Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Power System Analysis and Stability Subject Question Bank
Încărcat de
Naveen RajDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Power System Analysis and Stability Subject Question Bank
Încărcat de
Naveen RajDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING NAME OF THE SUBJECT: POWER SYSTEM ANALYSIS AND STABILITY SUBJECT CODE:
608EET04 YEAR / SEM: III / VI QUESTION BANK UNIT I PART A
1. Define per unit value. 2. List the two advantages of per-unit computations or What are the advantages of per unit system? 3. What is transient stability? 4. What is the single (or one) line diagram? 5. A generator rated at 30MVA, 11KV has a reactance of 20%. Calculate its per unit reactance for a base of 50MVA and 10KV. 6. Define the steady state limit. 7. Write the equation for per unit impedance. 8. Represent a short transmission of 3 phase into its equivalent single phase circuit. 9. What is the need for system analysis in planning and operation of power system? 10.The reactance of a generator designated X is given as 0.2 p.u based on the generators name plate rating of 20kV, 500 MVA. The base for calculations is 22 kV, 100MVA. Find X on the new base. 11.List the different components of power system.
PART B
1. Draw the reactance diagram using a base of 50MVA and 13.8KV on generator G1.
Generator, G1 = 20MVA, 13.8KV, X=20% Generator, G2 = 30MVA, 18.0KV, X=20% Generator, G3 = 30MVA, 20.0KV, X=20% Transformer, T1 = 25MVA, 220/13.8KV, X=10% Transformer, T2 = 3 single phase units each rated at 10MVA, 127/18KV, X=10% Transformer, T3 = 35MVA, 220/22KV, X=10%
2. Draw the structure of an electrical power system and describe the components of the system with typical values.
3. The three phase ratings of a 3 winding transformer are Primary: star connected, 110KV, 20MVA Secondary: star connected, 13.2KV, 15MVA Tertiary: delta connected, 2.1K, 0.5MVA Three short-circuit tests performed on this transformer yielded the following results: i) Primary excited, secondary shorted: 2290v, 55.2A
ii) Primary excited, tertiary shorted:
1785V, 52.5A
iii) Secondary excited tertiary shorted: 148V, 328A Find the p.u impedances of the star-connected single-phase equivalent circuit for base of 20MVA, 110kv in primary circuit .neglect resistance. 3. a)Draw a single line diagram for the system shown in fig and mark all reactances in per unit on 20mV,6.6KV basis Generator, G1 = 10mVA, 6.6kV, 0.1p.u. Generator, G2 = 20mVA, 11.5kV, 0.1p.u. Transformer, T1 = 10mVA,3-phase,6.6kV/115KV,0.15p.u. Transformer, T2 = three single phase units, each 10mVA, 7.5KV/75kV, 0.1p.u.
b) i) What is the need for system analysis in planning and operation of power system? Explain. ii) Explain in detail about the general aspects relating to short circuit and stability analysis.
4. Obtain the per unit impedance (reactance) diagram of the power system shown in fig
Generator, G1 = 30MVA, 10.5KV, X=1.6 ohm Generator, G2 = 15MVA, 6.6KV, X=1.2 ohm Generator, G3= 25MVA, 6.6KV, X=0.56 ohm Transformer, T1 (3phase) =15MVA, 33/11KV, X=15.2ohms per phase on high tension side Transformer, T2 (3phase) =15MVA, 33/6.2KV, X=16ohms per phase on high tension side Transmission line: 20.5 ohms/phase Load A: 15MW, 11KV, 0.9p.f lagging Load B: 40MW, 6.6KV, 0.85 lagging p.f.
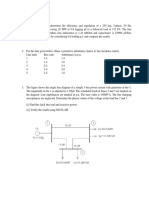
5. A 60MVA, Y connected 11KV synchronous generator is connected to a 60MVA, 11/132KV /Y transformer .the sub transient reactance Xd of the generator is 0.12p.u. on a 60MVA base, while the transformer reactance is 0.1p.u. On the same base .the generator is unloaded when a symmetrical fault is suddenly placed at a point P as shown in fig. Find the sub transient symmetrical fault current in p.u. amperes and actual amperes on both sides of the transformer. phase to neutral voltage of the generator at no load is 1.0p.u.
6. a) What are the step by step procedures to be followed to find the per-unit impedance diagram of a power system? b) List the advantages of per unit computations. c) A single line transformer is rated 110/440 V, 2.5 KVA. Leakage reactance measured from the LT side is 0.06. Determine the leakage reactance in p.u.
