Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Attitude
Încărcat de
Sweta SinghDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Attitude
Încărcat de
Sweta SinghDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Attitude
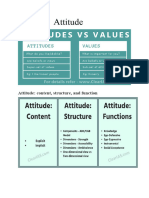
An attitude is a hypothetical construct that represents an individual's degree of like or dislike for something. Attitudes are generally positive or negative views of a person, place, thing, or event this is often referred to as the attitude object. People can also be conflicted or ambivalent toward an object, meaning that they simultaneously possess both positive and negative attitudes toward the item in question. Jung's definition of attitude is a "readiness of the psyche to act or react in a certain way" (Jung, [1921] 1971:par. 687). Attitudes very often come in pairs, one conscious and the other unconscious. Within this broad definition Jung defines several attitudes.
Attitude formation:Unlike personality, attitudes are expected to change as a function of experience. Tesser (1993) has argued that hereditary variables may affect attitudes - but believes that they may do so indirectly. For example, consistency theories, which imply that we must be consistent in our beliefs and values. The most famous example of such a theory is Dissonance-reduction theory, associated with Leon Festinger, although there are others, such as the balance theory. Emotion and attitude change:Emotion is a common component in persuasion, social influence, and attitude change. Much of attitude research emphasized the importance of affective or emotion components. Emotion works hand-in-hand with the cognitive process, or the way we think, about an issue or situation. Emotional appeals are commonly found in advertising, health campaigns and political messages. Recent examples include no-smoking health campaigns and political campaign advertising emphasizing the fear of terrorism. Attitudes and attitude objects are functions of cognitive, affective and conative components. Attitudes are part of the brain s associative networks, the spider-like structures residing in long term memory that consist of affective and cognitive nodes. By activating an affective or emotion node, attitude change may be possible, though affective and cognitive components tend to be intertwined. In primarily affective networks, it is more difficult to produce cognitive counterarguments in the resistance to persuasion and attitude change. Affective forecasting, otherwise known as intuition or the prediction of emotion, also impacts attitude change. Research suggests that predicting emotions is an important component of decision making, in addition to the cognitive processes. How we feel about an outcome may override purely cognitive rationales.
In terms of research methodology, the challenge for researchers is measuring emotion and subsequent impacts on attitude. Since we cannot see into the brain, various models and measurement tools have been constructed to obtain emotion and attitude information. Measures may include the use of physiological cues like facial expressions, vocal changes, and other body rate measures. For instance, fear is associated with raised eyebrows, increased heart rate and increase body tension (Dillard, 1994). Other methods include concept or network mapping, and using primes or word cues. Attitudes are evaluative statement favorable or unfavorable related to person, object or event. They reflect that how one feel about something. For example if someone says that I like my job. This statement expresses his attitude towards his job. Each and every person has different attitude at different conditions. There are three components of attitude:1: Cognitive component: It refers that's part of attitude which is related in general know how of a person, for example, he says smoking is injurious to health. Such type of idea of a person is called cognitive component of attitude. 2: Effective component: This part of attitude is related to the statement which affects another person. For example, in an organization a personal report is given to the general manager. In report he point out that the sale staff is not performing their due responsibilities. The general manager forwards a written notice to the marketing manager to negotiate with the sale staff. 3: Behavioral Component: The behavioral component refers to that part of attitude which reflects the intension of a person in short run or in long run. For example, before the production and launching process the product. Report is prepared by the production department which consists of there intention in near future and long run and this report is handed over to top management for the decision. Functions of Attitudes:Attitudes serve four major functions for the individual: (1) the adjustments function, (2) the ego defensive function, (3) the value expressive function (4) the knowledge function. Ultimately these functions serve people s need to protect and enhance the image they hold of themselves. In more general terms, these functions are the motivational bases which shape and reinforce
