Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Science Year 7 & 8
Încărcat de
Ezyan272Descriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Science Year 7 & 8
Încărcat de
Ezyan272Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Lower Secondary Science Scheme of Work for SECONDARY ONE
No. 1.0 1.1 Topic / Sub-topic INTRODUCING SCIENCE Laboratory safety Objectives Students should be able to: state the basic laboratory safety rules including the standard evacuation procedure in case of fire in the laboratories; explain first aid treatment in common laboratory mishaps (chemical spills on body and eye, burn from hot water or apparatus); identify common laboratory apparatus and state their functions (test tube, dropper, evaporating dish, conical flask, boiling tube, test tube holder, glass rod, beaker, measuring cylinder, dropper, evaporating dish, conical flask, filter funnel, wire gauze, tripod stand); draw sectional diagrams of common laboratory apparatus; identify the different parts of a Bunsen burner or Labo gas burner (chimney, collar and air hole); state the function of the different parts of a Bunsen burner and Labo gas burner; carry out the proper technique of lighting a Labo gas burner; show an awareness of the limitations of human sense organs and thus the need for measuring instruments; state the SI units for length, area, volume, time, mass and temperature; carry out inter-conversion of units e.g. kilometres to metres, centimetres to metres and kilograms to grams; Time Frame (Weeks) 11
Suggested Activities / Resources
Practical Activity 1.1 OHT 1.1 OHT1.5 a OHT 1.5 b Practical Activity 1.2 Practical Activity 1.3 (Part A and B only) Practical Activity 1.4 OHT 1.2 and overlay OHT 1.2
1.2
Handling common laboratory apparatus
1.3
Measurements
Practical Activity 1.5
No. 1.3.1
Topic / Sub-topic Length, volume area and
Objectives recognise how to read meter rule correctly (parallax error); calculate the area of a regular-shaped object; estimate the approximate area of an irregular-shaped object e.g. the palm of the hand, the foot or the leaf; calculate the volume of a regular-shaped object; recognise how to read the volume using the meniscus level of the measuring cylinder; carry out an activity to find the volume of an irregularshaped object using the displacement of liquid method; show proficiency in the proper use of stopwatch, stop clock, beam balance and electronic balance; show an awareness of the accuracy of an electronic balance; define density as mass of a substance in one cubic centimetre; use the formula of density in calculations; state that solids of the same substance have the same density irrespective of shape and size. carry out an activity to find out that different substances will have different densities; recognise that floating depends on the density of matter with reference to: i) floating of a liquid on another liquid (limit to two liquids only); and ii) floating of a solid on a liquid;
Time Frame (Weeks)
Suggested Activities / Resources Practical Activity 1.6 Part A only (Part B can be done as homework). Practical Activity 1.7
1.3.2
Mass and time
Practical Activity 1.8 Practical Activity 1.9
1.3.3
Density
Practical Activity 1.10 Practical Activity 1.11 Practical Activity 1.12
No. 1.3.4
Topic / Sub-topic Temperature
Objectives state that temperature is a measure of the degree of hotness or coldness; show an understanding of the safety precautions when handling the mercury thermometer; read the mercury and alcohol thermometers; state the limitations of mercury and alcohol thermometers; state the fixed points (ice point and steam point); show an understanding that in carrying out scientific experiments, three basic steps are recognised e.g. planning, observation and conclusion; and recognise that in carrying out scientific experiments, basic science process skills are required (observing, recording, measuring, communicating).
Time Frame (Weeks)
Suggested Activities / Resources Practical Activity 1.13
1.4
Process skills scientific investigations
in
Practical Activity 1.14
2.0 2.1
WATER States of water
Students should be able to:
state the three states of water: solid (ice), liquid (water) and gas
http://lgfl.skoool.co.uk
(steam); observe the changes of water in different states of matter (with reference to boiling point, melting point and freezing point); state the difference between evaporation and boiling in terms of temperature; demonstrate and state that a solid (solute) dissolves in water (solvent) to form a solution with reference to salt, sugar, sodium hydroxide pellet, copper sulphate; state that gases also dissolve in water with reference to carbon dioxide and ammonia gas only;
Practical Activity 2.1 OHT 7.1 and overlay OHT 7.1
No. 2.2
Topic / Sub-topic Separation technique
Objectives use appropriate techniques for separating constituents of mixtures by physical means (i.e. filtration, evaporation, chromatography and distillation); describe and use paper chromatography; and interpret chromatograms in terms of the number of different dyes present. Use only food colourings and ink. Students should be able to:
Time Frame (Weeks)
Suggested Activities / Resources Practical Activity 2.2 Practical Activity 2.3 Practical Activity 2.4 OHT 2.6 a and 2.6 b
3.0
CLASSIFICATION
http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools /websites/11_16/site/science .shtml
3.1 3.2
Characteristics of living things
list the main differences between living and non living things; recognise that there is a variety of plants and animals which can be grouped on the basis of observable external characteristics; classify an assortment of objects based on observable features e.g. colour, shape, size, smell as an introduction to classification skill; classify plants and animals according to common observable characteristics into Plants: algae, fern, seed plants (flowering and non-flowering plants); Animals: animals without backbones (worms, molluscs, arthropods); animals with backbones (fishes, reptiles, mammals, amphibians and birds); construct a simple classification key and use it to identify organisms; and show an awareness of the existence of microorganisms such as fungi, bacteria and viruses which are not classified as either plants or animals; 3 Practical Activity 3.1 Practical Activity 3.2 Practical Activity 3.3 Practical Activity 3.4 Practical Activity 3.5 OHT 4.1 and overlay OHT 4.1 OHT 4.2 and overlay OHT 4.2 OHT 4.3 and overlay OHT 4.3 OHT 4.4 and overlay OHT 4.4
Diversity and classification of plants and animals
4.0
FORCES
Students should be able to:
http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools /websites/11_16/site/science .shtml
4.1
Types of forces
identify the different forms of forces (i.e. push, pull, friction, force of gravity, magnetic force and turning) and what they can do; 4
No. 4.2
Topic / Sub-topic Effects of forces
Objectives observe and infer the effects of forces through experiments and students daily experiences that a force can produce: i) change in speed; ii) change in direction; iii) change in size; and iv) change in shape;
Time Frame (Weeks)
Suggested Activities / Resources Practical Activity 4.1 Practical Activity 4.2 Practical Activity 4.3
4.3
Measurement of forces Line graphs
measure force using spring balance and state the unit of force as Newton (N); differentiate between force in Newtons and energy in Joules; show an understanding of what a line graph is; plot a line graph including how to set the scale for the horizontal and vertical axes; read and interpret line graphs; define pressure as force per unit area; relate pressure with force and area: Pressure = Force Area 2 state that 1 N/m = 1 Pa; calculate pressure from force and the area on which it acts; perform simple calculations to determine the pressure in N/m2 or N/cm2 or in Pa exerted by a body such as a brick, a slab, a boy, a box and so on; state that pressure in a liquid: i) acts throughout the liquid in all directions; and ii) increases with depth; explain pressure in a gas using the particle model; state that the atmospheric pressure is due to the weight of the air; state that the normal atmospheric pressure at sea level is 760mm of mercury; and 5
Practical Activity 4.4
4.4
4.5
Pressure
Practical Activity 4.5 Practical Activity 4.6
No. 4.5 5.0
Topic / Sub-topic Pressure
Objectives state that a barometer ( mercury and aneroid) is used to measure atmospheric pressure.
