tense "will" is followed by the verb + -ing.
Present Continues Tense with "Going To"- The present continues tense with "going to" & the future continues tense can be used interchangeable. That is the structure of the future continuous tense? Subject 1+ Auxiliary Verb will + Auxiliary Verb be + Main Verb verb + -ing
How to build sentences with the future continuous verb tense? The future continuous verb tense uses 3 kinds of verbs, 2 auxiliary verbs and 1 main verb.
In English, the auxiliary verb "to be" does not change to the subject See charts. The auxiliary verb "will" always stays in the base form. See charts. The -ing is added to the main verb is added to the end of the base form of the main verb.
Negative sentences are formed by adding "not" between the auxiliary verb "will" and the auxiliary verb "to be" and the main verb. See chart. For questions the order of the sentence is changed. The verb "to be" comes before, then the subject. See chart. Positive Sentences
Subject
Auxiliary Verb "Will"
Auxiliary + Verb "to be"
Main Verb
Continue the Sentence
I, We, They, You, He, She, It Plural Nouns Singular Nouns Uncountable Nouns
will
be
verb + -ing
Examples:
I will be at that party on Monday night. You will be working for the next few days. The children will be starting school next week. My mother will be coming to the States next month. The storm will be coming soon.
Negative Sentences Subject + Auxiliary Verb "will" + Not + Auxiliary Verb "to be" + Main Verb I ,We, They, You, He, She, It + will + not + be + verb + -ing Plural Nouns Singular Nouns Uncountable Nouns Examples:
I will not be coming to work next week. I will not be on vacationing in July. You will not be singing in the concert on Tuesday. The buses will not be running on Sunday, they are going on strike. My sister will not be going to Paris this summer. The wind will not be getting any stronger the storm is over.
Questions Mai n Ver b
Auxiliar y Verb "will"
Subject I, we, they, you, he, she, it plural nouns singular nouns uncountab le nouns
Auxiliar y Verb "to be"
Continue the Sentence
Will
be
verb + -ing
Examples:
Will Will Will Will Will Will
I be working this weekend? you be singing at the wedding tonight? we be sleeping in the hotel or at grandma's house? the dog be coming with us on the trip? you call us when you get home? the snow be stopping today?
Future Simple Perfect Verb Tense The future simple perfect verb tense is used: The future simple perfect verb tense often used with "by" and "not", "for" and "until" to state that the action or event will be completed at time in the future. The future simple perfect verb tense is used to state an action that occurs into the future until a later time in the future. To state an event or action that will finish before an other action event in the future. Rules for using the future simple perfect verb tense: The future simple perfect verb tense is used for actions that are non continuous. A specific time is usually stated or is understood. It is common to use the future simple perfect verb tense to clarify the order of 2 future events. The future simple perfct verb tense can't be used with "time claueses" such as when, while, "by the time", soon, before, after, if, unless, until etc. The future simple pefect verb tense is also known as the "future perfect verb tense". The future period of time if usually states :
Examples:
next year next week next month etc. the exact came can be stated the approximate can can be stated
We will have worked at the school 25 years next week. My brother will be tired when he gets here, because he will have fl owen 12 hours. The students will have finished all their exams tomorrow. I sure they will be happy
What is the structure of the simple future perfect verb tense? Subject = + Auxiliary Verb Will + Auxiliary Verb have + Main Verb Verb + -ed/V3-past participle = =
Building sentences with the simple future perfect verb tense.
1.
2. 3.
The future perfect verb tense uses 3 kinds of verbs, 2 auxiliary verbs and 1 main verb. - The auxiliary verb "will" does not changes according to the subject. - The auxiliary verb "have" always stays in the base form, and does not change form. -The main verb uses the past participle/V3 form. - Regular verbs -ed is add to the end of the verb's base form. - Irregular verbs use the past participle/V3. For negative sentences "not" is added between the auxiliary verb "Will" See chart. For questions the order of the sentence is changed. The auxiliary verb "will" comes first, then the subject. See chart.
