Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Urinary Embryology
Încărcat de
ameerabestDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Urinary Embryology
Încărcat de
ameerabestDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
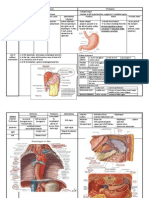
DEVELOPMENT OF KIDNEY Primordia : Intermediate mesoderm Cervical part nephrotomes.
. Caudal part nephrogenic cords 3 sets appear following each other : PRONEPHROS MESONEPHROS - 5-7 pairs of small hollow balls of - mesonephric tubules are more caudal, epithelium (pronephric tubules more numerous 80 are connected to pronephric duct Mesonephric tubules differentiate into a cup-shaped Pronephric tubules Bowmans capsule (that is degenerates by 4th week invaginated by capillaries forming the glomerulus) Pronephric duct persists Bowmans capsule + glomerulus = and extend caudally to make up the renal corpuscle become mesonephric duct - mesonephros has NO special duct it uses the pronephric duct now called the mesonephric duct mesonephric duct elongates and opens into the cloaca mesonephric tubules connect to mesonephric duct (Wolffian duct) persisting mesonephric duct gives: - duct system in male - para-ophron, epo-ophron & Garterners duct in female
METANEPHROS COLLECTING PART SECRETORY PART from ureteric bud from metanephric cap - ureteric bud arises from the - metanephric cap divides into small lower end of metanephric bud masses (one opposite each of collecting then invaginate the nephrogenic tubules) cord (which is now called the metanephrogenic cap or - part of metanephric cap canalizes to blastema) form vesicles - vesicles elongate & canalize to form nephrons (Bowmans capsule, renal tubules) and open into collecting tubules
- ureteric bud elongates forming the ureter, major calyces, minor calyces & collecting tubules
- most primitive kidney - non-functional in mammals
- mesonephric kidney is the functional adult kidney of fish and some amphibians
LATE CHANGES - Branching system becomes larger forming the pelvis and calyces - Kidneys undergo cranial ascend from the pelvic region to the abdominal region lateral displacement brings them in contact with the developing adrenal glands that fuse to their cranial pole rotate 90 so that the renal pelvis is facing the midline CONGENITAL ANOMALIES Renal agenesis means failure of formation of one or the two kidneys - always associated with oligohydraminos Polycystic kidney abnormal development of the collecting system, or failure of the collecting tubules and nephrons to join Pelvic kidney due to failure of the kidney to ascend to the abdomen where it is kept in the pelvis Horseshoe kidney both kidneys fail to ascend, and their lower poles fuse together
pelvic kidney
horse shoe kidney
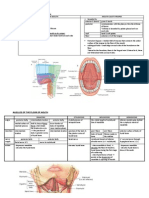
Terminal part of hindgut (cloaca, endodermal in origin) is divided by cloacal septum into: 1. Primitive urogenital sinus (anterior part) 2. Anorectal canal (posterior part) rectum & upper part of anal canal primordia URETER ureteric bud from mesonephric duct (mesoderm) - develops from the caudal part of mesonephric duct - its cranial end dilates to form pelvis of ureter
Primitive urogenital sinus gives : 1. primitive urinary bladder, cranially 2. definitive urogenital sinus, caudally URETHRA 1. the constriction in between gives - male = upper pt of prostatic urethra - female = urethra 2. definitive urogenital sinus - male = 1) cranial (pelvic) part lower part of prostatic urethra + membranous urethra 2) caudal (phallic) part penile urethra except fossa navecularis (ectodermal) - female = vestibule of vagina
URINARY BLADDER urogenital sinus (endoderm) 1) Upper part primitive urinary bladder continuous with allantois (obliterated later) 2) Middle part (constriction) urethra 3) Lower part (definitive urogenital sinus) - male = penile urethra - female = vestibule
- the developing bladder absorbs most of the lower part of mesonephric duct till the origin of ureter - caudal part of mesonephric duct is absorbed into the posterior wall of primitive urinary bladder till the origin of the ureters the absorbed part will form the trigone (mesodermal)
double ureter - early splitting of ureter (complete/partial) - split ureters might open into bladder separately, or unite and open as usual
1. Urachal fistula - caused by persisting allantois. * urine may drain from the umbilicus. 2. Urachal cyst - caused by failure of obliteration of middle part of allantois 3. Urachal sinus - caused by failure of obliteration of proximal or distal part of allantois
congenital anomalies
4. Ectopia Vesicae (Extrophy of bladder) - rare severe anomaly - both anterior abdominal wall and the anterior wall of the bladder are absent and the posterior wall of the bladder (trigone and ureteric orifices) are exposed and protruded to the outside dribbling urine 5. Congenital recto-vesical or recto uretheral fistula 6. Hypospadius - urethra opens on the under surface of the glans penis. It might be perineal (scrotal), penile, or terminal - a common anomaly that might be an isolated defect or may be associated with other anomalies of the male genital system 7. Epispadius
