Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Statique Du Solide
Încărcat de
Nedia RawenTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Statique Du Solide
Încărcat de
Nedia RawenDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
1
Cours de statique des solides
3
me
anne licence contrle et commande
des systmes numriques
prsent par Imed Kari
Ingnieur Principal
Anne universitaire 2011/2012
Ecole suprieure des sciences
et technologies de Hammam Sousse
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
2
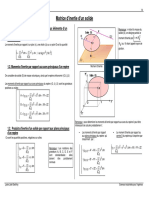
RAPPEL MATHEMATIQUE
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
3
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
4
INTRODUCTION
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
5
La statique tudie
Les
exerces sur des corps
actions mcaniques
Indformables et en quilibre
?
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
6
S
B
A
Cste AB alors S B et A = e
temps du cours au
AB
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
7
La statique tudie
Les
exerces sur des corps
actions mcaniques
Indformables et en quilibre
?
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
8
ACTIONS MECANIQUES
DEFINITION
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
9
D'une faon gnrale, on appelle action mcanique toute
cause physique susceptible de :
maintenir un corps au repos,
dformer un corps.
crer, maintenir ou modifier un mouvement
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
10
Elles peuvent tre rparties en 2 grandes familles
Les FORCES
(tourner/tordre autour d'un axe) (pousser/tirer selon un axe)
Les MOMENTS
F
C
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
11
ACTIONS MECANIQUES
MODELISATION
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
12
Les actions mcaniques sont modlises par des vecteurs
car elles en possdent toutes les proprits :
Point dapplication
Norme
Sens
Direction
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
13
Les FORCES sont reprsentes par une simple flche
Unit : NEWTON (N)
F
Les MOMENTS sont reprsents par une double flche
Unit : NEWTON mtre (Nm)
M
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
14
ACTIONS MECANIQUES
CLASSIFICATION
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
15
Les actions mcaniques sont classes en deux familles:
Actions mcaniques
De contact distance
Action de la pesanteur
Actions magntiques
(Sans contact)
Dans les liaisons
mcaniques
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
16
g m P =
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
17
2
1
N
N
S
S
Aimants permanents
2 1
F
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
18
Tout contact, provoque une action mcanique
On les classe en 3 types suivant la forme du contact
3
1
2
2 3
F
2 1
F
2 1
F
A
C
B
A
C
B
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
19
ACTION / CONTACT PONCTUEL
2 1
F
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
20
ACTION / CONTACT LINEAIRE
}
= dl p F .
F
p
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
21
ACTION / CONTACT SURFACIQUE
}}
= dS p F .
F
p
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
22
Les actions mcaniques sont classes en deux familles:
Actions mcaniques
De contact distance
Action de la pesanteur
Actions magntiques
(Sans contact)
Dans les liaisons
mcaniques
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
23
LIAISONS MECANIQUES
NOTIONS DE DEGRE DE LIBERTE
(DEGRE DE MOBILITE)
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
24
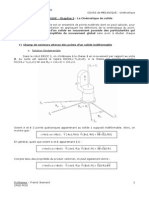
x
z
y
1
x
1
O
1
y
1
z
O
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
25
x
z
y
1
x
1
O
1
y
1
z
1
o
O
1
OO
1 1 1 1
O o Oo OO + =
x
T
y
T
z
T
x
o
1
y
o