Time Frame (Weeks)
Suggested Activities / Resources
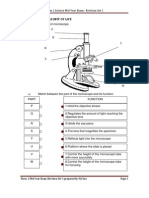
CELL STRUCTURE Students should be able to: AND ORGANISATION Basic microscopy and scientific drawing skills identify the basic parts of a microscope (mirror, stage, large knob, small knob, eyepiece, objective lens, tube, clips) and state the function of each part. show proficiency in mounting a specimen on a microscope slide. prepare fresh biological specimen (cheek cell and onion cell) draw biological specimen through observation under a microscope of a prepared slide identify and draw simple cell structures of a plant and animal cells by microscopic and photographic study; state the functions of cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, and vacuole; list the differences between plant and animal cells recognise the importance of division of labour and that in multicellular organisms, cells are organised into: Tissue organ system give examples of some systems to explain the concept of the importance of cellular organisations;
http:lgfl.skoool.co.uk
5.1
Practical Activity 5.1 OHT 1.3 and overlay OHT 1.3
5.2
Main structures of plant and animal cells
Practical Activity 5.2 Practical Activity 5.3 Practical Activity 5.4 http://www.bbc.o.uk/schools/ websites/11_16/site/science. shtml http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/ websites/11_16/site/science. shtml
5.3
Tissues, organ and system
5.4
Gross structure and identify the main organs of digestive, transport, breathing and functions of body reproductive systems; and systems state the gross function of each of the body systems.
Practical Activity 5.5 Practical Activity 5.6
No. 6.0 6.1
Topic / Sub-topic ENERGY, WORK AND POWER Sources and forms of energy
Objectives Students should be able to: state that energy is the capacity to do work; identify the various sources of energy (sun, wind, fossil fuels, food and batteries); identify the different forms of energy (stored or potential energy, kinetic energy, heat energy, light energy, sound energy, chemical energy, nuclear energy and electrical energy); list some of the energy resources in Brunei Darussalam; state that one form of energy can be converted to another e.g; Potential energy Kinetic energy identify the energy conversions in everyday applications including energy converters; state that in any energy conversion, the total amount of energy is conserved (conservation of energy in energy converters, simple systems e.g. electric lamp, hydroelectric plant and a free-falling body); identify the unit for energy in SI unit as the joules (J); state that 1 J of energy is required to lift 1 Newton of weight through a vertical distance of 1 m; relate work to the product of the force and the distance moved in the direction of the force i.e; Work (J) = Force (N) x Distance (m) identify the unit of work in SI unit as the joule (J); perform calculations involving force and distance moved;
Time Frame (Weeks) 3
Suggested Activities / Resources http:lgfl.skoool.co.uk
Practical Activity 6.1 Practical Activity 6.2 OHT 3.1 http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/ websites/11_16/site/science. shtml Practical Activity 6.3 Practical Activity 6.4 OHT 3.3 http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools /websites/11_16/site/science. shtml
6.2
Conversion of energy
6.3
Conservation of energy
6.4
Work
Practical Activity 6.5
No. 6.5
Topic / Sub-topic Power
Objectives relate power to the rate of work done and measured in watts i.e; Power (Watts) = Work (Energy) Time calculate a students power when he runs up a flight of steps; and differentiate between the units of energy (J), force (N) and power (W). Students should be able to:
Time Frame (Weeks)
Suggested Activities / Resources Practical Activity 6.6
7.0
PLANT AND ANIMAL NUTRITION Photosynthesis
http:lgfl.skoool.co.uk
7.1
outline the process of photosynthesis by which plants manufacture food using raw materials (mention conversion of light energy to chemical energy) in the form of word equation; state the conditions (chlorophyll and light) and raw materials (carbon dioxide and water) which are necessary for photosynthesis;
Practical Activity 7.1 OHT 9.5 and overlay OHT 9.5 http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/ websites/11_16/site/science. shtml
7.2
Food and its importance
state that plants are the primary food source; infer that food is a source of energy for living things; identify and describe the dietary importance of the main classes of food (protein, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, mineral salts including water and roughage); compare the relative energy values of fats, carbohydrates and proteins; investigate and describe one test for starch, sugar, protein and fat; explain the need for a balanced diet; state the effects of unbalanced diet with reference to obesity and coronary related conditions; Practical Activity 7.2 Practical Activity 7.3 OHT 9.1 OHT 9.2
7.3
Classes of food
7.4
Balanced diet
No. 7.5
Topic / Sub-topic Food additives and food processing
Objectives show awareness of the harmful effects of processed food: i) children become too active; ii) obesity; and iii) cancer-causing; state the different types of teeth in human beings; state the function of each of the different types of teeth in human beings; describe the role of teeth in mastication; state that there are two different sets of teeth in human beings (milk teeth and permanent teeth); state reasons why food must be digested; identify the main structures of the alimentary canal (mouth, salivary glands, oesophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, liver, gall bladder, pancreas, rectum and anus; state the main function (s) of the structures of the alimentary canal (mouth, stomach, small intestine and large intestine); describe how the digestive system helps in the digestion and assimilation of food and the part played by teeth and enzymes in digestion (limit to the three classes of enzymes: carbohydrases, proteases and lipases); and investigate how insoluble starch can be converted by saliva into a soluble form before diffusion can take place;
Time Frame (Weeks)
Suggested Activities / Resources Practical Activity 7.4 http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/ websites/11_16/site/science. shtml Practical Activity 7.5 OHT 9.3 and overlay OHT 9.3
7.6
Structure and function of teeth
7.7
Digestion in animals
Practical Activity 7.6 OHT 9.4 and overlay OHT 9.4 http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/ websites/11_16/site/science. shtml
Lower Secondary Science Scheme of Work for Secondary Two
