Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Assessment DM
Încărcat de
Lean MallaboDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Assessment DM
Încărcat de
Lean MallaboDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Assessment Subjective
pakiramdam ko palagi nalnang akong uhaw at gutom as verbalized by a patient.
Diagnostic exam
Random blood glucose test for a random blood glucose test, blood can be drawn at any time throughout the day, regardless of when the person last ate. A random blood glucose level of 200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L) or higher in persons who have symptoms of high blood glucose suggests a diagnosis of diabetes. Fasting blood glucose test fasting blood glucose testing involves measuring blood glucose after not eating or drinking for 8 to 12 hours (usually overnight). A normal fasting blood glucose level is less than 100 mg/dL. A fasting blood glucose of 126 mg/dL (7.0 mmol/L) or higher indicates diabetes. The test is done by taking a small sample of blood from a vein or fingertip. It must be repeated on another day to confirm that it remains abnormally high. Hemoglobin A1C test (A1C) The A1C blood test measures the average blood glucose level during the past two to three months. It is used to monitor blood glucose control in people with
Nursing intervention
1. Advice patient about the importance of an individualized meal plan in meeting weekly weight loss goals and assist with compliance. Assess patients for cognitive or sensory impairments, which may interfere with the ability to accurately administer insulin. Demonstrate and explain thoroughly the procedure for insulin self-injection. Help patient to achieve mastery of technique by taking step by step approach. Review dosage and time of injections in relation to meals, activity, and bedtime based on patients individualized insulin regimen. Instruct patient in the importance of accuracy of insulin preparation and meal timing to avoid hypoglycemia. Explain the importance of exercise in maintaining or reducing weight. Advise patient to assess blood glucose level before strenuous activity and to eat carbohydrate snack before exercising to avoid hypoglycemia. Assess feet and legs for skin temperature, sensation, soft tissues injuries, corns, calluses, dryness, hair distribution, pulses and deep tendon reflexes. Maintain skin integrity by protecting feet from breakdown.
2.
Objective
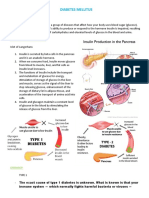
Being very thirsty Urinating often Feeling very hungry or tired Losing weight without trying Having sores that heal slowly Having dry, itchy skin Losing the feeling in your feet or having tingling in your feet Having blurry eyesight
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
known diabetes, but is not normally used to diagnose diabetes. Normal values for A1C are 4 to 6 percent .The test is done by taking a small sample of blood from a vein or fingertip. Oral glucose tolerance test Oral glucose tolerance testing (OGTT) is the most sensitive test for diagnosing diabetes and prediabetes. However, the OGTT is not routinely recommended because it is inconvenient compared to a fasting blood glucose test.
10. Advice patient who smokes to stop smoking or reduce if possible, to reduce vasoconstriction and enhance peripheral flow.
