Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Ulangkaji Akhir Menjelang SPM Answer
Încărcat de
Hee Ting WongTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Ulangkaji Akhir Menjelang SPM Answer
Încărcat de
Hee Ting WongDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Ulangkaji Terakhir Menjelang SPM STRUCTURE OF ATOM 1
CHEMISTRY
Table 1 shows the incomplete information about 3 atoms; X, Y and Z. Atom X Y Z Proton number 6 17 Table 1 (a) State the name of subatomic particles that are found in nucleus of an atom. Proton, neutron . [1 mark] (b) (i) What is the term of the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom? Nucleon number .. [1 mark] (ii) The total number of protons and neutrons for atom Z is 35. What is the number of neutron in atom Z? 35-17=18 .. [1 mark] (iii) Write the symbol for atom Z in the form of
35 A Z
Number of neutron 8 6
Number of electron 6 17
X.
Z 18 [1 mark] (iv) Draw the atomic structure of atom Z. 17 protons Z 2.8.7 18 neutrons
[1 mark]
Ulangkaji Terakhir Menjelang SPM (c)
CHEMISTRY
Atom X and atom Y are isotopes of an element. (i) What is the proton number of atom X? 6 [1 mark] (ii) Write the electron arrangement of atom Y. 2.4 [1 mark] (iii) What is valence electron of atom X? 4 [1 mark] (iv) Why atom X and atom Y has same chemical properties? They have same valence electron. [1 mark] (v) State one use of the isotope X in archaeology field. Estimate the age of the fossils [1 mark]
Diagram 2 shows the chemical symbols which represent three elements X, Y and Z The letters used are not the actual symbols of the elements. 9 X 4 15 Diagram 2 (a) (i) What is meant by proton number? Number of protons in the atom .. [1 mark] (ii) State the proton number for atom X 4 .. [1 mark] (b) What is represented by the number 32 for the element Y? 32 Y 15 31 Z
Ulangkaji Terakhir Menjelang SPM
CHEMISTRY
Nucleon number [1 mark] (c) (i) Atom Y and Z are isotopes. State the difference between the two atoms. Number of neutron // nucleon number [1 mark] (ii) State one use of isotopes in daily life. Carbon 14 estimate the age of fossils [1 mark] (d) (i) Write the electron arrangement of atom Y. 2.8.5 .. [1 mark] (ii) Determine the number of valence electron for atom Y. 5 .. [1 mark] (ii) Draw the electron arrangement for atom Z.
2.8.5
[2 marks]
Ulangkaji Terakhir Menjelang SPM 3
CHEMISTRY
Diagram 3.1 shows the arrangement of particles of substance X at different temperatures.
60 oC
Diagram 3
90 oC
(a) What is the physical state of substance X at (i) (ii) (b) 60 oC 90 oC : solid...................................... : liquid ......................................................... [2 marks] State the movement of particles of substance X at 60 oC. Vibrate and rotate at fix position , cannot move freely [1 mark] (c) Graph 3.2 shows the graph of temperature against time when substance X is heated from 60 oC to 90 oC. Temperature / oC 90 78 60 t0 t1 t2 Graph 3.2 (i) What is meant by melting point? Temperature at which solid change to liquid at certain pressure [1 mark] (ii) Based on Graph 3.2, state the melting point of substance X. 78 oC [1 mark] (iii) Explain why the temperature remains constant from t1 to t2. Heat absorbed is used to overcome the force of attraction between particles t3 Time / s
Ulangkaji Terakhir Menjelang SPM
CHEMISTRY
[2 marks] (d) (i) Substance X cannot conduct electricity in any state. State the type of particles of substance X. Molecules ................................................................................. [1 mark] (ii) Table 3.3 shows two substances. Magnesium oxide Carbon dioxide Table 3.3 Which substance has the same type of particles as substance X? Tick ( ) the correct answer. [1 mark]
CHEMICAL FORMULAE & EQUATIONS 4 (a) Diagram 4 shows that a magnesium atom is two times heavier compare to a carbon atom. Relative atomic mass of carbon is 12.
Carbon atoms Atom karbon Diagram 1 (i) Complete the following equation. Relative atomic mass ..
Magnesium atom Atom magnesium
= The average mass of one atom of an element 1/12 the mass of an atom of carbon-12 [1 mark]
Ulangkaji Terakhir Menjelang SPM
CHEMISTRY
(ii) One atom of element X is two times heavier than one magnesium atom. What is the relative atomic mass of element X? 48 ................................................... [1 mark] (b) A student heats 20 g of calcium carbonate strongly. It decomposes according to the equation below. CaCO3 CaO + CO2 (i) State the name of the products. Calcium oxide and carbon dioxide ... [1 mark] (ii) Describe the chemical equation in terms of quantitative aspect. 1 mol of calcium carbonate decomposes to form 1 mol of calcium oxide and 1 mol of carbon dioxide gas ... [1 mark] (iii) Calculate the mass of calcium oxide produced. [ Relative atomic mass: C = 12 ; O = 16 ; Ca = 40] Mol of CaCO3 = 20/100 = 0.2 mol Ratio: CaCO3 CaO From equation 1 1 From calculation 0.2 0.2 Mass of CaO = mol x molar mass of CaO = 0.2 x 56 = 11.2 g [3 marks] (iv) Calculate the volume of carbon dioxide produced at room conditions. [Molar volume of gas = 24 dm3 mol-1 at room conditions] Mol of CaCO3 = 20/100 = 0.2 mol Ratio: CO2 CaCO3 From equation 1 1 From calculation 0.2 0.2 Volume of CO2 = mol x molar volume = 0.2 x 24= 4.8 dm3 = 4800 cm3
[2 marks]
Ulangkaji Terakhir Menjelang SPM
CHEMISTRY
PERIODIC TABLE OF ELEMENTS & CHEMICAL BONDS 5 Diagram 5 shows the symbols of the atoms of element X, Y and Z. The letters used are not the actual symbols of the elements.
23
39
X
3 11
Y
19 Diagram 5
(a)
What is the valence electron of the atom of element X. 1 .......................... [1 mark]
(b)
(i)
Identify the position of element Y in the Periodic Table of Elements. Group 1, Period 3 ................ [1 mark]
(ii)
Explain why element Y is placed at the position identified in (b) (i). It has 1 valence electron, 3 electron shell filled with electron ................ [1 mark]
(c)
Element X, Y and Z can react with water. (i) Which of the element most reactive in their reactions with water. Z ................ [1 mark] (ii) Explain your answer in (c) (i). Z has largest atomic radius compare to Y and X. Attraction force between nucleus and valence electron becomes weaker. The valence electron is easier to be released to achieve stable octet electron arrangement. [3 marks] Write the chemical equation for the reaction between element that you choose in (c) (i) and water. 2Z + 2H2O 2ZOH + H2 ............... [2 marks]
(iii)
Ulangkaji Terakhir Menjelang SPM (d)
CHEMISTRY
Argon is placed at the same period with element Y in the Periodic Table of Elements. (i) Compare the atomic size argon and element Y. [ Given that proton number of argon is 18 ] Y has larger atomic size than Argon ............... [1 mark] (ii) Explain your answer in (d) (i). Argon has more protons compared to Y. Attraction force between nucleus and valence electron become stronger. Valence electrons are pulled nearer to the nucleus, smaller atomic size. [2 marks]
Diagram 6 shows part of the Periodic Table of Elements. Q, T, X, Y and Z do not represent the actual symbol of the elements.
