Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Ques What Is Computer Networking
Încărcat de
Palav JainnDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Ques What Is Computer Networking
Încărcat de
Palav JainnDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Ques What is computer networking?
Ans Computer networking permits multiple computers to communicate and share resources either through wired or wireless access. Or It is a system where computers are interconnected to share information. Ques What is the use of networking? Networking is needed because 1 Communication: It breaks the barrier of distance. 2 Resource sharing: Hardware can be connected to network and thus printers or scanners can be used by all the computer system in the network. 3 Cost effective: A software program can be installed in one system and can be used by other computers in the network there by reducing the cost of buying several copies. High reliability The copy of a document can be made available on many machines so if one system is not available , the other could be used. Networking transmission media Data transmission is sending a stream of bits or bytes from one place to another with the CDs, PEN DRIVES, BLUETOOTH, INFRARED or RADIO WAVES etc. The data transmission technology is divided into 1 Wired technology 2 Wireless technologies Wired technology is a method where, the data is send from one place to another through wires Wireless technologies is the transfer of information between two or more points that are not physically
connected. Distances can be short, such as a few meters for eg television remote control, or as far as thousands or even millions of kilometers for deep-space radio communications Physical /wired Communication Three basic types of guided or wired communication medium are Co-axial Cable Ethernet Cable Fiber Optic A coaxial cable is used to transmit signals, such as video, radio and data. The cables are round and of a uniform radius from end to end. Or
A coaxial cable is most commonly used to hook a television to a cable provider. These have a insulating outer case and a copper wire on the inside An Ethernet cable is a cable used to connect network devices as modems or routers. If a computer is connected to the inter net with a Ethernet cable,
Fiber optics A technology that uses glass (or plastic) threads (fibers) to transmit data. A fiber optic cable consists of a bundle of glass threads, each of which is capable of transmitting messages modulated onto light waves.
Fiber optics has several advantages over traditional metal communications lines: Fiber optic cables have a much greater bandwidth than metal cables. This means that they can carry more data. Fiber optic cables are much thinner and lighter than metal wires.
Data can be transmitted digitally (the natural form for computer data) rather than analogically.
The main disadvantage of fiber optics is that the cables are expensive to install. In addition, they are more fragile than wire and are difficult to splice. Fiber optics is a particularly popular technology for localarea networks. In addition, telephone companies are steadily replacing traditional telephone lines with fiber optic cables. In the future, almost all communications will employ fiber optics. Wireless communication Medium Short range communication 1. Infrared -they are used for short range communicationie communication between the devices which are not very far from each other such as remote control to a television or DVDs player.
2.
bluetooth Bluetooth is the name of a wireless technology that is standard for connecting devices without cables. Bluetooth works by using radio signals to transmit information over short distances that are generally 33 feet or less.
Long range communication Radio link Microwave link Satellite link GSM CDMA CSMA
Radio link "Radio waves" transmit music, conversations, pictures and data invisibly through the air, often over millions of miles. Eg FM with different frequencies. At low frequency they travel in all directions and at high they travel in straight line.
Microwave It is used for long distance telephonic communication, cell phone communication etc.It travel in straight line and unlike radio waves, microwavws donot pass through obstacles
Satellite link A satellite link is a communications subsystem that involves a link between a transmitting Earth station and a receiving Earth station via a communications satellite
Short for Code-Division Multiple Access, a digital cellular technology that uses spread-spectrum techniques. Unlike competing systems, such as GSM, that use TDMA, CDMA does not assign a specific frequency to each user. Instead, every channel uses the full available spectrum. Individual conversations are encoded with a pseudo-random digital sequence. CDMA consistently provides better capacity for voice and data communications than other commercial mobile technologies,
allowing more subscribers to connect at any given time, and it is the common platform on which 3G technologies are built.