1
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
26
x
z
y
1
x
1
O
1
y
1
z
O
1
x
1
y
1
u
1
u
x
y
1
x
1
y
z z =
1
) , ( ) , (
1
1
1
y y x x = = u
z
R
| |
|
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
1 0 0
0 ) cos( ) sin(
0 ) sin( ) cos(
1 1
1 1
u u
u u
z
R
z z =
1
z
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
27
1
x
z
y
O
x
1
z
2
u
x
z
1
x
1
z
y y =
1
) , ( ) , (
1 1
2
z z x x = = u
2
u
y
R
1
x
1
O
1
y
1
z
| |
|
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
) cos( 0 ) sin(
0 1 0
) sin( 0 ) cos(
2 2
2 2
u u
u u
y
R
y y =
1
y
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
28
x x =
1
z
y
O
1
z
1
y
3
u
3
u
y
z
1
y
1
z
x x =
1
) , ( ) , (
1
1 3
z z y y = = u
x
R
1
x
1
O
1
y
1
z
| |
|
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
) cos( ) sin( 0
) sin( ) cos( 0
0 0 1
3 3
3 3
u u
u u
x
R
x
x
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
29
x
z
y
1
x
1
O
1
y
1
z
O
| | | | | | | |
x y z
R R R R =
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
30
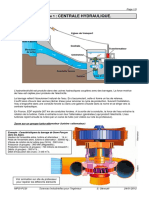
x
z
y
O
S
x
R
x
T
z
T
y
T
z
R
y
R
Trois translations
z
y
x
T
T
T
Trois rotations
z
y
x
R
R
R
6 degrs de libert dans lespace (3 dans le plan)
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
31
Les actions mcaniques sont classes en deux familles:
Actions mcaniques
De contact distance
Action de la pesanteur
Actions magntiques
(Sans contact)
Dans les liaisons
mcaniques
?
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
32
LIAISONS MECANIQUES
CLASSIFICATION
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
33
Encastrement
Reprsentation plane
Reprsentation spatiale
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
34
Torseur statique
Torseur cinmatique
Encastrement
0
0
0
0
0
0
t
e Cinmatiqu
N
M
L
Z
Y
X
Statique
t
P
P
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
35
Reprsentation plane
Reprsentation spatiale
Glissire (axe ) ) , ( x O
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
36
Torseur statique
Torseur cinmatique
0
0
0
0
0 u
e Cinmatiqu
t
N
M
L
Z
Y
Statique
0
t
P
P
Glissire (axe ) ) , ( x O
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
37
Reprsentation plane
Reprsentation spatiale
Pivot (axe ) ) , ( x O
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
38
Torseur statique
Torseur cinmatique
0
0
0
0
0
o
t
e Cinmatiqu
N
M
Z
Y
X
Statique
0
t
) , ( x O Pe
) , ( x O Pe
Pivot (axe ) ) , ( x O
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
39
Reprsentation plane
Reprsentation spatiale
Pivot glissant (axe ) ) , ( x O
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
40
Torseur statique
Torseur cinmatique
0
0
0
0
u
e Cinmatiqu
o
t
N
M
Z
Y
Statique
0 0
t
) , ( x O Pe
) , ( x O Pe
Pivot glissant (axe ) ) , ( x O
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
41
Reprsentation plane
Reprsentation spatiale
Rotule (centre O)
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
42
Torseur statique
Torseur cinmatique
0
0
0
|
o
t
e Cinmatiqu
0
0
0
Z
Y
X
Statique
t
O
O
Rotule (centre O)
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
43
Reprsentation plane
Reprsentation spatiale
Appui plan (de normale ) ) , ( z O
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
44
Torseur statique
Torseur cinmatique
0
0
0
v
u
e Cinmatiqu
0
0
0
M
L
Z
Statique
t
Appui plan (de normale ) ) , ( z O
P
P
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
45
Reprsentation plane
Reprsentation spatiale
Linaire rectiligne (daxe de normale ) ) , ( z O ) , ( x O
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
46
Torseur statique
Torseur cinmatique
0
0 v
u
e Cinmatiqu
o
t
0
0
0
0
M
Z
Statique
t
) , ( z x plan Pe
) , ( z x plan Pe