Positive Sentences Auxiliary Verb "Will"
Subject I, We, They, You, He, She, It Singular Nouns Plural Nouns Uncountable Nouns Examples:
Auxiliary Verb "have"
Main Verb
Continue the Sentence
will
have
V3 past participle
On Sunday I have to work late. When I get home I will have eaten dinner. The test is in a week from tomorrow, I hope you will have prepared for it. Next week, we get our pay checks. We will have gotten paid, and we can go out to dinner. Please deliver the package after 6 o'clock in the evening; I will have arrived home by then. I will have taken all of my exams in a week from today.
Negative Sentences
Subject
Auxiliary Verb "Will"
Not
Auxiliary Verb "have"
Main Verb
Continue the Sentence
I, We, They, You, He, She, It Singular Nouns Plural Nouns Uncountable Nouns
will
not
have
V3/past participle
Examples: On Tuesday I will leave at eight o'clock in the morning, but will not have gotten to work in time for the meeting. My sister is coming to visit next week. I will not have moved into my new house by then. Next year I will not have seen my brother for 2 years. In I few weeks, the plants will not have grown enough to pick the fruit. Next month, I will not have worked long enough to get the bonus check.
Questions
Auxiliar y Verb "Will"
Subject I, we, they, you, he, she, it singular nouns plural nouns uncountable nouns
Auxiliar y Verb "have"
Main Verb
Continue the Sentence
Will
have
V3/past participle
Examples:
Will Will Will Will Will
I have worked here long enough to get a bonus check? you have saved enough money to come see me next year? the car have been fixed, by the time I come home from work? the train have arrived, by the time the time I finish work? the children have gone to sleep, when I call tonight?
Future Perfect Continuous Verb Tense The future perfect continuous verb tense is used to: emphasize how long an event will be in progress at a future time stress the the length of time of an event or action in the future is used to state the results of an action or event in the future. represent a continuous action that stated at some point, and continues into some point in the future state that results of a future action, after an other future action. (2 actions that will take place in the future, one action takes place before, the 2nd action)
Rules for using the future perfect continues verb tense: The future period of time if usually states :
next year next week next month etc. the exact came can be stated the approximate can can be stated
The period of time until the present point of time. The future perfect continuous verb tense is usually not used with static verbs. The future perfect continuous verb tense is also called the future perfect progressive tense. The future perfect continuous verb tense can't be used with "time clauses" such as when, while, "by the time", soon, before, after, if, unless, until etc. Examples:
In the fall I will have been studying here for 2 years. My son will have been in teaching for 10 years next month. The teacher will have been teaching my children for 5 years next month. The dogs will have been playing for 3 hours in 10 minutes. Tammy will be very tired when she comes home, because she will have been flying over 24 hours. What is the structure of the future perfect continuous verb tense?
The basic structure of the present continuous tense is stateded in the chart:
Subject + -
Auxiliary Verb will
+ -
Auxiliary Verb have
+ -
Auxiliary Verb + been
Main Verb -
verb + -ing How to build sentences using the future perfect verb continuous tense? The future perfect continuous verb tense uses 4 kinds of verbs, 3 auxiliary verbs and 1 main verb. - The auxiliary verb "will" does not change according to the subject. - The auxiliary verb "have" always stays in the base form. - -ing is added to the base form of the main verb. For negative sentences "not" is added between the auxiliary verb "will" and the main verb. See chart. For questions the order of the sentence is changed. The verb "will" comes first, then the subject. See chart.
Positive Sentences Subject + Auxiliary Verb "will" + Auxiliary Verb "have" + Auxiliary Verb "been" + Main Verb + Continue the Sentence I, We, They, You, He, She, it , Singular Nouns Examples: Plural Nouns Uncountable Nouns + will + have + been + verb + -ing
In ten minutes I will have been waiting 1 hour for the bus. We have been working here for 10 years in June. Robert will have been living in France for 1 year next month. We will have been saving money for many years, by the time you need to go to college. It will have been raining for a long time when the rain finally stops.
