Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
GSM Terms
Încărcat de
ooty25Descriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
GSM Terms
Încărcat de
ooty25Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
GSM Terms AMPS (Advanced Mobile Phone Service) AMPS was the original standard technology used on the
first analog wireless phone systems in the United States, and it is still one of the most widely used technologies today. AMPS which operates in the 800Mz band, covers the entire country, and is utilized by 80% of US mobile phone subscribers. Analog Initially all cellular phones employed analog communications which transmitted voice messages as if they were sound waves. When you speak into an analog wireless phone, your voice wave is modulated by a radio wave when it is transmitted over the air. First generation (1G) wireless phones are analog phones that transmitted your voice using what was known as the AMPS protocol systems. As technology evolved into newer digital systems analog systems are becoming increasingly rare today. Bluetooth Bluetooth is a computing and telecommunications industry specification that describes how mobile phones, computers, and personal digital assistants (PDAs) can easily interconnect with each other and with home and business phones and computers using a short-range wireless connection. Using this technology, users of cellular phones, pagers, and personal digital assistants such as the Palm Pilot will be able to buy a three-in-one phone that can double as a portable phone at home or in the office, get quickly synchronized with information in a desktop or notebook computer, initiate the sending or receiving of a fax, initiate a printout, and, in general, have all mobile and fixed computer devices be totally coordinated. The technology requires that a low-cost transceiver chip be included in each device. Products with Bluetooth technology are expected to appear in large numbers beginning in 2000. How It Works: Each device is equipped with a microchip transceiver that transmits and receives in a previously unused frequency band of 2.45 GHz that is available globally (with some variation of bandwidth in different countries). In addition to data, up to three voice channels are available. Each device has a unique 48-bit address from the IEEE 802 standard. Connections can be point-to-point or multipoint. The maximum range is 10 meters. Data can be exchanged at a rate of 1 megabit per second (up to 2 Mbps in the second generation of the technology). A frequency hop scheme allows devices to communicate even in areas with a great deal of electromagnetic interference. Built-in encryption and verification is provided. CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access) CDMA is a multiple access system used in radio communication. This digital technology separates communications by a code method. This way, the system can mix a number of calls into the same voice channel. When the cellular radio tower receives the information, it looks at the coding used and reassembles each individual call, completing the transmission. Cellular Phone Cellular or mobile phones are portable, wireless phone systems that typically operate in the 800 MHz frequency range. The cellular system, developed in the US, transmits voice calls using various types of technologies which are continuously evolving. Circuit Switched vs. Packet Switched There are two types of wireless data transmission - Circuit Switched and Packet Switched. Circuit Switched employs a dedicated voice channel to transmit and receive data, essentially like keeping a single phone line open during your entire conversation. A cellular modem uses Circuit Switched transmission, which allows you to dial up a computer over your wireless phone just like you would using a landline connection. Packet switched data transmission compresses the data and sends short data bursts between or during gaps in conversations on the voice channels. Packet data digital transmission is ideal