positive attitudes toward goal objects perceived as need satisfying and / or negative attitudes toward other objects perceived as punishing or threatening. These situations are diagrammed in Figure below. The functions themselves can help us to understand why people hold the attitudes they do toward psychological objects. Figure Punishing threatening up rewarding objects object Adjustment Function The adjustment function directs people toward pleasurable or rewarding objects and away from unpleasant, undesirable ones. It serves the utilitarian concept of maximizing reward and minimizing punishment. Thus, the attitudes of consumers depend to a large degree on their perceptions of what is needed satisfying and what is punishing. Because consumers perceive products, services and stores as providing need satisfying or unsatisfying experiences we should expect their attitudes toward these object to vary in relation to the experiences that have occurred. Ego Defensive Function Attitudes firmed to protect the ego or self image from threats help fulfill the ego defensive function. Actually many outward expressions of such attitudes reflect the opposite of what the person perceives him to be. For example a consumer who has made a poor purchase decision or a poor investment may staunchly defend the decision as being correct at the time or as being the result of poor advice from another person. Such ego defensive attitude helps us to protect out self image and often we are unaware of them. Value expression function Whereas ego defensive attitudes are formed to protect a person s self image, value expressive attitudes enable the expression of the person s centrally held values. Therefore consumers adopt certain attitudes in an effort to translate their values into something more tangible and easily expressed . Thus, a conservative person might develop an unfavorable attitude toward bright clothing and instead be attracted toward dark, pin striped suits. Marketers should develop an understanding of what values consumers wish to express about themselves and they should design products and promotional campaigns to allow these self expressions. Not all products lend themselves to this form of market segmentation however. Those with the greatest potential for value expressive segmentation are ones with high social negative Attitude Positive-- need satisfying
visibility. Cross pens, Saks Fifth Avenue clothes. Ferrari automobiles and Bang & Children stereo systems are examples. Knowledge function Humans have a need for a structured and orderly world, and therefore they seek consistency stability definition and understanding. Out of this need develops attitudes toward acquiring knowledge. In addition, the need to know tends to be specific. Therefore an individual who does not play golf, nor wish to learn the sport is unlikely to seek knowledge or an understanding of the game. This will influence the amount of information search devoted to this topic. Thus, out of our need to know come attitudes about what we believe we need or do not need to understand. In addition attitudes enable consumers to simplify the complexity of the real world. That is, as was pointed out in the chapter information processing, the real world is too complex for us to cope with so we develop mechanisms to simplify situations. We saw that this involves sensory thresholds and selective attention and it also involves attitudes. Attitudes allow us to categorize or group objects as a way of knowing about them. Thus, when a new object is experienced we attempt to categorize it into a group which we know something about. In this way the object can share the reactions we have for other objects in the same category. This is efficient because we do not have to spend much effort reacting to each new object as a completely unique situation. Consequently we often find consumers reacting in similar ways to ads for going out of business sales limited time offers American made goods etc. Of course there is some risk of error in not looking at the unique aspects or new information about objects but for better or worse, our attitudes have influenced how we feel and react to new examples of these situations.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Music DLP General Music 7th Grade Lesson PlanDocument17 paginiMusic DLP General Music 7th Grade Lesson PlanJohn RoaÎncă nu există evaluări
- W.H. Auden, Herod Considers The Massacre of The InnocentsDocument4 paginiW.H. Auden, Herod Considers The Massacre of The InnocentsJarrettMoran100% (2)
- AttitudeDocument9 paginiAttitudeAnupam ChaturvediÎncă nu există evaluări
- Functions of AttitudesDocument2 paginiFunctions of Attitudessmartboy9211Încă nu există evaluări
- Function of AttitudeDocument4 paginiFunction of AttitudeUbaid M. KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter Seven The Nature of Consumer AttitudeDocument7 paginiChapter Seven The Nature of Consumer AttitudeSualih OumerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Consumer Behaviour Unit-3Document17 paginiConsumer Behaviour Unit-3shikha kashyapÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wa0026.Document6 paginiWa0026.sibghamehboob6Încă nu există evaluări
- CB AssignmentDocument8 paginiCB AssignmentAreej FatimaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Attitudes: What Are They?Document14 paginiAttitudes: What Are They?Archana NairÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is AttitudeDocument9 paginiWhat Is AttitudeMahmud AsiÎncă nu există evaluări
