Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Organic Molecules I 6th Ed
Încărcat de
Thalia SandersDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Organic Molecules I 6th Ed
Încărcat de
Thalia SandersDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
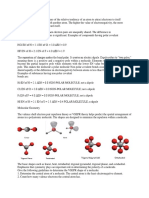
Organic Molecules I By the end of this week here are the basic concepts you should understand about
Organic Molecules: 1. 2. The differences and similarities between Carbohydrates and Lipids or Fats The basic unit for any of these groups is termed a MONOMER or basic building block. Monomers link together to form more complex compounds know as POLYMERS The process used to synthesize or build a polymer is termed DEHYDRATION SYNTHESIS this literally means the loss of water to put materials together. When the body goes through the process of digestion it uses another practice to break the polymers into smaller units. This process is termed HYDROLYSIS or literally splitting with water. We will learn more about this soon in the digestion portion of Unit 2. Carbohydrates have three basic monomers glucose, fructose and galactose all three of these have 6 carbons, 12 hydrogens, and 6 oxygens. They all have the same chemical formula but each of these monomers is structured slightly differently. This is termed an ISOMER An isomer has the same chemical formula but differs structurally. Through dehydration synthesis the monomers join together to form polysaccharides (the polymer of the carbohydrate). These are: a. starch remember we looked at that in the second lab it is the storage form of glucose in plants. b. glycogen this is the storage form of glucose in humans it is stored in liver and muscle tissue. When your blood sugar drops glucagon produced by the pancreas breaks liver glycogen down into blood sugar. c. And finally cellulose cellulose is found in plants like celery those strings in celery are cellulose fibers they provide support. Make sure you read the information on Diabetes in the Human Biology: Condensed. There are two basic types Type I also termed Juvenile diabetes and Type II or adult onset diabetes this typically occurs in individuals who are overweight and can even occur in younger children if they gain a lot of weight. Lipids or fats are also broken down into monomers triglycerides which can either be saturated or mono or poly unsaturated are built from glycerol (a three carboned sugar and fatty acids)
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10. 11.
If the fatty acids have all single bonds then they are termed saturated. If the fatty acids have one or more double bonds then they are termed unsaturated. If they have one double bond they are termed monounsaturated and if they have two or more double bonds they are called polyunsaturated. Another lipid type is the phospholipids this is found in cell membranes its monomers are the phosphate head, the glycerol group and the TWO not THREE (like in the triglycerides) fatty acid chains. Remember that steroids and the sex hormones are lipids. How to read a food label How to calculate the grams of carbohydrates remember to multiply grams by 4 (for the kcals) How to calculate the grams of protein remember to multiply grams by 4 (for the kcals) How to calculate the grams of fat remember fat stores MORE energy so you multiply grams of fat by 9. Calories are the energy content in food.
12.
13. 14. 15.
16.
17.
18.
PRACTICE PROBLEMS: 1. Which of the following groups best represents the monomers for carbohydrates? a. glucose, fructose and lactose b. glucose, amino acids, nucleotide c. glucose, fructose, galactose d. glucose, fructose, sucrose Which of the following best represents a modified triglyceride? a. steroid b. wax c. phospholipid d. cellulose Which of the following best represents the characteristics of a saturated fatty acid. a. often hydrogenated b. many single bonds present, solid at room temperature c. one or more double bonds present and liquid at room temperature d. both a and c are correct If you have a polymer and you want to make it smaller you would perform: a. dehydration synthesis b. hydration c. neither of these two processes would work Hydration or hydrolysis is: a. the addition of water b. the removal of water c. the addition of water to make things smaller d. the loss of water to make things large Type II diabetes. a. is also known as juvenile diabetes b. occurs because there are insufficient receptors on the cell membrane c. occurs because the pancreas does not produce enough insulin d. occurs when you are overweight e. both b and d are correct Type I diabetes. a. is also know as juvenile diabetes b.. occurs because there are insufficient receptors on the cell membrane c. occurs because the pancreas does not produce enough insulin d. occurs when you are overweight e. both a and c are correct
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
Glucose and Fructose are: a. isomers and monomers b. isotopes and monomers c. monomers only d. none of the above C, 13 C are examples of a. isomers b. isotopes c. neither an isomer or an isotope The items in question 9 above differ in their number of a. protons b. neutrons c. electrons d. protons, neutrons and electrons
12
9.