for using your phone to send short messages, including E-mail, or access news headlines, and stock quotes from the Internet. Digital Phone Digital systems convert the sound wave created by your voice into a stream of 1's and 0's. When digitized, the information is compressed, manipulated, and transmitted in such a way that your conversations are more clear and static-free, and your conversation is made more secure from electronic "eavesdropping". Digital wireless technology also allows networks to carry more conversations at one time and allow additional features such as text messaging, fax, e-mail transmission, and internet access to be available to the user. Dual Band A Dual Band wireless phone can operate on either an 800 MHz system or on a 1900 MHz frequency system. Therefore, if a phone used a single technology (e.g. TDMA) but was dual band (e.g. 800 MHz and 1900 MHz) that phone could operate in the TDMA mode on either an 800 MHz system or a 1900 MHz system. Dual Mode A Dual Mode wireless phone can operate in two different transmission technologies, such as AMPS or TDMA. Since the phone is dual mode, it can operate on an 800 MHz system using either the AMPS mode or the TDMA technology mode. Dual Band, Dual Mode A Dual Band, Dual Mode wireless phone can operate using a combination of two different frequencies and two different transmission technologies. A Dual Band, Dual Mode phone could operate at either 800 MHz or 1900 MHz and support both AMPS technology and TDMA technology. Typically, for your wireless phone to work, you must be within the wireless phone system area that supports the same technology and frequency with which that phone was designed to work.. With a Dual Band, Dual Mode phone, however, you can take your phone outside of your home service area and generally continue to have wireless service available. EDGE (Enhanced Data Rates for GMS Evolution) EDGE (Enhanced Data GSM Environment), a faster version of the Global System for Mobile (GSM) wireless service, is designed to deliver data at rates up to 384 Kbps and enable the delivery of multimedia and other broadband applications to mobile phone and computer users. The EDGE standard is built on the existing GSM standard, using the same time-division multiple access (TDMA) structure and existing cell arrangements. Ericsson notes that, when available, its base stations can be updated with software. EDGE is expected to be commercially available in 2001. It is regarded as an evolutionary standard on the way to Universal Mobile Telecommunications Service (UMTS). GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) is a packet-based wireless communication service that, when available in 2000, promises data rates from 56 up to 114 Kbps and continuous connection to the Internet for mobile phone and computer users. The higher data rates will allow users to take part in video conferences and interact with multimedia Web sites and similar applications using mobile handheld devices as well as notebook computers. GPRS is based on Global System for Mobile (GSM) communication and will complement existing services such circuit-switched cellular phone connections and the Short Message Service (SMS). In theory, GPRS packet-based service should cost users less than circuit-switched services since communication channels are being used on a shared-use, as-packets-are-needed basis rather than dedicated only to one user at a time. It should also be easier to make applications available to mobile
users because the faster data rate means that middleware currently needed to adapt applications to the slower speed of wireless systems will no longer be needed. Once GPRS becomes available, mobile users of a virtual private network VPN will be able to access the private network continuously rather than through a dial-up connection. GPRS will also complement Bluetooth, a standard for replacing wired connections between devices with wireless radio connections. In addition to the Internet Protocol (IP), GPRS supports X.25, a packet-based protocol that is used mainly in Europe. GPRS is an evolutionary step toward Enhanced Data GSM Environment (EDGE) and Universal Mobile Telephone Service (UMTS). GSM (Global System for Mobile communication) GSM (Global System for Mobile communication) is a digital mobile telephone system that is widely used in Europe and other parts of the world. GSM uses a variation of time division multiple access (TDMA) and is the most widely used of the three digital wireless telephone technologies (TDMA, GSM, and CDMA). GSM digitizes and compresses data, then sends it down a channel with two other streams of user data, each in its own time slot. It operates at either the 900 MHz or 1800 MHz frequency band. GSM is the de facto wireless telephone standard in Europe. GSM has over 120 million users worldwide and is available in 120 countries, according to the GSM MoU Association. Since many GSM network operators have roaming agreements with foreign operators, users can often continue to use their mobile phones when they travel to other countries. American Personal Communications (APC), a subsidiary of Sprint, is using GSM as the technology for a broadband personal communications service (PCS). The service will ultimately have more than 400 base stations for the palm-sized handsets that are