8.0 8.1 REPRODUCTION IN PLANTS Floral parts Students should be able to: identify the main floral parts of a named insect pollinated flower (petal, sepal, anther, filament, stamen, stigma, style, ovary, ovule and carpel); state the functions of the main floral parts; draw the main floral parts of a named insect pollinated flower using scientific drawing skills; state that pollination is the transfer of pollen grains from an anther to a stigma; list the agents of pollination; briefly describe the floral parts associated with pollination and the role of insects in pollination; describe the mechanism and importance of seed dispersal with reference to a named local seed or fruit; show awareness that plants have different methods of dispersal; observe different stages of seed germination; and investigate conditions necessary for germination. 4 Practical Activity 8.4 Practical Activity 8.3 3 Practical Activity 8.1 Practical Activity 8.2
8.2 Pollination 8.3 Seed dispersal 8.4 Germination
Practical Activity 8.5 Practical Activity 8.6
9.0 9.1
MATTER Matter around us
Students should be able to: state some basic resources on the earth (water, air, rocks, soil, living things); show awareness of the abundance of the earths resources; show awareness of the everyday use of the earths resources and their exhaustibility;
10
No. 9.2
Topic / Sub-topic States of matter
Objectives state that matter exists as solids, liquids and gases; explain the properties of the three states of matter with reference to the Kinetic Theory of matter; list the properties of matter in terms of shape, volume and mass; classify some of earths resources into respective states of matter; state diffusion as the movement of particles; observe and explain the movement of particles in solid, liquid and gas; define the terms element, compound and mixture; identify examples of elements, compounds and mixtures; state that elements combine to form compounds; and state the properties of compounds and mixtures;
Time Frame (Weeks)
Suggested Activities / Resources Practical Activity 9.1 Practical Activity 9.2 Practical Activity 9.3 Practical Activity 9.4
9.3
Movement of particles Elements, compounds and mixtures
Practical Activity 9.5 Practical Activity 9.6 Practical Activity 9.7 Practical Activity 9.8 Practical Activity 9.9 Practical Activity 9.10 http://lgfl.skoool.co.uk Practical Activity 10.1 Practical Activity 10.2 Practical Activity 10.3 Practical Activity 10.4
9.4
10.0 10.1
MAGNETISM Magnets and magnetic field
Students should be able to: observe that a freely-suspended magnet comes to rest in North-South direction; state that a magnet has two poles; infer that like poles repel; unlike poles attract; infer that there is a magnetic field around a magnet ; identify a magnetic material experimentally; state that iron, steel, nickel and cobalt are magnetic materials; observe and draw magnetic field patterns using iron filings: i) around a magnet; ii) between two like poles arranged end to end; and iii) between two unlike poles arranged end to end. list some of the uses of magnets in everyday applications.
11
No. 11.0 11.1 11.2
Topic / Sub-topic GASES Gases in the air Properties of gases
Objectives Students should be able to: list the constituents of gases in the air in percentages (%); briefly describe the physical and chemical properties of the gases in the air (oxygen, carbon dioxide, nitrogen, noble gases and water vapour); differentiate oxygen, carbon dioxide, nitrogen and water vapour through simple laboratory tests; list the uses of the gases (oxygen, carbon dioxide, nitrogen and noble gases); state the properties of hydrogen; describe the preparation and collection of hydrogen by the reaction of reactive metals on dilute acids; state the word equation for the preparation of hydrogen gas; and state the uses of hydrogen.
Time Frame (Weeks) 3
Suggested Activities / Resources
Practical Activity 11.1 Practical Activity 11.2
11.3
Hydrogen
Practical Activity 11.3
12.0 12.1
ABUSES TO LIFE PROCESSES Drugs
Students should be able to: state the definition of drugs; describe some uses of drugs; list some commonly abused drugs; list some signs and symptoms shown by a person addicted to drugs; state the consequences of drug abuse in relation to addiction, crime and transmission of AIDS; show an awareness of the existing laws concerning abused drugs and the role of the Anti Narcotics Bureau in Brunei Darussalam; state the harmful effects of excessive consumption of alcohol by an alcoholic; state the consequences of harmful effects of alcoholics on their families and the community; 12
3 Practical Activity 12.1
12.2
Alcohol
No. 12.3
Topic / Sub-topic Tobacco
Objectives list the harmful chemicals present in tobacco smoke (tar, nicotine and carbon monoxide); state the harmful effects of active and passive smoking; and state ways to encourage public to refrain from smoking;
Time Frame (Weeks)
Suggested Activities / Resources
13.0 13.1
CURRENT ELECTRICITY Electric current
Students should be able to: state that electricity is the flow of electrons; state that the dry cell drives the electrons around a complete circuit in one direction; identify symbols of simple electric components (dry cell, switch, lamp, resistor, ammeter and voltmeter); carry out investigations to set up simple electric circuits in series and parallel; draw simple electric circuit diagrams for series and parallel circuits; infer that a resistor will reduce the current in an electric circuit; carry out investigations to connect ammeters and voltmeters correctly to an electric circuit and take readings correctly; describe the effects of increasing number of: i) cells in series and parallel; and ii) lamps in series and parallel by measuring the voltage and current flow; infer that resistance is the opposition to the flow of current; calculate the effective resistance when resistors are connected: i) in series; and ii) in parallel; state the unit of resistance as ohm;
13.2
Simple electric circuits
Practical Activity 13.1 Practical Activity 13.2 Practical Activity 13.3 Practical Activity 13.4 Practical Activity 13.5 Practical Activity 13.6 Practical Activity 13.7 Practical Activity 13.8 Practical Activity 13.9 Practical Activity 13.10 Practical Activity 13.11 Practical Activity 13.12 Practical Activity 13.13 Practical Activity 13.14
13
No. 13.3
Topic / Sub-topic Household wiring and safety devices
Objectives construct a circuit with two or more lamps and switches to operate them independently; explain the function of a fuse; explain the function of earthing the metal casing of an electrical appliance; carry out wiring a three pin fused plug correctly; and describe safety rules in the use of electricity.
Time Frame (Weeks)
Suggested Activities / Resources Practical Activity 13.15 Practical Activity 13.16
14.0 14.1
ACIDS, ALKALIS & SALTS Acids and alkalis
Students should be able to: state the properties of acids and alkalis; list some chemicals which dissolve in water to produce acids or alkalis; define neutralisation; state the word equation for neutralisation; state the importance of neutralisation in daily life; observe and describe the effects of various solutions on litmus paper and classify them as acids, alkalis or neutral solutions; and compare the degree of acidity / alkalinity of the solution given by using pH paper / Universal Indicator / pH meter.