Linaire rectiligne (daxe de normale ) ) , ( z O ) , ( x O
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
47
Reprsentation plane
Reprsentation spatiale
Linaire annulaire (daxe ) ) , ( x O
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
48
Torseur statique
Torseur cinmatique
0
0
u
e Cinmatiqu
|
o
t
0
0
0 0
Z
Y
Statique
t
O
O
Linaire annulaire (daxe ) ) , ( x O
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
49
Reprsentation plane
Reprsentation spatiale
Ponctuelle (de normale ) ) , ( z O
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
50
Torseur statique
Torseur cinmatique
0
v
u
e Cinmatiqu
|
o
t
0
0
0
0
0
Z
Statique
t
) , ( z O Pe
) , ( z O Pe
Ponctuelle (de normale ) ) , ( z O
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
51
Reprsentation plane
Reprsentation spatiale
Hlicodale (daxe ) ) , ( x O
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
52
Torseur statique
Torseur cinmatique
=
0
2
v
p u
e Cinmatiqu
t
o
|
o
t
=
N
M
X
p
L
Z
Y
X
Statique
t
t
2
) , ( x O Pe
) , ( x O Pe
Hlicodale (daxe ) ) , ( x O
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
53
PRINCIPE FONDAMENTAL
DE LA STATIQUE
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
54
PRINCIPE FONDAMENTAL
DE LA STATIQUE (PFS)
PRINCIPE DES ACTIONS MUTUELLES
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
55
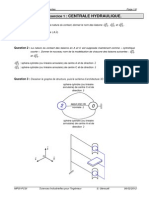
Pour deux solides en contact et en quilibre, laction
exerce par le solide 1 sur le solide 2 est gale et
directement oppose laction du solide 2 sur le solide 1
On isole 1 On isole 2
A
1
2
A A
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
56
1
2
A A A
1 / 2
F
2 / 1
F
2 / 1 1 / 2
F F =
Sil ny a pas de frottement, les actions sont
perpendiculaires au plan tangent aux 2 surfaces de
contact et sont diriges vers lintrieur de la matire
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
57
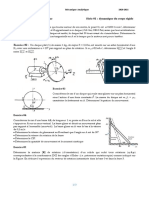
y
x
1
2
A A
1 / 2
F
Sil y a frottement, les actions ne sont plus
perpendiculaires au plan tangent
A
1 / 2
F
y
F
) 1 / 2 (
=
=
N F
T F
y
x
) 1 / 2 (
) 1 / 2 (
x
F
) 1 / 2 (
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
58
y
x
A
1 / 2
F
x
F
) 1 / 2 (
y
F
) 1 / 2 (
=
=
N F
T F
y
x
) 1 / 2 (
) 1 / 2 (
f
N
T
tg = = ) (
Coefficient de frottement
>
s
N f T glissement de cas le Dans
N f T adhrence d cas le Dans '
Lois de Coulomb
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
59
PRINCIPE FONDAMENTAL
DE LA STATIQUE (PFS)
ENONCE
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
60
Dans un repre Galilen, pour tout systme isol (S) en
quilibre par rapport ce repre, la somme des toutes les
actions mcaniques extrieures exercs sur S est nulle
0
1
=
n
i
F A M
n
F A
i
=
0
1
) ( /
criture vectorielle
{ } { } A
n
A
i
=
0
1
t
criture torsorielle
S
T
A
T
I
Q
U
E
D
E
S
S
O
L
I
D
E
S
Imed Kari, Ingnieur Principal
61
Tlchargement cours introductif en format PDF
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Théorie et conception des filtres analogiques, 2e édition: Avec MatlabDe la EverandThéorie et conception des filtres analogiques, 2e édition: Avec MatlabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Les Liaisons 2020Document1 paginăLes Liaisons 2020Mohamed AbedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapitre Torseur 200928Document25 paginiChapitre Torseur 200928fatou100% (1)
- Chapitre 2 TorseursDocument13 paginiChapitre 2 TorseursHediFatnassiÎncă nu există evaluări
- TD 17 Corrigé - Liaisons ÉquivalentesDocument6 paginiTD 17 Corrigé - Liaisons ÉquivalentesJawad Hamriti50% (2)
