Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
New Rich Text Document
Încărcat de
OMKA3416Descriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
New Rich Text Document
Încărcat de
OMKA3416Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
15.1.
2 Tooth Profile Error, ff Tooth profile error is the summation of deviation between actual tooth profile and correct involute curve which passes through the pitch point measured perpendicular to the actual profile. The measured band is the actual effective working surface of the gear. However, the tooth modification area is not considered as part of profile error. 15.1.3 Runout Error of Gear Teeth, Fr This error defines the runout of the pitch circle. It is the error in radial position of the teeth. Most often it is measured by indicating the position of a pin or ball inserted in each tooth space around the gear and taking the largest difference. Alternately, particularly for fine pitch gears, the gear is rolled with a master gear on a variable center distance fixture, which records the change in the center distance as the measure of teeth or pitch circle runout. Runout causes a number of problems, one of which is noise. The source of this error is most often insufficient accuracy and ruggedness of the cutting arbor and tooling system. 15.1.4 Lead Error, fb Lead error is the deviation of the actual advance of the tooth profile from the ideal value or position. Lead error results in poor tooth contact, particularly concentrating contact to the tip area. Modifications, such as tooth crowning and relieving can alleviate this error to some degree. Shown in Figure 15-2 is an example of a chart measuring tooth profile error and lead error using a Zeiss UMC 550 tester. Table 15-3 presents the allowable tooth profile, runout and lead errors per JIS B 1702-1976. 15.1.5. Outside Diameter Runout and Lateral Runout To produce a high precision gear requires starting with an accurate gear blank. Two criteria are very important: 1. Outside diameter (OD) runout. 2. Lateral (side face) runout. The lateral runout has a large impact on the gear tooth accuracy. Generally, the permissible runout error is related to the gear size. Table 15-4 presents equations for allowable values of OD runout and lateral runout.
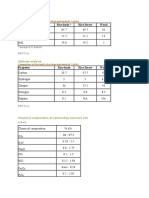
Table 15-3 The Value of Allowable Tooth Profile Error, Runout Error and Lead Error, mm
Grade Tooth Profile Error ff Fr Fb JIS 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 0.71m + 2.24 1.4W + 4.0 0.63(0.1b + 10) Runout Error of Gear Groove Lead Error
1.0m + 3.15 2.0W + 5.6 0.71(0.1b + 10) 1.4m + 4.5 2.8W + 8.0 0.80(0.1b + 10) 2.0m + 6.3 4.0W + 11.2 1.00(0.1b + 10) 2.8m + 9.0 5.6W + 16.0 1.25(0.1b + 10) 4.0m + 12.5 8.0W + 22.4 1.60(0.1b + 10) 5.6m + 18.0 11.2W + 31.5 8.0m + 25.0 22.4W + 63.0 11.2m + 35.5 2.00(0.1b + 10) 2.50(0.1b + 10) 3.15(0.1b + 10)
45.0W + 125.0
where: W = Tolerance unit = b = Tooth width (mm) m = Module (mm)
The total lead mismatch between mating teeth is dependent upon: 1. Gear tooth manufacturing accuracy 2. Alignment of axis of rotation of the gears 3. Elastic deflections 4. Bearing clearance 5. Thermal distortion 6. Centrifugal deflections 7. Tooth crowning and end relief
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (894)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- Consumer Behaviour Towards AppleDocument47 paginiConsumer Behaviour Towards AppleAdnan Yusufzai69% (62)
- Uk GR PeopleDocument2 paginiUk GR PeopleOMKA3416Încă nu există evaluări
- World Wonders IndiaDocument2 paginiWorld Wonders IndiaOMKA3416Încă nu există evaluări
- MCS July12Document7 paginiMCS July12OMKA3416Încă nu există evaluări
- New Text DocumentDocument2 paginiNew Text DocumentOMKA3416Încă nu există evaluări
- World Wonders UkDocument2 paginiWorld Wonders UkOMKA3416Încă nu există evaluări
- Trademark in India1Document8 paginiTrademark in India1OMKA3416Încă nu există evaluări
- Automobile Air Conditioning1Document17 paginiAutomobile Air Conditioning1OMKA3416Încă nu există evaluări
- The Warli or Varli Are An Indian Scheduled TribeDocument3 paginiThe Warli or Varli Are An Indian Scheduled TribeOMKA3416Încă nu există evaluări
- Proximate Analysis of Rice HuskDocument2 paginiProximate Analysis of Rice HuskOMKA3416100% (3)
