Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Lect 24
Încărcat de
Aswin SivaramanDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Lect 24
Încărcat de
Aswin SivaramanDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Physics 212 Physics 212
L ctur 24: P l riz ti n L ctur 24: P l riz ti n Lecture 24: Polarization Lecture 24: Polarization
Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 1 1
Music
Who is the Artist? Who is the Artist? Who is the Artist? Who is the Artist?
A) A) Stephane Grappelli Stephane Grappelli
B) B) Pearl Django Pearl Django B) B) Pearl Django Pearl Django
C) C) Mark OConnors Hot Swing Trio Mark OConnors Hot Swing Trio
D) D) Bob Wills Bob Wills
E) E) Hot Club of Cowtown Hot Club of Cowtown
Theme of the Week Theme of the Week
HEADLINERS AT FOLK & ROOTS FESTIVAL! HEADLINERS AT FOLK & ROOTS FESTIVAL!
Hot Club of Hot Club of Cowtown Cowtown (2010) (2010)
Pokey Pokey LaFarge LaFarge (2011) (2011)
G t Li Sh !!!! G t Li Sh !!!! Great Live Show !!!! Great Live Show !!!!
Hour Exam 3: 3 weeks from yesterday (Wed. Nov. 30) covers Hour Exam 3: 3 weeks from yesterday (Wed. Nov. 30) covers
L19 L19--26 inclusive (LC circuits to lenses. Sign up for conflicts, 26 inclusive (LC circuits to lenses. Sign up for conflicts,
etc NOW (no later than Fri Nov 18 at 10:00 p m ) etc NOW (no later than Fri Nov 18 at 10:00 p m )
Your Comments Your Comments
This was quite confusing There are a lot of things that happen when light is
etc. NOW (no later than Fri. Nov. 18 at 10:00 p.m.) etc. NOW (no later than Fri. Nov. 18 at 10:00 p.m.)
This was quite confusing. There are a lot of things that happen when light is
polarized. It would be nice to break those down into smaller steps one at a time.
The linearly polarized stuff made sense but the circular things were terrifying.
Could we go over those and the checkpoints more in depth? Also and I can't believe Could we go over those and the checkpoints more in depth? Also, and I can t believe
I'm asking for this, could we do a calculation with the circular birefringent or a
combo of both polarizers?
I'm not sure what the phase angle's for. I m not sure what the phase angle s for.
Aren't the x and y components always
perpendicular to each other?
I don't get quarter wave slabs. Are they
Lots of questions about circular Lots of questions about circular
polarization polarization we will dissect it! we will dissect it!
how can a firebinging material make
two different velocities. Isn't it the
When light passes through any medium it is When light passes through any medium it is
b b d d b b d d itt d f itt d f
g q y
like, magic or something?
Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 3 3
05
same uniform material, so how are
the components velocities different.
Also what is a quarter wave plate
absorbed and re absorbed and re--emitted: for one emitted: for one
component of light, it happens more often component of light, it happens more often
Quantum Communication
I d t d th i t h l i ti i d i th l ld b t
I HAVE to get at least one question on the powerpoint in my lifetime. COME ON!
I understand there are instances where polarization is used in the real world, but
what are some special cases where circular polarization is used?
Communicate and know for sure if message has been looked
at by someone else (quantum mechanics): P. Kwiat, et al.
Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 4 4
So far we have considered plane waves that look like this: So far we have considered plane waves that look like this:
From now on just draw E and remember that B is still there: From now on just draw E and remember that B is still there:
Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 5 5
Linear Polarization Linear Polarization
I was a bit confused by the introduction of the "e-hat" vector
( i it / f l ) (as in its purpose/usefulness)
Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 6 6
Polarizers Polarizers
The molecular structure of a polarizer causes the component of The molecular structure of a polarizer causes the component of
the the EE field perpendicular to the Transmission Axis to be absorbed. field perpendicular to the Transmission Axis to be absorbed.
Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 7 7
Quick ACT Quick ACT
The molecular structure of a The molecular structure of a
polarizer causes the component of polarizer causes the component of
the the EE field perpendicular to the field perpendicular to the
Transmission Axis to be absorbed. Transmission Axis to be absorbed.
Suppose we have a beam traveling in the + z Suppose we have a beam traveling in the + z- -direction. direction.