7. Write short notes on single line diagram and change of base.
8. Draw the reactance diagram for the power system shown in fig. Neglect resistance and use a base of 100MVA, 220 KV in K line. The ratings of the generator motor and transformer are given below.
Generator: 40MVA, 25 KV, X=20% Synchronous motor: 50MVA, 11 KV, X=30% Y-Y Transformer: 40MVA, 33/220 KV, X = 15% Y- Transformer: 30MVA, 11/220 KV (/Y), X = 15%
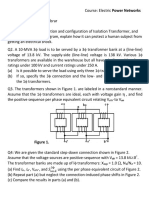
9. The single line diagram of an unloaded system is shown in fig. reactances of the two sections of the transmission line are shown on the diagram. The generators and transformers are rated as follows: Generator, G1 = 20MVA, 11KV, Xd=0.25p.u Generator, G2 = 30MVA, 18KV, Xd=0.25p.u Generator, G3 = 30MVA, 20KV, Xd=0.21p.u Transformer, T1 = 25MVA, 220 Y/13.8 KV, X=0.15p.u Transformer, T2 = single phase units each rated at 10MVA, 127/18KV, X=0.15p.u Transformer, T3 = 35MVA, 220 Y/22 Y KV, X=0.15p.u Draw the impedance diagram with all reactances marked in p.u. choose a base of 50MVA and 11KV on generator G1
10.Fig shows a single line diagram of unloaded three generator power system with interconnection between the generators by means of three transformers and a transmission line with two sections with their impedances marked on the diagram. The ratings of generators and transformers are given below: Generator, G1 = 25MVA, 6.6KV, Xd=0.20p.u Generator, G2 = 15MVA, 6.6KV, Xd=0.15p.u Generator, G3 = 30MVA, 13.2KV, Xd=0.15p.u Transformer, T1 = 30MVA, 6.9 /115 Y KV, X=10% Transformer, T2 = 15MVA, 6.9 /115 Y KV, X=10%
Transformer, T3 = single phase units, each rated at 10MVA, 6.9/69KV, X=10% Draw an impedance diagram and mark all values in p.u. choosing a base of 30MVA and 6.6KV in generator 1 circuit.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- PSE 6TH SEM UNIT 1 & 2 PER UNIT IMPEDANCE DIAGRAMSDocument33 paginiPSE 6TH SEM UNIT 1 & 2 PER UNIT IMPEDANCE DIAGRAMSMahesh SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pse Problems Group AssignmentDocument14 paginiPse Problems Group AssignmentSajid KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power System AnalysisDocument23 paginiPower System AnalysisSaeed Al BlooshiÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE2351 POWER SYSTEM ANALYSIS UNIT-I INTRODUCTIONDocument11 paginiEE2351 POWER SYSTEM ANALYSIS UNIT-I INTRODUCTIONdrmsrmurty9473Încă nu există evaluări
- BE Semester-VI (Electrical Engineering) Question Bank (E 605 Electrical Power System - Ii) All Questions Carry Equal Marks (10 Marks)Document5 paginiBE Semester-VI (Electrical Engineering) Question Bank (E 605 Electrical Power System - Ii) All Questions Carry Equal Marks (10 Marks)Adesh Bhortakke100% (1)
- Ee2351 Psa Im 2013Document11 paginiEe2351 Psa Im 2013ZARGHAM KHAN100% (1)
- EET301 Tutorial 2-Chapter 2-Session 2017-2018Document4 paginiEET301 Tutorial 2-Chapter 2-Session 2017-2018Nazir AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- MEHRAN UNIVERSITY BE EXAM 2009 POWER SYSTEM ANALYSISDocument2 paginiMEHRAN UNIVERSITY BE EXAM 2009 POWER SYSTEM ANALYSISkeerthanavijayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PSADocument25 paginiPSAramyadspÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power System Steady State Analysis Assignment ProblemsDocument3 paginiPower System Steady State Analysis Assignment Problemsosama munirÎncă nu există evaluări
- 0.psa - As - Pu System PDFDocument4 pagini0.psa - As - Pu System PDFanandÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial Pse - 2012-2013Document23 paginiTutorial Pse - 2012-2013Mahesh SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 1Document2 paginiAssignment 1sadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power System Analysis-BE (PT) NEWDocument13 paginiPower System Analysis-BE (PT) NEWMATHANKUMAR.SÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial PSE 2011-2012Document23 paginiTutorial PSE 2011-2012Mahesh Singh100% (1)
- Experiment 6 Perunit Calculations and Impedance DiagramsDocument3 paginiExperiment 6 Perunit Calculations and Impedance DiagramsJaved Ahmed LaghariÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE6501-Question BankDocument16 paginiEE6501-Question BankBelayneh TadesseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power System Analysis-IiDocument115 paginiPower System Analysis-IiSrinivasReddy100% (2)
- Assignment 2Document2 paginiAssignment 2ksajjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Per Unit CalculationsDocument7 paginiPer Unit Calculationsanbuelectrical100% (1)
- Assignment - 1 - Pu SystemsDocument3 paginiAssignment - 1 - Pu SystemsDeepak ThapaÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE-311 Tutorial Sheet Fault CurrentsDocument5 paginiEE-311 Tutorial Sheet Fault CurrentsRishabh Kalia100% (1)