3 Q 7
4 T 9
6 X 12
7 Y 14
8 Z 16
Diagram 6 Using the letters in the Periodic Table of the Elements in Diagram 3, answer the following questions. (a) (i) Write the electron arrangement of atom Q. 2.1 .. ............................... [1 mark] (ii) Write the formula of ion Q. Q+ .. ...............................
Ulangkaji Terakhir Menjelang SPM
CHEMISTRY [1 mark]
(b) State one element which exists as a diatomic molecule. Z .. ............................... [1 mark] (c) (i) Arrange the elements Q, T, X, Y and Z according to the atomic size in descending order. Q T X Y Z .. ............................... [1 mark] (ii) Explain your answer in (c) (i) based on nuclei attraction force on the valence electrons. Across the period from left to right, the number of proton of element increases. Attraction force between nucleus and valence electron become stronger. Valence electrons are pulled nearer to the nucleus, smaller atomic size. [ 2 marks] (d) X reacts with Z to form a compound. (i) What is the type of the compound formed? Covalent compound [1 mark] (ii) State one physical property of the compound formed. low melting and boiling point. OR cannot conduct electricity in any state. OR soluble in organic solvent, insoluble in water.
[ANY one]
[1 mark]
(iii) Draw the electron arrangement for the compound formed. Draw XZ2 [CO2]
[2 marks]
Ulangkaji Terakhir Menjelang SPM 7 (a)
10
CHEMISTRY
Element X reacted with oxygen to form a compound which cannot conduct electricity at any state. Suggest one example of element X. Write chemical equation between element X and oxygen.
Element X: Carbon dioxide X + O2 CO2
[3 marks]
(b)
Table 7 shows the proton number of elements P, Q and R. Element P Q R Proton number 6 (2.4) 11(2.8.1) 17(2.8.7) [6 marks]
Explain the formation of a compound that has high melting point.
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Electron arrangement of Q atom is 2.8.1 + A Q atom loss one electron to achieve stable electron arrangement to form Q ion. Electron arrangement of R atom is 2.8.7 A R atom receive 1 electron from Q atom to achieve stable octet electron arrangement to form R ion. + The Q ion and R ion are attracted by strong electrostatic force ionic compound, QR. Diagram
(c) + water Solution Y Can conduct electricity Change litmus paper
1.
U
+ Solvent V Solution Z Can not conduct electricity No change with litmus paper
Identify U and solvent V. Explain the differences between two solutions.
U is an ionic compound, for example, glacial hydrogen chloride, that soluble in water to form free moving Hydrogen and chloride ions that can conduct electricity in molten/aqueous state and change the blue litmus paper to red.
2. U is insoluble in organic solvent V, for example, propanone. So the ions are still in the fix position and cannot move freely. Thus, it cannot conduct electricity and no change the litmus paper. (d) (i) Sodium chloride Carbon dioxide
Sodium chloride Ionic compound Ionic bond Ions Carbon dioxide Covalent compound Covalent bond molecules
State the type of compound, type of bond and type of particles of two substances
Type of compound Bond Particles
(ii)
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8.
Explain the formation of carbon dioxide and draw the electron arrangement.
Atom Carbon has four valence electrons, with an electron arrangement of 2.4 It needs four more electrons to achieve the stable octet electron arrangement One atom of C contributes 4 electrons for sharing Atom O has six valence electrons, with an electron arrangement of 2.6 It needs two more electron to achieve the stable octet electron arrangement One atom of C share two pairs of electrons with two atoms of O Covalent compound of CO2 is formed. Diagram
Ulangkaji Terakhir Menjelang SPM
11
CHEMISTRY
7. Table 7.1 shows the electron arrangement of elements U, V and W.
Element U V W
Electron arrangement 2.6 2.1 2.8.1 Table 7.1
a) Based on the Table 7.1, b) i) Identify one metal and one non-metal element. Metal: W OR V; non metal: U [2 marks] ii) (iii) State the group and period of element W in the Periodic Table of Elements. Group 1, Period 3 [2 marks] The reaction between element U and W produces a compound. State one property for the compound formed. high melting and boiling point. OR can conduct electricity in molten/aquesous state. OR soluble in water, insoluble in organic solvent. [ANY one] Draw the electron arrangement for the compound formed. Draw ionic compound, W2U [3 marks]
b) Table 7.2 shows the observations of element V and element W when react with water. Element Unsur Observation Pemerhatian Element V Unsur V V water air Element V, moves slowly at random on the water surface with a little fizzing sound. The solution formed turns red litmus paper to blue.
Ulangkaji Terakhir Menjelang SPM
12
CHEMISTRY
Element W Unsur W W water air Element W, moves rapidly at random on the surface of the water with a hissing sound. The solution formed turns red litmus paper to blue. Table 7.2 Write the chemical equation when element V reacts with water. 2V + 2 H2O 2 VOH + H2 [3 marks] (ii) Compare the reactivity of elements V and W when react with water. Explain your answer. 1. W has higher reactivity compared to V when react with water. 2. W has larger atomic radius compare to V. 3. Attraction force between nucleus and valence electron becomes weaker. 4. The valence electron is easier to be released to achieve stable octet electron arrangement. [4 marks] (c) Diagram 7 show the set up apparatus used to compare the electrical conductivity of solutions P and Q. Bulb lights up
Mentol menyala
(i)
Bulb does not light up
Mentol tak menyala
Carbon electrode
Elektrod karbon
Solution Q
Solution P Larutan P Larutan Q
Diagram 7
Based on the observations in Diagram 7, (i) (ii) Identify the type of compound of solution P and solution Q. P: ionic compound; Q: covalent compound [2 marks] Explain why there is a difference in the observations. In molten/aqueous states, the ions in solution P can move freely to carry electrical charges => bulb lights up. Solution Q are Covalent compounds exist as molecules; there are no free moving ions, so they cannot conduct electricity in any state. [4 marks]
Ulangkaji Terakhir Menjelang SPM ELECTROCHEMISTRY 8
13
CHEMISTRY
(a) Table 8.1 show the set up of apparatus of two experiments to investigate electrolysis process by using different electrodes. Experiment
A
Apparatus set-up
Copper electrodes Copper(II) sulphate solution
Carbon electrodes II Elektrod karbon Copper(II) sulphate solution
A
Table / Jadual 8.1 Compare and contrast Experiment I and Experiment II. Include in your answer, the observations at the anode and cathode, the name of the products formed at the anode and cathode and half equations for the reactions at the electrodes in both cells. [10 marks] (b) A student intends to electroplate an iron spoon with copper to prevent it from rusting. Design a laboratory experiment to electroplate the iron spoon. Your answer should consist of the following Procedures of the experiment. A labelled diagram showing the set up of apparatus. Half equations for the reactions at both electrodes. Observation at both electrodes [8 marks]
Ulangkaji Terakhir Menjelang SPM a) Observation
14 Experiment I Experiment II
CHEMISTRY
1 Anode: copper electrode dissolve// becomes thinner 3a) Cathode: Brown solid is deposited // Copper electrode becomes thicker.
