Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Chapt 05 Lect02
Încărcat de
Shanmukha SundaramDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Chapt 05 Lect02
Încărcat de
Shanmukha SundaramDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
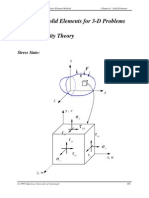
Lecture Notes: Introduction to Finite Element Method Chapter 5.
Plate and Shell Elements
1999 Yijun Liu, University of Cincinnati 129
II. Plate Elements
Kirchhoff Plate Elements:
4-Node Quadrilateral Element
DOF at each node:
y
w
y
w
w
, , .
On each element, the deflection w(x,y) is represented by
1
]
1
+ +
4
1
) ( ) ( ) , (
i
i yi i xi i i
y
w
N
x
w
N w N y x w
,
where N
i
, N
xi
and N
yi
are shape functions. This is an
incompatible element! The stiffness matrix is still of the form
V
T
dV EB B k ,
where B is the strain-displacement matrix, and E the stress-
strain matrix.
x
y
z
t
1 2
3
4
1
1
1
, ,
,
_
,
_
y
w
x
w
w
2
2
2
, ,
,
_
,
_
y
w
x
w
w
Mid surface
Lecture Notes: Introduction to Finite Element Method Chapter 5. Plate and Shell Elements
1999 Yijun Liu, University of Cincinnati 130
Mindlin Plate Elements:
4-Node Quadrilateral 8-Node Quadrilateral
DOF at each node: w,
x
and
y
.
On each element:
. ) , (
, ) , (
, ) , (
1
1
1
n
i
yi i y
n
i
xi i x
n
i
i i
N y x
N y x
w N y x w
Three independent fields.
Deflection w(x,y) is linear for Q4, and quadratic for Q8.
x
y
z
t
1 2
3
4
x
y
z
t
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Lecture Notes: Introduction to Finite Element Method Chapter 5. Plate and Shell Elements
1999 Yijun Liu, University of Cincinnati 131
Discrete Kirchhoff Element:
Triangular plate element (not available in ANSYS).
Start with a 6-node triangular element,
DOF at corner nodes:
y x
y
w
x
w
w
, , , , ;
DOF at mid side nodes:
y x
, .
Total DOF = 21.
Then, impose conditions 0
yz xz
, etc., at selected
nodes to reduce the DOF (using relations in (15)). Obtain:
At each node:
,
_
,
_
y
w
x
w
w
y x
, , .
Total DOF = 9 (DKT Element).
Incompatible w(x,y); convergence is faster (w is cubic
along each edge) and it is efficient.
x
y
z
t
1
2
3
4
5
6
x
y
z
1
2
3
Lecture Notes: Introduction to Finite Element Method Chapter 5. Plate and Shell Elements
1999 Yijun Liu, University of Cincinnati 132
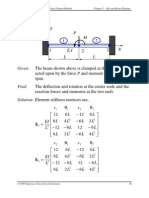
Test Problem:
ANSYS 4-node quadrilateral plate element.
ANSYS Result for w
c
Mesh
w
c
( PL
2
/D)
22
0.00593
44
0.00598
88
0.00574
1616
0.00565
: :
Exact Solution 0.00560
Question: Converges from above? Contradiction to what
we learnt about the nature of the FEA solution?
Reason: This is an incompatible element ( See comments
on p. 177).
x
y
z
L/t = 10, = 0.3
C
L
L
P
Lecture Notes: Introduction to Finite Element Method Chapter 5. Plate and Shell Elements
1999 Yijun Liu, University of Cincinnati 133
III. Shells and Shell Elements
Shells Thin structures witch span over curved surfaces.
Example:
Sea shell, egg shell (the wonder of the nature);
Containers, pipes, tanks;
Car bodies;
Roofs, buildings (the Superdome), etc.
Forces in shells:
Membrane forces + Bending Moments
(cf. plates: bending only)
Lecture Notes: Introduction to Finite Element Method Chapter 5. Plate and Shell Elements
1999 Yijun Liu, University of Cincinnati 134
Example: A Cylindrical Container.
Shell Theory:
Thin shell theory
Thick shell theory
Shell theories are the most complicated ones to formulate
and analyze in mechanics (Russians contributions).
Engineering Craftsmanship
Demand strong analytical skill
p
p
internal forces:
membrane stresses
dominate
p
p
Lecture Notes: Introduction to Finite Element Method Chapter 5. Plate and Shell Elements
1999 Yijun Liu, University of Cincinnati 135
Shell Elements:
cf.: bar + simple beam element => general beam element.
DOF at each node:
Q4 or Q8 shell element.
+
plane stress element
plate bending element
flat shell element
u
v
w
y
Lecture Notes: Introduction to Finite Element Method Chapter 5. Plate and Shell Elements
1999 Yijun Liu, University of Cincinnati 136
Curved shell elements:
Based on shell theories;
Most general shell elements (flat shell and plate
elements are subsets);
Complicated in formulation.
u
v
w
z
i
i
Lecture Notes: Introduction to Finite Element Method Chapter 5. Plate and Shell Elements
1999 Yijun Liu, University of Cincinnati 137
Test Cases:
Check the Table, on page 188 of Cooks book, for
values of the displacement
A
under the various loading
conditions.
