Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Cover Page: Additional Mathematics SA2 Overall Revision Notes
Încărcat de
Mark MahonTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Cover Page: Additional Mathematics SA2 Overall Revision Notes
Încărcat de
Mark MahonDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Cover Page
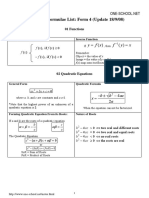
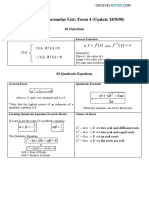
Topics tested for SA2 (Highlighted are paper 2) 1.)Simultaneous Equations 2.)Surds, Indices, Logarithms 3.)Quadratic Equations and Inequalities 4.)Polynomials and Partial Fractions 5.)The Modulus Function 6.)Binomial Theorem 7.)CoordinateAdditional Mathematics SA2 Overall Geometry Chapters 1 2
Revision Notes
Simultaneous Equations, Indices, Surds, Logarithms
Chapter 1: Simultaneous Equations There are 3 methods in solving simultaneous linear equations: 1.) Substitution Method 2.) Elimination Method 3.) Graphical Method There are several steps to follow: 1.) Express one unknown in terms of another unknown (avoid fractional expressions) 2.) Substitute this newly formed equation into the non-linear equation Chapter 2.2: Indices
a m a n = a m+n ( a m ) n = a mn a m b m = ( ab ) m a m a n = a mn a a m bm = ( )m b 0 a =1 1 a n = n a x x (a n ) = n a
m
Chapter 2.1: Surds m n = mn m n = m n
a m +b m = a+b m ( a + b )( a b ) = a b a+b k =c+d k a = c and b = d . Rationalising Denominator: Multiply the square root to both numerator and denominator.
Chapter 2.3: Logarithms
a n = n a m = (n a ) m
a x = an x = n When a > 1
Sum and Product of Roots In ax 2 + bx + c Sum of roots + = b a c Product of roots = a
Intersection Terms Crosses / Cuts 2 points of intersection, 2 real/distinct roots/ discriminant more than 0. 1 point of intersection, 2 real/equal roots/ discriminant = 0. 0 points of intersection, no real roots, discriminant < 0.
Touches / tangent Does not intersect / We can use the sum and productMathematics SA2 Overall Revision Notes of Additional meet roots to write an equation. Chapters 3 - 4 Discriminant more than or equal to Meet 0. x 2 (sum of roots)x + (product of roots) = 0 Quadratic Inequality
Quadratic Functions and Inequalities
Discriminant and Nature of Roots
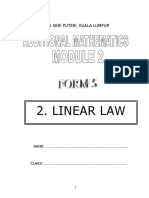
Chapter 8: Linear Law
The graph of a linear equation Y = mX + c is a straight line with gradient m and y intercept c. There are 2 parts to solving linear law questions: Draw a straight line graph to determine gradient and y-intercept, and to find the equation of the straight line. Key Steps: 1.) Force the equation into the form of Y = mX + c.
2.) Take some experimental values of x and y and compute the corresponding values of X and Y. 3.) Use these computed values to plot the points on a graph with X and Y axis. 4.) Draw a line passing through the plotted points. Always have more space at the lower end of
graph for the line to cut the Y axis for Y-intercept. 5.) Obtain the Gradient and the Y-intercept. Note: In Y = mX + Additional c
Mathematics SA2 Overall Revision Notes
Chapters 3 - 4
Polynomials/Partial Fractions
Polynom ial
An expression that is a sum of terms in the form axn where n is non-negative and a is constant.
To find unknown constants, either equate coefficients of like powers of x or substitute values of x. Remainder Theorem If a polynomial f(x) is divided by a linear divisor (x a), the remainder is f(a). Factor Theorem
If (x a) is a factor of the polynomial f(x), f(a) = 0.