2) Anode: colourless bubbles gas are released. 3b) Cathode: Brown solid is deposited // Copper electrode becomes thicker.
Products at
4. Anode:copper (II) ions 6a)Cathode: copper metal
5. Anode: oxygen gas 6b)Cathode: copper metal 8. Anode: 4OH- O2 + 2 H2O + 4e9b) Cathode: Cu2+ + 2e-Cu
Half Equation
7.Anode: Cu Cu2+ + 2e9a)Cathode: Cu2+ + 2e-Cu
b) Chemicals: 1.A: Battery, 250 cm3 beaker, connecting wires with crocodile clips, ammeter, switch, rheostat. M: 1 mol dm-3 silver nitrate, AgNO3 solution, silver plate, iron spoon, sandpaper. Procedure: 2. Iron ring is then connected to the negative plate on the battery 3. silver plate is connected to the positive terminal of the battery//Iron ring is made as cathode while silver plate is made as anode 4. Both plates are immersed into the silver nitrate solution. 5. The circuit is completed. Diagram:
6. Functional apparatus 7. Label (silver plate , Silver nitrate solution ,Iron spoon)
Silver plate Dilute Silver nitrate solution Half equation: 8. Cathode: Ag+ + e Ag Observation: 10. Cathode: Grey /silvery solid is deposited 11. Anode: silver become thinner//dissolved 9. Anode : Ag Ag+ +e
Ulangkaji Terakhir Menjelang SPM 7
15
CHEMISTRY
Diagram 7.1 shows the set-up of apparatus to investigate the electrolysis of magnesium chloride 1.0 mol dm-3 solution.
Carbon electrodes
Magnesium chloride 1.0 mol dm-3
A Diagram 7.1 (a) (i) Based on Diagram 7.1, state the name of the products at the cathode and the anode. Explain your answer in term of factor that affects discharge of ion. [8 marks] Predict the product at anode and cathode if magnesium chloride 1.0 mol dm-3 solution is replace by magnesium chloride 0.0001 mol dm-3 solution. [2 marks]
(ii)
(b)
Diagram 7.2 shows the set up of apparatus when cell X is combined with cell Y. V
Copper plate
Copper plate
Magnesium plate
Copper(II) sulphate solution
Cell X
Diagram 7.2
Cell Y
Compare cell X and cell Y base on ; the name of the cells, energy conversion, the observations and half equations for the reactions at the electrodes in both cells. . [10 marks]
Ulangkaji Terakhir Menjelang SPM 2. a)i) Ions Attracted to Ions selectively disharged Products Factor
16 Cathode (-ve) 1. Mg2+, H+ 3. H+ 5. Hydrogen gas 7. Hydrogen ion is located lower position in the ECS, easily discharged 2 H+ + 2e-H2 Colourless bubbles gas produced Anode (+ve) 2. OH-, Cl4. Cl6. Chlorine gas 8. The concentration of chloride ions is higer, selectively discharged. 2 Cl- + 2e-Cl2
CHEMISTRY
2 2 2 2
Half Equation Observation
Greenish yellow bubble gas produced
ii)
Anode: Oxygen gas; Cathode: hydrogen gas
b) Name of the cell Energy conversion Observation
Cell X 1. Electrolytic cell 3. Electrical chemical 5. Anode(P): copper plate dissolves // thinner 6. Cathode(Q): brown solid deposited Half equation 9.Anode: Cu Cu2+ + 2e10)Cathode: Cu2+ + 2e-Cu
Cell Y 2. Chemical / Voltaic cell 4. Chemical electrical 7. Anode (S): magnesium plate dissolved 8. Cathode (R): brown solid deposited 11. Anode: Mg Mg2+ + 2e12. Cathode: Cu2+ + 2e-Cu 2 2 Max 10 2 2 2
Ulangkaji Terakhir Menjelang SPM ACIDS AND BASES 5 (a)
17
CHEMISTRY
Diagram 1 shows the observation in test tube I and test tube II when hydrogen chloride in tetrachloromethane and hydrogen chloride in water are reacted with zinc powder.
Test tube
II
Apparatus set-up Susunan radas Hydogen chloride in tetrachloromethane + zinc powder Observation No change. Diagram 1 (i) State the ion that causes an acid shows its acidic properties. Hydrogen ion ........... [1 mark] (ii) Explain why the differences in observation in test tube I and II. Water enables hydrogen chloride to ionize to form hydrogen ions to react with zinc powder to produce hydrogen gas. In tetrachloromethane, hydrogen chloride still exist as molecules, no reaction with zinc. [2 marks] (iii) State the name of the gas produced in test tube II Hydrogen gas. ........... [1 mark] (iv) Write the chemical equation for the reaction between zinc and hydrochloric acid. 2 HCl + Zn ZnCl2 + H2 ........... [2 marks] Hydogen chloride in water + zinc powder Bubbles of gas are produced.
Ulangkaji Terakhir Menjelang SPM (b)
18
CHEMISTRY
Table 2 shows the information of the solution A, solution B and solution C. Solution of A, B and C might be an acid and an alkali. Solution Larutan A B C Information Maklumat Ionises completely. The solution remain colourless when phenolphthalein is added. Ionises partially. The solution remain colorless when phenolphthalein is added. Ionises completely. The solution turn to pink when phenolphthalein is added. Table 2 (i) Which solution has the lowest pH? Solution A [1 mark] (ii) Give a reason for your answer in (b) (i). It is strong acid that ionises completely. [1 mark] (iii) Vinegar consists of an ethanoic acid. Describe a chemical test to verify the acid without using an indicator. Add a little zinc powder into the test tube contains the vinegar. Colourless bubbles gas released that give a pop sound when a lighted wooden splinter is near to the mouth of the test tube. [2 marks]
Hydrochloric acid, HCl is a strong acid. Table 4.1 shows two solutions of hydrochloric acid, HCl with different concentration. Solution A B Concentration / mol dm-3 1.0 0.001 Table 4.1 pH 1.0 3.0
Ulangkaji Terakhir Menjelang SPM (a) what is meant by acid ?
19
CHEMISTRY
Substance that ionizes in water to produce hydrogen ions and give the pH value below 7.0. [1 mark] (b) pH value of the solution A and B are different. Explain why. In solution A, the concentration is higher compared to solution B. The higher the concentration, the number of hydrogen ions per unit volume is higher, thus pH value is lower. [3 marks] Diagram 4.2 shows the set-up of apparatus for titration of 25 cm3 of 1.0 mol dm-3 sodium hydroxide solution with 1.0 mol dm-3 sulphuric acid, using phenolphthalein as indicator.
(c)
Solution A
25 cm3 of 1.0 mol dm-3 sodium hydroxide solution Diagram 4.2 (i) State the colour change of the solution in the conical flask at the end point. Pink to colourless. ... [1 mark] State the type of the reaction occurred. Neutralization. ... [1 mark] (iii) Write the chemical equation for the reaction. H2SO4 + 2 NaOH Na2SO4 + 2 H2O ... [1 mark] (iv) Calculate the volume of sulphuric acid needed to neutralise the sodium hydroxide solution.