- Power SystemDocument4 paginiPower Systemj settyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit - 1 Short Questions (2 & 3 Marks)Document6 paginiUnit - 1 Short Questions (2 & 3 Marks)Sujit KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Per UnitDocument18 paginiPer UnitPeter CalvoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fault analysis and sequence networks of power systemsDocument7 paginiFault analysis and sequence networks of power systemsDenish Gupta0% (1)
- Power Systems-II Question Bank: Unit-IDocument8 paginiPower Systems-II Question Bank: Unit-ISoniya GJÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE8501-Power System AnalysisDocument8 paginiEE8501-Power System AnalysisthiyagusuperÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sessional Set 17Document1 paginăSessional Set 17Vikash TiwariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power System AnalysisDocument10 paginiPower System AnalysisAlluri Appa RaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power System Analysis Tutorial Sheet 01Document4 paginiPower System Analysis Tutorial Sheet 01Goyal100% (1)
- Tutorial 1 Per Unit PDFDocument4 paginiTutorial 1 Per Unit PDFSofia Nadhirah Binti Amluddin100% (1)
- Noida Institute of Engineering & Technology, Greater Noida: Section - ADocument3 paginiNoida Institute of Engineering & Technology, Greater Noida: Section - AVikash TiwariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial Faults - Update - 020413 - SV PDFDocument6 paginiTutorial Faults - Update - 020413 - SV PDFnanangÎncă nu există evaluări
- power system analysis importantDocument8 paginipower system analysis importantsparkle courageÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab WorkDocument22 paginiLab WorkTamil SelvanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Homework 02 Electric Power NetworksDocument2 paginiHomework 02 Electric Power NetworkswaleedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 2 PsDocument4 paginiAssignment 2 PsAmin RafidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment IDocument5 paginiAssignment IPrasenjit DeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Department of Electrical &electronics Engineering: Unit: I & IiDocument5 paginiDepartment of Electrical &electronics Engineering: Unit: I & IiArun MariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psa Ab - OptDocument16 paginiPsa Ab - OptJeeva KarunyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power System Analysis (Jan-2014)Document10 paginiPower System Analysis (Jan-2014)Likhitha YerraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lista de Ejercicios - Fallos AsimétricosDocument3 paginiLista de Ejercicios - Fallos AsimétricosCarlos Gustavo RVÎncă nu există evaluări
- Part - B (2 X 15 30 Marks) Answer All QuestionsDocument2 paginiPart - B (2 X 15 30 Marks) Answer All QuestionsGokul ChandrasekaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment1 of FaultDocument2 paginiAssignment1 of FaultsethÎncă nu există evaluări
- Question Paper CodeDocument6 paginiQuestion Paper Codeprasad powerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ee1351 PsaDocument16 paginiEe1351 PsaStephen Kenth La GuerreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 1Document4 paginiAssignment 1Preetham ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab QPDocument8 paginiLab QPpmahesh268Încă nu există evaluări
- Planning and operational analysis of power systemsDocument20 paginiPlanning and operational analysis of power systemsgopalakrishnanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unta BeranakDocument6 paginiUnta Beranakharis kunkunÎncă nu există evaluări
- PSA SolutionDocument5 paginiPSA SolutionviswaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power System Analysis Assignment Fault CurrentsDocument2 paginiPower System Analysis Assignment Fault CurrentsdeepanshuÎncă nu există evaluări
- VSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsDe la EverandVSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetDe la EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetDe la EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetEvaluare: 2 din 5 stele2/5 (1)
- Some Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetDe la EverandSome Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1De la EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Evaluare: 2.5 din 5 stele2.5/5 (3)
- Power System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)De la EverandPower System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)Încă nu există evaluări
