Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Wireless
Încărcat de
Ajeet Kumar GametiDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Wireless
Încărcat de
Ajeet Kumar GametiDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
PRACTICAL NO: 6
AIM:Study of wireless communication protocol.
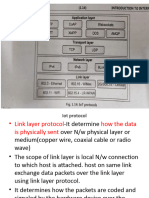
IrDA:
The infrared data association (IrDA) promotes interoperable, low cost, infrared data communication that support a walk up and point-to-point user mode. Data transfer rate of 9.6 kbps and 4 Mbps. IrDA hardware deployed in notebook computers, printers, PDAs, digital cameras, public phones, cell phones. Lack of suitable drivers has slowed use by applications.
BLUETOOTH:
New, global standard for wireless connectivity. Based on low-cost, short-range radio link. Connection established when within 10 meters of each other. No line-of-sight required.
e.g., Connect to printer in another room.
IEEE 802.11 WIRELESS PROTOCOL:In 1997 the IEEE adopted the first wireless local area network (WLAN) standard, IEEE 802.11. This standard defines the media access control (MAC) and physical (PHY) layers for a LAN with wireless connectivity. It addresses local area networking where the connected devices communicate over the air to other devices that are within close proximity to each other There are two different ways to configure a network. 1. Infrastructure network 2. Ad-hoc network
WIRELESS LAN IN INFRASTRUCTURE MODE: This architecture uses fixed network access points with which mobile nodes can communicate. System is divided into small cells called BSS which are connected to each other through a infrastrucure. It widden LAN s capablity by bridging wireless nodes to wired nodes. It is similar to present day cellular network.
WIRELESS LAN IN AD HOC MODE: In this network, there is no infrastructure or access point. The nodes form a cluster and communicate with each other. Special algorithms are designed to select a master station from given stations.
IEEE 802.11 STANDARDS:-
THE 802.11 LAYER DESCRIPTION:The IEEE places parameters for both physical and MAC layers of the network.
PHY LAYER:
physical layer.
handles transmission of data between nodes. provisions for data transfer rates of 1 or 2 Mbps. operates in 2.4 to 2.4835 GHz frequency band (RF). also operates in 300 to 428,000 GHz (IR) frequency band.
The physical layer is divided into three layers
FREQUENCY-HOPPING SPREAD SPECTRUM:- this layer contains clocking information to synchronise the receivers clock to the clock of transmitted packet.
DIRECT SEQUENCE SPREAD SPECTRUM:- this layer is responsible for synchronizing and receiving data bits correctly.
INFRARED: - infrared provide line of sight transmission so it is considered a secure medium for transmission.
MAC LAYER: medium access control layer protocol responsible for maintaining order in shared medium collision avoidance/detection performs fragmentation, retransmission of packets, acknowledgment.
THE CSMA/CA PROTOCOL:-
In this protocol the following steps are performed to send a data
When a node has to transmit a data, it first sense the channel is free or not. It sends RTS(Request to send) packet of full length. If the channel is free, the receiver send a short CTS (clear to send) packet.
Otherwise it chooses a back-off factor, which determines the time for which it waits, until it is allowed to send the packet.
