Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
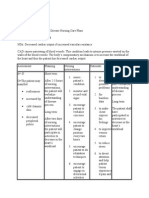
1 Ineffective Airway Clearance
Încărcat de
Esel Mae Dinamling0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
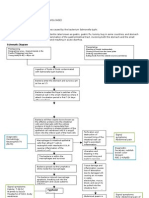
184 vizualizări8 paginiCOPD is an inIlammatory response to the oIending microorganism. The deIense mechanisms oI the lungs lose eIIectiveness and allow organisms to penetrate the sterile respiratory tract. The increased secretions make it diIIicult to maintain a patent airway.
Descriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentCOPD is an inIlammatory response to the oIending microorganism. The deIense mechanisms oI the lungs lose eIIectiveness and allow organisms to penetrate the sterile respiratory tract. The increased secretions make it diIIicult to maintain a patent airway.
Drepturi de autor:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
184 vizualizări8 pagini1 Ineffective Airway Clearance
Încărcat de
Esel Mae DinamlingCOPD is an inIlammatory response to the oIending microorganism. The deIense mechanisms oI the lungs lose eIIectiveness and allow organisms to penetrate the sterile respiratory tract. The increased secretions make it diIIicult to maintain a patent airway.
Drepturi de autor:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 8
1 Ineffective Airway Clearance
COPD is an inIlammatory response to the oIIending microorganism. The deIense mechanisms oI
the lungs lose eIIectiveness and allow organisms to penetrate the sterile respiratory tract, as a
result inIlammation develops. The inIlammation and increased secretions make it diIIicult to
maintain a patent airway.
Assessment
Nursing
Diagnosis
Planning
Nursing Inter-
ventions
Rationale
Expected
Outcome
S:O: The may
patient maniIest
the IIg.:~with
wheezes/crackle
s upon
auscultation on
the BLF
~with subcostal
retraction
~with nasal
Ilaring
~presence oI
non-productive
cough
~increase RR
above normal
range
IneIIectiv
e airway
clearance
related to
retained
and
excessive
secretions
and
ineIIective
coughing
Short
term:AIter 4-5
hours oI
nursing
interventions
the patient will
demonstrate
eIIective
clearing oI
secretions.Lon
g term:AIter 2
days oI nursing
interventions,
the patient will
maintain
eIIective
airway
clearance.
~Establish rapport
to the pt. and
SO~Assess the
patient
condition~Monito
r and record
V/S~Position head
midline with
Ilexion on
appropriate Ior
age/condition
~Elevate HOB
~Observe S/Sx oI
inIections
~Auscultate
breath sounds &
assess air mov`t
~Instruct the
patient to increase
Iluid intake
~Demonstrate
eIIective coughing
and deep-
breathing
techniques.
~Keep back dry
~Turn the patient
q 2 hours
~To gain trust
and active
participation~T
o know the
condition oI the
pt~To have a
baseline
data.~To gain or
maintain open
airway
~To decrease
pressure on the
diaphragm and
enhancing
drainage
~To identiIy
inIectious
process
~To ascertain
status & note
progress
~To help to
liqueIy
secretions.
~To maximize
eIIort
~To prevent
Iurther
complications
~To prevent
Short
term:The
patient shall
have
demonstrated
eIIective
clearing oI
secretions.Lon
g term:The
patient shall
have
maintained
eIIective
airway
clearance.
~Demonstrate
chest
physiotherapy,
such as bronchial
tapping when in
cough, proper
postural drainage.
~Administer
bronchodilators
iI prescribed.
possible
aspirations
~These
techniques will
prevent possible
aspirations and
prevent any
untoward
complications
~More
aggressive
measures to
maintain airway
patency.
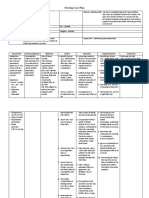
Ineffective Breathing Pattern
The presence oI microorganisms in the lungs causes body to increase the secretory activity oI
goblet cells to get rid oI the invading organism but the mechanism is not enough which allows
the stasis oI mucus secretion leading to ineIIective breathing pattern.