Negative Sentences
Subject
Auxiliary Verb "Will"
not
Auxiliary Verb "Have"
I, We, They, You, Plural Nouns He, She, It Singular Nouns Uncountable Nouns Examples:
will
not
have
I have not been waiting a long time. The cookies have not been baking 5 minutes. It takes them time before they are done. I have not been studying for many years; I guess it is time to go back to school. We have not been living in this house for 2 weeks, and already the walls are dirty. This car has not been working properly for the last few years, I think it is time to buy a new car.
Questions
Auxiliary Verb "Will"
Subject I, we, they, you, plural nouns he, she, it , singular nouns uncountable nouns
Auxiliary Verb "Have"
+ been + Verb ing
Will
have
+ been + Verb-ing
Examples:
Will I have been working here long enough to get an extra week vacation this summer? Will we have been living in the states long enough to get citizenship next year? Will the children have slept enough, if I wake them up when I come?
Present Continuous Verb Tense Used As A Future Tense Present Continuous Verb Tense is used to state future events or actions when it is clearly stated or understood that the action or event is in the future. Pre-arranged Plans -to describe planes that have be arranged before the time of speaking.
We are traveling to Europe in a few weeks. The girls taking the S.A.T. next week.
Informal Actions or Events - is used an informal actions or events
We are planning to watch T. V. tonight. The girls are singing on Friday night at the local club.
Personal Information - is used to for personal information
I am finishing my doctorate degree next year. We are moving to a new house next week.
Important -
it is not used for official purposes the subject of the sentence must be a person, not a thing the present continuous tense can't be used to predict a future event or action, based on a present event or action. static verbs are not used
English Verb Tenses Main Verbs Tenses What is a Main Verb Tense? The main verb tense states the action of the subject. The main verb can be the only verb in the sentence, but the main verb can also be used with an auxiliary verb or a verb. The auxiliary verb and the modal verb must be used with a main verb tense. The main verb tense is:
The main verb tense can be in its infinitive/basic form (simple past/v2), past participle/v3. The main verb tense states what the action of the subject. -ed -ing -s -es are some common endings that can be added to the main verb according to the tense. It is common that the main verb doesn't change form, because the auxiliary words change form. When using the continuous tense and the perfect verb tense auxiliary verb(s) are used with the main verb tense. When an auxiliary verb is used the main verb doesn't change form according to the subject. The main verb tense can change form when an auxiliary verb is used to according to the verb form. Examples:
The The The The The
cat eats fish. cats eat the fish cat has eaten the fish. cat ate the fish. cat has been eating the fish.
English Verb Tenses Group What is a verb tense group? A verb tense group consists of a main verb tense and an auxiliary verb or a verb. Any combination on of verbs can be used to create a verb tense group. Verb groups are needed in certain kinds of sentence structures according to the type of verb. Examples:
I am going to the store. The teachers have been teaching for many years. The have sung for a long time.
Auxiliary Verbs What are auxiliary verbs? 1. Auxiliary verbs (sometimes known as helping verbs) are verbs that are used to assist the verb. Auxiliary verbs can not be used without a main verb. Auxiliary Auxiliary Auxiliary Auxiliary verbs verbs verbs verbs can not be used with modal verbs. are used to make sentences negative. are used to ask questions. are used in the sentence structure of the verb sentence.
2. 3.
4. 5. 6. 1.
The 3 most common auxiliary verbs are:
Do - Does - Did Do is used with the present simple tense. Do-Does are used as part of the sentence structure for negative statements/sentences with the present simple tense Do- Does are used as part of the sentence structure for questions, with the present simple tense. Did is used with the past simple tense. Did is used as part of the sentence structure for negative statements/sentences with the past simple tense Did is used as part of the sentence structure for questions, with the past simple tense.