M a Va a M b Vb b
(ii)
Ma = 1.0, Va = ?, Mb = 1.0, Vb = 25, a =1, b = 2 Mb = 12.5 cm-3
[3 marks]
Ulangkaji Terakhir Menjelang SPM SALT 7 (a)
20
CHEMISTRY
A student has carried out an experiment to construct an ionic equation for the formation of lead(II) iodide. Seven test tubes of the same size were labelled 1 to 7. A fixed volume of 5.0 cm3 of 1.0 mol dm-3 potassium iodide solution was placed in each test tube. 0.5 cm3 of 1.0 mol dm-3 lead(II) nitrate solution was added into test tube 1, 1.0 cm3 into test tube 2 and so on until 3.5 cm3 was added into test tube 7. The heights of the precipitate formed in each test tube were measured. The results are shown in Table 7.1 Test tube Volume of 1.0 moldm lead(II) nitrate solution / cm3
-3
1 0.5 1.1
2 1.0 2.2 Table 7.1
3 1.5 3.4
4 2.0 4.4
5 2.5 5.5
6 3.0 5.5
7 3.5 5.5
Height of precipitate /cm
(i)
Based on Table 7.1, plot a graph of the height of the precipitate against volume of lead(II) nitrate solution on the graph paper provided. [3 marks] Determine the volume of lead(II)nitrate solution that had reacted completely with 5.0 cm3 of 1.0 mol dm-3 potassium iodide. 2.5 cm3 [1 mark] Using the volume obtained in (a) (ii), calculate the number of moles of lead(II) ions and iodide ions that are required for the formation of lead(II) iodide. Number of mol of lead (II) ions = MV 1.0(2.5) 0.0025 mol
1000 1000 MV 1.0(5) Number of mol of iodide ions = 0.005 mol 1000 1000
(ii)
(iii)
Then, calculate the number of moles of iodide ions that has reacted with 1 mol of lead(II) ions. 0.0025 mol of lead(II) ions reacts with 0.005 mol of iodide ions, 1.0 mol of lead (II) ions reacts with 2.0 mol of iodide ions. [4 marks] (iv) Write the ionic equation for the formation of lead(II) iodide. Pb2+ + 2 I- PbI2
[2 marks]
Ulangkaji Terakhir Menjelang SPM (b)
21
CHEMISTRY
Diagram 7.2 shows a series of reactions for compound A. Compound A is insoluble in water. Colourless gas B Compound A Heat turns lime water (Green powder) + sulphuric acid
Black powder C
Colourless gas B Blue solution D
turns lime water
(i)
Diagram 7.2 State the name of substances A , B , C and D. [4 marks] A: Copper (II) carbonate; B: carbon dioxide; C: copper (II) oxide; D: copper (II) sulphate State the ion presence in solution D that give the blue colour. Describe a chemical test to verify the ion. [3 marks] Copper (II) ions. Add NaOH until excess into the solution, a blue precipitate is formed, Cu2+ is present// Add a little NH3 into the solution, a blue precipitate is formed. Excess NH3, the blue precipitate dissolved to form dark blue solution, Cu2+ is present. Why does gas B turns lime water milky? Write the chemical equation for the reaction occurred.
(ii)
(iii)
[3 marks]
Carbon dioxide gas reacts with calcium hydroxide (limawater) to form calcium carbonate and water. CO2 + Ca(OH)2 CaCO3 + H2O
Ulangkaji Terakhir Menjelang SPM 9
22
CHEMISTRY
Diagram 9 shows a series of reaction starting from lead(II) carbonate, PbCO3. Solution X Larutan X Heat panaskan Gas Y Crystallisation Penghabluran Solid X Pepejal X Diagram / Rajah 9 (a) Based on Diagram 9 : Identify gas Y. Describe a chemical test to verify gas Y. Y: carbon dioxide gas. Bubbles the gas Y into the limewater. The limewater turs milky. Describe a chemical test to determine the presence of anion in the solution X. - Anions: Nitrate ion. - Add 2 cm3 of dilute sulphuric acid and 2 cm3 of iron (II) sulphate solution into the solution - Concentrated sulphuric acid is added slowly along the wall of the test tube - Brown ring is formed shows the presence of nitrate ion. Compare and contrast the observation when solid X and lead(II) carbonate, PbCO3 are heated. 2 Pb(NO3)2 2 PbO +4 NO2 + O2 Brown solid when hot, yellow solid when cold is formed, Brown gas which turns moist blue litmus red released. Another gas released relighted glowing splinter. PbCO3 PbO + CO2 Brown solid when hot, yellow solid when cold is formed. A gas turns the limewater milky released.
PbCO3 + HNO3
Gas Y
+ H2O
PbO +
MANUFACTURED SUBSTANCES 1 (a) Diagram 1.1 shows ammonium sulphate formed from the reaction between substance X and substance Y. Substance X is produced from Contact process whereas substance Y from Haber process. Contact process Proses Sentuh X Ammonium sulphate Ammonium sulfat Haber process Proses Haber Y
Ulangkaji Terakhir Menjelang SPM
23
CHEMISTRY
(i)
Diagram / Rajah 1.1 State the name of substance X and substance Y. X : sulphuric acid Y : ammonia [2 marks]
(ii)
State one use of ammonium sulphate in agriculture field. As fertilisers [1 mark]
(iii)
Write the chemical equation for the reaction between substance X and substance Y. H2SO4 + 2 NH3 (NH4)2SO4 [2 marks]
(b)
Diagram 1.2 shows the structure formula of a polymer.
H C H
Cl C H n
Diagram /Rajah 1.2 (i) State the name of the polymer. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) [1 mark] (ii) Draw the structure formula of it monomer.
H C H
Cl C H [1 mark]
Ulangkaji Terakhir Menjelang SPM (iii)
24
CHEMISTRY
Disposal of the polymer by burning is not suitable. Give a reason. Cause air pollution [1 mark]
(iv)
The polymer is not suitable to be buried for disposing. Give a reason. It non-biodegradable s [1 mark]
(v)
Suggest how to solve the problems in (b) (iii) and (b) (iv). Recycle. [1 mark]
(b)
There are four types of glasses that are used in our daily lives. (i) Name the major component of glass. Silica // silicon dioxide ......... ..... [1 mark] (ii) Table 2 shows three types of glasses and their uses. Complete the table. Type of glass/ Jenis kaca Borosilicate glass Kaca borosilikat Lead glass Soda-lime glass
Uses / Kegunaan Cookware / Alatan memasak Laboratory glassware / Alatan kaca makmal Decorative lamp /Lampu hiasan Prism / Prisma Bottle / Botol Mirrors / Cermin Table 2 [2 marks]
(iii)
Why is borosilicate glass suitable to make cookware and laboratory glassware? Withstand high temperature [1 mark]
Ulangkaji Terakhir Menjelang SPM 1
25
CHEMISTRY
Diagram 1 shows railway tracks and the arrangement of atom in alloy that made the railway tracks.
Atom M
Atom iron /Atom ferum Alloy X / Aloi X Diagram / Rajah 1 (a) State the name of alloy X. Steel ..... [1 mark] (b) State the name of atom M. Carbon ..... [1 mark] (c) (i) Draw the arrangement of atom in pure iron.