Assessment
Nursing
Dx
Planning
NursingInter-
ventions
Rationale
Expected
Outcome
S: Reports
oI
dyspneaO:
The patient
may
maniIest
the
maniIest
the IIg.:~
with
wheezes
/crackles
upon
auscultation
on BLF~
increase RR
above
normal
range
IneIIective
breathing
pattern
related to
retained
mucus
secretions
Short
term:AIter
4-5 hours oI
nursing
interventions
the patient
will improve
breathing
pattern.Long
term:AIter 2
days oI
nursing
interventions
the patient
will
maintain a
respiratory
rate within
normal
limits.
~Establish rapport
to the pt. and
SO~Assess the
patient
condition~Monitor
and record V/S
especially
RR~Provide rest
periods
~Place pt in semi-
Iowlers position
~Increase Iluid
intake
~Keep patient
back dry
~Change position
~To gain trust
and active
participation~To
know the
condition oI the
pt~To have a
baseline
data.~To reduce
Iatigue and
obtain rest
~To have a
maximum lung
expansion
~To liqueIy
secretions
~To avoid stasis
oI secretions
Short
term:The
patient shall
have
improved
breathing
pattern.Long
term:The
patient shall
have
maintained a
respiratory
rate within
normal
limits.
~presence
oI
productive
cough
~use oI
accessory
muscle
when
breathing
~presence
oI nasal
Ilaring and
retractions
every 2 hours
~PerIorm CPT
~Place a pillow
when the client is
sleeping
~Instruct how to
splint the chest
wall with a pillow
Ior comIort during
coughing and
elevation oI head
over body as
appropriate
~Maintain a patent
airway, suctioning
oI secretions may
be done as ordered
~Provide
respiratory
support. Oxygen
inhalation is
provided per
doctor`s order
~Administer
prescribed cough
suppressants and
analgesics and be
cautious, however,
because opioids
may depress
respirations more
than desired.
and avoid
Iurther
complication
~To Iacilitate
secretion mov`t
and drainage
~To loosen
secretion
~To provide
adequate lung
expansion while
sleeping.
~To promote
physiological
ease oI maximal
inspiration
~To remove
secretions that
obstructs the
airway
~To aid in
relieving patient
Irom dyspnea
~To promote
deeper
respirations and
cough
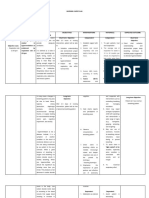
Impaired Gas Exchange
The disruption oI the mechanical deIenses oI cough and ciliary motility leads to colonization oI
the lungs and subsequent inIection leading to inIlammation and accumulation oI secretions.
InIlamed and Iluid-Iilled alveolar sacs cannot exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide eIIectively.
Assessment
Nursing
Dx
Planning
NursingInter-
ventions
Rationale
Expected
Outcome
S:O: The
patient may
maniIest the
IIg.:~Appearance
oI bluish
extremities when
in cough
(cyanosis),
lips~Lethargy
~Restlessness
~Hypercapnea
~Hypoxemia
~Abnormal rate,
rhythm, depth oI
breathing
~Diaphoresis
Impaired
gas
exchange
related to
altered
oxygen
Short
term:AIter
4-5 hours oI
nursing
interventions
the patient
will improve
ventilation
and
adequate
oxygenation
oI
tissuesLong
term:AIter 2
days oI
nursing
interventions
the patient
will
minimize or
totally be
Iree oI
symptoms oI
respiratory
distress.
~Establish rapport
to the pt. and
SO~Assess the
patient
condition~Monitor
and record
V/S~Monitor level
oI consciousness
or mental status
~Assist the client
into the High-
Fowlers position
~Increase patient`s
Iluid intake
~Encourage
expectoration
~Encourage
Irequent position
changes
~Encourage
adequate rest &
limit activities to
within client
tolerance
~Promote
calm/restIul
environments
~Administer
supplemental
oxygen
judiciously as
indicated
~Administer meds
as indicated such
as bronchodilators
~To gain trustand
active
participation~To
know the condition
oI the pt~To have
a baseline data.
~Restlessness,
anxiety,
conIusion,
somnolence are
common
maniIestation oI
hypoxia and
hypoxemia.
~The upright
position allows Iull
lung excursion and
enhances air
exchange
~To help liqueIy
secretions
~To eliminate
thick, tenacious,
copious secretions
which contribute
Ior the impairment
oI gas exchange.