being made by Ericsson, Motorola, and Nokia. The handsets include a phone, a text pager, and an answering machine. GSM together with other technologies is part of an evolution of wireless mobile telecommunication that includes High-Speed Circuit-Switched Data (HSCSD), General Packet Radio System (GPRS), Enhanced Data GSM Environment (EDGE), and Universal Mobile Telecommunications Service (UMTS). i-mode Although relatively unknown in the United States, i-mode is a wireless service launched in Japan in the spring of 1999 by NTT DoCoMo. The service is accessed by a wireless packet network and allows the user to access the Internet and send short-text messages on their digital wireless phone. i-Mode is hugely popular in Japan and may be a primary influence in the digital wireless world market. PCS (Personal Communications Service) PCS is the name adopted by the new, digital wireless service providers who operate new phone systems in the 1900 MHz frequency range. PCS networks employ a range of technologies including GSM, TDMA and CDMA-One. Roaming When you purchase a service plan with a cellular phone, you are subscribing to a particular type of technology provided by your wireless system carrier. Roaming enables you to utilize your mobile phone via the network facilities of another provider outside of your subscribed service area. Second Generation (2G) Second generation (2G) wireless phones are digital and are capable of providing voice / data / fax transfer as well as a range of other value-added services. Currently 2G systems are constantly evolving with higher data rates through new technologies such as TDMA, CDMA, GSM, PCS, and GPRS. TDMA (Time Division Multiple Access)
TDMA is a digital technology that allows multiple users to share the same voice channel by having each conversation transmitted alternately over short periods of time. Some versions of TDMA use the IS-136 specification for advanced digital wireless services. It is also one of the worlds most widely deployed digital wireless systems. TDMA technology evolved from the original analog AMPS networks, and attracted many new network operators. It provides unlimited capacity, efficient coverage, and is well suited to emerging applications, such as wireless virtual private networks (VPNs). TDMA is also the ideal platform for PCS phones. TDMA breaks voice signals into sequential data pieces of defined length and sends each piece into an information conduit at specific time intervals. TDMA then reconstructs the pieces at the end of the conduit on the receiving phone. GSM and US-TDMA standards accommodates a much larger number of users by more finely dividing a radio frequency into time slots and allocating these slots to multiple calls. Third Generation (3G) Third generation (3G) mobile phones and communication systems use high-speed data transfer technologies and state-of-the-art radio terminal technology. These technologies enable advanced user features on wireless handsets including multimedia, advanced text messaging, and access to e-mail and the Internet. WAP (Wireless Application Protocol) The de facto worldwide standard for providing Internet communications and advanced telephony services on digital mobile phones, pagers, digital assistants, and other wireless terminals. The WAP Forum was established in 1997 by several wireless phone companies and Unwired Planet (now Phone.com). The Panasonic Wireless Design Center is one of Its current members now comprising over 200 leading firms in the wireless communication field. Wireless Phone Frequencies For a phone to work in an area other than its "home" area, it must be in a system that supports the technology used by that phone in the frequency which the phone is designed to work. 800 Megahertz (800 MHz) is the radio frequency that was originally assigned to cellular phones by the FCC in 1983. Cellular phones using AMPS, NAMPS, TDMA, and CDMA technologies are all currently available in this frequency range. 1900 Megahertz, (1900 MHz) is the radio frequency range added by the FCC in order to create additional competition in wireless phone services. Wireless phones using PCS, GSM, TDMA, and CDMA technologies are currently available using this frequency range.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- RACF Utilities: KOIRUG April 2016Document40 paginiRACF Utilities: KOIRUG April 2016dinesh nali100% (1)
- A Practical Hands-On Approach To Database Forensics: Nhien-An Le-Khac Kim-Kwang Raymond ChooDocument302 paginiA Practical Hands-On Approach To Database Forensics: Nhien-An Le-Khac Kim-Kwang Raymond ChoolarkaaÎncă nu există evaluări
- BAdi2 For MM02Document14 paginiBAdi2 For MM02raju221756_843567682100% (1)