3 Practical Activity 14.1 Practical Activity 14.2 Practical Activity 14.3 Practical Activity 14.4 Practical Activity 14.5
14.2
Neutralisation
14
No. 15.0
Topic / Sub-topic
Objectives
Time Frame (Weeks) 2
Suggested Activities / Resources
TRANSPORT Students should be able to: SYSTEM IN HUMAN BEINGS Structure of the heart state the function of the heart; briefly describe the transport (circulatory) system in human beings with reference to the heart and blood vessels; identify the main parts of the heart and the main blood vessels ( the four chambers, pulmonary artery, aorta, vena cava and valve); identify the three main types of blood vessels (arteries, veins and capillaries) and state the function of each blood vessel; state the functions of the blood; and list the substances that are transported by the blood (oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients and waste products); and show an awareness of the heartbeat, pulse and blood pressure.
15.1
Practical Activity 15.1 Practical Activity 15.2 Practical Activity 15.3
15.2
Blood
15
No. 16.0 16.1
Topic / Sub-topic REPRODUCTION IN HUMAN BEINGS Male and female reproductive organs Sexual characteristics
Objectives Students should be able to: draw and identify the male and female reproductive organs; state the functions of the male and female reproductive organs; show an awareness of the physical changes during puberty; briefly describe the menstrual cycle with reference to ovulation, fertilisation and menstruation; state that ovulation is the ejection of an egg from the ovary; state that fertilisation is the fusion of a sperm and an egg and which occurs in the oviduct; state that menstruation is the erosion of the uterine lining in the absence of fertilisation; show awareness of causes and harmful effects of sexually transmitted diseases (syphilis, gonorrhoea, AIDS); and state ways how to prevent sexually transmitted diseases.
Time Frame (Weeks) 3
Suggested Activities / Resources
Practical Activity 16.1
16.2
Practical Activity 16.2 Practical Activity 16.3 Practical Activity 16.4
16.3
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs)
16
Summary of Topics Selected in Lower Secondary Science Syllabus (Interim Stage)
Bil. 1.0 1.1 Topic / Subtopic /Additional Topic Introducing Science Laboratory safety state the basic laboratory safety rules including the standard evacuation procedure in case of fire in the laboratories. explain first aid treatment in common laboratory mishaps (chemical spills on body and eye, burn from not water or apparatus) Yr.1 Yr.2 Yr.3 & Yr.4 / Yr.5 Omit Tching Weeks Reason / Remarks
1.2
Handling common laboratory apparatus identify the different parts of a bunsen burner and Labo gas burner. carry out the proper technique of lighting a Labo gas burner. state the function of the different parts of a Bunsen burner and Labo gas burner. Identify common laboratory apparatus and state their functions (test tube, boiling tube, test tube holder, glass rod, beaker, measuring cylinder, dropper, evaporating dish, conical flask, filter funnel, wire gauze, tripod stand) draw sectional diagrams of common laboratory apparatus.
1.3
Measurements show an awareness of the limitations of human sense organs and thus the need for measuring instruments. state the SI units for length, area, volume, time, mass and temperature.
17
Bil.
Topic / Subtopic /Additional Topic carry out inter-conversion of units e.g. kilometers to metres, centimeters to metres and kilograms to grams.
Yr.1
Yr.2
Yr.3 & Yr.4 / Yr.5
Omit
Tching Weeks
Reason / Remarks
1.31
Length, area and volume recognise how to read the volume using the meniscus level of the measuring cylinder. recognise how to read metre rule correctly (parallax error) calculate the area of a regular-shaped object. estimate the approximate area of an irregular-shaped object e.g. the palm of the hand, the foot or the leaf. carry out an activity to find the volume of an irregularshaped object using the displacement of liquid method.
1.32
Mass and time show proficiency in the proper use of stopwatch, stopclock, beam balance and electronic balance. show an awareness of the accuracy of an electronic balance.
1.33
Density define density as mass of a substance in one cubic centimetre. use the formula of density in calculations show an awareness that solids of the same substance have the same density irrespective of shape and size and that two different substances will have different densities. recognise that floating depends on the density of matter with reference to floating of a liquid on another liquid and floating of a solid on a liquid (limit to two liquids only). Transfer from Yr. 2 of Water, to keep topics on Density together.
18
Bil. 1.34
Topic / Subtopic /Additional Topic Temperature state that temperature is a measure of the degree of hotness or coldness. show an understand of the safety precautions when handling the mercury thermometer. read the mercury and alcohol thermometers. state the limitations thermometers. of mercury and alcohol
Yr.1
Yr.2
Yr.3 & Yr.4 / Yr.5
Omit
Tching Weeks
Reason / Remarks
state the fixed points (ice point and steam point). Calibration of thermometer Transfer to Yr.3 because students find it difficult to understand at Yr.1 Done in Comb.Sci & Pure Phys.
1.4
Clinical thermometer Process skills in scientific investigations show an understanding that in carrying out scientific experiments, three basic steps are practised e.g. planning, observation and conclusion. recognise that in carrying out scientific experiments, basic science process skills are required (observing, recording, measuring, communicating).
2.0 2.1
Water States of water Existence of water in the form of ice, liquid and steam Water cycle in nature: evaporation, condensation Not done in Comb.Sci or Pure Sciences
19
Bil.
Topic / Subtopic /Additional Topic Boiling and freezing of water. Simple idea in terms of temperature to show differences between boiling and evaporation of water Substances that are soluble in water. Introduction to the idea of solute, solvent and solution.
Yr.1
Yr.2
Yr.3 & Yr.4 / Yr.5
Omit
Tching Weeks
Reason / Remarks
2.2
Solubility of water Effects of temperatures on solubility (simple experiments to illustrate these) Solubility of gases in water with reference to SO2, CO2, O2 and NH3 The importance of dissolved gases in water with CO2 and O2 e.g. maintaining aquatic life in water. Mention sea water has dissolved gases. Purification of water for drinking purposes Different stages in the purification of water supply Conservation of water Construction of a simple water filter in the laboratory Done in Comb.Sci & Pure Chem Done in Comb.Sci & Pure Chem Done in Comb.Sci & Pure Chem Done in Comb.Sci & Pure Chem Done in Comb.Sci & Pure Chem Done in Comb.Sci & Pure Chem Not done in Comb. Sci & Pure Chem Transfer from Matter Delete crystallisation because explanation of saturated solution is transferred to Yrs.3 & 4.
2.3
Separation technique Separation techniques of mixture by physical means (e.g. filtration, evaporation, chromatography, distillation) Describe and use paper chromatography Interpret chromatograms in terms of the number of different dyes present. Use only food colourings and ink.