[1 mark] (d) Explain the difference of hardness of alloy Y and pure iron 1. In pure iron, the layer of atoms are arranged in orderly manner//same size 2. easily slides over each other when external force is applied on them. 3. The different size of foreign atoms in alloy are disrupt the orderly arrangement of atoms // prevent the layers of atom from slide each other when external force is applied.
Ulangkaji Terakhir Menjelang SPM RATE OF REACTION 2
26
CHEMISTRY
Diagram 2 shows the set-up of apparatus to study the rate of reaction between hydrochloric acid with sodium tiosulphate solution. Observer eye
250 cm3 conical flask
Sodium thiosulphate solution + hydrochloric acid
sign X Diagram 2
White paper
In this reaction, a 250 cm3 conical flask contained 50 cm3 of 0.2 mol dm-3 sodium thiosulphate solution, Na2S2O3 is placed on a white paper marked with the sign. X 5.0 cm3 of 2.0 mol dm-3 hydrochloric acid was added to the sodium thiosulphate solution and the mixture swirled. At the same time the stopwatch was started. The time is taken as soon as the sign is no longer X visible.
(a)
In this reaction, a precipitate is formed. What is the colour of the precipitate? Pale yellow .. [1 mark]
(b)
Calculate the number of moles of HCl and the number of moles of Na2S2O3 used in the experiment. Number of mol of HCl = MV 2.0(5) 0.01 mol
1000 1000
Number of moles of Na2S2O3 = MV 0.2(50) 0.01 mol
1000 1000
[2 marks]
Ulangkaji Terakhir Menjelang SPM (c)
27
CHEMISTRY
The chemical equation for the reaction occurred in this reaction is : Na2S2O3 + 2HCl 2NaCl + S + SO2 + H2O Based on the calculation in (b) and the chemical equation above, calculate the mass of the precipitate formed. [Given that the relative atomic mass of S = 32] Ratio: HCl S From equation 2 1 From calculation 0.01 0.005 Mass of S = mol x molar mass = 0.005 x 32= 0.16 g [2 marks]
(d)
(i)
State two factors that affect the rate of reaction in this experiment. Temperature of sodium thiosulphate solution, concentration of acid / sodium thiosulphate [2 marks]
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 9
By using any one of the factor that you are stated in (d) (i), explain how the factor that you are stated in (d) (i) affect the rate of reaction. Higher temperature will increase the kinetic energy of thiosulphate ions. Frequency of collisions between the H+ ion and thiosulphate ions increases. More collisions can overcome the activation energy. More effective collisions can be produce by thisulphate ion and hydrogen ion. [4 marks] Higher rate of reaction when temperature is higher. (a) Table 9 shows the data from Experiment I, Experiment II and Experiment III that were carried out to investigate the factors that affects the rate of reaction. Temperature /0C 30 Time taken for all the magnesium to dissolve /s 50
(ii)
Experiment
Reactants Excess hydrochloric acid + 0.2g magnesium ribbon Excess hydrochloric acid + 0.2g magnesium ribbon Excess hydrochloric acid + 0.2g magnesium ribbon + copper(II) sulphate solution
II
40
20
III
40
15
Ulangkaji Terakhir Menjelang SPM
28 Table 9
CHEMISTRY
(i)
Write the chemical equation for the reaction between magnesium and hydrochloric acid. Calculate the maximum volume of hydrogen gas produced. [ Relative atomic mass : Mg =24 ; molar gas volume : 24 dm3 mol-1 at room condition ] Mg + 2 HCl MgCl2 + H2 Number of mol of Mg = Ratio: From equation From calculation Mg 1 0.0083 H2 1 0.0083
mass 0.2 0.0083 mol molar mass 24
Volume of gas = mol x molar volume = 0.0083 x 24= 0.2 dm3 = 200 cm3 [5 marks] (ii) Compare the rate of reaction between Experiment I and Experiment II or
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
With reference to collision theory , explain why there is difference in the rate of reaction. Experiment I and Experiment II 1. Exp II has a higher ROR than Exp I. 2. Higher temperature will increase the kinetic energy of hydrogen ions and magnesium atom. 3. Frequency of collisions between the H+ ion and magnesium atom increases. 4. More collisions can overcome the activation energy. 5. More effective collisions can be produce by Magnesium and hydrogen ion. 6. Higher rate of reaction when temperature is higher. Experiment II and Experiment III. Exp III has a higher ROR than II Catalyst provides an alternative pathway, which required lower activation energy. Catalyst lowers the activation energy of a reaction. More collisions between H+ ion and magnesium atom can overcome the lower activation energy. Frequency of effective collisions increase. Hence, a higher rate of reaction with the presence of catalyst. [5 marks] (b) By using either the factor of size of reactant or concentration, describe an experiment how this factor affecting the rate of reaction. [10 marks]
Ulangkaji Terakhir Menjelang SPM CARBON COMPOUND 1
29
CHEMISTRY
Diagram 1 shows the structural formula of two of hydrocarbons. H C H Ethene Diagram 1 (a) State the name of the homologous series in which compound Y is placed. Alkane .. [1 mark] (b) Write the general formula of the homologous series that you are stated in (a). CnH2n+2 , n=1,2,3 .. [1 mark] (c) Write the molecular formula of compound Y C2H6 .. [1 mark] (d) What is observation when bromine water is added to ethene ? Brown bromine water decolourises. .. [1 mark] (e) State the type of reaction when bromine water is reacted with ethene. Addition reaction // bromintation .. [1 mark] (f) (i) State the name of the products formed when ethene burnt completely in excess oxygen. Carbon dioxide and water ... [1 mark] (ii) Write the chemical equation for the reaction in (f) (i). C2H4 + 3 O2 2 CO2 + 2 H2O ... [2 marks] H C H H H C H H C H H
compound Y
Ulangkaji Terakhir Menjelang SPM 10
30
CHEMISTRY
Diagram show structural formula of four hydrocarbons.
(a) (b)
(c)
Which two of structural formulae are isomer. Explain your answer. B and C. They have same molecular formula but different structural formula. Choose one hydrocarbon above, state the products formed when the hydrocarbon is burning and write the equation involved. A: Products: carbon dioxide and water C4H8 + 6 O2 4 CO2 + 4 H2O Describe a chemical test how to differentiate hydrocarbon A and D. 1 cm3 of liquid bromine is added into a test tubes containing A and D. A decolourise the brown bromine water. But D does not decolourise the bromine water Describe the preparation of ester ethylethanoate 1. 2 cm3 of ethanoic acid is poured into a test tube. 2. 4 cm3 of ethanol is added into ethanoic acid. 3. By using dropper, few drops of concentrated sulphuric acid are added slowly into the mixture and shaken. 4. the mixture is heated until boil. 5. the content is poured into a beaker half filled with water. 6. ethylethanoate is formed on the top of the water layer.
(d)
Ulangkaji Terakhir Menjelang SPM OXIDATIOAN & REDUCTION 5
31
CHEMISTRY
Diagam 5 shows the set-up of apparatus to investigate the reaction between iron(II) sulphate solution and acified potassium dichromate(VI) solution through the transfer of electrons at a distance.