- Cours ElectroniqueDocument61 paginiCours ElectroniquegajoneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Corrigé TD 10 - Comportement Cinématique Des SystèmesDocument5 paginiCorrigé TD 10 - Comportement Cinématique Des Systèmesbhs channelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chap3 Cinematique Du Solide OkDocument16 paginiChap3 Cinematique Du Solide OkmatozoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exercices MIP MAPDocument3 paginiExercices MIP MAPyounesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cours StatiqueDocument13 paginiCours StatiqueMouss TachegachtÎncă nu există evaluări
- TD 3 CinemaTiqueDocument15 paginiTD 3 CinemaTiqueMohamed OuladÎncă nu există evaluări
- DYN Cours - Dynamique Et Énergétique Des Systèmes de Solides Indéformables - CorrigéDocument22 paginiDYN Cours - Dynamique Et Énergétique Des Systèmes de Solides Indéformables - CorrigéCandy Soundouss100% (1)
- TD1 Mec Ana 2020 ÉnoncéDocument3 paginiTD1 Mec Ana 2020 ÉnoncéMeddour WassimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrotechnique Theoremes FondamentauxDocument12 paginiElectrotechnique Theoremes Fondamentauxbolaye0% (1)
- TD 17 - Liaisons Équivalentes PDFDocument5 paginiTD 17 - Liaisons Équivalentes PDFAbdelhakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exo2 - Composition Des MouvementsDocument6 paginiExo2 - Composition Des MouvementsToufikJalalEddineÎncă nu există evaluări
- MecaniqueDocument18 paginiMecaniqueStephane Durel MbidaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Génie Électrique Compteur Sunchrone 2012 2013 (Aiissa)Document13 paginiGénie Électrique Compteur Sunchrone 2012 2013 (Aiissa)nicegtoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 Bis - Bilan Liaisons Mecanique V MCDocument2 pagini2 Bis - Bilan Liaisons Mecanique V MCnadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- c2 Notion de TorseurDocument6 paginic2 Notion de TorseurbilalwikiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elmsup PDFDocument105 paginiElmsup PDFAsmaELMourafikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cinématique 2022Document51 paginiCinématique 2022said houmairiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bascule S NewDocument128 paginiBascule S NewR.s. FélixÎncă nu există evaluări
- TorseurDocument46 paginiTorseurnooneoveroneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exercices Avec Solution StatiqueDocument5 paginiExercices Avec Solution StatiqueJérémy LobetÎncă nu există evaluări
- 228351P00 PDFDocument264 pagini228351P00 PDFchristophe100% (1)
- 06 Resume Cours Statique GraphiqueDocument2 pagini06 Resume Cours Statique GraphiqueYassine Lakhal100% (2)
- Transmission de Puissance Avec Transformation de MouvementDocument19 paginiTransmission de Puissance Avec Transformation de MouvementPhil ČhrýstaĺÎncă nu există evaluări
- CNC 1987 MP PhysiqueDocument5 paginiCNC 1987 MP Physiqueanass grini100% (1)
- TD 20 - Loi Entrée-Sortie À L'aide D'un Produit Scalaire Constant de Deux Vecteurs D'orientationDocument6 paginiTD 20 - Loi Entrée-Sortie À L'aide D'un Produit Scalaire Constant de Deux Vecteurs D'orientationibrahim rabbajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exercice Esa PDFDocument53 paginiExercice Esa PDFAnonymous z1YdjrQt7Q50% (2)
- Exercices de Statique TSI 1Document31 paginiExercices de Statique TSI 1Mamoun DrissiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sujet Mai-2018 - Poste de Perçage Automatique PDFDocument19 paginiSujet Mai-2018 - Poste de Perçage Automatique PDFdiassaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Les Liaisons MécaniquesDocument6 paginiLes Liaisons Mécaniquesabdelhi74100% (2)
- C02 Cinematique - Cours2Document57 paginiC02 Cinematique - Cours2basilecoqÎncă nu există evaluări
- 14 Modelisation CinematiqueDocument10 pagini14 Modelisation Cinematiquemezziwalid099411Încă nu există evaluări