- Cybershot CatalogueDocument14 paginiCybershot CatalogueBabaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 6Document7 paginiWeek 6Nguyễn HoàngÎncă nu există evaluări
- BMXNRPDocument60 paginiBMXNRPSivaprasad KcÎncă nu există evaluări
- VARCDocument52 paginiVARCCharlie GoyalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Product Catalog 2016Document84 paginiProduct Catalog 2016Sauro GordiniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Startups Helping - India Go GreenDocument13 paginiStartups Helping - India Go Greensimran kÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 - Complex IntegralsDocument89 pagini4 - Complex IntegralsryuzackyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Levels of Attainment.Document6 paginiLevels of Attainment.rajeshbarasaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fisher FIELDVUE DVC2000 Digital Valve Controller: Instruction ManualDocument108 paginiFisher FIELDVUE DVC2000 Digital Valve Controller: Instruction ManualsrinuvoodiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Overview for Report Designers in 40 CharactersDocument21 paginiOverview for Report Designers in 40 CharacterskashishÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brooks Cole Empowerment Series Becoming An Effective Policy Advocate 7Th Edition Jansson Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument36 paginiBrooks Cole Empowerment Series Becoming An Effective Policy Advocate 7Th Edition Jansson Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFlois.guzman538100% (12)
- Medical filter performance specificationsDocument1 paginăMedical filter performance specificationsPT.Intidaya Dinamika SejatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biomechanics of Advanced Tennis: January 2003Document7 paginiBiomechanics of Advanced Tennis: January 2003Katrien BalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrocardiography - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument18 paginiElectrocardiography - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediapayments8543Încă nu există evaluări
- Write 10 Lines On My Favourite Subject EnglishDocument1 paginăWrite 10 Lines On My Favourite Subject EnglishIrene ThebestÎncă nu există evaluări
- SOP for Troubleshooting LT ACB IssuesDocument9 paginiSOP for Troubleshooting LT ACB IssuesAkhilesh Kumar SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- CV Abdalla Ali Hashish-Nursing Specialist.Document3 paginiCV Abdalla Ali Hashish-Nursing Specialist.Abdalla Ali HashishÎncă nu există evaluări
- AIATS 2021 (OYMCF) Test 01 Offline - Code A - SolutionsDocument34 paginiAIATS 2021 (OYMCF) Test 01 Offline - Code A - Solutionsbhavyakavya mehta100% (1)
- Using Snapchat For OSINT - Save Videos Without OverlaysDocument12 paginiUsing Snapchat For OSINT - Save Videos Without OverlaysVo TinhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Models of Health BehaviorDocument81 paginiModels of Health BehaviorFrench Pastolero-ManaloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nqs PLP E-Newsletter No68Document5 paginiNqs PLP E-Newsletter No68api-243291083Încă nu există evaluări
- Mythic Magazine 017Document43 paginiMythic Magazine 017William Warren100% (1)
- Compare and Contrast High School and College EssayDocument6 paginiCompare and Contrast High School and College Essayafibkyielxfbab100% (1)
- Types of LogoDocument3 paginiTypes of Logomark anthony ordonioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Body Scan AnalysisDocument9 paginiBody Scan AnalysisAmaury CosmeÎncă nu există evaluări
- ArtigoPublicado ABR 14360Document14 paginiArtigoPublicado ABR 14360Sultonmurod ZokhidovÎncă nu există evaluări
- Principles of Management NotesDocument61 paginiPrinciples of Management Notestulasinad123Încă nu există evaluări
- Future Design of Accessibility in Games - A Design Vocabulary - ScienceDirectDocument16 paginiFuture Design of Accessibility in Games - A Design Vocabulary - ScienceDirectsulaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Addition and Subtraction of PolynomialsDocument8 paginiAddition and Subtraction of PolynomialsPearl AdamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brochure - Truemax Concrete Pump Truck Mounted TP25M4Document16 paginiBrochure - Truemax Concrete Pump Truck Mounted TP25M4RizkiRamadhanÎncă nu există evaluări