10.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- 1-Complaint6 Ceridian HCM Vs Chumash IndiansDocument6 pagini1-Complaint6 Ceridian HCM Vs Chumash IndiansThalia SandersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Western Sky Cert Stage ReplyDocument22 paginiWestern Sky Cert Stage ReplyThalia SandersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jackson Cert Opp Brief WesternSkyFinancial v. D.jacksonDocument42 paginiJackson Cert Opp Brief WesternSkyFinancial v. D.jacksonThalia SandersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Edward v. SouthcarolinaDocument11 paginiEdward v. SouthcarolinaThalia SandersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mapp v. Ohio 367 U.S. 643, 81 S.Ct. 1684Document26 paginiMapp v. Ohio 367 U.S. 643, 81 S.Ct. 1684Thalia SandersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jackson Cert Opp Brief WesternSkyFinancial v. D.jacksonDocument42 paginiJackson Cert Opp Brief WesternSkyFinancial v. D.jacksonThalia SandersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gideon v. Wainwwright 372 U.S. 335, 83 S.ct. 792Document10 paginiGideon v. Wainwwright 372 U.S. 335, 83 S.ct. 792Thalia SandersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bell at Corp v. Twombly 550 U.S. 544, 127 S.ct. 1955Document36 paginiBell at Corp v. Twombly 550 U.S. 544, 127 S.ct. 1955Thalia SandersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Goldberg v. Miller 371 Md. 591, 810 A.2d 947Document15 paginiGoldberg v. Miller 371 Md. 591, 810 A.2d 947Thalia SandersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rafferty v. PGC 423 F.supp. 1045Document21 paginiRafferty v. PGC 423 F.supp. 1045Thalia SandersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Washington v. Texas 388 U.S. 14-87 S.ct. 1920Document8 paginiWashington v. Texas 388 U.S. 14-87 S.ct. 1920Thalia SandersÎncă nu există evaluări
- James Et Al v. Freder Cty Pub Sch. 441 F.supp.2d 755Document8 paginiJames Et Al v. Freder Cty Pub Sch. 441 F.supp.2d 755Thalia SandersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ibarra v. US 120 F.3d 472Document6 paginiIbarra v. US 120 F.3d 472Thalia SandersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sta-Rite v. Peterson 876 So.2d 571Document2 paginiSta-Rite v. Peterson 876 So.2d 571Thalia SandersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Goldberg v. Miller 371 Md. 591, 810 A.2d 947Document15 paginiGoldberg v. Miller 371 Md. 591, 810 A.2d 947Thalia SandersÎncă nu există evaluări
- LaShawn A. v. Gray Progress Report November 21 2011Document199 paginiLaShawn A. v. Gray Progress Report November 21 2011Thalia SandersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ashcroft v. Iqubal 129 S.ct. 1937Document25 paginiAshcroft v. Iqubal 129 S.ct. 1937Thalia SandersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Marvin Vs Marvin 18cal.3d660Document19 paginiMarvin Vs Marvin 18cal.3d660Thalia SandersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mar 24 2014Document9 paginiMar 24 2014Thalia SandersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plaintiffs ResponsetoMotiontoIntervene11 VannDocument14 paginiPlaintiffs ResponsetoMotiontoIntervene11 VannThalia SandersÎncă nu există evaluări
- New York Life Ins. Co. v. Brown, 84 F .3d 137 141Document18 paginiNew York Life Ins. Co. v. Brown, 84 F .3d 137 141Thalia SandersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mar 26 2014 Int' Bus MGMTDocument8 paginiMar 26 2014 Int' Bus MGMTThalia SandersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wiwa v. Royal Dutch Petroleum Co., 626 F. Supp. 2d 377 - DistDocument9 paginiWiwa v. Royal Dutch Petroleum Co., 626 F. Supp. 2d 377 - DistThalia SandersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Palsgraf v. Long Island Railroad 222 App. Div. 166Document4 paginiPalsgraf v. Long Island Railroad 222 App. Div. 166Thalia SandersÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1989-6-20 DC Lashawn ComplaintDocument48 pagini1989-6-20 DC Lashawn ComplaintThalia SandersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wiwa v. Royal Dutch Petroleum Co., DistDocument16 paginiWiwa v. Royal Dutch Petroleum Co., DistThalia SandersÎncă nu există evaluări