At t = 0 and z = 0 the electric field is aligned along the At t = 0 and z = 0 the electric field is aligned along the
E
o
At t = 0 and z = 0, the electric field is aligned along the At t = 0 and z = 0, the electric field is aligned along the
positive x positive x- -axis and has a magnitude equal to E axis and has a magnitude equal to E
oo
z
y
What is the component of What is the component of EE
oo
along a direction in the x along a direction in the x- -y y
l th t k l f l th t k l f uu ith t t th ith t t th plane that makes an angle of plane that makes an angle of uu with respect to the x with respect to the x--
axis? axis?
B) E
o
cosu A) E
o
sinu C) 0 D) E
o
/sinu E) E
o
/cosu
u
E
o
Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 8 8
y
What is the only angle for which What is the only angle for which EE
oo
has no (zero) projection? has no (zero) projection?
Linear Polarizers
This stuff is so
wicked awesome! Go wicked awesome! Go
over the Law of
Malice though.
Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 9 9
Two Polarizers
Checkpoint 1a
An unpolarized EM wave is incident on two orthogonal polarizers.
What percentage of the intensity gets through both polarizers?
A. 50% B. 25% C. 0%
the horizontal and vertical components would go through
after the 1st one only half of it remains and then after the 2nd is half of it
Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 10 10
Because the polarizers are at 90 degrees to each other intensity is zero
because cos(pie/2) =0.
Two Polarizers
Checkpoint 1a
An unpolarized EM wave is incident on two orthogonal polarizers.
What percentage of the intensity gets through both polarizers?
A. 50% B. 25% C. 0%
The second polarizer is orthogonal to the first
Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 11 11
no light will come through. cos(90
o
) = 0
Two Polarizers
Checkpoint 1b
An unpolarized EM wave is incident on two orthogonal polarizers.
Is it possible to increase this percentage by inserting another
Polarizer between the original two?
A. Yes B. No
any diagonal will do
Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 12 12
It wouldn't help any because it is all in the y direction after the first
polarizer
Two Polarizers
Checkpoint 1b
An unpolarized EM wave is incident on two orthogonal polarizers.
Is it possible to increase this percentage by inserting another
Polarizer between the original two?
A. Yes B. No
Any non-horizontal polarizer after the first polarizer
will produce polarized light AT THAT ANGLE
Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 13 13
Part of that light will make it through the horizontal
polarizer
There is no reason that There is no reason that || has to be the same for has to be the same for EE
xx
and and EE
yy
::
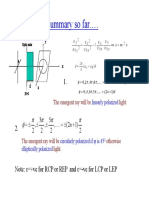
Making Making ||
xx
different from different from ||
yy
causes circular or elliptical polarization: causes circular or elliptical polarization: gg
xx yy
p p p p
90
t
| |
Example Example::
At t=0 At t=0
90
2
| | = =
x y
45 4 u t = =
0
cos( )
2
x
E
E kz t e =
0
i ( )
E
E k t
Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 14 14
0
sin( )
2
y
E kz t e =
RCP
Q: Q: How do we change How do we change
the relative phase the relative phase
between between EE
xx
and and EE
yy
??
AA Bi f i Bi f i A: A: Birefringence Birefringence
By picking the right By picking the right By p ck ng the r ght By p ck ng the r ght
thickness we can change thickness we can change
the relative phase by the relative phase by
exactly 90 exactly 90
oo
. .
This changes This changes linear linear to to
circular circular polarization polarization
and is called a and is called a
Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 15 15
and is called a and is called a
quarter wave plate quarter wave plate
Right hand Right hand
rule rule
NOTE: No NOTE: No
Does Birefringent Material
absorb intensity?
NOTE: No NOTE: No
Intensity is lost Intensity is lost
passing through passing through
h QWP ! h QWP ! the QWP ! the QWP !
BEFORE QWP:
(
+
j i
2 2 2
(
+
=
2
) sin(
j i
t kz E E
o
e
2 2 2
y x o o
E E c E c I + = = c c
2
1
) ( sin
2 2
2 2
2 2
o o
o o
o
E c t kz
E E
c c e c =
|
|
|
|
+ =
2 2 2
o o o
|
.
\
AFTER QWP:
| | ) sin(
) cos(
2
t kz j t kz i
E
E
o
e e + =
2 2 2
y x o o
E E c E c I + = = c c
2
) ( sin ) ( cos
2
2 2
2
t kz t kz
E
c
o
o
e e c + =
2 2
Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 16 16
2
1
2
2 2
o
o
o
o
E
c
E
c c c = =
THE SAME !!