The standard OGTT includes a fasting blood glucose test. The person then drinks a 75 gram liquid glucose solution (which tastes very sweet, and is usually cola or orange-flavored). Two hours later, a second blood glucose level is measured.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- GUIDE ON HOW TO LOWER BLOOD SUGAR: Learn all it takes to lower blood sugar naturally and enjoy a healthy lifestyleDe la EverandGUIDE ON HOW TO LOWER BLOOD SUGAR: Learn all it takes to lower blood sugar naturally and enjoy a healthy lifestyleÎncă nu există evaluări
- An LapDocument2 paginiAn LapMaychelle LAÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is The Oral Glucose Tolerance TestDocument2 paginiWhat Is The Oral Glucose Tolerance TestBianca Camille100% (1)
- Praktikum Block Endocren 2018Document15 paginiPraktikum Block Endocren 2018stella pangestikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reading Test - 5 Diabetes Text A: Clinical AssessmentDocument16 paginiReading Test - 5 Diabetes Text A: Clinical AssessmentJisha JanardhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fasting Blood SugarDocument5 paginiFasting Blood SugarKhamron BridgewaterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kuliah SBLM Prak Endo 2018Document19 paginiKuliah SBLM Prak Endo 2018meryati sinambelaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oral Glucose Tolerance TestDocument29 paginiOral Glucose Tolerance TestAhmedmmhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blood Glucose: Test OverviewDocument3 paginiBlood Glucose: Test OverviewDiana MuañaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ORAL REVALIDA (Diabetes Mellitus)Document5 paginiORAL REVALIDA (Diabetes Mellitus)Aubrey Unique EvangelistaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data KlinikDocument68 paginiData KlinikSiti Zamilatul AzkiyahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oral Glucose Tolerance TestDocument4 paginiOral Glucose Tolerance TestCyna Jane Yao AlcularÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clinical 2Document12 paginiClinical 2yalewzeleke3710Încă nu există evaluări
- DM Brochure For NCM 106Document12 paginiDM Brochure For NCM 106Kimsha ConcepcionÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is DiabetesDocument6 paginiWhat Is Diabetesmkthakur6410Încă nu există evaluări
- Case Study of DMDocument6 paginiCase Study of DMbuzz Q0% (1)
- Diabetes MelitusDocument6 paginiDiabetes Melitusharisman trialviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hemo Glucose TestDocument3 paginiHemo Glucose TestrocheÎncă nu există evaluări
- Glucose, Blood (Blood Sugar, Fasting Blood Sugar (FBS) ) Type of Test Blood Normal FindingsDocument4 paginiGlucose, Blood (Blood Sugar, Fasting Blood Sugar (FBS) ) Type of Test Blood Normal FindingsreskyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Glucose Tolerance TestDocument4 paginiGlucose Tolerance TestNikhil KanikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Diabetes Mellitus and There SymptomsDocument6 paginiTypes of Diabetes Mellitus and There SymptomsApril Joy DoradoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Print Article - Glucose Tests - Glucose Test - Blood Sugar - Blood Glucose - Fasting Blood Glucose - Oral Glucose Tolerance Test - OGTT - GTT - Urine Glucose - Lab Tests OnlineDocument9 paginiPrint Article - Glucose Tests - Glucose Test - Blood Sugar - Blood Glucose - Fasting Blood Glucose - Oral Glucose Tolerance Test - OGTT - GTT - Urine Glucose - Lab Tests OnlineHinaRaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diabetes MellitusDocument6 paginiDiabetes MellituscrisrimartÎncă nu există evaluări
- Imbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body Requirements - Diabetes - NCPDocument5 paginiImbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body Requirements - Diabetes - NCPJulie Ann Jimenez Manlangit50% (4)
- Glucose Tolerance TestDocument3 paginiGlucose Tolerance TestdechychyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diabetes: Jumarang, Kim Enrico M. BSN401 STI - Global CityDocument5 paginiDiabetes: Jumarang, Kim Enrico M. BSN401 STI - Global CityKim Enrico JumarangÎncă nu există evaluări