Partial Fractions
Chapter 5: The Modulus Functions
Chapter 6: Binomial Theorem
For a real number x, |x| represents n n (a + b) n = a n + a n 1b + a n 2b 2...+ b n the modulus / absolute value of x. It is 1 2 always non-negative. that cannot be factorised is to be remained in the same form. A repeated Basically, a linear factor
n n n n 1 n A B n To draw a modulus + b) 2 graph of the (1 + x) n = 1 + 2 . x + x 2 + x3 + ... + + linear factor like (ax is to be split into 2: x +x (ax + b) ( ax + b 1 ) function, first draw the function then 2 3 n 1 reflect the part of the function which n n(n 1)( n 2)...(n r + 1) is below the x axis upwards. = r! r Formulas:
x = k x = k or x = k f ( x ) = g ( x), g ( x ) 0 f ( x) = g ( x) , f ( x) = g ( x) ab = a b a a = b b Properties: 1.) Have n+1 terms 2.) Sum of powers of a and b = n.
n nr r n r r+1th term: Tr +1 = a b or Tr +1 = b r r
Chapter 7: Coordinate Geometry
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsDe la EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (8)
- O Level Additional Maths NotesDocument8 paginiO Level Additional Maths NotesRenny LowÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simultaneous Equations, Indices, Surds, Logarithms: Additional Mathematics SA2 Overall Revision NotesDocument8 paginiSimultaneous Equations, Indices, Surds, Logarithms: Additional Mathematics SA2 Overall Revision NotesVikas PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Matrix Theory and Applications for Scientists and EngineersDe la EverandMatrix Theory and Applications for Scientists and EngineersÎncă nu există evaluări
- O Level Additional Maths Notes PDFDocument8 paginiO Level Additional Maths Notes PDFDavid Ardiansyah100% (1)
- Maths Concepts and Formulae: y FX F y XDocument16 paginiMaths Concepts and Formulae: y FX F y XAt TanwiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Additional Mathematics SA2 Overall RevisDocument8 paginiAdditional Mathematics SA2 Overall RevisAnaya DonaldsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- To Graph A Relation, We Need To Plot Each Given Ordered PairDocument11 paginiTo Graph A Relation, We Need To Plot Each Given Ordered PairSungmin KimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 3 Quadratic FunctionsDocument13 paginiLesson 3 Quadratic FunctionsChet Jerry AckÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 3 Math OverviewDocument7 paginiUnit 3 Math OverviewmicjenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Part4 Linear EquationsDocument39 paginiPart4 Linear Equationszepozepo06Încă nu există evaluări
- MathematicsDocument7 paginiMathematicsJay LiÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 2 Linear Equations 11Document28 paginiCH 2 Linear Equations 11zhero7Încă nu există evaluări
- Bab 1Document8 paginiBab 1jak92Încă nu există evaluări
- Class Xii Chapter Wise Concept MapDocument18 paginiClass Xii Chapter Wise Concept MapAnu Radha40% (5)
- Chapter 26 - Remainder - A4Document9 paginiChapter 26 - Remainder - A4GabrielPaintingsÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 System of Linear EquationDocument12 pagini5 System of Linear EquationAl Asad Nur RiyadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices: Shirley HuangDocument51 paginiSystems of Linear Equations and Matrices: Shirley HuangShu RunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ah FormulaeDocument5 paginiAh FormulaeVijay RajuÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.6.3 Practice - Quadratic Functions (Practice)Document11 pagini2.6.3 Practice - Quadratic Functions (Practice)johnnyhockey91Încă nu există evaluări
- NA 5 LatexDocument45 paginiNA 5 LatexpanmergeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Math T Short Note (For Memory Flash Back Only)Document10 paginiMath T Short Note (For Memory Flash Back Only)Victor Hah Chang WahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mas de Regresion MultivariadaDocument10 paginiMas de Regresion MultivariadanerinconqÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10th Samacheer Kalvi Maths All Units Points To RememberDocument10 pagini10th Samacheer Kalvi Maths All Units Points To RememberArvind RanganathanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optimization Techniques: Dr. Muhammad Naeem Dr. Ashfaq AhmedDocument64 