After this exchange, the time when the channel is free, the sender waits for a short time (back-off time) and then transmits the data. Since the possibility that two sender chooses same back-off time is less, so the chances of collision are minimized. When the packet is received successfully as determined by cyclic redundancy check (CRC) , the receiving node transmit a acknowledgment (ACK) packet to the sender.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- III 1 Electrification 1 28Document35 paginiIII 1 Electrification 1 28SannyBombeoJomoc100% (1)
- Generalised Cockcroft-Walton Voltage MultipliersDocument2 paginiGeneralised Cockcroft-Walton Voltage MultipliersfeelblastÎncă nu există evaluări
- En FM-Pro4, Pro4 3G DatasheetDocument5 paginiEn FM-Pro4, Pro4 3G DatasheetJoko PitoyoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.2 Standards and NetworkingDocument43 pagini2.2 Standards and NetworkingallaboutanalogÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data Communication and NetworksDocument12 paginiData Communication and NetworksChitranshi SaxenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- IOT Unit 1.4Document11 paginiIOT Unit 1.4Umesh BhosaleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter2.3 MACDocument74 paginiChapter2.3 MACJanvi SahuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Internet of Things (Iot) : L2. Zigbee Protocol - IntroductoryDocument33 paginiInternet of Things (Iot) : L2. Zigbee Protocol - IntroductoryGGÎncă nu există evaluări
- IoT ZigbeeDocument90 paginiIoT ZigbeePranjal YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4 NetworkingDocument57 paginiChapter 4 NetworkingAyush KakdeÎncă nu există evaluări
- VSATDocument11 paginiVSATShashwat TiwariÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHAP 2bDocument47 paginiCHAP 2bGANESAN AÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 03Document36 paginiCH 03FathimaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Networking Leson 6Document23 paginiNetworking Leson 6Sofia De GuzmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 03 Lan, Wan, ManDocument110 pagini03 Lan, Wan, ManStefanus ChristianÎncă nu există evaluări
- 03 Lan, Wan, ManDocument122 pagini03 Lan, Wan, Manjefri fransÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cse 3003: Computer Networks: Dr. Sanket Mishra ScopeDocument56 paginiCse 3003: Computer Networks: Dr. Sanket Mishra ScopePOTNURU RAM SAIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 3Document61 paginiModule 3Devankit SanuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presented By: IEEE 802.11 Wireless LANDocument17 paginiPresented By: IEEE 802.11 Wireless LANGaurav KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Switched Media Technologies: LAN Switches Are Used To Interconnect Multiple LAN Segments. LANDocument10 paginiSwitched Media Technologies: LAN Switches Are Used To Interconnect Multiple LAN Segments. LANapi-26570979Încă nu există evaluări
- Komunikasi Data Dan Jaringan Komputer - Pertemuan 4Document38 paginiKomunikasi Data Dan Jaringan Komputer - Pertemuan 4Ksatria AFKÎncă nu există evaluări
- MN - Unit 2Document50 paginiMN - Unit 212c04gokulsboaÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE-379 Embedded Systems and Applications: Introduction To EthernetDocument25 paginiEE-379 Embedded Systems and Applications: Introduction To EthernetJohn HowardÎncă nu există evaluări
- IoT-Lecture-11 - Networking and Communication - IVDocument19 paginiIoT-Lecture-11 - Networking and Communication - IVARNAV JAINÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data Comunication CH 1Document22 paginiData Comunication CH 1Desalegn sirnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data Communication Data Communication & Networking & NetworkingDocument47 paginiData Communication Data Communication & Networking & NetworkingNida ShahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Name - Prachi M. Jichkar Roll No - 221 Reg. No - 19010919 Subject - Wireless Sensor NetworkDocument6 paginiName - Prachi M. Jichkar Roll No - 221 Reg. No - 19010919 Subject - Wireless Sensor Networkprachi jichkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of NetworksDocument13 paginiTypes of NetworkssumitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lec 15, 16Document19 paginiLec 15, 16Atif MahmoodÎncă nu există evaluări