~To promote
drainage oI
secretions
~Helps limit
oxygen
needs/consumption
~To
Short
term:The
patient shall
have
improved
ventilation
and
adequate
oxygenation
oI
tissuesLong
term:The
patient shall
have
minimized
or totally be
Iree oI
symptoms
oI
respiratory
distress.
correct/improve
existing
deIiciencies
~May correct or
prevent worsening
oI hypoxia.
~To treat the
underlying
condition
Sleep Pattern Disturbance
COPD patients need a comIortable position such as the High-Fowler`s position during sleeping
in order to promote lung expansion. Lying Ilat on bed promotes the occurrence oI DOB and
makes the patient uncomIortable due to the impaired alveolar ventilation which the body
processes at night can`t be controlled
Assessment
Nursing
Dx
Planning
NursingInter-
ventions
Rationale
Expected
Outcome
S:O: The patient may
maniIest the
IIg.:~irritability~restlessn
ess
~lethargy
~changes in posture
~diIIiculty oI breathing
which worsens at night
Sleep
pattern
disturban
ce related
to
diIIiculty
oI
breathing
Short
term:AIter
4-5 hours oI
nursing
intervention
s the patient
will identiIy
individually
appropriate
intervention
s to promote
sleep.Long
term:AIter 2
days oI
nursing
intervention
s, the patient
will be able
to report
improvemen
ts in
sleep/rest
pattern.
~Establish
rapport to the pt.
and SO~Assess
the patient
condition~Monit
or and record
V/S~Monitor
level oI
consciousness or
mental status
~Promote
comIort
measures such
as back rub and
change in
position as
necessary
~Observe
provision oI
emotional
support
~To gain trust
and active
participation~T
o know the
condition oI the
pt~To have a
baseline
data~Restlessne
ss, anxiety,
conIusion,
somnolence are
common
maniIestation oI
hypoxia and
hypoxemia.
~To provide
non
pharmagcologic
management
~Lack oI
knowledge and
Short
term:The
patient shall
have
identiIied
individually
appropriate
intervention
s to promote
sleepLong
term:The
patient shall
have
reported
improvemen
ts in pt.`s
sleep/rest
~Provide quiet
environment.
~Increase
patient`s Iluid
intake
~Encourage
expectoration
~Limit the Iluid
intake in
evening iI
nocturia is a
problem
~Obtain
Ieedback Irom
SO regarding
usual bedtime,
rituals/routines
~Provide saIety
Ior patient sleep
time saIety
~Recommend
midmorning nap
iI one required
~Administer
pain medication
as ordered.
problems,
relationships
may create
tension.
InterIering with
sleep routines
based on adult
schedules may
not meet child`s
needs.
~To promote an
environment
conducive to
sleep.
~To help
liqueIy
secretions
~To eliminate
thick, tenacious,
copious
secretions which
contribute Ior
the DOB
~To reduce
need Ior
nighttime
elimination
~To determine
usual sleep
patterns &
provide
comparative
baseline
~To promote
comIort/saIety
~Napping esp.
in the aIternoon
can disrupt
normal sleep
pattern
~To relieve
discomIort and
take maximum
advantage oI
sedative eIIect
Risk for Spread of Infection
Once the bacteria, virus, or Iungus enter the lungs, they usually settle in the air sacs oI the lung
where they rapidly grow in number. This area oI the lung then becomes Iilled with Iluid and pus
as the body attempts to Iight the inIection. Disruption oI the mechanical deIenses oI cough and
ciliary motility leads to colonization oI the lungs and subsequent inIection
Assessment
Nursing
Dx
Planning
NursingInter-
ventions
Rationale
Expected
Outcome
S:O: The patient
may
maniIest:~Body
temperature above
normal
range~dehydration
~increase WBC
count
~presence oI
increase mucus
production
Risk Ior
spread oI
inIection
related to
stasis oI
secretions
and
decreased
ciliary
action.
Short
term:AIter 4-
5 hours oI
nursing
interventions
the patient
will identiIy
interventions
to prevent
and/or reduce
the risk oI
inIectionLong
term:AIter 2
days oI
nursing
interventions
the patient
will have
minimize or
totally be Iree
Irom the risk
oI inIection.