Be - Am - Is - Are -Was - Were Have - Has -Had
DO', 'BE' and 'HAVE' are the English auxiliary verbs used in a negative structure, a question or to show tense. DESCRIPTIONS OF ENGLISH AUXILIARY VERBS: 1. 'DO', 'DON'T', 'DOES' and 'DOESN'T' are used for questions and negatives in the Present Simple Tense, and 'DID' and 'DIDN'T' are used in the Past Simple Tense. 2. 'BE' is used with the Present Participle in Continuous (Progressive) Verbs. It is also used with the Past Participle in the Passive. 3. 'HAVE' is used with the Past Participle to form the Perfect Aspect. The Verb Tense "to be What is the English verb "to be"? The verb "to be" can be used as the main verb tense or as the auxiliary verb. The verb to be is used as the main verb tense to state that something or someone exists. Rules for using the verb tense "to be": The verb tense "to be" changes form according to the subject when used as both the auxiliary verb and the main verb. The verb "to be" changes form according to the subject when used as both the auxiliary verb or as the main verb. When the verb tense "to be" is used as a main verb tense it is used in the simple tense only. When the verb tense "to be" is the only verb, when used as a main verb. When the verb tense "to be" is used as the main verb tense. Negative statements/sentence use the word "not" without "do - does - did". - - - Questions are formed by putting the verb "to be:" before the subject. The verb "to be" is an irregular verb.
Verb Tense "to be" Subject Base Form am We, They, You, Plural Nouns He, She, It Singular nouns Uncountable nouns are is Simple Past/V2 was were was Past Participle/V3 been been was
What is the difference between ESL - EFL - ESOL? What the difference between ESL, EFL and ESOL? A common question is what is the difference between ESL and EFL? ESL - English as a Second Language - it is a term used when English is taught in a country where English is not the country's first language. ESL is usually taught by teachers whose native language is English.
EFL - English as a Foreign Language - Is a term used when English is taught in a country where English is not the country's first language. EFL is usually taught by teachers whose native language is not English. Modal Verbs Eveyone can understand Modal Verbs! What are model verbs? Model verbs are also called auxiliary verbs, helping verbs and model auxiliaries. Model verbs are not complete verbs, and they can only be used with a verb. The usage of model verbs: Model verbs stay in the base form - bare infinitive - the bare infinitive is the infinitive without "to" before the verb. The following model verbs are used to with the present tense: can, will, shall, ought to, must, need, may The following model verbs are used in the past tense: would, should, could, might Model verbs are used to answer questions in the short form yes, I do. yes, we can. No, I don't. Model verbs can be used as part of the grammar structure of the sentence, such as when used with the perfect tenses. When are model verbs used: Prediction - Will and Shall Will and shall can be used to state predict that an event or an action will take place or will occur The model verbs can used to make a prediction about an event or action about the future.
I think we will be able to go and see the move tonight. My mother thinks we will not get home be it starts to rain.
Requests - Offers - Suggestions - Can - Could - May - Shall To make requests, offers or suggestions can be stated with the model verbs Permission - Can - Could - May - Might Can, could, may and might are model verbs that can be used to give permission or deny permission to do something or to someone. Can I help you cook dinner? You may not watch T. V. after dinner.
Certainty - Possibility - Can - Might - may- Could - Shall -Can, might - and could are model verbs that can be used to state certainty and possibility. Do you think it might rain tomorrow night? I might be home before midnight. You can come over tonight if you would like to. Ability - Inability - Can - Could - Able to My father hopes that we will be able to go to the moves. I can not go to Europe with you. Rules for using verb tenses: Sentences using verbs do not use "auxiliary verbs". "Not" after the verb is used to make a verb negative, including when using the simple verb tenses. To make questions using verbs, the verb comes before the subject. Modal verbs do not change there form. "To" is not used after a verbs do have, except with "ought to". The main verb is always in its base form when used with a verb modal verbs stay in the base form - bare infinitive - the bare infinitive is the infinitive without "to" before the verb. The following modal verbs are used to with the present verb tense:
can, will, shall, ought to, must, need, may
The following modal verbs are used in the past tense:
would, should, could, might
modal verbs are used to answer questions in the short form
yes, I do. yes, we can. No, I don't.