- BCENT - Basic Cisco Entry Networking Technician: Introducing Wide-Area NetworksDocument41 paginiBCENT - Basic Cisco Entry Networking Technician: Introducing Wide-Area NetworksmanuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ec8004-Wireless Networks - HandoutsDocument30 paginiEc8004-Wireless Networks - HandoutsGtecEceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bluetooth Architecture and Protocol StackDocument17 paginiBluetooth Architecture and Protocol StackArun K KollamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4: Network Access: ObjectivesDocument10 paginiChapter 4: Network Access: Objectivesovidiu0702Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit - Iv Local Area Networks: Course ContentDocument9 paginiUnit - Iv Local Area Networks: Course ContentMaheedhar ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Network Sizes and IEEE 802.X StandardsDocument28 paginiNetwork Sizes and IEEE 802.X StandardsVim SamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intra-Organizational Electronic Commerce: Chapter 12: Appendix By: Anna Janinah E. RamosDocument34 paginiIntra-Organizational Electronic Commerce: Chapter 12: Appendix By: Anna Janinah E. RamosAnna JaninahÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7 IT Section: 7.1 Network AdministrationDocument16 pagini7 IT Section: 7.1 Network AdministrationRavi K YaddehigeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer NetworksDocument63 paginiComputer Networkskcmaharshi100% (2)
- WiFi OverviewDocument33 paginiWiFi OverviewAbhijeet PadoleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Fundamental CSE 111Document24 paginiComputer Fundamental CSE 111Azharul IslamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wide Area Network (WAN)Document36 paginiWide Area Network (WAN)Nikhil PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ec8004-Wireless Networks - HandoutsDocument30 paginiEc8004-Wireless Networks - HandoutsSanthanaprabhuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Networks: Types of Networks: Network ArchitecturesDocument65 paginiComputer Networks: Types of Networks: Network ArchitecturesAyush MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Networks Networking - HardwareDocument21 paginiComputer Networks Networking - HardwareShujaat YousufÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHAPTER 2 Local-Area Networks and LAN SwitchingDocument114 paginiCHAPTER 2 Local-Area Networks and LAN Switchingmikeyas meseretÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zigbee Technology: Wireless Control That Simply WorksDocument45 paginiZigbee Technology: Wireless Control That Simply Worksarun134Încă nu există evaluări
- 2009 New Presentation On WimaxDocument68 pagini2009 New Presentation On WimaxHarazneh Abu HazemÎncă nu există evaluări
- IEEE 802.11 Wireless LAN: Draft StandardDocument23 paginiIEEE 802.11 Wireless LAN: Draft Standardswapankumar62Încă nu există evaluări
- Computer Networks and Cloud ComputingDocument61 paginiComputer Networks and Cloud ComputingIndra RakhimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wireless Technologies: Digital CommunicactionDocument46 paginiWireless Technologies: Digital CommunicactionErick Vicente Yagual GuevaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial 4Document9 paginiTutorial 4susmita lamsalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data Comm & NetworkingDocument8 paginiData Comm & NetworkingTea BletaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8 WlansDocument78 pagini8 WlansMahendra MunirathnamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wireless Comm PrinciplesDocument95 paginiWireless Comm PrinciplesSenthilathiban ThevarasaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optical NWDocument39 paginiOptical NWAbhijeet NandanwankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Motivation For Cross-Layer Protocol Design: Name - Deepshikha Bhattacharya Reg. No. - Mp19Coe001Document45 paginiMotivation For Cross-Layer Protocol Design: Name - Deepshikha Bhattacharya Reg. No. - Mp19Coe001Vishal Raj (MT19CPS020)Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit 5Document24 paginiUnit 5nkkameshÎncă nu există evaluări
- DCN Unit - 4Document115 paginiDCN Unit - 4Rohan SaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- WN Chapter 4 WPANDocument27 paginiWN Chapter 4 WPANRdsharukh DaroorÎncă nu există evaluări