- African Island NationsDocument5 paginiAfrican Island NationsThalia SandersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coolidge v. New Hampshire - 403 U.S. 443 (1971)Document49 paginiCoolidge v. New Hampshire - 403 U.S. 443 (1971)Thalia SandersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mar 25 2014 Int'l Bus Mngmt.Document7 paginiMar 25 2014 Int'l Bus Mngmt.Thalia SandersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Washington Post EXPRESS - 12032010Document40 paginiWashington Post EXPRESS - 12032010Thalia SandersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (587)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (265)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- DIETARY PRINCIPLES FOR LIFE Presentation & Research File MSU 2018Document30 paginiDIETARY PRINCIPLES FOR LIFE Presentation & Research File MSU 2018Siphiwe SitholeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry of Oils & Fats and Their Health Effects: Rummi Devi SainiDocument16 paginiChemistry of Oils & Fats and Their Health Effects: Rummi Devi SainiKasirao MScÎncă nu există evaluări
- Queen LongevityDocument9 paginiQueen Longevityfabiandionisio100% (1)
- Peanut Research PaperDocument9 paginiPeanut Research PaperrosoproductsÎncă nu există evaluări
- What are Lipids? The Building Blocks of Cell MembranesDocument4 paginiWhat are Lipids? The Building Blocks of Cell MembranesLanzBognotXDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reviewer For Physical ScienceDocument13 paginiReviewer For Physical ScienceTimothy James Tolentino BruceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Manual - Organic Titration - Determination of SaturationDocument4 paginiLab Manual - Organic Titration - Determination of SaturationAbdul HalimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lipids: Structures, Functions, PropertiesDocument28 paginiLipids: Structures, Functions, Propertiesdessa delacruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Managing NAFLD - Hamilton Health Sciences PDFDocument12 paginiManaging NAFLD - Hamilton Health Sciences PDFrutnomleniÎncă nu există evaluări
- English For Nutritionist by Novia RosdamayantiDocument26 paginiEnglish For Nutritionist by Novia RosdamayantiNovia RD100% (2)
- Oxidation in Omega-3 Oils: An OverviewDocument8 paginiOxidation in Omega-3 Oils: An Overviewjorge alberto regalado arcayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Characterization of LipidsDocument4 paginiCharacterization of LipidsEzraela Neriah AmodoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spinal Touch CatalogDocument53 paginiSpinal Touch CatalogJose J. HerreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Our Objective: What Are Fatty Acids?Document5 paginiOur Objective: What Are Fatty Acids?Sunita MauryaÎncă nu există evaluări
- XX Virgin Coconut OilDocument10 paginiXX Virgin Coconut OilTeguh Shaleh TahirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of FatDocument3 paginiTypes of FatDennis Mark PalimaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lipide: Saturated FatsDocument3 paginiLipide: Saturated FatsMonica CreangaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Swank MS DietDocument8 paginiSwank MS DietSilvia RadulescuÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Are CarbohydratesDocument7 paginiWhat Are CarbohydratesconstantinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gold MedalDocument256 paginiGold MedalAnonymous XK3Cp2Pk3Încă nu există evaluări
- Isolation, Purification, and Partial Characterization of A Lipid Extract From NutmegDocument12 paginiIsolation, Purification, and Partial Characterization of A Lipid Extract From NutmegJulio Francisco100% (2)
- Nutritional Biochemistry 1 - LIPIDSDocument62 paginiNutritional Biochemistry 1 - LIPIDSAdnan AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- 48.1 Nutrients: Chapter 48: Digestive and Excretory SystemDocument19 pagini48.1 Nutrients: Chapter 48: Digestive and Excretory Systemapi-520057338Încă nu există evaluări
- LipidsDocument60 paginiLipidsEuneun Bustamante100% (1)
- Lab Exercise 6Document3 paginiLab Exercise 6clarence manegdegÎncă nu există evaluări
- Raven Biology of Plants: Eighth EditionDocument43 paginiRaven Biology of Plants: Eighth EditionMoath EnnabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Notes On LipidsDocument4 paginiNotes On LipidsCheyenne Kaye EspirituÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 8 Lecture Notes: Lipids Structure and FunctionsDocument26 paginiChapter 8 Lecture Notes: Lipids Structure and FunctionsNeenu RajputÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3 Lipids PDFDocument55 paginiChapter 3 Lipids PDFVinz TombocÎncă nu există evaluări
- Triacylglycerol and Fatty Acid ClassificationDocument6 paginiTriacylglycerol and Fatty Acid ClassificationGil Angelo VillaluzÎncă nu există evaluări