Verb Tense "Can" How is the verb tense "can" used? The verb tense "can" is used as both an auxiliary verb and a modal verb? Can is almost always used with a main verb. Can is used to: Can't is used to state:
to request something to request a favor from someone
to state the something is not allowed to request something not be done
to ask for help to state the possibility of an event/activity to state the ability of someone/something
to state the inability of something or someone
to deny permission
to request permission from someone or for something to ask for permission from someone or for something Examples of the verb tense "can":
The cat can go to the store. Can I go to school late on Tuesday? You can't go to school late on Tuesday? We can't help you clean the house.
The structure of the verb tense "can": 1. 2. 3. When using as a verb or an auxiliary verb the verb tense "can" stays in its base form. Can doesn't change form according to the subject. Can is followed by a main verb tense. The main verb tense also stays in its base form. (The main verb tense that is used with can doesn't change form according to the subject.) Positive Sentences Negative Sentences Questions** Subject I -All subjects* We - All subjects* Can "Can" can can they not "Main Verb" go go go to the store to the store to the store
* All subjects is I, we, they, you, plural nouns, singular nouns and uncountable nouns. **Questions - Questions using the verb tense "can" the verb tense "can comes before the subject. English Verb Tense & The Use of "Could" How is the verb tense "could" used? The English verb "could" is used as both an auxiliary verb and a modal verb? Could is almost always used with a main verb tenes.
Could is used as the past tense of "can". Could is used to is used to request something in the present tense. Usually when could is used in the present tense, it is used to ask a question.
Examples:
Could the girls come with me to the store? I could not go to the moves last night, I had to study. We couldn't help you clean the house.
Structure of "could":
1.
When using as a model verb or an auxiliary verb the verb "could" stays in its base form.
2.
3.
Could doesn't change form according to the subject. Could is followed by a main verb. The main verb also stays in its base form. (The main verb that is used with could doesn't change form according to the subject.) Positive Sentences Negative Sentences Questions** Subject I We Could "could" could could they not "Main Verb" go go go to the store to the store to the store
* All subjects are: I, we, they, you, plural nouns, singular nouns and uncountable nouns. **Questions - When could is used to ask a question, could comes before the subject. The Verb Tense Tense Structure "Could" The Structure of the Verb Tense "could".
1.
2.
3.
When using as a verb or an auxiliary verb tense the verb "could" stays in its base form. Could doesn't change form according to the subject. Could is followed by a main verb. The main verb tense also stays in its base form. The main verb tense doesn't change form according to the subject. the verb "cou ld" coul d coul d they
--
Subject
"Main Verb Tense" go go go
Positive Sentences Negative Sentences Questions **
I We Could
no t -
to the store to the store to the store
* The subjects are I, we, they, you, plural nouns singular nouns and uncountable nouns. **Questions - When could is used to ask a question "could" comes before the subject. Wishes & Verb Tenses How do we use the grammar form "wish"? Wishes is used to state the desire of a situation to be different. Wishes can be used to used in the past, present and future. Rules for wishes: The verb tense is different then the time. Past Tense - uses the Past Perfect Verb Tense Examples:
I wish I had studied for my test last night. I wish my car hadn't broken down.
Present Tense - uses the Past Tense (were is used for all subjects, was is not used). Examples:
I wish it weren't raining all day. I wish I were rich.
Future Tense - after wish would is used. Examples:
I wish it would stop raining. I wish the people next door would lower there radio.
Modal Verbs and Wishes - When verbs are used with wishes the sentence structure is Modal Verb + Have + V3/Past Participle The Verb Tense - "Have" In all the simple tenses, the verb "have" can be used as the main verb. In all the perfect tenses the verb "have" is used as an auxiliary verb. When the verb "have" is used as the main verb, it is usually used only in the simple form (static verbs). The verb "have" can be used in the progressive tense, only in the present and future. The verb have can not be used in the past progressive tenses. Have as the Main Verb in Positive Sentences Subject I We You The cars Natalie Her father Main Verb "Have" have /had/will have have /had/will have have/had/will have have/had/will have has/had/will have has/had/will have Continue the Sentence a car. a lot of homework. a nice house. new tires. a great time in the States. a very good job.