- Reference Dynamique Du RotorDocument7 paginiReference Dynamique Du Rotorromy94496Încă nu există evaluări
- Matrice D'inertieDocument4 paginiMatrice D'inertieJean AbelaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Examen de Synthèse de Mécanique Du SolideDocument3 paginiExamen de Synthèse de Mécanique Du SolideMESSAOUI0% (1)
- Mecanique 1BTSDocument30 paginiMecanique 1BTSKonan Wilfried100% (1)
- Chapitre 5 ExercicesDocument5 paginiChapitre 5 ExercicesYahiyaoui SofyaneÎncă nu există evaluări
- TD2 Cinematique Corrige PHY12ab 2014Document13 paginiTD2 Cinematique Corrige PHY12ab 2014MohamedBejjaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liaisons 2001 PDFDocument6 paginiLiaisons 2001 PDFerzrzretgertfertge100% (1)
- Fonction Transmettre Transmission de Puissance Poulie Courroie ExercicesDocument9 paginiFonction Transmettre Transmission de Puissance Poulie Courroie ExercicesHamid MchachraÎncă nu există evaluări
- TD 1 CorrectionDocument0 paginiTD 1 Correctionm-roi2005Încă nu există evaluări
- TD Mecanique Du Solide PC RibiereDocument26 paginiTD Mecanique Du Solide PC RibiereAnouar MekkaouiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comportement Statique Des SystèmesDocument23 paginiComportement Statique Des Systèmeskokonut84Încă nu există evaluări
- 0 - Rappel Cinématique &Document2 pagini0 - Rappel Cinématique &Kamel HamdiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exercices d'Ondes, d'Optique et d'ÉlectromagnétismeDe la EverandExercices d'Ondes, d'Optique et d'ÉlectromagnétismeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simulation des vibrations mécaniques, 2e édition: par Matlab, Simulink et AnsysDe la EverandSimulation des vibrations mécaniques, 2e édition: par Matlab, Simulink et AnsysÎncă nu există evaluări
- Isaac Newton vs Robert Hooke sur la loi de la gravitation universelleDe la EverandIsaac Newton vs Robert Hooke sur la loi de la gravitation universelleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Formation 3D par la pratique avec C#5 et WPF: Modeliser des moleculesDe la EverandFormation 3D par la pratique avec C#5 et WPF: Modeliser des moleculesÎncă nu există evaluări
- FreeCAD | étape par étape: Apprenez à créer des objets 3D, des assemblages et des dessins techniquesDe la EverandFreeCAD | étape par étape: Apprenez à créer des objets 3D, des assemblages et des dessins techniquesÎncă nu există evaluări
- TD Ihm N2Document2 paginiTD Ihm N2Nedia Rawen100% (1)
- Skype GuideDocument15 paginiSkype GuideNedia RawenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exercice Java Traite LeDocument3 paginiExercice Java Traite LeNedia RawenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tuto JEE PDFDocument174 paginiTuto JEE PDFNedia RawenÎncă nu există evaluări
- TD 2 - Cryptographie Asymétrique (Corrigé)Document2 paginiTD 2 - Cryptographie Asymétrique (Corrigé)Nedia Rawen87% (31)
- Examen Corriges MI2EL3 20072008Document21 paginiExamen Corriges MI2EL3 20072008cultiniumÎncă nu există evaluări
- IntroductionDocument3 paginiIntroductionBadr Eddine LaaroussiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gestion de ProjetDocument136 paginiGestion de ProjetNedia RawenÎncă nu există evaluări
- AdminlinuxDocument89 paginiAdminlinuxlinuxesiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Statique Des PoutresDocument46 paginiStatique Des PoutresNedia RawenÎncă nu există evaluări
- GEMMADocument7 paginiGEMMANedia RawenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Les Liaisons MécaniquesDocument6 paginiLes Liaisons Mécaniquesabdelhi74100% (2)