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Sex, Gender and Society (Fragment), Ann OakleyDocument29 paginiSex, Gender and Society (Fragment), Ann OakleyLeandro293Încă nu există evaluări
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- Escaping The Friend Zone ReportDocument12 paginiEscaping The Friend Zone Reportelbobero100% (1)
- Exercise 1-3Document9 paginiExercise 1-3Patricia MedinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- GFAS Resetting Impression PDFDocument14 paginiGFAS Resetting Impression PDFyayan19Încă nu există evaluări
- Flight PatternsDocument4 paginiFlight PatternshudgensrÎncă nu există evaluări
- @acute Nephritic SyndromeDocument3 pagini@acute Nephritic Syndromeameerabest100% (1)
- Cme Bronchial AsthmaDocument28 paginiCme Bronchial AsthmaameerabestÎncă nu există evaluări
- @ovary Cyst ComparisonDocument2 pagini@ovary Cyst ComparisonameerabestÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genital EmbryologyDocument6 paginiGenital EmbryologyameerabestÎncă nu există evaluări
- Semen AnalysisDocument3 paginiSemen Analysisameerabest80% (5)
- @tumors of The Breast 1Document2 pagini@tumors of The Breast 1ameerabestÎncă nu există evaluări
- OSCE DermaDocument8 paginiOSCE DermaameerabestÎncă nu există evaluări
- #MediastinumDocument4 pagini#Mediastinumameerabest100% (1)
- PleuraDocument6 paginiPleuraameerabest100% (1)
- Extracorporial Circulation (Ecc) Heart Lung Machine Cardio-Pulmonary Bypass (CPB)Document2 paginiExtracorporial Circulation (Ecc) Heart Lung Machine Cardio-Pulmonary Bypass (CPB)ameerabestÎncă nu există evaluări
- #LungDocument1 pagină#LungameerabestÎncă nu există evaluări
- #Chest TraumasDocument4 pagini#Chest Traumasameerabest100% (3)
- Parotid Gland Submandibular Gland Sublingual GlandDocument5 paginiParotid Gland Submandibular Gland Sublingual GlandameerabestÎncă nu există evaluări
- PharynxDocument2 paginiPharynxameerabest0% (1)
- Oesophagus & StomachDocument3 paginiOesophagus & StomachameerabestÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mouth Cavity, Palate, TongueDocument8 paginiMouth Cavity, Palate, Tongueameerabest100% (1)
- EisaJocson MaterialPacket PDFDocument17 paginiEisaJocson MaterialPacket PDFGabyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cléo DuboisDocument3 paginiCléo DuboisGregor SamsaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Savitribai PhuleDocument2 paginiSavitribai PhuleKrishnan CoolÎncă nu există evaluări
- K 3Document4 paginiK 3kirankumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Strain TheoryDocument2 paginiGeneral Strain TheoryArmin ValdezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aldovino, Karl Christian Bencito, Ryan James Rodriguez, MosesDocument35 paginiAldovino, Karl Christian Bencito, Ryan James Rodriguez, MosesRose RazoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Duke of ManhattanDocument232 paginiDuke of ManhattanRose May LlosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Socio-Cultural Impact of TourismDocument25 paginiSocio-Cultural Impact of Tourismdevhan1233% (3)
- Mizoram Profile: Total Rural Urban Population SizeDocument2 paginiMizoram Profile: Total Rural Urban Population SizejohntluangaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Marital Rape - DraftDocument11 paginiMarital Rape - DraftFarhat YunusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sex, or The Unbearable by Lauren Berlant and Lee EdelmanDocument17 paginiSex, or The Unbearable by Lauren Berlant and Lee EdelmanDuke University Press100% (4)
- Homosexuality in Ancient RomeDocument19 paginiHomosexuality in Ancient RomeIlsondeBacellarJrÎncă nu există evaluări
- GIZ Publication - Gender Takes Centre Stage PDFDocument44 paginiGIZ Publication - Gender Takes Centre Stage PDFBojan VojvodicÎncă nu există evaluări
- 237 Reasons Why Women Have SexDocument7 pagini237 Reasons Why Women Have SexJed Diamond73% (11)
- Chap # 1: Presented By: Ammarah Farhat AbbasDocument23 paginiChap # 1: Presented By: Ammarah Farhat AbbasAbdullah khalidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paraphrasing and SummarisingDocument8 paginiParaphrasing and SummarisingUmiFaridaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Human Body Intro WebquestDocument2 paginiHuman Body Intro Webquestapi-234361888Încă nu există evaluări
- InsiangDocument3 paginiInsiangFeliceHolmesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Immersion NarrativeDocument13 paginiImmersion NarrativeRen-ren MirafloresÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6981 and 7877Document3 pagini6981 and 7877111111Încă nu există evaluări
- Q1 &Q2 1st Summative Test Science 5 EDITEDDocument14 paginiQ1 &Q2 1st Summative Test Science 5 EDITEDTrishaAnnSantiagoFidel100% (2)
- Bvix Fvebv: JW K Wez K©I Cöwzcv'Document27 paginiBvix Fvebv: JW K Wez K©I Cöwzcv'Mamoon AskariÎncă nu există evaluări
- GujratiDocument5 paginiGujratimyeyesrbeautÎncă nu există evaluări
- Factors Associated With Menstrual Cycle Irregularity and MenopauseDocument11 paginiFactors Associated With Menstrual Cycle Irregularity and MenopauseRyan IlhamÎncă nu există evaluări