Right or Left ???
Right circularly polarized Right circularly polarized
Do right hand rule Do right hand rule Do right hand rule Do right hand rule
Fingers along slow direction Fingers along slow direction
Cross into fast direction Cross into fast direction
If th b i t i di ti f ti RCP If th b i t i di ti f ti RCP
Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 17 17
If thumb points in direction of propagation: RCP If thumb points in direction of propagation: RCP
Circular Light on Linear Polarizer
Q: Q: What happens when circularly What happens when circularly
polarized light is put through a polarized light is put through a
polarizer along the polarizer along the xx (or (or yy) axis ? ) axis ?
A) I = 0
B) I = I
0
C) C) I = I
0
2 2
E E
2
0
c = I c E
1 1
XX
2 2
0
c = +
x y
c E E
2
2
0
0
cos ( ) c e =
E
c kz t
Half Half of before of before
2
0 0
1 1
2 2
c = cE
XX
Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 18 18
0
( )
2
1 2
Half Half of before of before
Identical linearly polarized light at 45
o
from the y-axis and propagating along the z
axis is incident on two different objects. In Case A the light intercepts a linear polarizer
with polarization along the y-axis In Case B, the light intercepts a quarter wave plate
with vast axis along the y-axis.
Checkpoint 2a
A
B
g y
Compare the intensities of the light waves after transmission.
A. I
A
< I
B
B. I
A
= I
B
C. I
A
> I
B
In case 1, the polarizer absorbs some of the intensity while for case 2 it just
changes its phase.
The polarizer and quarter wave plate have the same effect
Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 19 19
The polarizer and quarter wave plate have the same effect.
it looses more intensity when it passes through a birefringent material.
Identical linearly polarized light at 45
o
from the y-axis and propagating along the z
axis is incident on two different objects. In Case A the light intercepts a linear polarizer
with polarization along the y-axis In Case B, the light intercepts a quarter wave plate
with vast axis along the y-axis.
Checkpoint 2a
A
B
g y
Compare the intensities of the light waves after transmission.
A. I
A
< I
B
B. I
A
= I
B
C. I
A
> I
B
Case A:
E
x
is absorbed
) 45 ( cos
2
0
o
A
I I =
Case B:
(E
x
,E
y)
phase changed
Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 20 20
) 45 ( cos
0 A
I I
0
2
1
I I
A
= 0
I I
B
=
2 2
(
Intensity:
2 2
0 x y
I c E E c
(
= +
QW Plate QW Plate
Both E Both E and E and E
Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 21 21
Both E Both E
xx
and E and E
yy
are still there, so are still there, so
intensity is the same intensity is the same
2 2
0 x y
I c E E c
(
= +
Polarizer Polarizer
EE is missing so is missing so
Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 22 22
EE
xx
is missing, so is missing, so
intensity is lower intensity is lower
Checkpoint 2b
A
Identical linearly polarized light at 45
o
from the y-axis and propagating along the z
axis is incident on two different objects. In Case A the light intercepts a linear polarizer
with polarization along the y-axis In Case B, the light intercepts a quarter wave plate
with vast axis along the y-axis. heckpo nt b
A
B
Checkpoint 2b
A
B
g y
What is the polarization of the light wave in Case B after it passes through the
quarter wave plate?.
A. linearly polarized B. left circularly polarized
C. right circularly polarized D. undefined g y p
the fast side will make the light polarize linearly
the vertical component will be ahead of the horizontal component. Since the horizontal
component is in the positive x direction it is left CP
Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 23 23
Right hand rule from slow to fast means that it travels in the positive z which in this
case means right circularly polarized.
It is at 45 degrees from the y-axis thus it is undefined.
Checkpoint 2b
A
Identical linearly polarized light at 45
o
from the y-axis and propagating along the z
axis is incident on two different objects. In Case A the light intercepts a linear polarizer
with polarization along the y-axis In Case B, the light intercepts a quarter wave plate
with vast axis along the y-axis. heckpo nt b
A
B
Checkpoint 2b
A
B
g y
What is the polarization of the light wave in Case B after it passes through the
quarter wave plate?.