- DuPontT Polymères TechniquesDocument153 paginiDuPontT Polymères TechniquesAslam JarrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- FR CFSDFSDFSD WCWXWCWXDocument14 paginiFR CFSDFSDFSD WCWXWCWXHamzaKadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Serie Cinetique Chimique 2015-2016Document4 paginiSerie Cinetique Chimique 2015-2016Daghsni Said25% (4)
- Emd 2 MMC 2012Document2 paginiEmd 2 MMC 2012Houcine Cool75% (4)
- Exemple de Calcul Des Poutres Suivant Le BaelDocument12 paginiExemple de Calcul Des Poutres Suivant Le BaelYuùri GimmsÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 Filtration Doc AZDocument11 pagini1 Filtration Doc AZasmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fasc 8 Feuille ExcelDocument2 paginiFasc 8 Feuille ExcelMalik AtikÎncă nu există evaluări
- MEC222 Cours01Document28 paginiMEC222 Cours01lamaj hugoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fiche D'exercices N°3 - Révisions Sur Nombre Dérivé - Fonctions DérivéesDocument2 paginiFiche D'exercices N°3 - Révisions Sur Nombre Dérivé - Fonctions Dérivéeszelda wegrzyniakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dimensionnement CanalisationDocument28 paginiDimensionnement Canalisationlaurhan100% (2)
- Introduction VenturieDocument4 paginiIntroduction VenturiewalidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Série D'exercices 20 - Math - Complexe - Espace - Logaritme - Suite - Integrale - Bac Sciences Exp (2017-2018) MR RommaniDocument2 paginiSérie D'exercices 20 - Math - Complexe - Espace - Logaritme - Suite - Integrale - Bac Sciences Exp (2017-2018) MR RommaniMohamed Helmi ChebbiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3.3 - M. Akchiche - Modelisation-Cesar LCPC PDFDocument33 pagini3.3 - M. Akchiche - Modelisation-Cesar LCPC PDFSMAILZEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rapport Construction Metallique Pylone 2Document70 paginiRapport Construction Metallique Pylone 2sofie100% (2)
- DT3987 PDFDocument12 paginiDT3987 PDFomarbossÎncă nu există evaluări
- Projet DidactiqueDocument3 paginiProjet DidactiqueCiubuca GetaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 1 Chapitre - 3Document3 pagini4 1 Chapitre - 3Ahmed GoudaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cours de Commande Robuste H Infini PDFDocument45 paginiCours de Commande Robuste H Infini PDFHamzaKadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oeuvre (1) Jollivet-Castelot PDFDocument12 paginiOeuvre (1) Jollivet-Castelot PDFpapusienÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2010 Liban Exo2Document176 pagini2010 Liban Exo2Tko ToolÎncă nu există evaluări
- M04 Series de Fourier 2Document3 paginiM04 Series de Fourier 2Saad SebÎncă nu există evaluări
- RDMDocument28 paginiRDMABIRADAMÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 Brochure Spread Tube Acier Revetu 1Document8 pagini1 Brochure Spread Tube Acier Revetu 1dimachampionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modelisation Du Laminage A Froid Des Aciers. Etude Des Aspects Metallurgiques. Analyse Par La Methode Des TranchesDocument7 paginiModelisation Du Laminage A Froid Des Aciers. Etude Des Aspects Metallurgiques. Analyse Par La Methode Des TranchesphukaifrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Controle HydroDocument2 paginiControle HydroAnonymous 80p9OVÎncă nu există evaluări
- L05 PHR004 2010 PDFDocument22 paginiL05 PHR004 2010 PDFMarwane OuadadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Traitement de Surface Des Meta - NAJIM Mohammed - 253 PDFDocument32 paginiTraitement de Surface Des Meta - NAJIM Mohammed - 253 PDFRebahi FaresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practica 1 TeoremasDocument5 paginiPractica 1 TeoremasEdson JoelÎncă nu există evaluări