Diagram 5
(a)
What is the colour of iron(II) sulphate solution? Pale green .. [1 mark]
(b)
(i)
Write the half equation for the reaction occur at X. Fe2+ Fe3+ + e- ... [1 mark]
(ii)
State the change in oxidation number of iron. +2 to +3 ... [1 mark]
(c)
The incomplete half equation occur at Y is : Cr2O72- + 14 H+ Complete the equation. + 6e 2 Cr3+ + 7 H2O [1 mark] [1 mark]
(d)
On the diagram above, show the direction of electrons flow.
Ulangkaji Terakhir Menjelang SPM (e) You are provided with the following : (i) Bromine water Potassium iodide solution Carbon electrodes Beaker Porous pot Connecting wire
32
CHEMISTRY
By using the given materials and apparatus, draw the set-up of apparatus to investigate the redox reaction through transfer of electron at a distance.
2 marks] (ii) On your diagram in (e) (i), indicate the positive and negative terminal. [1 mark] (iii) State the change in oxidation number for bromine in this reaction. 0 to -1 ... [1 mark] 5. Diagram 5 shows the set-up of apparatus to investigate the reaction occurred in test tubes A and B.
Diagram 5
Ulangkaji Terakhir Menjelang SPM (a) (i) Based on test tube A,
33
CHEMISTRY
Name the reaction occurred. Redox reaction ............................................................................................... [1 mark] Write the ionic equation for the reaction. Cl2 + 2 Fe2+ 2 Cl- + 2 Fe3+ ..................................................................... [2 marks]
(ii)
(iii)
State a chemical test to verify the product formed. Add Potassium thiocyanate, KSCN solution, a blood red solution produced, show the present of Fe3+ ions. [2 marks]
(b)
Based on test tube B, (i) State the observation involved. No dark blue precipitate formed......................................................... [1 mark] (ii) Experiment is repeated by using copper to replace zinc. State the observation involved. A lot of dark blue precipitate formed. [1 mark]
(c)
Compare the answer in (b)(i) and (b) (ii) and explain why there is a difference in the observation.
When two metals are in contact with each other, the more electropositive metal will loss electrons (undergoes oxidation) and become corroded, and the less electropositive metal will be protected from being corroded. [2 marks] (d) When iron is exposed to water and oxygen, it rusts easily. State one method to prevent the rusting of iron. Alloying .................................. [1 mark]
Ulangkaji Terakhir Menjelang SPM
34
CHEMISTRY
THERMOCHEMISTRY (a) Diagrams 10.1 and 10.2 show two energy level diagrams. 10 Energy
Mg + FeSO4 H= - 200 kJ
Energy
CaCO3 + 2NaCl
H= + 12.6 kJ
MgSO4 + Fe
CaCl2 + Na2CO3
Diagram 10.1 (i)
Diagram 10.2
Compare both the energy level diagrams above. Your explanation should include the following : ionic equations type of chemical reactions energy content of reactants and products Diagram 10.1 Diagram 10.2 Ionic equation Mg + Fe2+ Mg2+ + Fe Ca2+ + CO32- CaCO3 Chemical reaction Displacement of metal Precipitation reaction Energy content Energy content of reactants is Energy content of reactants is higher than products lower than products [6 marks] Based on Diagram 10.1, calculate the change in temperature of the solution if excess magnesium powder is added to 50 cm3 of 0.2 mol dm-3 iron(II) sulphate solution. [Specific heat capacity of solution : 4.2 J g -1 oC-1] Number of mol = 0.2(50)/1000 = 0.01 mol H =
(ii)
Q Q => Q = 200000 x 0.011 = 2000 J mol 0.001
Q = mc => = 2000/50(4.2) = 9.5 oC (b) [3 marks] Table 2.2 shows the heat released for Experiment I, II and III using different acid that has been reacted with sodium hydroxide solution. Experiment Chemical Equation I HCl + NaOH NaCl + H2O II III CH3COOH + NaOH CH3COONa + H2O H2SO4 + 2NaOH Na2SO4 + 2H2O Heat released (kJ) 57 54 114
Table 2.2 Based on Table 3.2, explain the difference in heat released between :
Ulangkaji Terakhir Menjelang SPM (i) (ii)
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7.
35
CHEMISTRY
Experiment I and Experiment II Experiment I and Experiment III
The heat of reaction in Experiment I is lower than that of Experiment III Hydrochloric acid is a monoprotic acid mol of hydrochloric acid ionises completely in water to produce 1 mol of hydrogen ion HCl H+ + ClSulphuric acid is a diprotic acid mol of sulphuric acid ionises completely in water to produce 2 mol of hydrogen ions. H2SO4 2H+ + SO42Therefore, the heat of neutralisation of sulphuric acid is twice as much as the heat of neutralisation of hydrochloric acid
8. (c)
[6 marks] Describe a laboratory experiment to determine the heat of displacement of metal by a more electropositive metal. In your description, include the following aspects: Materials and apparatus needed Procedure of experiment A table to collect data Calculation method [10 marks]
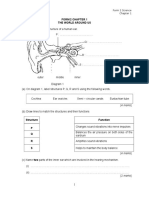
CONSUMER (a) Diagram 8.1 shows the structure of anion parts of a soap and a detergent. These anions consist of part 8 A and part B as shown in the diagram. Anion of a soap
Anion of a detergent
Part A Diagram 8.1 (i)
Part B
Name part A and part B of the anions. State the solubility of part A and part B in the cleansing action. Part A: hydrophobic tail soluble in grease Part B: hydrophilic head soluble in water [4 marks]
(ii)
Compare the effectiveness of the cleansing action of the two anions shows in the diagram 8.1 in hard water. Explain your answer. Write an ionic equation to show the reaction of anion of soap in hard water.