A. linearly polarized B. left circularly polarized
C. right circularly polarized D. undefined
RCP
g y p
Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 24 24
Z
RCP
1/4
Checkpoint 2c
A
Identical linearly polarized light at 45
o
from the y-axis and propagating along the z
axis is incident on two different objects. In Case A the light intercepts a linear polarizer
with polarization along the y-axis In Case B, the light intercepts a quarter wave plate
with vast axis along the y-axis. heckpo nt c
A
B
Checkpoint 2c
A
B
g y
If the thickness of the quarter-wave plate in Case B is doubled, what is the
polarization of the wave after passing through the wave plate?
A. linearly polarized B. circularly polarized C. undefined
If it's a half wave plate the waves will be 180 degrees out of phase rather then 90 If it s a half wave plate, the waves will be 180 degrees out of phase rather then 90
degrees and be linearly polarized
I think it would still be the same it would just increase the difference between the
component phases.
Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 25 25
p p
The x component would lag the y component by half a period, so for half the period the
wave would be linearly polarized in the y direction and then for the other half would be
linearly polarized in the x direction.
Checkpoint 2c
A
Identical linearly polarized light at 45
o
from the y-axis and propagating along the z
axis is incident on two different objects. In Case A the light intercepts a linear polarizer
with polarization along the y-axis In Case B, the light intercepts a quarter wave plate
with vast axis along the y-axis. heckpo nt c
A
B
Checkpoint 2c
A
B
g y
If the thickness of the quarter-wave plate in Case B is doubled, what is the
polarization of the wave after passing through the wave plate?
A. linearly polarized B. circularly polarized C. undefined
Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 26 26
Z
Z
Executive Summary: Executive Summary:
Circularly or Un-polarized Light
Polarized Light
Polarizers & QW Plates: Polarizers & QW Plates:
Birefringence Birefringence
E
RCP
0
cos( )
2
=
x
E
E kx
0
sin( )
2
y
E
E kx =
Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 27 27
2
y
Demos:
What else can we put in there to change the polarization? What else can we put in there to change the polarization?
Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 28 28
What else can we put in there to change the polarization? What else can we put in there to change the polarization?
Calculation Calculation
Light is incident on two linear polarizers and a quarter wave plate (QWP) as shown.
y
45
o
fast
What is the intensity I
3
in terms of I
1
?
x
y
II
11
60
o
z
II
11
II
22
II
33
Conceptual Analysis
Linear Polarizers: absorbs E field component perpendicular to TA
Quarter Wave Plates: Shifts phase of E field components in fast-slow
d directions
Strategic Analysis
Determine state of polarization and intensity reduction after each object
Multiply individual intensity reductions to get final reduction
Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 29 29
Multiply individual intensity reductions to get final reduction.
Calculation Calculation
Light is incident on two linear polarizers and a quarter wave plate (QWP) as shown.
y
45
o
fast
x
y
II
11
60
o
E
1
E
x
E
y
RCP
z
II
11
II
22
II
33
/4
What is the polarization of the light after the QWP?
(A) LCP (B) RCP (C) (D) (E) unpolarized
x
y
x
y
Light will be circularly
polarized after QWP
Light incident on QWP is linearly
polarized at 45
o
to fast axis
C l fi f RH b k t f t
Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 30 30
LCP or RCP? Easiest way:
Right Hand Rule:
Curl fingers of RH back to front
(slow crossed into fast). Thumb
points in dir of propagation
if right hand polarized.
RCP
Calculation Calculation
Light is incident on two linear polarizers and a quarter wave plate (QWP) as shown.
y
45
o
fast
x
y
II
11
60
o
E
x
E
y
RCP
E
1
z
II
11
II
22
II
33
/4
What is the intensity I
2
of the light after the QWP?
(A) I
2
= I
1
(B) I
2
= I
1
(C) I
2
= I
1
No absorption: Just a phase change !
BEFORE:
1
sin( )
2
x
E
E kz t e =
AFTER:
1
cos( )
2
x
E
E kz t e = 2 2
0 x y
I c E E c
(
= +
Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 31 31
1
sin( )
2
y
E
E kz t e =
1
sin( )
2
y
E
E kz t e =
Same before & after !
Calculation Calculation
Light is incident on two linear polarizers and a quarter wave plate (QWP) as shown.
y
45
o
fast
x
y
II
11
60
o
E
1
E
x
E
y
E
3
RCP
z
II
11
II
33
/4
II
2 2
= I = I
11
What is the polarization of the light after the 60
o
polarizer?