*have is used in the present simple tense. *has is used in the past simple tense. *will have is used in the future simple tense. Have as the Main Verb in Negative Subject I We They The car Our teacher My father Auxiliary verb do/did/will do/did/will do/did/will does/did/will does/did/will does/did/will Not not not not not not not Main Verb "Have" have have have have have have Continue the Sentence time to visit him. to cook dinner when I got home. a lot of time to visit Mary. a new paint job. a hard time teaching us. me spent a lot of money on candy.
*Do is used in the present simple tense with the following pronouns I. you, we, they, and plural nouns.
*Does is used in the Present Simple Tense with the following pronouns he, she, it and plural nouns and uncountable nouns. Question with the verb "have" as the main verb Wh - word (if needed) When Why When Does/Did/Will Why Auxiliary Verb do/did/will Do/Did/Will do/did/will does/did/will our teacher does/did/will Subject I we they the car have your father Main Verb "Have" have have have have a hard time teaching us?. have so much candy in the car?. Continue the Sentence time to visit him? to cook dinner when we got home? little homework? to get a new paint job?
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Adjectives: Teacher: Morelba BriceñoDocument9 paginiAdjectives: Teacher: Morelba BriceñoLeon_77Încă nu există evaluări
- Mr. Robert's Amazing Compact English Grammar BookDe la EverandMr. Robert's Amazing Compact English Grammar BookEvaluare: 1.5 din 5 stele1.5/5 (5)
- AdjectivesDocument30 paginiAdjectivesACy YelÎncă nu există evaluări
- AdjectivesDocument3 paginiAdjectivesمحمد الأصفرÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comparative Sand SuperlativesDocument15 paginiComparative Sand SuperlativessamayeariasÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Use Adjectves Together.: AdjectivesDocument8 paginiHow To Use Adjectves Together.: Adjectivessalaudin_alayyubiÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Are Adjectives?Document8 paginiWhat Are Adjectives?Allan BÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Are Adjectives?Document8 paginiWhat Are Adjectives?Allan BÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Are Adjectives?Document8 paginiWhat Are Adjectives?Allan BÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 3 AdjectivesDocument14 paginiLesson 3 AdjectivesShaira Nicole PelaezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Order of AdjectivesDocument5 paginiOrder of AdjectivesJanine EspinedaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comparatives and SuperlativesDocument3 paginiComparatives and SuperlativesMouaci NwlÎncă nu există evaluări
- ADJECTIVEDocument8 paginiADJECTIVEABREHAMÎncă nu există evaluări
- RULES FOR ComparativeDocument3 paginiRULES FOR ComparativeAli AsadÎncă nu există evaluări
- AdjectivesDocument39 paginiAdjectivesRicky UrsabiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Examples of Adjectives and TheirDocument4 paginiExamples of Adjectives and TheirAngie MartinezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 10 Blog InglesDocument14 paginiUnit 10 Blog InglesLuis CoboÎncă nu există evaluări
- BCN Languages Grammar File Comparative and Superlative 1Document3 paginiBCN Languages Grammar File Comparative and Superlative 1tbilisisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comparatives and SuperlativesDocument2 paginiComparatives and SuperlativesSANTANABAZANELIMM389FM1Încă nu există evaluări
- Grammar: English - Form 3Document39 paginiGrammar: English - Form 3bellbeh1988Încă nu există evaluări
- Adjectives NotesDocument7 paginiAdjectives NotesLINEHELOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comparative and Superlative Adjectives: Noun (Subject) + Verb + Comparative Adjective + Than + Noun (Object)Document10 paginiComparative and Superlative Adjectives: Noun (Subject) + Verb + Comparative Adjective + Than + Noun (Object)sehamÎncă nu există evaluări