Ulangkaji Terakhir Menjelang SPM
36
CHEMISTRY
[6 marks] (b) Diagram 8.2 shows the label of soft drink. Ingredient : Water, citric acid, aspartame, octyl butanoate and tartazine. Expiry date : 03 Jan 2011
Diagram 8.2 Based on the ingredient used, classify the type of food additives that contained in this soft drink. Citric acid: antioxidant Aspartame: flavoring Octyl butanoate: flavoring Tartazine: flavoring [4 marks] (c) A patient is suffering from tuberculosis for a period of time. Suggest a type of medicine that should be taken and the prescription should be followed by the patient. 1. Antibiotic streptomycin. 2. Patients should take full course of the antibiotic even if he feels better because: 3. To make sure that all the bacteria are killed. Otherwise he may become ill again and the bacteria become more resistant to the antibiotic. Stronger antibiotic is needed to fight the same [4 marks] infection.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Chemistry - Textbook Answers Chapter 5Document20 paginiChemistry - Textbook Answers Chapter 5angelina_boseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understanding States of Matter and Chemical BondingDocument46 paginiUnderstanding States of Matter and Chemical Bondingsaz14Încă nu există evaluări
- Modul F2 Science C2Document14 paginiModul F2 Science C2NorelyanaAli67% (3)
- The 1855 Weber-Kohlrausch Experiment (The Speed of Light)Document10 paginiThe 1855 Weber-Kohlrausch Experiment (The Speed of Light)Frederick David TombeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Millennium Earth Changes 1-3Document246 paginiMillennium Earth Changes 1-3richx7100% (9)
- Lesson Plan of Atomic Structure Grade IxDocument3 paginiLesson Plan of Atomic Structure Grade IxKhadija33% (6)
- HSC Physics Paper II Exam with 17 MCQs and 9 Short Answer QuestionsDocument3 paginiHSC Physics Paper II Exam with 17 MCQs and 9 Short Answer QuestionsShaziaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structured Question: Analysis of Past Year Questions From 2003 - 2008Document27 paginiStructured Question: Analysis of Past Year Questions From 2003 - 2008Nazreen NashruddinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Form 4 Physics RevisionDocument5 paginiForm 4 Physics RevisionannmarieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Latihan Sains Tingkatan 3 Bab 4Document11 paginiLatihan Sains Tingkatan 3 Bab 4李友志67% (3)
- SPM Chemistry Paper 2Document19 paginiSPM Chemistry Paper 2AnneLeongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemical Equations and FormulasDocument7 paginiChemical Equations and FormulasJonathan LingÎncă nu există evaluări
- SPM Chemistry Trial 2015-2017 ModuleDocument119 paginiSPM Chemistry Trial 2015-2017 Modulekhangsiean8950% (2)
- Kimia Module 1 5 Diagnostik f4 PDFDocument70 paginiKimia Module 1 5 Diagnostik f4 PDFJuan DavisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Worksheet States of Matter ks3Document2 paginiWorksheet States of Matter ks3Edward edwardÎncă nu există evaluări
- f4 Chem Mid-Year Exam 2011Document12 paginif4 Chem Mid-Year Exam 2011matleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chem Test 1 2018 SECTION BDocument7 paginiChem Test 1 2018 SECTION BAmirah Noor AffandiÎncă nu există evaluări
- MPHG2009-Chapter 9 ElectronicsDocument34 paginiMPHG2009-Chapter 9 ElectronicsMohd Khairul Anuar100% (6)
- STF Mid Year Science Form 1 2009 Paper2Document12 paginiSTF Mid Year Science Form 1 2009 Paper2Syahrul67% (3)
- Science Form 1 Chapter 3Document7 paginiScience Form 1 Chapter 3huisinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science Form 1 Chapter 1Document13 paginiScience Form 1 Chapter 1huisin100% (1)
- Chemistry Form 4 - Paper 1Document13 paginiChemistry Form 4 - Paper 1adikmuk0% (1)
- Add Math SPM 2013Document36 paginiAdd Math SPM 2013tuntejaputeriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Form 3 Chapter 4Document7 paginiForm 3 Chapter 4Lau Lee LingÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 Chemical Formulae and EquationDocument43 pagini3 Chemical Formulae and EquationmawarhanifÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics Form 4 Chapter 4Document33 paginiPhysics Form 4 Chapter 4Eric LengÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modul Sains SPM Section CDocument25 paginiModul Sains SPM Section CJaaizah JaafarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exercise Physics Form 4 Chapter 1Document7 paginiExercise Physics Form 4 Chapter 1Wa Wa Jackson WongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jawapan Bagi Bahan Bengkel Seminar Kimia SPM 2014 Oleh Cikgu AduraDocument63 paginiJawapan Bagi Bahan Bengkel Seminar Kimia SPM 2014 Oleh Cikgu AduraCikgu FaizalÎncă nu există evaluări
- SPM Chemistry Form 5 – Oxidation and ReductionDocument22 paginiSPM Chemistry Form 5 – Oxidation and ReductionCk OoiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Form 2 Science Chapter 1 - The World Around UsDocument6 paginiForm 2 Science Chapter 1 - The World Around UsAnonymous o7B02XWOJpÎncă nu există evaluări
- SPM Form 4 Exercise Periodic Table of ElementsDocument3 paginiSPM Form 4 Exercise Periodic Table of Elementsasparagus1996Încă nu există evaluări
- Light 7Document5 paginiLight 7ahmeiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Functions & Quadratic Equations SolvedDocument2 paginiFunctions & Quadratic Equations SolvedALAN LIEW KOK PINÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 9-Electronics (Teacher's Guide)Document37 paginiChapter 9-Electronics (Teacher's Guide)Mohd Khairul Anuar100% (6)
- Soalan Ulangkaji Bab 5 Tingkatan 4 PDFDocument22 paginiSoalan Ulangkaji Bab 5 Tingkatan 4 PDFIsmaliza Ishak0% (1)
- 2021 SPM Modul Sarawak Chemistry Latihan TopikalDocument237 pagini2021 SPM Modul Sarawak Chemistry Latihan TopikalNex Then100% (1)
- 49 Question Trial SPM ChemistryDocument1 pagină49 Question Trial SPM ChemistrychongpeisiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sains Form1 Final ExamDocument10 paginiSains Form1 Final ExamNOR SUAKMA BT JAAFARÎncă nu există evaluări
- Form 1 Chapter 3 MatterDocument6 paginiForm 1 Chapter 3 Matterjj9821100% (1)
- Chemistry Perfect Score Module Form 4 2011 No LogoDocument96 paginiChemistry Perfect Score Module Form 4 2011 No Logohome8008100% (2)
- Force and Motion EquationsDocument13 paginiForce and Motion EquationsniknadhiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Revision Pack Science Form 1 + Form 2Document21 paginiRevision Pack Science Form 1 + Form 2Shureen Baskaran100% (1)
- Sexual and Asexual Reproduction GuideDocument23 paginiSexual and Asexual Reproduction GuideHazira HaidzirÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHEMISTRY Form 4 CHAPTER 4-The Periodic TableDocument47 paginiCHEMISTRY Form 4 CHAPTER 4-The Periodic TableAngie Kong Su MeiÎncă nu există evaluări
- SPM Chemistry Analysis 2008-2014Document1 paginăSPM Chemistry Analysis 2008-2014SHARIN HANUM AB RAHMANÎncă nu există evaluări
- Periodic Table of Elements Guide to Chemical BondsDocument19 paginiPeriodic Table of Elements Guide to Chemical Bondsalanisln100% (1)
- Chapter 11 Introduction To SetsDocument7 paginiChapter 11 Introduction To SetsJu WenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Form 3 Chapter 2Document9 paginiForm 3 Chapter 2Mariana AhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exercise Introduction To ScienceDocument17 paginiExercise Introduction To ScienceShu85Încă nu există evaluări
- Exercise SC Form 1 Chapter 6Document2 paginiExercise SC Form 1 Chapter 6Nor AdilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Periodic Table Trends WorksheetDocument4 paginiPeriodic Table Trends WorksheetSHEILA MAE VILLANTESÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paper 2 QuestionDocument15 paginiPaper 2 QuestionNoridaAnisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry SPM Kbat Form 4Document14 paginiChemistry SPM Kbat Form 4Gloria Yong100% (1)