20
Bil. 3.0 3.1 3.2
Topic / Subtopic /Additional Topic Classification Characteristics of living things Diversity and classification of plants and animals Variety of plants and animals in Negara Brunei Darussalam Introduction to classification Use of classification key
Yr.1
Yr.2
Yr.3 & Yr.4 / Yr.5
Omit
Tching Weeks
Reason / Remarks
4.0 4.1
Forces Types of forces Teach only push, pull, friction and turning as example of forces. Compression and tension transferred to Yr.3 because done in Pure Physics Lever is not done Comb.Sci & Pure Physics in
4.2
Lever
Effects of forces Change in speed, direction, shape and size
4.3
Measurement of force Unit of force as Newton (N) show an understanding what is a line graph. show an understanding how to plot a line graph including how to divide the scale on the horizontal and vertical axes. read and interpret line graphs. Line graph is a new subtopic. This is added in order to reinforce on practical skills at an early stage. It is done in context with the activity of measuring the weight of objects and other concrete examples are used.
21
Bil. 4.4 Pressure
Topic / Subtopic /Additional Topic
Yr.1
Yr.2
Yr.3 & Yr.4 / Yr.5
Omit
Tching Weeks
Reason / Remarks Effect and application of atmospheric pressure transferred to Yr.3 because done in Pure Physics
5.0
Relationship of a force, area and pressure (N / m2) Pressure exerted by solid, liquid and gas including atmospheric pressure Recognise the relationship between structure and function of specialised cells: root hair, xylem vessel, phloem, red blood cells and white blood cells transferred to Yr.3 since it is done in Comb.Sci & Pure Bio. New sub-topic introduced in context. To reinforce on practical skills at an early stage.
Cell Structure and organisation
5.1
Basic microscopy and scientific drawing skills
identify the basic parts of a microscope(mirror, stage, large knob, small knob, eyepiece, objective lens, tube, clips) and state the function of each part. show proficiency in mounting a specimen on a microscope slide. prepare fresh biological specimen (cheek cell and onion cell) draw biological specimen through observation under a microscope of a prepared slide.
5.2 5.3
Main structure of plant and animal cells Tissues, organs and systems
22
Bil. 5.4 5.5
Topic / Subtopic /Additional Topic Different major tissues and organs Gross structure of some body systems and their importance Topic / Subtopic /Additional Topic Energy Heat and our sense of touch Light energy and our sight Sound energy and our hearing
Yr.1
Yr.2
Yr.3 & Yr.4 / Yr.5
Omit
Tching Weeks
Reason / Remarks
Bil.
Yr.1
Yr.2
Yr.3 & Yr.4 / Yr.5
Omit
Tching Weeks
Reason / Remarks The topic on Energy is completely transferred to Yr.3 & 4 since it is done in Comb.Sci & Pure Sciences.
6.0
Energy, Work and Power
This topic is transferred from Yr.3 to Yr.1 because it provides good basic knowledge for pupils . This topic is also combined with Energy Around Us which is Yr.1
6.1
Sources and forms of energy Sources to include the sun, wind, fossil fuels, food and batteries Forms of energy to include stored or potential energy, kinetic, heat, light, sound and electrical energy Illustrate potential energy in springs, pendulums and masses at a height above the ground. Mention nuclear energy.
6.2
Conversion of energy One form of energy can be converted to another e.g. potential energy to kinetic energy
23
6.3
Conservation of energy Discuss the conservation of energy in energy converters, simple systems like an electric lamp, a hydro-electric plant and a free-falling body. Unit of energy is Joule (J) Topic / Subtopic /Additional Topic Work Unit of work (energy) is Joule. W = F x d (Calculations using the work equation may be set) Yr.1 Yr.2 Yr.3 & Yr.4 / Yr.5 Omit Tching Weeks Reason / Remarks
Bil. 6.4
6.5
Power Unit of power is watt Rate of work (energy) is power. P =W / t (Students should perform experiments to estimate power when they run up a flight of steps. Emphasis on concept attainment of energy (J), work (J), force (N) and power (W) This topic is transferred from Yr.2 to Yr.1 since it is only a small topic.
7.0
Plant nutrition
7.1
Photosynthesis Mention conversion of light energy to chemical energy Encourage pupils to plan / manage their investigations where applicable Done in Pure Biology Two new objectives added: state the equation for photosynthesis in words state and explain how a leaf is modified for photosynthesis
24
7.2 7.21
Animal Nutrition Nutrition Food and its importance Classes of food Foods tests Balanced diet
Bil. 7.3 7.4 7.5
Topic / Subtopic /Additional Topic Food additives and food processing
Yr.1
Yr.2
Yr.3 & Yr.4 / Yr.5
Omit
Tching Weeks
Reason / Remarks
Dentition and dental care Structure and function of teeth Action of bacteria on teeth Dental health
Done in Comb.Sci & Pure Bio.
Done in Comb.Sci & Pure Bio. Done in Comb.Sci & Pure Bio.
7.6
Digestion in animals Plant nutrition Transferred to Yr.1 since the content is simple enough to be understood by students.
7.7
Respiration Aerobic cellular respiration Done in Comb.Sci & Pure Bio.
7.8
Transport Importance of water Transport in plants Done in Comb.Sci & Pure Bio. Done in Comb.Sci & Pure Bio.
25
Transport of animals
Done in Yr.2 as a separate topic entitled Blood Circulatory System Reason / Remarks
Bil. 8.0 8.1
Topic / Subtopic /Additional Topic Reproduction in plants Floral parts Floral parts and functions of a named insect pollinated flower Drawing of biological specimen
Yr.1
Yr.2
Yr.3 & Yr.4 / Yr.5
Omit
Tching Weeks
This new sub-topic is introduced in context. Students can practise their scientific drawing skills with the flowers.
8.2
Pollination Agents of pollination Self and cross pollination. Done in Comb.Sci & Pure Bio.
8.3
Seed dispersal Methods of seed dispersal Importance of seed dispersal Fertilisation and seed formation Done in Comb.Sci & Pure Bio.
8.4
Germination Germination of a bean seed This topic is transferred from Yr.1 toYr.2 because it is difficult for students to understand in Yr.1
9.0
Matter
9.1
Matter around us Some basic resources on earth e.g. water, air, rocks,
26
soil, living things 9.2 States of matter. Introduce physical properties of matter with reference to water, air, soil and other basic earths resources Topic / Subtopic /Additional Topic Movement of particles 9.4 Gas, liquid and semi-solid. Diffusion of gases and liquids. Changes of matter. Temporary and permanent change of matter and their examples Not needed in Comb.Sci & Pure Sciences. Yr.1 Yr.2 Yr.3 & Yr.4 / Yr.5 Omit Tching Weeks Reason / Remarks
Bil. 9.3
Kinetic Theory of matter. Simple treatment in terms of movement of atoms and molecules.
9.5
Elements, compounds and mixtures. Elements as building blocks of mixtures and compounds. Elements as building blocks of matter Elements from the Periodic Table Properties of mixtures and compounds
10. 10.1
Magnetism Magnets and magnetic field Properties of a magnet Methods of making magnets Magnetic fields around magnet Done in Comb.Sci & Pure Phys. Delete observe and draw magnetic field patterns using iron filings around current-carrying wire.