- Psas Ut2-QbDocument5 paginiPsas Ut2-QbNaveen RajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psps Ut 2 QBDocument6 paginiPsps Ut 2 QBNaveen RajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modelling and Analysis of Electric Power SystemsDocument161 paginiModelling and Analysis of Electric Power SystemsSami Ahmed ZiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psps Unit 1 QBDocument9 paginiPsps Unit 1 QBNaveen RajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Concrete Testing Guide BookDocument242 paginiConcrete Testing Guide BookSiegfred Racca100% (4)
- LF10 air pressure switchesDocument1 paginăLF10 air pressure switchesJulio Luis Guzman MarañonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engineering Report: McFarland ApartmentsDocument7 paginiEngineering Report: McFarland ApartmentsPennLiveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Saral FinalDocument2 paginiSaral FinalAung Kyaw OoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inspection and Test Plan: Contract NoDocument2 paginiInspection and Test Plan: Contract NoAhmed Samir SalimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Career: CornerDocument1 paginăCareer: CornerJohn AnthoniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Isbn Icosi2019 Final PDFDocument511 paginiIsbn Icosi2019 Final PDFyulianingsari pramesthiriniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Declaration of Conformity XPS 5cmDocument1 paginăDeclaration of Conformity XPS 5cmSenidaBektašÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bibliography - Helical Piles A Practical Guide To Design and Installation PDFDocument17 paginiBibliography - Helical Piles A Practical Guide To Design and Installation PDFFernando SmithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transrail LED Highbay HBLDocument1 paginăTransrail LED Highbay HBLmadanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prof Pprac Summary MegDocument14 paginiProf Pprac Summary MegShara Marimon100% (1)
- Beam and Slab Type Combined FootingDocument6 paginiBeam and Slab Type Combined FootingVasanthakumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- LRFD Steel Design PDFDocument648 paginiLRFD Steel Design PDFbong2rmÎncă nu există evaluări
- Non Destructive Testing BRIDGES NO. 355, 366, 388 & 390 Mumbai Division of W. RDocument30 paginiNon Destructive Testing BRIDGES NO. 355, 366, 388 & 390 Mumbai Division of W. RArindam NandyÎncă nu există evaluări
- IEEE Recommended Practice For Routine Impulse Test For Distribution TransformersDocument56 paginiIEEE Recommended Practice For Routine Impulse Test For Distribution TransformersIngTec2016 IngTec2016Încă nu există evaluări
- 529A Deadman Anchor Type 1 PDFDocument1 pagină529A Deadman Anchor Type 1 PDFAnonymous sfkedkymÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1972 - Scrivener - Reinforced Masonry - Seismic Behaviour and Design - CleanDocument13 pagini1972 - Scrivener - Reinforced Masonry - Seismic Behaviour and Design - CleanAbd ElRahman Abd AllahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Especs AA Equipos Paquete RheemDocument40 paginiEspecs AA Equipos Paquete Rheemairemex100% (1)
- Samsung Klima 2012 Katalogus Catalogue SACDocument79 paginiSamsung Klima 2012 Katalogus Catalogue SACKadiri Olanrewaju0% (1)
- Project Steel SEPTEMBER 2016Document8 paginiProject Steel SEPTEMBER 2016Muhd FaridÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Relationship Between National Culture and Organizational CultureDocument104 paginiThe Relationship Between National Culture and Organizational CulturepecescdÎncă nu există evaluări
- AutoCAD Courses, AutoCAD Institute, CAD Training in ChennaiDocument10 paginiAutoCAD Courses, AutoCAD Institute, CAD Training in ChennaiCadd CentreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Foreign ReciprocityDocument44 paginiForeign ReciprocityJessa Marie GarciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Peiko connection schedule for beams, columns and wallsDocument6 paginiPeiko connection schedule for beams, columns and wallsANKUR GHOSHÎncă nu există evaluări
- ACN College of EngineeringDocument1 paginăACN College of EngineeringMohammad ShoebÎncă nu există evaluări
- Investigation On The Mechanical Properties of 3D PDocument13 paginiInvestigation On The Mechanical Properties of 3D PMd Jalal Uddin RumiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanical Engineering: Department ofDocument50 paginiMechanical Engineering: Department ofUsman SarwarÎncă nu există evaluări
- ELEHA01-Guide For Electrical Area ClassificationDocument20 paginiELEHA01-Guide For Electrical Area Classificationsubodh sarin100% (4)