(A) LCP (B) RCP (C) (D) (E) unpolarized
x
y
x
y
60
o
60
o
Absorption: only passes components of E parallel to TA (u = 60
o
)
3
E
y
( )
1
3
sin( )
2
E
E kz t e u = +
3
sin cos
x y
E E E u u = +
E
3
Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 32 32
60
o
E
x
( )
1
3
cos( ) sin sin( ) cos
2
E
E kz t kz t e u e u = +
( )
2
3
Calculation Calculation
Light is incident on two linear polarizers and a quarter wave plate (QWP) as shown.
y
45
o
fast
x
y
II
11
60
o
E
x
E
y
E
3
RCP
E
1
II
33
z
II
11
/4
II
33
= I = I
11
II
2 2
= I = I
11
What is the intensity I
3
of the light after the 60
o
polarizer?
(A) I
3
= I
1
(B) I
3
= I
1
(C) I
3
= I
1
3
E
y
1
3
2
E
E =
E
3
3 1
1
2
I I =
2
I E
Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 33 33
NOTE: This does not depend on u !!
60
o
E
x
3
Follow Up 1 Follow Up 1
Replace the 60
o
polarizer with another QWP as shown.
x
y
45
o
fast
E
E
RCP
slow
II
11
/4
E
x
E
y
II = I = I
fast
E
y
E
x
E
3
II
z
II
2 2
= I = I
11
What is the polarization of the light after the last QWP?
y y
II
33
(A) LCP (B) RCP (C) (D) (E) unpolarized
x
y
x
y
E
Brings E
x
and E
y
back in phase !!
Easiest way:
E
fast
is /4 ahead of E
slow
Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 34 34
Follow Up 2 Follow Up 2
Replace the 60
o
polarizer with another QWP as shown.
x
y
45
o
fast
E
E
RCP
slow
II
11
/4
E
x
E
y
II = I = I
fast
E
y
E
x
E
3
z
II
2 2
= I = I
11
What is the intensity I
3
of the light after the last QWP?
II
3 3
= I = I
11
(A) I
1
(B) I
1
(C) I
1
No absorption: Just a phase change !
E
AFTER:
BEFORE:
Intensity = < E
2
>
1
cos( )
2
y
E
E kz t e =
1
cos( )
2
x
E
E kz t e =
1
cos( )
2
x
E
E kz t e =
1
sin( )
2
y
E
E kz t e =
2
1
2
after
E
I =
2
1
2
before
E
I =
Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 35 35
2
2
2
2
Follow Up 3 Follow Up 3
Consider light incident on two linear polarizers as shown. Suppose I
2
= 1/8 I
0
x
y
60
o
E
1
II = 1/8 I = 1/8 I
II
00
60
o
II
11
E
2
II
11
= I = I
00
z
What is the possible polarization of the INPUT light?
II
22
= 1/8 I = 1/8 I
00
11
00
(A) LCP
x
y
(B)
After first polarizer: LP along y-axis with intensity I
1
After second polarizer: LP at 60
o
wrt y-axis
Intensity: I
2
= I
1
cos
2
(60
o
) = I
1
(C) unpolarized
(D) all of above
Question is: What kind of light loses of its
intensity after passing through vertical polarizer?
45
o
y
2 1 1
I
2
= 1/8 I
0
I
1
= I
0
Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide Physics 212 Lecture 24, Slide 36 36
(D) all of above
(E) none of above
intensity after passing through vertical polarizer?