- SUPERLATIVE AND COMPARATIVE - ActivitiesDocument8 paginiSUPERLATIVE AND COMPARATIVE - ActivitiesBondfriendsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Report - AdjectiveDocument27 paginiReport - AdjectiveJessa Mae David Tuazon100% (1)
- Adjective or AdverbDocument27 paginiAdjective or AdverbNery SimmonsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nouns, Pronouns, Adjectives, Verbs, Adverbs (Notes)Document22 paginiNouns, Pronouns, Adjectives, Verbs, Adverbs (Notes)ika_nikan91% (11)
- Grammar Review Comparison: By: Betti Widianingsih, S.S.,M.HumDocument14 paginiGrammar Review Comparison: By: Betti Widianingsih, S.S.,M.HumAlif HaidarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tugas COMPARISONDocument15 paginiTugas COMPARISONMuhammad Irfan DzakyÎncă nu există evaluări
- SuperlativesDocument1 paginăSuperlativesotiliacamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adjectives Comparative SuperlativeDocument3 paginiAdjectives Comparative SuperlativeOmar EduardoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ingles Unidad 2Document20 paginiIngles Unidad 2Deiissy ChagalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Adjectives: AdjectiveDocument7 paginiTypes of Adjectives: AdjectiveWindi NininÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comparative and Superlative ExplanationDocument4 paginiComparative and Superlative Explanationapi-244557975Încă nu există evaluări
- 2023-2024 - Grade 5 1 - English Quiz 1-2 - HELPFUL TIPSDocument4 pagini2023-2024 - Grade 5 1 - English Quiz 1-2 - HELPFUL TIPSdaliclar466Încă nu există evaluări
- Comparative SuperlativeDocument4 paginiComparative SuperlativesdasdasdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Degree of ComparisonDocument3 paginiDegree of ComparisonMuhamad Jordi Juniarto83% (6)
- Noun - A Word That Names A Person, Place, Things, Ideas or An EventDocument15 paginiNoun - A Word That Names A Person, Place, Things, Ideas or An EventBernardo Villavicencio VanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comparative/superlative: 1-Syllable Adjectives: Add - Er To The AdjectiveDocument4 paginiComparative/superlative: 1-Syllable Adjectives: Add - Er To The AdjectiveandersonturisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Draft Handout English IntermediateDocument20 paginiDraft Handout English Intermediateandro prasetioÎncă nu există evaluări
- ADJECTIVESDocument8 paginiADJECTIVESDounia LaouarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Subject Verb AgreementDocument5 paginiSubject Verb Agreementmaisarah_rahimÎncă nu există evaluări
- English TipsDocument21 paginiEnglish TipsLaura HallÎncă nu există evaluări
- Functions of Adjectives: ExamplesDocument9 paginiFunctions of Adjectives: ExamplesКики Богојоска ШтабескаÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8 Parts of SpeechDocument31 pagini8 Parts of SpeechPASACAS, MARY ROSE P.Încă nu există evaluări
- Forming Comparative and Superlative AdjectivesDocument11 paginiForming Comparative and Superlative AdjectivesJasm SaadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adjectives 2019Document13 paginiAdjectives 2019ERNA JOSEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adjectives 2019Document13 paginiAdjectives 2019ERNA JOSEÎncă nu există evaluări
- SEE 5 Unit 6Document11 paginiSEE 5 Unit 6Almere AzurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Degrees of ComparisonDocument8 paginiDegrees of ComparisonUmaDevi Yarasu DeviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Text 2Document7 paginiText 2Daniela Ramos EduardoÎncă nu există evaluări
- AdjectivesDocument15 paginiAdjectivesSumithra KrishnanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comparative Superlative 2Document10 paginiComparative Superlative 2arnold aldoÎncă nu există evaluări
- English Notes Third Term 2021.Document5 paginiEnglish Notes Third Term 2021.Luisa RodriguesÎncă nu există evaluări
- English Project 13Document19 paginiEnglish Project 13Dinesh AhirwarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pronouns Dan AdjectiveDocument8 paginiPronouns Dan AdjectiveNancy IndahÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Comparative Adjective Is Used To Compare Two ThingsDocument4 paginiA Comparative Adjective Is Used To Compare Two ThingsAndrés Gu ValdezÎncă nu există evaluări