10.2
Electromagnetism
27
Magnetic effect of electromagnet Factors affecting strength of electromagnet
Done in Comb.Sci & Pure Phys. Done in Comb.Sci & Pure Phys. Reason / Remarks
Bil. 10.3
Topic / Subtopic /Additional Topic Application of magnetism List should include electric motors, loud-speakers, microphones, door stoppers and notice board buttons Fundamental ideas of the relationship between electricity and magnetism
Yr.1
Yr.2
Yr.3 & Yr.4 / Yr.5
Omit
Tching Weeks
Done in Pure Phys. Done in Pure Phys.
11.0 11.1
Gases Gases in the air Composition of air in the atmosphere
11.2
Properties of air Physical and chemical properties of gases in the air : oxygen, carbon dioxide, nitrogen, water vapour and noble gases Carry out simple gas test of carbon dioxide, oxygen and water vapour
11.3
Hydrogen Preparation of hydrogen gas. Properties and uses of hydrogen gas. Simple gas test of hydrogen gas
11.4
Air pollution Air pollution and disruption of air composition Green house effect Done in Comb.Sci. & Pure Bio. Done in Comb.Sci. & Pure Bio.
28
Bil. 12.0 12.1
Topic / Subtopic /Additional Topic Abuses to life processes Drugs Abuse of drugs
Yr.1
Yr.2
Yr.3 & Yr.4 / Yr.5
Omit
Tching Weeks
Reason / Remarks
12.2 12.3 12.4 13.0 13.1
Alcohol Tobacco AIDS Current electricity Electric current Atomic structure Electricity as the flow of electrons A cell makes the electrons to flow in one direction (conventional direction) Done in Pure Phys.
13.2
Simple electric circuits Simple circuit diagrams Series and parallel circuits Circuit symbols Resistors in electrical circuits Use of ammeters and voltmeters Effects of increasing the number of cells in series and parallel. Resistors in series and parallel
29
Bil. 13.3
Topic / Subtopic /Additional Topic Household wiring and safety devices Functions of a switch Wiring a three pin fused plug The International colour code (old and new) Electricity bill
Yr.1
Yr.2
Yr.3 & Yr.4 / Yr.5
Omit
Tching Weeks
Reason / Remarks
Not required to know since some meters are prepaid already.
14.0 14.1
Rules and precautions to be taken with respect to electricity
Acids, alkalis and salts Acids and alkalis Properties of acids and alkalis Substances which dissolve in water to produce acids or alkali
14.2
Neutralisation Uses of pH paper, litmus paper, universal indicator, pH meter Done in Comb.Sci & Pure Chem.
14.3 15.0 15.1
Action of metals on acids and water Transport system in human beings Structure of the heart Heart and the main blood vessels in the transport system in human beings
15.2
Functions of the blood Substances transported by the blood
30
Bil. 16.0 16.1
Topic / Subtopic /Additional Topic Reproduction in human beings Male and female reproductive organs Gross structure and functions of the male and female reproductive organs
Yr.1
Yr.2
Yr.3 & Yr.4 / Yr.5
Omit
Tching Weeks
Reason / Remarks
16.2
Sexual characteristics Secondary sexual characteristics Menstrual cycle
16.3
Sexually transmitted diseases Causes and harmful effecrs of sexually transmitted diseases such as AIDS, syphilis and gonorrhoea. Not needed in Combined Sci & Pure Biology. Not needed in O Level. Done in Combined Sci & Pure Biology.
16.4 16.5 17.0
Gestation, giving birth and parental care Health care and health services Living things and their ecosystems
31
Comparison of Current and Interim Stage Lower Secondary Science Syllabus
Current Topics in Lower Secondary Science Syllabus Menengah 1 Menengah 2 Menengah 3
1. 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 2. 2.1 2.2 3. 3.1 3.2 3.3 Introducing science Laboratory safety Handling common laboratory apparatus Measurements Skills in the scientific approach Matter Matter around us Gases in the air Energy around Us Sources and forms of energy Transformation of energy Conservation of energy Grouping of living things Characteristics of living things Diversity and classification of plants and animals Cell structure, organisation and systems 7. 7.1 7.2 7.3 8. 8.1 8.2 8.3 9. 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 10.0 10.1 10.2 Water and solutions Water Hydrogen, acids, alkalis and salts Action of metals on acids and water Energy Heat and our sense of touch Light energy and our sight Sound energy and our hearing Life processes and abuses Nutrition Respiration Transport Abuses to life processes Electricity and its applications at home More on electrical circuits Resistors in series and parallel 11. 11.1 11.2 11.3 12. 12.1 12.2 12.3 13. 13.1 13.2 14. 14.1 14.2 14.3 Reproduction in plants and animals Sexual reproduction in a named flowering plant Sexual reproduction in human beings Health care and health services Forces at work Lever and turning forces Pressure Energy, work and power Living things and their ecosystems Energy flow and nutrient cycles Interdependence Magnetism Magnets and magnetic fields Electromagnetism Application of magnetism
Topics in Lower Secondary Science (Interim Stage) Year 1 Year 2
1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0 6.0 7.0 Introducing science (11) Water (3) Classification (3) Forces (3) Cell structure and organisation (4) Energy, work and power (3) Plant and animal nutrition (3) Total = 31 weeks 8.0 9.0 10.0 11.0 12.0 13.0 14.0 15.0 16.0 Reproduction in plants (3) Matter (4) Magnetism (2) Gases (3) Abuses to life processes (3) Current electricity (8) Acids, alkalis and salts (3) Transport system in human beings (2) Reproduction in human beings (3) Total = 31 weeks
4. 4.1 4.2 4.3
32
5. 5.1 5.2 5.3 6. 6.1 6.2 6.3
Basic ideas of electricity Electric current Simple electrical circuits Use of ammeters and voltmeters
10.3
Household wiring and safety devices
Forces in our everyday life Types of forces Effects of force Measurement of force
33
LIST OF COMMITTEE MEMBERS
Chairman
Awang Hj Zulkifli bin Hj Md Yusuf Curriculum Development Department Dayang Hjh Siti Hamizah binti Abdullah Curriculum Development Department Awang Ng Thye Wan Curriculum Development Department Dayang Hasliza binti Hj Sapar Sekolah Menengah Sultan Sharif Ali Dayang Hjh Rosinah binti Hj Sabli Maktab Sains Paduka Seri Begawan Sultan Dayang Susan Philipose Sekolah Menengah Sayyidina Husain Dayang Hjh Junaidah binti Hj Tahir Sekolah Menengah Sultan Muhammad Jamalul Alam Dayang Yong Sui Yan Sekolah Menengah Menglait Awang Hj Md Izul Akmal bin Hj Salleh Sekolah Menengah Rimba Awang Md Sabri bin Judin Sekolah Menengah Rimba
Deputy Chairman : Secretary Members : :
34