~Establish rapport
to the pt. and
SO~Assess the
patient
condition~Monitor
& record
V/S~Review
importance oI
breathing
exercises,
eIIective cough,
Irequent position
changes, and
adequate Iluid
intake
~Turn the patient
q 2 hours
~Encourage
increase Iluid
intake
~Stress the
importance oI
handwashing to
SO`s
~To gain trust and
active
participation~To
know the condition
oI the pt~To have
a baseline data and
Iever may be
present because oI
inIection and/or
dehydration~These
activities promote
mobilization and
expectoration oI
secretions to
reduce the risk oI
developing
pulmonary
inIection.
~To Iacilitate
secretion mov`t
and drainage
~To liqueIy
secretions
~Handwashing is
the primary
Short
term:The
shall have
identiIied
interventions
to prevent
and/or reduce
the risk oI
inIectionLong
term:The
patient shall
have
minimized or
totally be Iree
Irom the risk
oI inIection.
~Teach the SO`s
how to care Ior
and clean
respiratory
equipment
~Teach the SO`s
the maniIestations
oI pulmonary
inIections (change
in color oI sputum,
Iever, chills) , selI-
care and when to
call the physician
~Recommend
rinsing mouth with
water
~Administer
antimicrobial such
as ceIuroxime as
indicated.
deIense against the
spread oI inIection
~Water in
respiratory
equipment is a
common source oI
bacterial growth
~Early recognition
oI maniIestations
can lead to a rapid
diagnosis.
~To prevent risk
oI oral candidiasis.
~Given
prophylactically to
reduce any
possible
complications
Other nursing diagnoses:
O High risk Ior suIIocation
O High risk Ior aspiration
O Anxiety RT acute breathing diIIiculties
O Activity Intolerance RT inadequate oxygenation
O Imbalanced Nutrition: Less than body requirements RT reduced appetite and dyspnea
(Ior empysema)
Once the bacteria, virus, or Iungus enter the lungs, they usually settle in the air sacs oI the lung where they
rapidly grow in number. This area oI the lung then becomes Iilled with Iluid and pus as the body attempts to
Iight the inIection. Disruption oI the mechanical deIenses oI cough and ciliary motility leads to colonization oI
the lungs and subsequent inIection
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Wk2 NCP Edited2012Document6 paginiWk2 NCP Edited2012Jessely Caling SalasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument1 paginăIneffective Airway ClearanceChristineAlaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care PlanDocument10 paginiNursing Care PlanSittie Rohaina SabanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 Coronary Artery Disease Nursing Care PlansDocument6 pagini5 Coronary Artery Disease Nursing Care PlansMichelle Danica Vicente PaswickÎncă nu există evaluări
- Student NurseDocument2 paginiStudent NurseTAYABAN, KENNETH JAKE, Q.Încă nu există evaluări
- Asthma Care PlanDocument3 paginiAsthma Care PlanSam ParkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cu 4Document3 paginiCu 4Paul SahagunÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP For StokeDocument5 paginiNCP For StokeMemedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Retinopathy of PrematurityDocument15 paginiRetinopathy of Prematuritymarissa ulkhairÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ineffective Airway Clearance CareplanDocument6 paginiIneffective Airway Clearance CareplanderreshaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Content: Outline Form Only Make A Separate Sheet For The Content. The Health Teaching Plan Should Focus On Home Care For Patients With Mood DisorderDocument4 paginiContent: Outline Form Only Make A Separate Sheet For The Content. The Health Teaching Plan Should Focus On Home Care For Patients With Mood DisorderRaffy Sebastian Seballos100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan FinalDocument16 paginiNursing Care Plan FinalErickson OcialÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 paginiAssessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationjennelyn losantaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan For Special ChildrenDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan For Special Childrenharas_dcsaisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drugs (Chino&anna)Document15 paginiDrugs (Chino&anna)Nic JiÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument4 paginiNCP Ineffective Breathing PatternSeika SouiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amanda AquiliniDocument2 paginiAmanda AquilinineoclintÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care PlanDocument15 paginiNursing Care PlanZhel Geron MercadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scientific Explanation of Expected Outcomes and InterventionsDocument4 paginiScientific Explanation of Expected Outcomes and InterventionsGensen Cu RoxasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nutrition diagnosis: Imbalanced nutrition less than requirementsDocument3 paginiNutrition diagnosis: Imbalanced nutrition less than requirementsIlisa ParilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Instillation