- LessonsDocument9 paginiLessonsIreneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kinds of NounsDocument57 paginiKinds of NounsAna GrapeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Uses of AdjectivesDocument6 paginiUses of AdjectivespauÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 PrsntPerfDocument3 pagini3 PrsntPerfNayeli0% (1)
- SBI2Document40 paginiSBI2bhaskarrao01Încă nu există evaluări
- Future Perfect Story 3Document7 paginiFuture Perfect Story 3jasnas7550% (2)
- NounsDocument56 paginiNounsFadjayota AdindaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Perfect AspectDocument20 paginiPerfect AspectLiannne WoodsÎncă nu există evaluări
- English PTDocument5 paginiEnglish PTJessa Mae BanquirigÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reflexive and Intensive ProununnnnnnDocument4 paginiReflexive and Intensive ProununnnnnnJerome MetierreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tema 22 Multiword VerbsDocument13 paginiTema 22 Multiword VerbsRachelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sentence Correction Solved 2000 To 2012Document14 paginiSentence Correction Solved 2000 To 2012Safdar AzizÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 - Rus' Textbook - Rus Russian BookDocument51 pagini1 - Rus' Textbook - Rus Russian BookMichael JobÎncă nu există evaluări
- English Grammar Notes For Competitive Exams PDF DownloadDocument43 paginiEnglish Grammar Notes For Competitive Exams PDF DownloadPradeep Naga100% (2)
- Characteristics of The Modern Korean Language. Phonetics, Morphology and Syntax.Document7 paginiCharacteristics of The Modern Korean Language. Phonetics, Morphology and Syntax.Tania ZazaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Group 4 Possessive and DemonstrativeDocument10 paginiGroup 4 Possessive and DemonstrativeVevencio BiabeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lang211 MidtermDocument4 paginiLang211 Midterm2 - GUEVARRA, KYLE JOSHUA M.Încă nu există evaluări
- English Textbook - 1.4Document12 paginiEnglish Textbook - 1.4Paul GillettÎncă nu există evaluări
- Terms of Grammar in Korean1Document4 paginiTerms of Grammar in Korean1Ira Kim Maala GatdulaÎncă nu există evaluări
- TUGAS 1 Mata Kuliah Bahasa InggrisDocument4 paginiTUGAS 1 Mata Kuliah Bahasa InggrisI WAYAN MIGOM MÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adjective Declensions: German For English SpeakersDocument1 paginăAdjective Declensions: German For English SpeakersMonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tier 1 Irregular VerbsDocument3 paginiTier 1 Irregular VerbsRobert GloverÎncă nu există evaluări
- French For BeginnerDocument5 paginiFrench For BeginnerGuruÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topnotch 2A Unit 1-5Document13 paginiTopnotch 2A Unit 1-5Alexander Iza100% (1)
- The Pronouns Y and enDocument14 paginiThe Pronouns Y and enNoah KimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rule #1 - 7 Quy tắc học tiếng Anh - Effortless EnglishDocument0 paginiRule #1 - 7 Quy tắc học tiếng Anh - Effortless EnglishEffortless English Fanclub Community - EEFC.VN100% (1)
- Lesson 5Document13 paginiLesson 5Iosifina100% (1)
- Narrative and Anecdote (Assignment)Document5 paginiNarrative and Anecdote (Assignment)IraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Colors in ArabicDocument2 paginiColors in ArabicErin Morgan100% (1)
- Elements of A Short StoryDocument12 paginiElements of A Short StoryCayo BernidoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Always Usually Regularly Often Sometimes Occasionally Seldom Rarely NeverDocument3 paginiAlways Usually Regularly Often Sometimes Occasionally Seldom Rarely NeverUmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practice 4. NounsDocument5 paginiPractice 4. NounsDariany del Carmen Pérez DíazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 9 Physiography of IndiaDocument16 paginiLesson 9 Physiography of IndiasanjeevreddyinÎncă nu există evaluări