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Year 8 Science TestDocument3 paginiYear 8 Science TestHanan MdSomÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2011 Year 9 Science Acid Base AssessmentDocument6 pagini2011 Year 9 Science Acid Base AssessmentvleeeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Coordination And ResponseDe la EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Coordination And ResponseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elements, Compounds, Mixtures - Part 3 Writing Balanced EquationsDocument18 paginiElements, Compounds, Mixtures - Part 3 Writing Balanced EquationsHassan mahmudÎncă nu există evaluări
- Form 1 Science Mid Year Exam Revision Set 2Document4 paginiForm 1 Science Mid Year Exam Revision Set 2theeba86Încă nu există evaluări
- Year 7 Science Quiz Cells and Matter Quiz 6 Year 7 AnswerDocument14 paginiYear 7 Science Quiz Cells and Matter Quiz 6 Year 7 AnswerSithar DeviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Booklist 2019-20Document8 paginiBooklist 2019-20Furqan KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Year 7 Mathematics Assessment: Key Terms and ConceptsDocument3 paginiYear 7 Mathematics Assessment: Key Terms and Conceptseunife biscarraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practical Paper 3 NotesDocument22 paginiPractical Paper 3 NotesSuperRuhalÎncă nu există evaluări
- THEME 2 - Light QUESTIONS PDFDocument2 paginiTHEME 2 - Light QUESTIONS PDFIsra WaneeÎncă nu există evaluări
- O Level Biology Practice For Structured Questions Transport In HumansDe la EverandO Level Biology Practice For Structured Questions Transport In HumansÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gcse Exam Questions On Area and PerimeterDocument10 paginiGcse Exam Questions On Area and PerimeterLubnaLatifÎncă nu există evaluări
- Level 2 Physics Mechanics Revision Booklet 2012Document26 paginiLevel 2 Physics Mechanics Revision Booklet 2012ctremblaylcsd150Încă nu există evaluări
- Success International English Skills For Igcse Student S Book Cambridge Education Cambridge Uni SamplesDocument4 paginiSuccess International English Skills For Igcse Student S Book Cambridge Education Cambridge Uni SamplesHumaira KaleemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yr. 8 Science Exam 2019 Semester 2Document20 paginiYr. 8 Science Exam 2019 Semester 2Neil MenezesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Energy Stores PowerpointDocument16 paginiEnergy Stores PowerpointnowarabdullaaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry Exam Review PackageDocument30 paginiChemistry Exam Review PackageSagar ArenjaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SCIENCE PMR Notes and ExperimentsDocument221 paginiSCIENCE PMR Notes and ExperimentsAzlina Ahmad100% (1)
- Sow Combined Science Year 9 (2+3 Programme) v2 - 3 YearsDocument56 paginiSow Combined Science Year 9 (2+3 Programme) v2 - 3 YearsYenny Tiga100% (2)
- IGCSE Maths 5080 SOW Core 3 YearsDocument16 paginiIGCSE Maths 5080 SOW Core 3 YearsYenny Tiga0% (1)
- Chemical Ideas ContentsDocument4 paginiChemical Ideas ContentsJake RileyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Year 7: 7H Energy Stores and Transfers Notes and Resources Name: - FormDocument14 paginiYear 7: 7H Energy Stores and Transfers Notes and Resources Name: - FormJason Monteroso TulodÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8F and 8G Homework Booklet Sept & Oct 20 12Document20 pagini8F and 8G Homework Booklet Sept & Oct 20 12Mostafa100% (1)
- Kinetic Particle Theory WorksheetDocument2 paginiKinetic Particle Theory WorksheetFandy ArdyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Checkpoint AnswersDocument2 paginiCheckpoint Answerswpd0% (1)
- KS3 Year 8 Maths 2011 - Paper 1 - Level 4-6Document28 paginiKS3 Year 8 Maths 2011 - Paper 1 - Level 4-6Joseph Loroy100% (1)
- Year 8 Revision NotesDocument16 paginiYear 8 Revision NotesSathiya DeviÎncă nu există evaluări
- GCSE Mathematics 1MA1 Problem-Solving Questions 1: Higher Tier: BronzeDocument27 paginiGCSE Mathematics 1MA1 Problem-Solving Questions 1: Higher Tier: BronzeABBIE ROSEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Igcse Maths Year 11 Revision Topics Dec 2014Document3 paginiIgcse Maths Year 11 Revision Topics Dec 2014api-241068594Încă nu există evaluări
- S 495160Document4 paginiS 495160Khondokar Tarakky0% (1)
- Science Questions on Food, Nutrients, Cells, MicrobesDocument3 paginiScience Questions on Food, Nutrients, Cells, MicrobesMichael EllisÎncă nu există evaluări
- 0417 m17 QP 31Document8 pagini0417 m17 QP 31Popi MastroianniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Curriculum Map - Year 7 - PhysicsDocument6 paginiCurriculum Map - Year 7 - PhysicsDanielÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sow For Combined Science Year 9 (2+2 Programme) v2 - 2 YearsDocument80 paginiSow For Combined Science Year 9 (2+2 Programme) v2 - 2 YearsYenny TigaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Measuring Speed with Speedometers, Stopwatches & Light GatesDocument20 paginiMeasuring Speed with Speedometers, Stopwatches & Light GatesEric ChewÎncă nu există evaluări
- KSP Year 7 HandbookDocument36 paginiKSP Year 7 HandbookKSPWEBÎncă nu există evaluări
- 999906664X-2005 Ks3 Science Level 3-6 Paper 2Document32 pagini999906664X-2005 Ks3 Science Level 3-6 Paper 2pmhzsiluÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mid Year Maths Paper 2 (Ver 2)Document12 paginiMid Year Maths Paper 2 (Ver 2)Eng KengÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCEA Level 2 Physics - WavesDocument11 paginiNCEA Level 2 Physics - WavesPratik SoniÎncă nu există evaluări
- 0546 Scheme of Work (For Examination From 2022)Document39 pagini0546 Scheme of Work (For Examination From 2022)arvinp89Încă nu există evaluări
- GCSE Scince Bio Mixed QsDocument13 paginiGCSE Scince Bio Mixed QsSkyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Year 8 Biology Revision GuideDocument13 paginiYear 8 Biology Revision GuideKHAUSALYA A/P VERAKUMARÎncă nu există evaluări
- Moles and Mole CalculationsDocument14 paginiMoles and Mole CalculationsAhmadElgindyÎncă nu există evaluări
- KS3 Mathematics: Homework Pack E: Level 7Document31 paginiKS3 Mathematics: Homework Pack E: Level 7Elmor 2019Încă nu există evaluări
- Test Paper ScienceDocument28 paginiTest Paper ScienceRamin ShokuriÎncă nu există evaluări
- GCSE EnzymesDocument32 paginiGCSE EnzymesFrankie BarnesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Y9 Physics Revision BookletDocument20 paginiY9 Physics Revision BookletMaoga2013Încă nu există evaluări