- SemSim CCNA Cram SheetsDocument9 paginiSemSim CCNA Cram SheetsMohan KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advances in Analog and RF IC Design for Wireless Communication SystemsDe la EverandAdvances in Analog and RF IC Design for Wireless Communication SystemsGabriele ManganaroEvaluare: 1 din 5 stele1/5 (1)
- One Word Substitution Capsule of 85 Words PDFDocument3 paginiOne Word Substitution Capsule of 85 Words PDFSelvaraj VillyÎncă nu există evaluări
- EntropyDocument10 paginiEntropyRajesh TripathyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Format of CVDocument1 paginăFormat of CVAjeet Kumar GametiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gate 2012 BrochureDocument16 paginiGate 2012 BrochureShantanu ChakrabortyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Demand Factor-Diversity Factor-Utilization Factor-Load FactorDocument13 paginiDemand Factor-Diversity Factor-Utilization Factor-Load FactorYousif_Abdalhalim100% (1)
- Real Time Control: TimersDocument48 paginiReal Time Control: TimersGovind ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Item Name Description 1.0 WS-C3750X-24T-S Line Number Service DurationDocument2 paginiItem Name Description 1.0 WS-C3750X-24T-S Line Number Service DurationBarce Lamasia CatalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 6: Advance Engineering MathematicsDocument2 paginiModule 6: Advance Engineering MathematicsSanty Enril Belardo Jr.Încă nu există evaluări
- Lighting Controls Patterns For Design PDFDocument299 paginiLighting Controls Patterns For Design PDFJankovski22 MaksÎncă nu există evaluări
- CS6461 - Computer Architecture Fall 2016 Instructor Morris LancasterDocument28 paginiCS6461 - Computer Architecture Fall 2016 Instructor Morris Lancaster闫麟阁Încă nu există evaluări
- How To Completely Test LCD Inverter TransformeDocument9 paginiHow To Completely Test LCD Inverter Transformeعلی اصغر هاشمیÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Science: Lecture-5: Topic-Nodal and Mesh AnalysisDocument13 paginiElectrical Science: Lecture-5: Topic-Nodal and Mesh Analysisi_khandelwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Axiomatic Manual UMAX0318x0Document52 paginiAxiomatic Manual UMAX0318x0Miguel 1856Încă nu există evaluări
- Beckwith-Generator Protection 1Document188 paginiBeckwith-Generator Protection 1Catrina FedericoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 02 PDFDocument39 pagini02 PDFbond29Încă nu există evaluări
- Basic Busway TrainingDocument44 paginiBasic Busway TrainingThức Võ100% (1)
- SB 22BDocument8 paginiSB 22Bghiles100% (1)
- Air DolphinDocument4 paginiAir DolphinChristian Mena CervantesÎncă nu există evaluări
- 13.a1701 OmDocument12 pagini13.a1701 Ommohd arif fahmi mohamad salehÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digital Communication (EC 691) Lab Manual Protected PDFDocument62 paginiDigital Communication (EC 691) Lab Manual Protected PDFPoulami RoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cylon KNX GatewayDocument4 paginiCylon KNX GatewayJulián HernándezÎncă nu există evaluări
- ABB Surge Arrester MWK - Data Sheet 1HC0075865 E01 ABDocument5 paginiABB Surge Arrester MWK - Data Sheet 1HC0075865 E01 ABsriniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 Slides - Overcurrent Protection of RelaysDocument68 paginiChapter 2 Slides - Overcurrent Protection of RelaysDale Steyn100% (3)
- Decca TreeDocument4 paginiDecca Treeiuridicaprima4Încă nu există evaluări
- Level Measurement QuestionsDocument6 paginiLevel Measurement QuestionsInstrumentation ToolsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ee321 ObjectivesDocument3 paginiEe321 ObjectivesJomar DadorÎncă nu există evaluări
- TestingDocument14 paginiTestingRaj Kumar PrajapatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- ATS01N209QN: Product DatasheetDocument5 paginiATS01N209QN: Product DatasheethajhdjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optimal Capacitor Configuration For Enhancement of System Reliability Using Genetic Algorithm: A Case Study of IEEE 30 Bus SystemDocument5 paginiOptimal Capacitor Configuration For Enhancement of System Reliability Using Genetic Algorithm: A Case Study of IEEE 30 Bus SystemIDESÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 1-5Document66 paginiLesson 1-5Gian Andrei BenaguaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Installation Booklet Shipyard Standards: Marine Institute of Memorial University of NewfoundlandDocument81 paginiElectrical Installation Booklet Shipyard Standards: Marine Institute of Memorial University of NewfoundlandHoangÎncă nu există evaluări