- The Simple PendulumDocument2 paginiThe Simple PendulumphoenixchiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics IRP - 3Document11 paginiPhysics IRP - 3Cart KartikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 Form 1Document3 paginiChapter 2 Form 1Lopak TikeÎncă nu există evaluări
- SPM Kimia Jul12 PDFDocument49 paginiSPM Kimia Jul12 PDFSyazwani RadziÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ulangkaji Akhir Menjelang SPMDocument32 paginiUlangkaji Akhir Menjelang SPMMThana BalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diagram 1.1: Revision For Year End ExaminationDocument16 paginiDiagram 1.1: Revision For Year End ExaminationsookchinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemical reactions and propertiesDocument14 paginiChemical reactions and propertiesHan LingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Form 4: Atom Proton Number Nucleon NumberDocument8 paginiForm 4: Atom Proton Number Nucleon NumberAzie Nurul AkhtarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paper 2 Kim F4-AdahDocument16 paginiPaper 2 Kim F4-AdahNOR ATIKAH BINTI TAKRUDDIN MoeÎncă nu există evaluări
- SPM Form 4 Chemistry Chap 4 ExercisesDocument14 paginiSPM Form 4 Chemistry Chap 4 ExercisesTee Xin Rui50% (2)
- Target & FocusDocument3 paginiTarget & FocusHee Ting WongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemical and Apparatus Quote Request for School LabDocument1 paginăChemical and Apparatus Quote Request for School LabHee Ting WongÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 0860 People Speech Bubble PGo 16 - 9Document4 pagini2 0860 People Speech Bubble PGo 16 - 9Hee Ting WongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wk201b Long ADocument6 paginiWk201b Long AHee Ting Wong100% (1)
- 2 352 Periodic Table PGo 16 - 9Document1 pagină2 352 Periodic Table PGo 16 - 9Hee Ting WongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kids - Tieng Anh Cho Tre emDocument96 paginiKids - Tieng Anh Cho Tre emVũ Minh SơnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemical Tube Test Data Charts For Powerpoint: 80% 60% Lorem Ipsum Lorem IpsumDocument3 paginiChemical Tube Test Data Charts For Powerpoint: 80% 60% Lorem Ipsum Lorem IpsumPutu juni wulandariÎncă nu există evaluări
- MakeX Spark Online CompetitionDocument4 paginiMakeX Spark Online CompetitionHee Ting WongÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 0783 Puzzle Arc PGo 16 - 9Document3 pagini2 0783 Puzzle Arc PGo 16 - 9Hee Ting WongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrochemical CellDocument2 paginiElectrochemical CellHee Ting WongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 5 AnswerDocument4 paginiChapter 5 AnswerHee Ting WongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrochemical CellDocument2 paginiElectrochemical CellHee Ting WongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Program 2S Topical Test Chapter 7 (Form 4) 2011 Name: - ClassDocument3 paginiProgram 2S Topical Test Chapter 7 (Form 4) 2011 Name: - ClassHee Ting WongÎncă nu există evaluări
- P2 Section ADocument13 paginiP2 Section AHee Ting WongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Keputusan Topikal Test 2 Chemistry 4nDocument3 paginiKeputusan Topikal Test 2 Chemistry 4nHee Ting WongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Program 2S Topical Test Chapter 7 (Form 4) 2011 Name: - ClassDocument3 paginiProgram 2S Topical Test Chapter 7 (Form 4) 2011 Name: - ClassHee Ting WongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Form 4 Answer SchemeDocument16 paginiForm 4 Answer SchemeHee Ting WongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Keputusan Topikal Test 2 Chemistry 4eDocument3 paginiKeputusan Topikal Test 2 Chemistry 4eHee Ting WongÎncă nu există evaluări
- p3 Analysis 2010Document1 paginăp3 Analysis 2010Hee Ting WongÎncă nu există evaluări
- p3 Analysis 2010Document1 paginăp3 Analysis 2010Hee Ting WongÎncă nu există evaluări
- TPT-1 Physics CourseDocument6 paginiTPT-1 Physics CourseSantosh SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- STA Third Periodical Test in Science and Health 5Document3 paginiSTA Third Periodical Test in Science and Health 5Marie Fe JambaroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pair Production by Schwinger and Breitwheeler Processes in Bifrequent FieldsDocument12 paginiPair Production by Schwinger and Breitwheeler Processes in Bifrequent Fieldszeyadwaeli500Încă nu există evaluări
- Atomic Structure 2009 Handouts FinalDocument150 paginiAtomic Structure 2009 Handouts FinalSalma Khoirunnisa0% (1)
- 1905 0244v2Document20 pagini1905 0244v2Łukasz OstrowskiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Css Subject Physics Syllabus DownloadDocument2 paginiCss Subject Physics Syllabus DownloadCH M AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Entry Test - 2 (JEE Eklavya 2023-Earlybird)Document45 paginiEntry Test - 2 (JEE Eklavya 2023-Earlybird)vwxyz technologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Karen Barad - Nature's Queer Performativity PDFDocument38 paginiKaren Barad - Nature's Queer Performativity PDFLeandro Sanhueza HuenupiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electricity & Magnetism ExplainedDocument59 paginiElectricity & Magnetism ExplainedkalyanamÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2nd PUC Question Papers Physics 2006-2010Document21 pagini2nd PUC Question Papers Physics 2006-2010Mohan Kumar P100% (1)
- Current Transport in Metal-Semiconductor Barriers: Solid-State ElectronicsDocument14 paginiCurrent Transport in Metal-Semiconductor Barriers: Solid-State ElectronicsKrishna KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ivanov Fundamentals of Physics Mir 1989 PDFDocument459 paginiIvanov Fundamentals of Physics Mir 1989 PDFkalpa_y100% (1)
- (Physics) 2010 TSSM Unit 4 ExamDocument37 pagini(Physics) 2010 TSSM Unit 4 ExamakashÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computed-Tomography (CT) ScanDocument86 paginiComputed-Tomography (CT) ScanlextercarmÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 1 Introduction To ChemistryDocument34 paginiLecture 1 Introduction To ChemistryAlvin RodrigoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Light and Quantized Energy Quantum Theory AtomDocument4 paginiLight and Quantized Energy Quantum Theory AtomKevin XavierÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry 1st Year Important Questions Chapter WiseDocument5 paginiChemistry 1st Year Important Questions Chapter Wiseknk950260Încă nu există evaluări
- Magnetism and MatterDocument58 paginiMagnetism and MatterAksay KanthanÎncă nu există evaluări
- METALLIC BONDING (Part I)Document14 paginiMETALLIC BONDING (Part I)Putri AzzahraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quantum Dots PaperDocument6 paginiQuantum Dots Paperdewesh1990Încă nu există evaluări
- CHEM F111: General Chemistry Semester II: AY 2021-22: Lecture-05, 20 May 2022, FridayDocument23 paginiCHEM F111: General Chemistry Semester II: AY 2021-22: Lecture-05, 20 May 2022, FridayROMIT RUNWALÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chem Workshop - Question Paper Compilation (Class Xi)Document212 paginiChem Workshop - Question Paper Compilation (Class Xi)aarzoopatel08100% (3)
- 9 Radiation SterilizationDocument7 pagini9 Radiation SterilizationSEPTIANA SAPUTRIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electronic Structure of Atoms - General ChemistryDocument92 paginiElectronic Structure of Atoms - General ChemistryDuc Anh NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exercise 1 Electricity: Grade 12 IPADocument13 paginiExercise 1 Electricity: Grade 12 IPAFredrick Felicio SusiloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atomic Radius and Electronegativity - QuestionsDocument4 paginiAtomic Radius and Electronegativity - QuestionsAnonymous Mj0pfScÎncă nu există evaluări