Difficulties in Application:
Non uniform thickness (turbo blades, vessels with
stiffeners, thin layered structures, etc.);
Should turn to 3-D theory and apply solid elements.
A
R
80
o
Roof
R
A
F
F
L/2
L/2
Pinched Cylinder
A
F
F
F
F
R
Pinched Hemisphere
q
A
F
2
F
1
b
L
Twisted Strip (90
o
)
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Chapt 07 Lect02Document4 paginiChapt 07 Lect02Shanmukha SundaramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapt 06 Lect03Document6 paginiChapt 06 Lect03Shanmukha SundaramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapt 07 Lect03Document5 paginiChapt 07 Lect03Shanmukha SundaramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 6. Solid Elements For 3-D Problems I. 3-D Elasticity TheoryDocument6 paginiChapter 6. Solid Elements For 3-D Problems I. 3-D Elasticity TheoryShanmukha SundaramÎncă nu există evaluări
- IV. Nature of Finite Element Solutions: Stiffening EffectDocument7 paginiIV. Nature of Finite Element Solutions: Stiffening EffectShanmukha SundaramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4. Finite Element Modeling and Solution TechniquesDocument2 paginiChapter 4. Finite Element Modeling and Solution TechniquesShanmukha SundaramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapt 02 Lect06Document7 paginiChapt 02 Lect06Shanmukha SundaramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapt 02 Lect02Document6 paginiChapt 02 Lect02Shanmukha SundaramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapt 01 Lect02Document6 paginiChapt 01 Lect02Shanmukha SundaramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Wner'S Anual: Led TVDocument32 paginiWner'S Anual: Led TVErmand WindÎncă nu există evaluări
- Application Form InnofundDocument13 paginiApplication Form InnofundharavinthanÎncă nu există evaluări
- IMCI Chart BookletDocument43 paginiIMCI Chart Bookletmysticeyes_17100% (1)
- Business Plan in BDDocument48 paginiBusiness Plan in BDNasir Hossen100% (1)
- 01 托福基础课程Document57 pagini01 托福基础课程ZhaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Friction: Ultiple Hoice UestionsDocument5 paginiFriction: Ultiple Hoice Uestionspk2varmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Leadership Styles-Mckinsey EdDocument14 paginiLeadership Styles-Mckinsey EdcrimsengreenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sandstorm Absorbent SkyscraperDocument4 paginiSandstorm Absorbent SkyscraperPardisÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2016 Closing The Gap ReportDocument64 pagini2016 Closing The Gap ReportAllan ClarkeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Development Developmental Biology EmbryologyDocument6 paginiDevelopment Developmental Biology EmbryologyBiju ThomasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technology Based Project: Special Track 1)Document14 paginiTechnology Based Project: Special Track 1)Kim ChiquilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Apple Change ManagementDocument31 paginiApple Change ManagementimuffysÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heimbach - Keeping Formingfabrics CleanDocument4 paginiHeimbach - Keeping Formingfabrics CleanTunç TürkÎncă nu există evaluări
- ML Ass 2Document6 paginiML Ass 2Santhosh Kumar PÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 6 - Vibration ControlDocument62 paginiLesson 6 - Vibration ControlIzzat IkramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Addiction Final (Term Paper)Document15 paginiDrug Addiction Final (Term Paper)Dessa Patiga IIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Resume: Mr. Shubham Mohan Deokar E-MailDocument2 paginiResume: Mr. Shubham Mohan Deokar E-MailAdv Ranjit Shedge PatilÎncă nu există evaluări
- WBDocument59 paginiWBsahil.singhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics (Cheg6121) : Review of Basic ThermodynamicsDocument74 paginiAdvanced Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics (Cheg6121) : Review of Basic ThermodynamicsetayhailuÎncă nu există evaluări
- YIC Chapter 1 (2) MKTDocument63 paginiYIC Chapter 1 (2) MKTMebre WelduÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fundaciones Con PilotesDocument48 paginiFundaciones Con PilotesReddy M.Ch.Încă nu există evaluări
- Sept Dec 2018 Darjeeling CoDocument6 paginiSept Dec 2018 Darjeeling Conajihah zakariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evolution Army 3 R DadDocument341 paginiEvolution Army 3 R DadStanisław DisęÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cable To Metal Surface, Cathodic - CAHAAW3Document2 paginiCable To Metal Surface, Cathodic - CAHAAW3lhanx2Încă nu există evaluări
- 8051 NotesDocument61 pagini8051 Notessubramanyam62Încă nu există evaluări
- PMP Assesment TestDocument17 paginiPMP Assesment Testwilliam collinsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of Combinational Circuit For Code ConversionDocument5 paginiDesign of Combinational Circuit For Code ConversionMani BharathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Catify To Satisfy - Simple Solutions For Creating A Cat-Friendly Home (PDFDrive)Document315 paginiCatify To Satisfy - Simple Solutions For Creating A Cat-Friendly Home (PDFDrive)Paz Libros100% (2)
- SSP 237 d1Document32 paginiSSP 237 d1leullÎncă nu există evaluări
- How He Loves PDFDocument2 paginiHow He Loves PDFJacob BullockÎncă nu există evaluări