- OrganisationalBehaviour BookDocument316 paginiOrganisationalBehaviour BookvidhyaaravinthanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Attitude: There Are Three Components of Attitude. 1: Cognitive ComponentDocument12 paginiAttitude: There Are Three Components of Attitude. 1: Cognitive ComponentVidur PandeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Study On Employee Attitude On Presidency Kid Leather LimitedDocument81 paginiA Study On Employee Attitude On Presidency Kid Leather LimitedBhaktha RagavanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 3Document14 paginiModule 3Labour lawÎncă nu există evaluări
- Theoretical Framework - Definition and Explanation: Cognitive ComponentDocument4 paginiTheoretical Framework - Definition and Explanation: Cognitive ComponentBen HiranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Attitudes and Attitude ChangeDocument4 paginiAttitudes and Attitude ChangeAmmara HaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- MBA III - Consumer Behavior (Unit 2)Document7 paginiMBA III - Consumer Behavior (Unit 2)Saurabh SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- AttitudeDocument2 paginiAttitudeRabia NaseemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Personality: An Overview of Personality: Its Nature and Their Application To Consumer BehaviourDocument11 paginiPersonality: An Overview of Personality: Its Nature and Their Application To Consumer BehaviourMortha KrishnaprasadÎncă nu există evaluări
- DOB Notes FinalDocument17 paginiDOB Notes FinalAzmat Shaikh100% (1)
- P I Lecture-3Document22 paginiP I Lecture-3Sanjida Akter LamiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Components of AttitudeDocument4 paginiThe Components of AttitudeikramÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Individual and The Organisation: AttitudesDocument28 paginiThe Individual and The Organisation: AttitudesFrancis PhiriÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5-Attitude & PersuasionDocument52 pagini5-Attitude & PersuasionayazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Attitude 2.1-Concept & Theories of Attitude 2.2 - Theories of Attitude FormationDocument19 paginiAttitude 2.1-Concept & Theories of Attitude 2.2 - Theories of Attitude FormationAhlam Assaih100% (1)
- CB 3Document9 paginiCB 3RIBIN VARUGHESE RAJANÎncă nu există evaluări
- Social PsychologyDocument6 paginiSocial PsychologyEDER AYALA PARCOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Attitude 2.1-Concept & Theories of Attitude 2.2 - Theories of Attitude FormationDocument19 paginiAttitude 2.1-Concept & Theories of Attitude 2.2 - Theories of Attitude FormationVarsha YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter-1 Employee Attitude AttitudeDocument26 paginiChapter-1 Employee Attitude AttitudeKrishna RajÎncă nu există evaluări
- AttitudeDocument4 paginiAttitudeAnkita SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adoption and Change: Col Zulfiquer Ahmed Amin Armed Forces Medical Institute (AFMI)Document49 paginiAdoption and Change: Col Zulfiquer Ahmed Amin Armed Forces Medical Institute (AFMI)Shekhar SunthaÎncă nu există evaluări
- AttitudeDocument28 paginiAttitudejainmoulik33Încă nu există evaluări
- Attitudes and Social CognitionDocument15 paginiAttitudes and Social CognitionArushi SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- OB Mid 1 Answer.Document9 paginiOB Mid 1 Answer.rushipavan5Încă nu există evaluări
- Attitude: Attitudes-Behaviour RelationshipDocument7 paginiAttitude: Attitudes-Behaviour RelationshipAbdul HayeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Textual Notes - Social InfluencesDocument29 paginiTextual Notes - Social InfluencesSandesh WaghmareÎncă nu există evaluări
- Attitude FormationDocument4 paginiAttitude FormationSimar ZuluÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psychological Factors of MotivationDocument13 paginiPsychological Factors of MotivationDrSivasundaram Anushan SvpnsscÎncă nu există evaluări
- Attitude 160403112216Document43 paginiAttitude 160403112216pallaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Study On Consumer Attitude Towards Spatter Automobile Spares Parts Private Limited at CoimbatoreDocument23 paginiA Study On Consumer Attitude Towards Spatter Automobile Spares Parts Private Limited at CoimbatoreAnonymous qRAAcePÎncă nu există evaluări
- SteroDocument4 paginiSteroSai SevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ca 1 MKT613Document21 paginiCa 1 MKT613Sooraj sÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bagian Sagung AdvancedDocument6 paginiBagian Sagung Advancedsagung anindyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activity 5Document3 paginiActivity 5Syahirah ZackÎncă nu există evaluări
- Individual Buyer BehaviourDocument12 paginiIndividual Buyer BehavioursulgenerisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Consumer Buying Behaviour: The 21 Century ConsumersDocument6 paginiConsumer Buying Behaviour: The 21 Century ConsumersAsad LaghariÎncă nu există evaluări
- PerceptionDocument7 paginiPerceptionSivaranjani RadhakrishnanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Attitudes and PersuationDocument37 paginiAttitudes and PersuationNauman ButtÎncă nu există evaluări
- Attitudes and BehaviorDocument9 paginiAttitudes and BehaviorGunay MahmudovaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Notes On The Introduction To AttitudesDocument4 paginiNotes On The Introduction To AttitudesPlacement officerÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 3 CB - AttitudeDocument9 paginiCH 3 CB - AttitudeKeyur KevadiyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Organizational Behavior SEMESTER I 2010/2011: Individual EssayDocument6 paginiOrganizational Behavior SEMESTER I 2010/2011: Individual EssayxaraprotocolÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 2Document22 paginiUnit 2vini2710Încă nu există evaluări