- How Is Diabtes DiagnoseDocument10 paginiHow Is Diabtes DiagnoseBethChay LacsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diagnosis of Diabetes MellitusDocument23 paginiDiagnosis of Diabetes MellitusNkosinathi ShongweÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diabetes MellitusDocument5 paginiDiabetes MellitusWendy EscalanteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Measuring Blood Glucose LevelDocument7 paginiMeasuring Blood Glucose LevelHuda BehroozÎncă nu există evaluări
- Monitoring Diabetes Control: Why Blood Test?Document6 paginiMonitoring Diabetes Control: Why Blood Test?sangkenyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Laboratory DiagnosisDocument2 paginiLaboratory DiagnosisLourdette TorrefielÎncă nu există evaluări
- Management of Diabetic IndividualDocument3 paginiManagement of Diabetic IndividualhabbouraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diabetes: EndocrinologyDocument8 paginiDiabetes: EndocrinologyZhanyar Omer Mustafa F210050Încă nu există evaluări
- Gestational Diabetes MellitusDocument11 paginiGestational Diabetes Mellitusjohn jumborock100% (1)
- Dacdac, Jeleah Grace 11 BSN 01Document3 paginiDacdac, Jeleah Grace 11 BSN 01Jeleya graceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diabetes Mellitus: Investagtion, Diagnosis & Management: DR - Vivek Reddy 1 M.D.SDocument36 paginiDiabetes Mellitus: Investagtion, Diagnosis & Management: DR - Vivek Reddy 1 M.D.SBHEEMREDDY VIVEKREDDY100% (1)
- What Is A Normal Blood Sugar LevelDocument3 paginiWhat Is A Normal Blood Sugar LevelexpertjatakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medical Abbreviation For Diabetes Mellitus With Endocrine System Abbreviation Medical Term Meaning / DefinitionDocument26 paginiMedical Abbreviation For Diabetes Mellitus With Endocrine System Abbreviation Medical Term Meaning / DefinitionCt AinnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pink Panther - Diabetes Management - Chapter 7Document16 paginiPink Panther - Diabetes Management - Chapter 7jennmoyerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gestational Diabetes MellitusDocument11 paginiGestational Diabetes Mellitusjohn jumborockÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Test: How Is It Used?Document5 paginiThe Test: How Is It Used?julia_jayronwaldoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diabetes MellitusDocument9 paginiDiabetes MellitusLorebellÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diabetes Mellitus (TYPE 1) : Risk FactorsDocument8 paginiDiabetes Mellitus (TYPE 1) : Risk FactorsLovely DaroleÎncă nu există evaluări
- I. Diagnostic Exams Used To Diagnose Diabetes Mellitus: MSN-AHN 202Document11 paginiI. Diagnostic Exams Used To Diagnose Diabetes Mellitus: MSN-AHN 202Mackie Pot PotÎncă nu există evaluări
- Signs of Insulin ResistanceDocument4 paginiSigns of Insulin ResistanceRatnaPrasadNalamÎncă nu există evaluări
- How Often Should People With Diabetes Check Their Blood Glucose?Document3 paginiHow Often Should People With Diabetes Check Their Blood Glucose?debabrata5976Încă nu există evaluări
- DiabetesDocument5 paginiDiabetesMarina RamharackÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blood Glucose TestDocument3 paginiBlood Glucose TestJed Kachel BugayongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diagnostic Exams Random Blood Glucose LevelDocument2 paginiDiagnostic Exams Random Blood Glucose LevelSheena IñigoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practical Biochemistry: Number of Experiment: (1) Name of Exp.:-Blood Glucose TestDocument6 paginiPractical Biochemistry: Number of Experiment: (1) Name of Exp.:-Blood Glucose TestHiba EmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Type 2 Diabetes MellitusDocument7 paginiType 2 Diabetes MellitusCadiz Etrama Di RaizelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abdurasad NSO HemoglucotestDocument5 paginiAbdurasad NSO HemoglucotestNader AbdurasadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Type2 Diabetes HandoutDocument1 paginăType2 Diabetes Handouthendra_darmawan_4Încă nu există evaluări
- Written ReportDocument8 paginiWritten ReportHazel Marie EchavezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Insulin AdministrationDocument8 paginiInsulin AdministrationskybluealiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blood Glucose Monitoring: Romulo D. Lopez JR, RN LPTDocument15 paginiBlood Glucose Monitoring: Romulo D. Lopez JR, RN LPTCarlojay IniegoÎncă nu există evaluări