of Eye DropsDocument4 paginiInstillation of Eye DropsratnafadliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Valdez Reflective-Questions PDFDocument3 paginiValdez Reflective-Questions PDFDexel Lorren ValdezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Breathing Pattern Assessment and InterventionDocument3 paginiBreathing Pattern Assessment and InterventionAziil LiizaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 paginiNursing Care PlanGabrielGitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cholera N C P BY BHERU LALDocument2 paginiCholera N C P BY BHERU LALBheru LalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Asthma Nursing Care Plan NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance CompressDocument2 paginiAsthma Nursing Care Plan NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance CompressMargarette GeresÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP PTBDocument6 paginiNCP PTBJay Dela VegaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessing Neurological FunctionsDocument12 paginiAssessing Neurological FunctionsGian Karlo GarridoÎncă nu există evaluări
- University of The East: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 paginiUniversity of The East: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationPATRICIA JEANNE JABIANÎncă nu există evaluări
- Knowledge DeficitDocument5 paginiKnowledge DeficitteamstrocaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manage Bronchiectasis Nursing Care PlanDocument5 paginiManage Bronchiectasis Nursing Care PlanPaola Marie VenusÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP BronchopneumoniaDocument8 paginiNCP BronchopneumoniaCrisantaCasliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan: Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Bleeding From Tonsillectomy Short TermDocument4 paginiNursing Care Plan: Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Bleeding From Tonsillectomy Short TermErika Danalle ArceoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument3 paginiImpaired Gas ExchangeBenedicto RosalÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 paginiNCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceEmirose Fatima TagabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 paginiNursing Care PlanDewi PurnamasariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Teaching Plan For DiarrheaDocument2 paginiTeaching Plan For DiarrheaSheila Nones50% (6)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 paginiNursing Care PlanMarielle SorianoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care PlanDocument14 paginiNursing Care PlanVin Landicho100% (1)
- Viii. Nursing Care Plan: Asessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 paginiViii. Nursing Care Plan: Asessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluationhehehe29Încă nu există evaluări
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Secretions As Evidence by Decrease in Respiratory Rate and NGT and ET Tube Attached and Crackles at The Left Base of The LungsDocument3 paginiNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Secretions As Evidence by Decrease in Respiratory Rate and NGT and ET Tube Attached and Crackles at The Left Base of The LungsSarah Ann Jamilla FaciolanÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCPDocument10 paginiNCPmsinsanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument4 paginiDecreased Cardiac OutputAdnan Khan100% (1)
- Acute PainDocument3 paginiAcute PainJayr ChinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oxygen Terapi Dan PrinsipelDocument16 paginiOxygen Terapi Dan PrinsipelAmrita KaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan EportfolioDocument14 paginiNursing Care Plan Eportfolioapi-279212367Încă nu există evaluări
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern Related To HyperventilationDocument4 paginiIneffective Breathing Pattern Related To HyperventilationVanessa Charlotte LagunayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Care of Eye - FOOT AND NAILS NCPDocument12 paginiCare of Eye - FOOT AND NAILS NCPchaitali shankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Care of Patients with Chest Drainage SystemsDocument29 paginiCare of Patients with Chest Drainage SystemsMSc. PreviousÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessing and Managing Risk of AspirationDocument6 paginiAssessing and Managing Risk of AspirationaianrÎncă nu există evaluări
- L&D Careplan 1 KarenDocument4 paginiL&D Careplan 1 KarenSimran SandhuÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Alcoholic NeuropathyDocument5 paginiNCP Alcoholic NeuropathyPeachy Marie Anca100% (1)
- Nursing Interventions CHFDocument3 paginiNursing Interventions CHFbanyenye25100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementio N EvaluationDocument3 paginiNursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementio N EvaluationAndrew James Javier Quidez100% (1)