- MPMC Student Lab ManualDocument107 paginiMPMC Student Lab ManualRohith ShashankÎncă nu există evaluări
- Health Check MG WDocument8 paginiHealth Check MG Wooty25Încă nu există evaluări
- Apg 43 CommandsDocument1 paginăApg 43 Commandsooty25Încă nu există evaluări
- Health Check MG WDocument8 paginiHealth Check MG Wooty25Încă nu există evaluări
- GPRS OverviewDocument9 paginiGPRS Overviewooty25Încă nu există evaluări
- Apg 43 CommandsDocument1 paginăApg 43 Commandsooty25Încă nu există evaluări
- Apg 43 CommandsDocument1 paginăApg 43 Commandsooty25Încă nu există evaluări
- Apg 43 CommandsDocument1 paginăApg 43 Commandsooty25Încă nu există evaluări
- Apg 43 CommandsDocument1 paginăApg 43 Commandsooty25Încă nu există evaluări
- Sqesp DTDocument3 paginiSqesp DTooty25Încă nu există evaluări
- Sqesp DTDocument3 paginiSqesp DTooty25Încă nu există evaluări
- MGW FeaturesDocument1 paginăMGW Featuresooty25Încă nu există evaluări
- MGW FeaturesDocument1 paginăMGW Featuresooty25Încă nu există evaluări
- Itu Kpi'sDocument27 paginiItu Kpi'sooty25Încă nu există evaluări
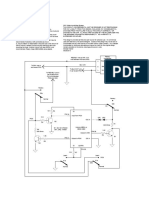
- GSM TermsDocument4 paginiGSM Termsooty25Încă nu există evaluări
- Mpls TrafficDocument20 paginiMpls Trafficooty25Încă nu există evaluări
- GSM TermsDocument4 paginiGSM Termsooty25Încă nu există evaluări
- DM - V4.98 - Release NotesDocument40 paginiDM - V4.98 - Release NotesFrancisco Lopez PosadasÎncă nu există evaluări
- I-7018 (R) (BL) (P), M-7018 (R) Quick Start GuideDocument4 paginiI-7018 (R) (BL) (P), M-7018 (R) Quick Start GuideData CommunicationÎncă nu există evaluări
- InDesign CS5.5 Scripting Read MeDocument9 paginiInDesign CS5.5 Scripting Read MexyzadsjkhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flip-Flop Types, Their Conversion and Applications - GeeksforGeeksDocument3 paginiFlip-Flop Types, Their Conversion and Applications - GeeksforGeeksRaJu AhMeDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Arduino Miata Immobilizer Bypass SchematicDocument1 paginăArduino Miata Immobilizer Bypass SchematicSzabó PéterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Unit III CC 2022Document71 paginiFinal Unit III CC 2022sairabanu pansareÎncă nu există evaluări
- Availability Is Not Equal To ReliabilityDocument5 paginiAvailability Is Not Equal To ReliabilityIwan AkurÎncă nu există evaluări
- HCRNC59 - TRS Datafill v1.2 - 11052015Document25 paginiHCRNC59 - TRS Datafill v1.2 - 11052015TuPro FessionalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Update 201101Document113 paginiUpdate 201101hoahongtangem249Încă nu există evaluări
- ReadmeengDocument3 paginiReadmeengIlanildo DiasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Incremental Migration (IMIG) : Before You Begin 1Document7 paginiIncremental Migration (IMIG) : Before You Begin 1jaleelpeace9157Încă nu există evaluări
- B7fy 2331 01enDocument155 paginiB7fy 2331 01enbelghin2Încă nu există evaluări
- 122 Ireceivables Implementation GuideDocument110 pagini122 Ireceivables Implementation GuideAbbasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compititive Programming - I ManualDocument79 paginiCompititive Programming - I ManualArun ChaudhariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Global Telecom Companies 2011Document2 paginiGlobal Telecom Companies 2011kpkevin69Încă nu există evaluări
- Fi 7260 DatasheetDocument2 paginiFi 7260 DatasheetDodi VenesiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Business Online Banking RequestDocument1 paginăBusiness Online Banking RequestashleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Panasonic 3DO FZ-10 Service Manual (E, For UK)Document40 paginiPanasonic 3DO FZ-10 Service Manual (E, For UK)AlessandroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Discussion Lab 9Document1 paginăDiscussion Lab 9thevand11100% (1)
- Artizo Digital Notebook by SlidesgoDocument48 paginiArtizo Digital Notebook by SlidesgoMary JoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mpi Sample ScriptDocument6 paginiMpi Sample Scriptjckim1201Încă nu există evaluări
- Windows Win32 API WinmsgDocument1.114 paginiWindows Win32 API WinmsgAbetiou SN - سفيان ابطيوÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trace - 2020-05-15 19 - 41 - 02 526Document29 paginiTrace - 2020-05-15 19 - 41 - 02 526Dhiki KurniawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- L2 Review Synchro Training 4 4Document45 paginiL2 Review Synchro Training 4 4Norbertt QuispeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manual Virtual ScopeDocument92 paginiManual Virtual ScopeBabasrinivas GuduruÎncă nu există evaluări
- ProjectDocument10 paginiProjectgvnviki17Încă nu există evaluări