- Utilitarian FunctionDocument2 paginiUtilitarian FunctionAdnan Al ShahidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1 and 2Document6 paginiChapter 1 and 2Adrita DasÎncă nu există evaluări
- AttitudesDocument21 paginiAttitudesNiranjan BeheraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Secrets of Dark Psychology: Recognizing the manipulatorsDe la EverandSecrets of Dark Psychology: Recognizing the manipulatorsEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- ES 13 Insightsonindia - com-SYNOPSIS Insights 70 Days Ethics Plan Day 13Document4 paginiES 13 Insightsonindia - com-SYNOPSIS Insights 70 Days Ethics Plan Day 13sunilÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Attitude Is A Hypothetical Construct That Represents An Individual'sDocument4 paginiAn Attitude Is A Hypothetical Construct That Represents An Individual'svaruunni10% (1)
- HRD Unit 3Document5 paginiHRD Unit 3ASNDC HOST9Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit 3: Consumer AttitudeDocument15 paginiUnit 3: Consumer Attitudedhruvi kakadiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- BookList Gr11 2022-23Document2 paginiBookList Gr11 2022-23NATAYA POWELLÎncă nu există evaluări
- Theoretical BackgroundDocument7 paginiTheoretical BackgroundRetarded EditsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rizal Street, Poblacion, Muntinlupa City Telefax:8828-8037Document14 paginiRizal Street, Poblacion, Muntinlupa City Telefax:8828-8037Marilou KimayongÎncă nu există evaluări
- HUM01-Philosophy With LogicDocument4 paginiHUM01-Philosophy With LogicJulioRamilloAureadaMercurioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Malaysian Online Journal of Educational Sciences: JANUARY 2021, 9Document19 paginiMalaysian Online Journal of Educational Sciences: JANUARY 2021, 9guanyitorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Approved Secure English Language Test CentresDocument1 paginăApproved Secure English Language Test CentresFranck Duprey MvogoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Research in The 21 ST CenturyDocument6 paginiNursing Research in The 21 ST CenturyBreezy ReveloÎncă nu există evaluări
- AIBL Background of The CompanyDocument6 paginiAIBL Background of The CompanySISkobir100% (1)
- School Facilities and Observation ChecklistDocument5 paginiSchool Facilities and Observation ChecklistMhadellaine JunatasÎncă nu există evaluări
- If You Are A ScientistDocument2 paginiIf You Are A ScientistCkysha TumpagÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Qualitative ResearchDocument28 paginiTypes of Qualitative ResearchGlazel Valenzuela Guardario GaudiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MPH@GW CurriculumDocument8 paginiMPH@GW CurriculumHenry SeamanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guidelines For Radio ProgramDocument4 paginiGuidelines For Radio ProgramTirtharaj DhunganaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ASA Acoustic Requirements For Schools PDFDocument50 paginiASA Acoustic Requirements For Schools PDFMohd Zulhairi Mohd NoorÎncă nu există evaluări
- College Tuition Cost Research PaperDocument8 paginiCollege Tuition Cost Research Paperhjuzvzwgf100% (1)
- Introduction To The Philosophy of Human Person Week 1: Human Persons As Oriented Towards Their Impending DeathDocument4 paginiIntroduction To The Philosophy of Human Person Week 1: Human Persons As Oriented Towards Their Impending DeathMariel Lopez - MadrideoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Broadcasting WorkshopDocument9 paginiBroadcasting WorkshopRyan De la TorreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hadleigh Markun - 2019 Vertical Articulation Sample and Activity No DirectionsDocument1 paginăHadleigh Markun - 2019 Vertical Articulation Sample and Activity No Directionsapi-510451077100% (1)
- Individual Differences, 48, 926-934.: Piers - Steel@haskayne - UcalgaryDocument44 paginiIndividual Differences, 48, 926-934.: Piers - Steel@haskayne - UcalgaryArden AriandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anju BalaDocument2 paginiAnju BalaSANDEEP SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Josaa Iit MandiDocument1 paginăJosaa Iit MandiRevant SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To EntrepreneurshipDocument35 paginiIntroduction To EntrepreneurshipAzizki WanieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reaction Paper On Rewards and RecognitionDocument8 paginiReaction Paper On Rewards and RecognitionMashie Ricafranca100% (2)
- Scoring RubricsDocument10 paginiScoring RubricsLyn GarciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nationalism Research PaperDocument28 paginiNationalism Research PaperCamille CatorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Teori Apple and Muysken (1987)Document3 paginiTeori Apple and Muysken (1987)Nadhirah AfendiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physical Education Practical 1Document10 paginiPhysical Education Practical 1Mitul LovrasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ebp Chart With DefsDocument2 paginiEbp Chart With Defsapi-265973793Încă nu există evaluări