Answer: Everything except LP at u other than 45
o
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- Teori Radar AntenaDocument71 paginiTeori Radar AntenaBambang GastomoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antenna and Radar EngineeringDocument141 paginiAntenna and Radar EngineeringArun Singh SumbriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lect 25Document33 paginiLect 25Aswin Sivaraman100% (1)
- Lect 19Document30 paginiLect 19Aswin SivaramanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lect 21Document27 paginiLect 21Aswin SivaramanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lect 17Document31 paginiLect 17Aswin SivaramanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lect 13Document27 paginiLect 13Aswin SivaramanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lect 11Document30 paginiLect 11Aswin Sivaraman100% (1)
- Lect 12Document31 paginiLect 12Aswin SivaramanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lect 02Document22 paginiLect 02Aswin SivaramanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lect 07Document26 paginiLect 07Aswin SivaramanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lect 06Document21 paginiLect 06Aswin SivaramanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lect 03Document25 paginiLect 03Aswin SivaramanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lect 01Document26 paginiLect 01Aswin Sivaraman100% (1)
- Bill Template and Directions (Spring 2011) - BrennanDocument3 paginiBill Template and Directions (Spring 2011) - BrennanAswin SivaramanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antenna Polarization - ASTRON WIRELESSDocument3 paginiAntenna Polarization - ASTRON WIRELESSStuart 'Stu' NofkeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 02 CommunicationSystemsDocument48 pagini02 CommunicationSystemsWiccioÎncă nu există evaluări
- POLARIZATIONDocument54 paginiPOLARIZATIONfunkpatel123Încă nu există evaluări
- Cross Yagi PolarizationDocument9 paginiCross Yagi PolarizationYusuf ArifandiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ch3 - 3 Fiber Optic CablesDocument32 paginiCh3 - 3 Fiber Optic CablesAkram KhorsheidÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Circularly-Polarized Isoflux Antenna Based On Anisotropic MetasurfaceDocument12 paginiA Circularly-Polarized Isoflux Antenna Based On Anisotropic Metasurfaceale0218Încă nu există evaluări
- A Ku Band Circularly Polarized 2x2 Microstrip Antenna Array For Remote Sensing ApplicationsDocument2 paginiA Ku Band Circularly Polarized 2x2 Microstrip Antenna Array For Remote Sensing ApplicationsChristopher ChrisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phase Contrast Microscopy, by DR IramDocument78 paginiPhase Contrast Microscopy, by DR IramimmmiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Array Calc 10 DDocument40 paginiArray Calc 10 DGustavo PaizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optical Devices and Comm SystemDocument9 paginiOptical Devices and Comm SystemAsif KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit5 EWRSDocument132 paginiUnit5 EWRSParth InamdarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paper Antena Wifi PDFDocument2 paginiPaper Antena Wifi PDFNagells RizhÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Review of Magneto-Optic Effects and Its Application: Taskeya HaiderDocument8 paginiA Review of Magneto-Optic Effects and Its Application: Taskeya HaiderkanchankonwarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Small Antennas For High FrequenciesDocument23 paginiSmall Antennas For High FrequenciesGumaMohamedÎncă nu există evaluări
- PolarizationoteDocument14 paginiPolarizationoteOvijit KarmokarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Applsci 02 00602Document27 paginiApplsci 02 00602Marcelo CostaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optical Rotatory DispersionDocument26 paginiOptical Rotatory DispersionPMHÎncă nu există evaluări
- L05 PolarDocument18 paginiL05 PolarGuadalajara JaliscoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Check Out This File: Engg Physics MCQs - Unit 1 - PolarizationDocument10 paginiCheck Out This File: Engg Physics MCQs - Unit 1 - PolarizationNikhil SatbhaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dokumen - Tips Practical Physics by R K ShuklaDocument328 paginiDokumen - Tips Practical Physics by R K Shuklafibewip542Încă nu există evaluări
- ITSO-Kenya-Instelsat-Presentation-V1.0 Basics of SatelliteDocument118 paginiITSO-Kenya-Instelsat-Presentation-V1.0 Basics of SatelliteabournaudÎncă nu există evaluări
- Polarization 4Document36 paginiPolarization 4wartÎncă nu există evaluări
- Applied Physics R20 - Unit-1Document28 paginiApplied Physics R20 - Unit-1MsprinceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understanding and Measuring Circular PolarizationDocument6 paginiUnderstanding and Measuring Circular PolarizationpremÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kraus Helix IdeaDocument10 paginiKraus Helix IdeaPavan NanduriÎncă nu există evaluări
- UNIT-2: 1. What Is Retarded Potential? Explain Different Approaches To Solve Radiation Problems? AnsDocument12 paginiUNIT-2: 1. What Is Retarded Potential? Explain Different Approaches To Solve Radiation Problems? AnsShiva Kumar PottabathulaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Faraday Effect: ObjectiveDocument24 paginiThe Faraday Effect: ObjectiveEdwin SizaÎncă nu există evaluări
- BSC Sem IV PhysicsPolarisationDocument12 paginiBSC Sem IV PhysicsPolarisationSidharth ThakurÎncă nu există evaluări