Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Common Source Amplifier
Încărcat de
jaswanthjDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Common Source Amplifier
Încărcat de
jaswanthjDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Common Source Amplifier
Aim: Design Common Source Amplifier by calculating the resistor & capacitor values for given specifications. Check the operation in Software and Hardware. Specifications: Transistor: 2N5459 VCC = 24 V RL = 120K ID = 1.5mA IDSS = 16mA VGS(off) = 8V f = 100Hz
For Software Execution Components Required: 1. P-IV Configured Computer System with Windows Xp 2. Tina Software For Hardware Execution Components Required: S. No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Components Regulated Power Supply Function Generator Resistors Capacitors Transistor CRO CRO Probes Connection Wires Bread Board Single Strand 2N5459 (0-20)MHz 1 1 2 Required 1 Specification (0-32)V (0-1)MHz Quantity 1 1
Theory: The design of FET bias circuits is just as simple as the design of BJT bias circuits. One major difference is that FET circuit design normally uses a graphical approach involving the drawing of a bias line on the device transfer characteristics, as in the case of FET circuit analysis. If the type number of the FET to be used in the circuit is known, the maximum and minimum transfer characteristics are available or can be plotted. A maximum drain current (ID(max)) is selected at a point on the maximum transfer characteristic and bias line is drawn through this point. As will be explained, this procedure applies to all types of bias circuits. The selected level of I D(max) is used to calculate the values of resistors connected to the drain and source terminals. Instead of using the maximum transfer characteristics, suppose that the minimum characteristics, or some characteristic between the maximum and minimum, is used in the circuit design. Now if the FET happens to have the maximum transfer characteristic for the device type
number, ID will be larger than the design value. Consequently, the resistor voltage drops (IDRD and IDRS) will be greater than the intended. In this case VDS will be smaller than its design level, the FET may be forced into the channel ohmic region of its characteristics, and the circuit is unlikely to its characteristics, and the circuit is unlikely to function correctly. Therefore, always use the device maximum transfer characteristic when designing a FET bias circuit. As already explained, a FET has a very high input resistance, so high-value bias resistors can be used at the gate terminal. However there are disadvantages to using extreme high resistance values. A charge accumulated at the gate can take a long time to leak off through a very high resistance. In this case, the gate voltage might not be a stable quantity, and consequently, the drain current could be unpredictable. High-value bias resistors also generate unwanted thermal noise and them readily pick-up stray radio-frequency signals. For these reasons, 1M is normally a reasonable upper limit for bias resistors. Design Calculations:
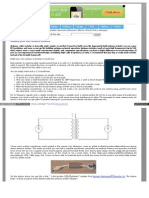
U1 24
R3 4.7M
R4 6.8k
C3 150n C1 20n T1 2N5459 R5 120k + VG1
VF1
VF2
R2 6.8k
R6 600
C2 10u
R1
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Electronic Measurements & Instrumentation 1Document18 paginiElectronic Measurements & Instrumentation 1Srinivas ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bs Lab ManualDocument116 paginiBs Lab Manualjaswanthj100% (1)
- Bs Lab ManualDocument116 paginiBs Lab Manualjaswanthj100% (1)
- Analog Communications LabDocument54 paginiAnalog Communications LabjaswanthjÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5784)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- New Grand I10 NiosDocument10 paginiNew Grand I10 NiosslohariÎncă nu există evaluări
- S13 SR20 Guide 08Document20 paginiS13 SR20 Guide 08Алексей Иванченко100% (1)
- Twido - Programmable Controller - TWDLMDA20DTK PDFDocument9 paginiTwido - Programmable Controller - TWDLMDA20DTK PDFyuda pramudhyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parts List For AstraLux 820DDocument10 paginiParts List For AstraLux 820DAstraluxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Current Differential Relay ManualDocument4 paginiCurrent Differential Relay Manualppraveenkumar79Încă nu există evaluări
- Micro MT Laser Tag System V18-01Document19 paginiMicro MT Laser Tag System V18-01Dylan SenkicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manual de Programador ASiDocument12 paginiManual de Programador ASitoques75Încă nu există evaluări
- Reg 31Document2 paginiReg 31Joe BidenÎncă nu există evaluări
- LTC2605 DS 31613 PDFDocument4 paginiLTC2605 DS 31613 PDFNarcis PatrascuÎncă nu există evaluări
- SB-1500 Slickline Electronic Perforating Tool AdvantagesDocument1 paginăSB-1500 Slickline Electronic Perforating Tool AdvantagesSusin LimÎncă nu există evaluări
- BetastarDocument66 paginiBetastarSamuel MorenoÎncă nu există evaluări
- LC221Document24 paginiLC221MisterMMÎncă nu există evaluări
- MFY-01 Brief OperationDocument2 paginiMFY-01 Brief OperationRajan GangarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Asl FD 260 - 380 (W)Document11 paginiAsl FD 260 - 380 (W)Comercial BrascomÎncă nu există evaluări
- 15k21e01 New Invicta PDFDocument101 pagini15k21e01 New Invicta PDFAriel GonzalezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solar Agro Sprayer: Non-Polluting Pesticide ApplicatorDocument4 paginiSolar Agro Sprayer: Non-Polluting Pesticide ApplicatormanikantaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Instruction Manual: Operates With ISO9001 Certified Quality SystemDocument13 paginiInstruction Manual: Operates With ISO9001 Certified Quality SystemdomagojÎncă nu există evaluări
- NPD HP PCs Nov19Document69 paginiNPD HP PCs Nov19Pedro Iván Mendoza FloresÎncă nu există evaluări
- 70-125 Ton Air-Cooled Chiller - Series R (TM) : Job InformationDocument1 pagină70-125 Ton Air-Cooled Chiller - Series R (TM) : Job InformationjavierÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interruptor RecloserDocument4 paginiInterruptor RecloserbleerÎncă nu există evaluări
- TLK38 ManualDocument12 paginiTLK38 ManualArtur DomańskiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 40XMH'11 40XW'11: (67TL) (67TK)Document50 pagini40XMH'11 40XW'11: (67TL) (67TK)Carlos NetoÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Belco Industrial Plugs & Sockets Reyrolle EasigoDocument32 paginiA Belco Industrial Plugs & Sockets Reyrolle Easigorocketvt100% (1)
- Brief Introduction: ADVANCE Brand. We Are The OE Supplier of Some FamousDocument21 paginiBrief Introduction: ADVANCE Brand. We Are The OE Supplier of Some FamousАлександр ФедоровÎncă nu există evaluări
- Operating Instructions for Linde Lift Trucks T16-T18-T20Document53 paginiOperating Instructions for Linde Lift Trucks T16-T18-T20colive133% (3)
- Antenna Isolator BuildDocument6 paginiAntenna Isolator BuildpegabendÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Mercedes-Benz C-ClassDocument61 paginiThe Mercedes-Benz C-ClassASIK1144Încă nu există evaluări
- NJQS Product and Service Code GuidanceDocument40 paginiNJQS Product and Service Code GuidanceAF Dowell MirinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sening® Nomix Cross-Over Prevention: We Put You First. and Keep You AheadDocument4 paginiSening® Nomix Cross-Over Prevention: We Put You First. and Keep You AheadJoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- HD44780 CommandsDocument3 paginiHD44780 CommandsPhani ChakravarthiÎncă nu există evaluări