- Year 10 SC Science BookletDocument108 paginiYear 10 SC Science Bookletstacie_ostle0% (1)
- 2019 Sec 4 Pure Biology-12sDocument571 pagini2019 Sec 4 Pure Biology-12sUZAIR MAHBUB BHUYAINÎncă nu există evaluări
- IGCSE / MYP / GCSE Exam Questions - AnglesDocument4 paginiIGCSE / MYP / GCSE Exam Questions - AnglesAhmed NallaÎncă nu există evaluări
- AQA GCSE Biology Practical Handbook PDFDocument60 paginiAQA GCSE Biology Practical Handbook PDFAhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- G10 worksheet for ElectrolysisDocument17 paginiG10 worksheet for Electrolysismuaz0% (2)
- Year 5 Science: HeatDocument8 paginiYear 5 Science: HeatRaj KingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Orientation Programme For Form 1 StudentsDocument24 paginiOrientation Programme For Form 1 StudentsVictor ManivelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Learning Area Learning Objectives Suggested Learning Activities Learning OutcomesDocument4 paginiLearning Area Learning Objectives Suggested Learning Activities Learning Outcomesnor shafiniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yearly Plan Form 1 EditedDocument15 paginiYearly Plan Form 1 EditedDianasalmie AhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE5801F GroupTDocument27 paginiEE5801F GroupTEzyan272Încă nu există evaluări
- Where Does The Learning Take Place - Sue PetersDocument19 paginiWhere Does The Learning Take Place - Sue PetersEzyan272Încă nu există evaluări
- Patients Action During Their Cardiac Event Qualitative Study Exploring Differences and Modifiable FactorsDocument11 paginiPatients Action During Their Cardiac Event Qualitative Study Exploring Differences and Modifiable FactorsEzyan272Încă nu există evaluări
- The Role of Schools - Perceived Human Resource PoliciesDocument12 paginiThe Role of Schools - Perceived Human Resource PoliciesEzyan272Încă nu există evaluări
- Term Dates 2012Document1 paginăTerm Dates 2012Ezyan272Încă nu există evaluări
- Final SPN21 Biology SoW - Topic 7Document14 paginiFinal SPN21 Biology SoW - Topic 7Ezyan2720% (1)
- Abdullah.1.Ubd Thinking SkillDocument14 paginiAbdullah.1.Ubd Thinking SkillEzyan272Încă nu există evaluări
- Ernst & Young: Public Sector Compensation ReviewDocument88 paginiErnst & Young: Public Sector Compensation ReviewThe Vancouver SunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Skellig - Chapters 16-20 QuestionsDocument1 paginăSkellig - Chapters 16-20 Questionselishasantos0% (1)
- Chapter One - Understanding The Digital WorldDocument8 paginiChapter One - Understanding The Digital Worldlaith alakelÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Perfect Prayer by by Jon Courson - Matthew 6 9-13 The Lords PrayerDocument6 paginiThe Perfect Prayer by by Jon Courson - Matthew 6 9-13 The Lords PrayerRobert Beaupre100% (1)
- New Democracy June-August 2017Document32 paginiNew Democracy June-August 2017Communist Party of India - Marxist Leninist - New DemocracyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Literature - Part I: Group InterventionsDocument14 paginiLiterature - Part I: Group InterventionsDanielÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paul Daugerdas IndictmentDocument79 paginiPaul Daugerdas IndictmentBrian Willingham100% (2)
- Origin and Development of Law of Sea PDFDocument135 paginiOrigin and Development of Law of Sea PDFkimmiahujaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ADSL Line Driver Design Guide, Part 2Document10 paginiADSL Line Driver Design Guide, Part 2domingohÎncă nu există evaluări
- German composer known for political worksDocument4 paginiGerman composer known for political worksGeorge PikÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHEST 6. Chest Trauma 2022 YismawDocument61 paginiCHEST 6. Chest Trauma 2022 YismawrobelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Software Security Engineering: A Guide for Project ManagersDocument6 paginiSoftware Security Engineering: A Guide for Project ManagersVikram AwotarÎncă nu există evaluări
- People v. Cresencia ReyesDocument7 paginiPeople v. Cresencia ReyesAnggling DecolongonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ns5e rw3 SB Ak HyeDocument24 paginiNs5e rw3 SB Ak HyeKeys Shield JoshuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Leading a Community Through Integrity and CourageDocument2 paginiLeading a Community Through Integrity and CourageGretchen VenturaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of Efficient Serial Divider Using HAN CARLSON AdderDocument3 paginiDesign of Efficient Serial Divider Using HAN CARLSON AdderInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blind and Visually ImpairedDocument5 paginiBlind and Visually ImpairedPrem KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Umair Mazher ThesisDocument44 paginiUmair Mazher Thesisumair_mazherÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 11, 12 Curve Tracing and EnvelopeDocument37 paginiChapter 11, 12 Curve Tracing and EnvelopeNitish PokhrelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Source: Sonia S. Daquila. The Seeds of RevolutionDocument6 paginiSource: Sonia S. Daquila. The Seeds of RevolutionJulliena BakersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Urban Process Design - Hamid ShirvaniDocument1 paginăUrban Process Design - Hamid ShirvaniCaramel LatteÎncă nu există evaluări
- 59-33 ATO Implementation Journal KSA 100Document18 pagini59-33 ATO Implementation Journal KSA 100nicolas valentinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Speakout Vocabulary Extra Advanced Unit 03Document3 paginiSpeakout Vocabulary Extra Advanced Unit 03shasha1982100% (2)
- Theo 5Document2 paginiTheo 5chingchongÎncă nu există evaluări
- ESL Lesson PlanDocument4 paginiESL Lesson PlanuarkgradstudentÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 2 - Content and Contextual Analysis of Selected Primary andDocument41 paginiModule 2 - Content and Contextual Analysis of Selected Primary andAngelica CaldeoÎncă nu există evaluări
- ArenavirusDocument29 paginiArenavirusRamirez GiovarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Method of IstinjaDocument24 paginiMethod of IstinjaIslamic LibraryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wjec Gcse English Literature Coursework Mark SchemeDocument6 paginiWjec Gcse English Literature Coursework Mark Schemef6a5mww8100% (2)