- Chronic Obstructive Bronchitis Is An Inflammation of The BronchiDocument9 paginiChronic Obstructive Bronchitis Is An Inflammation of The Bronchiinamaliit100% (1)
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument6 paginiIneffective Airway Clearanceapi-252726911Încă nu există evaluări
- NCP For PneumoniaDocument3 paginiNCP For PneumoniaKahMallari100% (10)
- NCP SDocument8 paginiNCP SMarvie CadenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCM 118 SDL#1 - Orcullo 4NFDocument5 paginiNCM 118 SDL#1 - Orcullo 4NFGerelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bronchitis Nursing Care PlanDocument8 paginiBronchitis Nursing Care PlanBryan NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of Typhoid Fever and Acute GastroenteritisDocument3 paginiPathophysiology of Typhoid Fever and Acute Gastroenteritisteddydeclines14100% (5)
- BMJ CPR JournalDocument7 paginiBMJ CPR JournalEsel Mae DinamlingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Breast Feeding MisconceptionsDocument3 paginiBreast Feeding MisconceptionsEsel Mae DinamlingÎncă nu există evaluări
- SoundDocument2 paginiSoundEsel Mae DinamlingÎncă nu există evaluări
- NURSING CARE PLAN The Child Undergoing Surgery For ScoliosisDocument3 paginiNURSING CARE PLAN The Child Undergoing Surgery For ScoliosisscrewdriverÎncă nu există evaluări
- Child Health Strategic Plan 2001-2004Document26 paginiChild Health Strategic Plan 2001-2004Sai BondadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Torture-Definition Quiroga JaransonDocument6 paginiTorture-Definition Quiroga JaransonAlfred KassarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 211 ManDocument24 pagini211 ManNicoleta LesanÎncă nu există evaluări
- BIOPHARMACEUTICS AND CLINICAL PHARMACOKINETICSDocument34 paginiBIOPHARMACEUTICS AND CLINICAL PHARMACOKINETICSYayuk Abay TambunanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Retinoblastoma Clinical and Pathological ClassificationDocument9 paginiRetinoblastoma Clinical and Pathological ClassificationSonia SaulésÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fall 2023 CultivateDocument13 paginiFall 2023 CultivateFlorida Horticulture for Health NetworkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pediatric BurnsDocument22 paginiPediatric BurnsdrsdineshÎncă nu există evaluări
- PEWS Training IndonesiaDocument36 paginiPEWS Training IndonesiaBbenq Prasetyo100% (1)
- Vaginal Dryness CIMDocument115 paginiVaginal Dryness CIMVirginia Abalos100% (1)
- EliminationDocument20 paginiEliminationHasan A AsFour100% (2)
- Clasic MindfullneseDocument15 paginiClasic Mindfullneseayu yuliantiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6 Back Massage Pressure Points For Relaxation and Stress Relief PDFDocument9 pagini6 Back Massage Pressure Points For Relaxation and Stress Relief PDFلوليتا وردةÎncă nu există evaluări
- Model of Decision MakingDocument34 paginiModel of Decision MakingPalalikesjujubesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cord Blood Banking Opening New Avenues for India's Growing Medical Tourism IndustryDocument29 paginiCord Blood Banking Opening New Avenues for India's Growing Medical Tourism IndustryPreeti KashyapÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alternative Modalities of Care: By: Firoz Qureshi Dept. Psychiatric NursingDocument68 paginiAlternative Modalities of Care: By: Firoz Qureshi Dept. Psychiatric NursingsanthiyasandyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maura Sills: Karuna InstituteDocument1 paginăMaura Sills: Karuna Instituteapi-266696024Încă nu există evaluări
- Beautiful Girls InsideDocument16 paginiBeautiful Girls InsideEnglishUrduDiaryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clinical Troubleshooting Checklist - OutpatientDocument4 paginiClinical Troubleshooting Checklist - Outpatientapi-477879262Încă nu există evaluări
- CT Scanning - Techniques and Applications PDFDocument358 paginiCT Scanning - Techniques and Applications PDFMinionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cara Penggunaan Minyak Atsiri OkDocument28 paginiCara Penggunaan Minyak Atsiri OkYuliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Task 1: Critical AnalysisDocument4 paginiTask 1: Critical AnalysismohdnasrulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Overactive BladderDocument4 paginiOveractive BladderRanda Hayudha SÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flexor Tendon Injuries. Hand Clinics. 2005Document152 paginiFlexor Tendon Injuries. Hand Clinics. 2005k2rojo100% (2)
- Drug StudyDocument5 paginiDrug Studytricia_fernandoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 360 Process Recording TemplateDocument13 pagini360 Process Recording Templateapi-252910411100% (9)
- CounselingDocument23 paginiCounselingrashmi patooÎncă nu există evaluări
- Single Visit EndodonticsDocument6 paginiSingle Visit EndodonticsSerene Kenny100% (1)
- Lumbar Traction Review2Document9 paginiLumbar Traction Review2Phooi Yee LauÎncă nu există evaluări