paginiOptimization Techniques: Dr. Muhammad Naeem Dr. Ashfaq AhmedMuhammad Ali Khan AwanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Systems and MatricesDocument15 paginiSystems and MatricesTom DavisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Add Maths Fast Track Sow Year 9 310807 v2Document9 paginiAdd Maths Fast Track Sow Year 9 310807 v2Ya YaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Numerical Solution Methods: 3.1.1 Matrices and Vectors in FortranDocument9 paginiNumerical Solution Methods: 3.1.1 Matrices and Vectors in FortranLucas SantosÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1&2 Take Home HAnd in 2 CalculusDocument3 pagini1&2 Take Home HAnd in 2 CalculusnbentzÎncă nu există evaluări
- NUS Math SyllabusDocument11 paginiNUS Math SyllabusAgus LeonardiÎncă nu există evaluări
- PC Exam ReviewDocument4 paginiPC Exam Reviewklb925Încă nu există evaluări
- SMP 16-19 Mathematics - Revision Notes Unit 5 - Calculus MethodsDocument2 paginiSMP 16-19 Mathematics - Revision Notes Unit 5 - Calculus MethodsPrincess KimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3 Lae1Document27 paginiChapter 3 Lae1razlan ghazaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Higher Maths: Formulae: Essential Trigonometric IdentitiesDocument5 paginiAdvanced Higher Maths: Formulae: Essential Trigonometric IdentitiesknoxmathsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Form 3-Chapter 12 Graphs of FunctionsDocument16 paginiForm 3-Chapter 12 Graphs of FunctionsAlyaa SyahidaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Formulae SheetDocument17 paginiFinal Formulae Sheetfatimahasnain410Încă nu există evaluări
- Graphing WorkbookDocument21 paginiGraphing WorkbookElaine zhuÎncă nu există evaluări
- LAWeek1 MA2006-2Document32 paginiLAWeek1 MA2006-2davidbehÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cpe-310B Engineering Computation and Simulation: Solving Sets of EquationsDocument46 paginiCpe-310B Engineering Computation and Simulation: Solving Sets of Equationsali ahmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ls. Linear SystemsDocument6 paginiLs. Linear SystemsZubinJainÎncă nu există evaluări
- SPM Add Maths Formula List Form4Document16 paginiSPM Add Maths Formula List Form4Alvin HonÎncă nu există evaluări
- WIN (2019-20) MAT1002 ETH AP2019205000028 Reference Material I Application of ODE PDFDocument177 paginiWIN (2019-20) MAT1002 ETH AP2019205000028 Reference Material I Application of ODE PDFEswar RcfÎncă nu există evaluări
- Linear LawDocument29 paginiLinear LawsusansoonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rational Functions: Rational Functions Are Quotients of Polynomial Functions. This Means ThatDocument16 paginiRational Functions: Rational Functions Are Quotients of Polynomial Functions. This Means ThatSalih AnwarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Matrices, Determinants & Linear SystemsDocument30 paginiMatrices, Determinants & Linear SystemssilviubogaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 4-Filled Out PDFDocument6 paginiLecture 4-Filled Out PDFShanay ThakkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ad Maths Formula ListDocument16 paginiAd Maths Formula ListZareena CarrimÎncă nu există evaluări
- HPDocument6 paginiHPFinsch KenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cha 6Document90 paginiCha 6makarappleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 6Document20 paginiChapter 6Shimeque SmithÎncă nu există evaluări
- A2 1st Sem Exam Review 2011Document5 paginiA2 1st Sem Exam Review 2011klb925Încă nu există evaluări
- ICSE Class - X Maths Booklet With Model Paper 2015Document24 paginiICSE Class - X Maths Booklet With Model Paper 2015Apex Institute100% (3)
- Calculus II: For Biology and MedicineDocument80 paginiCalculus II: For Biology and MedicineEulises ValenzuelaÎncă nu există evaluări
- DeterminantDocument14 paginiDeterminantNindya SulistyaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quadratic FunctionsDocument24 paginiQuadratic FunctionsDominic SavioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Matrices Dr.s.s.chauhanDocument22 paginiMatrices Dr.s.s.chauhanQadirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1 Chapter 3: Quadratic FunctionsDocument18 paginiUnit 1 Chapter 3: Quadratic FunctionsZlata OsypovaÎncă nu există evaluări