Carrier Sense Multiple Access (CSMA) is a probabilistic Media Access Control (MAC) protocol in which a node verifies the absence of other traffic before transmitting on a shared transmission medium, such as an electrical bus, or a band of the electromagnetic spectrum. "Carrier Sense" describes the fact that a transmitter uses feedback from a receiver that detects a carrier wave before trying to send. That is, it tries to detect the presence of an encoded signal from another station before attempting to transmit. If a carrier is sensed, the station waits for the transmission in progress to finish before initiating its own transmission. "Multiple Access" describes the fact that multiple stations send and receive on the medium. Transmissions by one node are generally received by all other stations using the medium. Wireless local loop (WLL), is a term for the use of a wireless communications link as the "last mile / first mile" connection for delivering plain old telephone service (POTS) and/or broadband Internet to telecommunications customers. Various types of
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (119)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (587)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2219)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (894)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- Rescue Triangle PDFDocument18 paginiRescue Triangle PDFrabas_Încă nu există evaluări
- Mechanical Questions & AnswersDocument161 paginiMechanical Questions & AnswersTobaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shimano Brakes ManualDocument36 paginiShimano Brakes ManualKon Arva100% (1)
- Marksmanship: Subject: III. Definition of TermsDocument16 paginiMarksmanship: Subject: III. Definition of TermsAmber EbayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- E PortfolioDocument76 paginiE PortfolioMAGALLON ANDREWÎncă nu există evaluări
- No.6 Role-Of-Child-Health-NurseDocument8 paginiNo.6 Role-Of-Child-Health-NursePawan BatthÎncă nu există evaluări
- Keberhasilan Aklimatisasi Dan Pembesaran Bibit Kompot Anggrek Bulan (Phalaenopsis) Pada Beberapa Kombinasi Media TanamDocument6 paginiKeberhasilan Aklimatisasi Dan Pembesaran Bibit Kompot Anggrek Bulan (Phalaenopsis) Pada Beberapa Kombinasi Media TanamSihonoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Product Catalog 2016Document84 paginiProduct Catalog 2016Sauro GordiniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Donny UfoaksesDocument27 paginiDonny UfoaksesKang Bowo D'wizardÎncă nu există evaluări
- ASD Manual and AISC LRFD Manual For Bolt Diameters Up To 6 Inches (150Document1 paginăASD Manual and AISC LRFD Manual For Bolt Diameters Up To 6 Inches (150rabzihÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 9-10 (PPE) Reinzo GallegoDocument48 paginiChapter 9-10 (PPE) Reinzo GallegoReinzo GallegoÎncă nu există evaluări
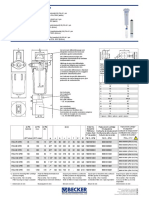
- Medical filter performance specificationsDocument1 paginăMedical filter performance specificationsPT.Intidaya Dinamika SejatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemical Cleaning Products Are Destroying The Ecosystem and Your Septic Tank - Organica BiotechDocument14 paginiChemical Cleaning Products Are Destroying The Ecosystem and Your Septic Tank - Organica BiotechKrispin FongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aquafine Optivenn Series Data SheetDocument8 paginiAquafine Optivenn Series Data SheetKenz ZhouÎncă nu există evaluări
- Denodo Job RoleDocument2 paginiDenodo Job Role059 Monisha BaskarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Obsolescence 2. Book Value 3. Depreciation 4. Depletion EtcDocument9 paginiObsolescence 2. Book Value 3. Depreciation 4. Depletion EtcKHAN AQSAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Levels of Attainment.Document6 paginiLevels of Attainment.rajeshbarasaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- HP 5973 Quick ReferenceDocument28 paginiHP 5973 Quick ReferenceDavid ruizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brooks Cole Empowerment Series Becoming An Effective Policy Advocate 7Th Edition Jansson Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument36 paginiBrooks Cole Empowerment Series Becoming An Effective Policy Advocate 7Th Edition Jansson Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFlois.guzman538100% (12)
- CCEE SWD Basic Levers ToolDocument28 paginiCCEE SWD Basic Levers ToolDivina Margarita Gómez AlvarengaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Migration (LIN 19/051: Specification of Occupations and Assessing Authorities) Instrument 2019Document28 paginiMigration (LIN 19/051: Specification of Occupations and Assessing Authorities) Instrument 2019Ajay palÎncă nu există evaluări
- January 2013 Igcse Timetable 22-06-2012Document2 paginiJanuary 2013 Igcse Timetable 22-06-2012Rizwanur RahmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 6Document7 paginiWeek 6Nguyễn HoàngÎncă nu există evaluări
- Learn Square Roots & Plot on Number LineDocument11 paginiLearn Square Roots & Plot on Number LineADAM CRISOLOGOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Febrile SeizureDocument3 paginiFebrile SeizureClyxille GiradoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Calculus: Performance TaskDocument6 paginiBasic Calculus: Performance TasksammyÎncă nu există evaluări
- UT Dallas Syllabus For Ee3311.002.07f Taught by Gil Lee (Gslee)Document3 paginiUT Dallas Syllabus For Ee3311.002.07f Taught by Gil Lee (Gslee)UT Dallas Provost's Technology GroupÎncă nu există evaluări
- Voltaire's Candide and the Role of Free WillDocument3 paginiVoltaire's Candide and the Role of Free WillAngy ShoogzÎncă nu există evaluări
- A.2.3. Passive Transport Systems MCQsDocument3 paginiA.2.3. Passive Transport Systems MCQsPalanisamy SelvamaniÎncă nu există evaluări