- MUCLecture 2022 5192228Document16 paginiMUCLecture 2022 5192228Hawta AbdullaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4.is It Suitable For Diagnosing Hypoglycemia 4mDocument2 pagini4.is It Suitable For Diagnosing Hypoglycemia 4mMin KookieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Insulin Secretion and FunctionDocument8 paginiInsulin Secretion and FunctionWendy EscalanteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Definition and ClassificationDocument36 paginiDefinition and Classificationplogiojayr8340Încă nu există evaluări
- Medical Fitness Certificate EdDocument1 paginăMedical Fitness Certificate EdMuneeb Ur RehmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Treatment of Chronic Graft-Versus-Host Disease - UpToDateDocument23 paginiTreatment of Chronic Graft-Versus-Host Disease - UpToDatemihaela popescuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Thesis HypertensionDocument7 paginiNursing Thesis Hypertensioncoawokugg100% (2)
- Oph 1Document100 paginiOph 1Nishant ShresthaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Balantidium ColiDocument12 paginiBalantidium ColiSalsabila Putri AmrilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hypersexual DisorderDocument8 paginiHypersexual DisorderAndra ComanÎncă nu există evaluări
- IE-Criteria and InvestigationsDocument11 paginiIE-Criteria and InvestigationsReetobaan DattaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Apical PeriodontitisDocument30 paginiApical PeriodontitisTooba Sd100% (1)
- Module 5 HandoutsDocument2 paginiModule 5 HandoutsJulie Mher AntonioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pediatric Quick Notes FullDocument177 paginiPediatric Quick Notes Fullnorma ocanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sphenoid Sinus BarotraumaDocument4 paginiSphenoid Sinus BarotraumawitariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Complement C3Document8 paginiComplement C3Akbar RihansyahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parkinson Treatment ExercisesDocument42 paginiParkinson Treatment Exercisesn&t3000Încă nu există evaluări
- Covid-19 Mitigation PlanDocument8 paginiCovid-19 Mitigation PlanEkum EdunghuÎncă nu există evaluări
- First - Aid Common Emergencies and Safety Practices in Outdoor ActivitiesDocument14 paginiFirst - Aid Common Emergencies and Safety Practices in Outdoor ActivitiesJhon Keneth NamiasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing InterventionsDocument2 paginiNursing InterventionsJanine Paola CabangilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Management of Behavioral and Social Problem in Children... - PPT Unit VIDocument265 paginiManagement of Behavioral and Social Problem in Children... - PPT Unit VIRahul DhakerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modes of InterventationDocument27 paginiModes of InterventationGeetanjali SaggarÎncă nu există evaluări
- CATest PDFDocument1 paginăCATest PDFAsrie Sukawatie PutrieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Colon CancerDocument14 paginiColon CancerCherrymae BenzonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physiotherapy and Occupational Therapy in Patients With StrokeDocument8 paginiPhysiotherapy and Occupational Therapy in Patients With Strokeilona ilincaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Infectious Complications of Cirrhosis: Oscar S. Brann, MDDocument8 paginiInfectious Complications of Cirrhosis: Oscar S. Brann, MDandreeaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pregnancy Induced Hypertension PathophysiologyDocument2 paginiPregnancy Induced Hypertension PathophysiologyCamille Grace100% (1)
- Ebook Comprehensive Radiographic Pathology 6Th Edition Eisenberg Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument46 paginiEbook Comprehensive Radiographic Pathology 6Th Edition Eisenberg Test Bank Full Chapter PDFsinapateprear4k100% (11)
- Pediatric Dilated CardiomyopathyDocument10 paginiPediatric Dilated CardiomyopathyRiduan Adoro Lumban GaolÎncă nu există evaluări
- M E T H O D TEACHING PLAN Student: - Cassie WilliamsDocument4 paginiM E T H O D TEACHING PLAN Student: - Cassie WilliamsCassandra100% (1)
- جورنال جاهزDocument4 paginiجورنال جاهزasrd ramiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Charaka Samhita R. Vidyanath Vol 2Document49 paginiCharaka Samhita R. Vidyanath Vol 2Desi RemixxÎncă nu există evaluări