- System of of Linear Linear Equations EquatioDocument47 paginiSystem of of Linear Linear Equations EquatioSandeep SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Differential Calculus BOOKDocument264 paginiDifferential Calculus BOOKAbdul Halil AbdullahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strassen's Matrix MultiplcationDocument13 paginiStrassen's Matrix MultiplcationSaurav SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 9 SolutionsDocument3 paginiChapter 9 SolutionsAli IÎncă nu există evaluări
- Motivation and Contribution Stabilizer Codes and Logical Pauli OperatorsDocument1 paginăMotivation and Contribution Stabilizer Codes and Logical Pauli OperatorsNarayanan RengaswamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Source Code Domain FrekuensiDocument12 paginiSource Code Domain FrekuensiTanisHamidÎncă nu există evaluări
- We Belong Together Matching Lab 4-07Document8 paginiWe Belong Together Matching Lab 4-07Carol H. APSI teacher83% (6)
- Assignment 1Document2 paginiAssignment 1Vibhanshu PrajapatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sinclair Coefficient PDFDocument1 paginăSinclair Coefficient PDFTing Hin YanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 01 02 Circles 2 PDFDocument21 pagini01 02 Circles 2 PDFrohit kumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Polar CoordinatesDocument10 paginiPolar CoordinatesIan RidzuanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trajectory Planning For Automatic Machines and RobotsDocument514 paginiTrajectory Planning For Automatic Machines and RobotsPromit ChoudhuryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sequence & SeriesDocument50 paginiSequence & SeriesShubham SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- HW 8Document2 paginiHW 8Huy NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- 11 - Numerical Differentiation and Integration-Integration of Equations - (Romberg Integration)Document8 pagini11 - Numerical Differentiation and Integration-Integration of Equations - (Romberg Integration)Mohannad QudahÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Peter Hosch) Solutions Symplectic GeometryDocument74 pagini(Peter Hosch) Solutions Symplectic Geometryfaudzi5505Încă nu există evaluări
- 2nd Periodical Test in Math G10 19-20Document3 pagini2nd Periodical Test in Math G10 19-20Dom BelloÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9) Trigonometric GraphsDocument10 pagini9) Trigonometric GraphsboobooÎncă nu există evaluări
- 20210605-Class - 8 Ls. No. 4. Cubes and Cube Roots SolutionDocument13 pagini20210605-Class - 8 Ls. No. 4. Cubes and Cube Roots SolutionHardik KarelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Math Pamphlet QandA Grade 10-12 PDFDocument465 paginiMath Pamphlet QandA Grade 10-12 PDFBenjamin Musonda85% (54)
- Question's 2Document9 paginiQuestion's 2Urnext bestalternwÎncă nu există evaluări
- Math 1151 Sample Questions For MID Exam Summer 2023Document8 paginiMath 1151 Sample Questions For MID Exam Summer 2023Shurav DasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alternative SortingDocument9 paginiAlternative SortingpriyanjayÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Dorian Goldfeld) Automorphic Forms and L-FunctionDocument509 pagini(Dorian Goldfeld) Automorphic Forms and L-Functioncharlyshaka1Încă nu există evaluări
- MODULE 3 Mathematics in The Modern World GNED 03 BSCPE & BSEE 101Document11 paginiMODULE 3 Mathematics in The Modern World GNED 03 BSCPE & BSEE 101Harold Q SolisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Address Calculation in ArraysDocument3 paginiAddress Calculation in ArraysAnonymous zrAfrkPOJ7Încă nu există evaluări
- Optimization - Lecture 2 - 2023Document16 paginiOptimization - Lecture 2 - 2023Ali ًSameerÎncă nu există evaluări
- TRANSFORMATIONSDocument20 paginiTRANSFORMATIONSSahana PotatoÎncă nu există evaluări
- PCD Lab Manual 2017Document46 paginiPCD Lab Manual 2017Shubhajit MallickÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.signals & Systems JtoisroDocument20 pagini2.signals & Systems JtoisroNarasimhamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Networkx TutorialDocument8 paginiNetworkx TutorialDan Iftodi100% (1)