Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Cefuroxime
Încărcat de
Almira Ballesteros CestonaDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Cefuroxime
Încărcat de
Almira Ballesteros CestonaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
cefuroxime
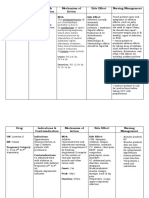
DRUG NAME Generic Name: cefuroxime
DRUG ACTION Inhibits cell wall synthesis promoting osmotic instability usually bactericidal
INDICATION/ DOSAGE Perioperative prevention 750 mg 1 tab BID
CONTRAINDICATIONS
ADVERSE EFFECTS CV: phlebitis, thrombophlebitis GI: diarrhea, anorexia, vomiting Hematologic: hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, transient neutropenia, eosinophilia
DRUG INTERACTIONS Aminoglycosides: May cause synergistic activity against some organisms.May increase nephrotoxicity. Monitor patients renal function closely.
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS Before giving dug. ask patient if she is allegic to penicillin or cephalosporin. Obtain specimen for culture and sensitivity tests before giving first dose. absorption of oral drug is induced.
Contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to drug or other cephalosporin. Use cautiously in patients hypersensitive to penicillin because of possibility of cross-sensitivity with other beta lactam antibiotics
Brand Name: Xorimix
Pharmalogical Class: 2nd generation cephalosporin
Therapeutic Class: Cephalosporin
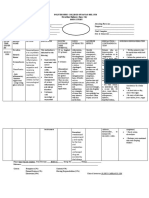
GENERIC NAME: Ranitidine BRAND NAME: Zantac
CLASSIFICATION Therapeutic: Anti-ulcer agents Pharmacologic: Histamine H2 antagonists
DOSAGE 20 mg IV q8h MECHANISM OF ACTION Inhibits the action of histamine at the H2 receptor site located primarily in gastric parietal cells, resulting in inhibition of gastric acid secretion. In addition, ranitidine bismuth citrate has some antibacterial action against H. pylori. INDICATION Treatment and prevention of heartburn, acid indigestion, and sour stomach.
CONTRA INDICATIONS Contraindicated in: Hypersensitivity, Cross-sensitivity may occur; some oral liquids contain alcohol and should be avoided in patients with known intolerance. Use Cautiously in: Renal impair- ment Geriatric patients (more susceptible to adverse CNS reactions) Pregnancy or Lactation
SIDE EFFECTS/ ADVERSE EFFECTS
CNS: Confusion, dizziness, drowsiness, hallucinations, headache CV: Arrhythmias GI: Altered taste, black tongue, constipation, dark stools, diarrhea, drug-induced hepatitis, nausea GU: Decreased sperm count, impotence ENDO: Gynecomastia HEMAT: Agranulocytosis, Aplastic Anemia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia LOCAL: Pain at IM site MISC: Hypersensitivity reactions, vasculitis NURSING IMPLICATIONS/RESPONSIBILITIES Assess patient for epigastric or abdominal pain and frank or occult blood in the stool, emesis, or gastric aspirate. Nurse should know that it may cause false-positive results for urine protein; test with sulfosalicylic acid. Inform patient that it may cause drowsiness or dizziness. Inform patient that increased fluid and fiber intake may minimize constipation. Advise patient to report onset of black, tarry stools; fever, sore throat; diarrhea; dizziness; rash; confusion; or hallucinations to health car professional promptly. Inform patient that medication may temporarily cause stools and tongue to appear gray black.
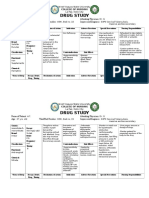
Epinephrine (adrenaline)
Brand Name: epinephrine bitartrate Pregnancy Category C Drug classes: Sympathomimetic drug, Alpha-adrenergic agonist, Beta1 and beta2-adrenergic agonist, Cardiac stimulant, Vasopressor, Bronchodilator,Antiasthmatic drug, Nasal decongestant, Mydriatic, Antiglaucoma drug
Therapeutic actions Naturally occurring neurotransmitter, the effects of which are mediated by alpha or beta receptors in target organs. Effects on alpha receptors include vasoconstriction, contraction of dilator muscles of iris. Effects on beta receptors include positive chronotropic and inotropic effects on the heart (beta1 receptors); bronchodilation, vasodilation, and uterine relaxation (beta2receptors); decreased production of aqueous humor.
Indications Intravenous: In ventricular standstill after other measures have failed to restore circulation, given by trained personnel byintracardiac puncture and intramyocardial injection; treatment and prophylaxis of cardiac arrest and attacks of transitory AV heart block with syncopal seizures (Stokes-Adams syndrome); syncope due to carotid sinus syndrome; acute hypersensitivity (anaphylactoid) reactions, serum sickness, urticaria, angioneurotic edema; in acute asthmatic attacks to relieve bronchospasm not controlled by inhalation or SC injection; relaxation of uterine musculature; additive to local anesthetic solutions for injection to prolong their duration of action and limit systemic absorption Injection: Relief from respiratory distress of bronchial asthma, chronic bronchitis, emphysema, other COPDs Aerosols and solutions for nebulization: Temporary relief from acute attacks of bronchial asthma, COPD Topical nasal solution: Temporary relief from nasal and nasopharyngeal mucosal congestion due to a cold, sinusitis, hay fever, or other upper respiratory allergies; adjunctive therapy in middle ear infections by decreasing congestion around eustachianostia
0.25%2% ophthalmic solutions: Management of open-angle (chronic simple) glaucoma, often in combination with miotics or other drugs 0.1% ophthalmic solution: Conjunctivitis, during eye surgery to control bleeding, to produce mydriasis
Contraindications Contraindicated with allergy or hypersensitivity to epinephrine or components of preparation (many of the inhalant and ophthalmic products contain sulfites: sodium bisulfite, sodium or potassiummetabisulfite; check label before using any of these products in a sulfite-sensitive patient); narrow-angle glaucoma; shock other than anaphylactic shock; hypovolemia; general anesthesia with halogenated hydrocarbons or cyclopropane; organic brain damage, cerebral arteriosclerosis; cardiac dilation and coronary insufficiency;tachyarrhythmias; ischemic heart disease; hypertension; renal dysfunction (drug may initially decrease renal blood flow); COPD patients who have developed degenerative heart disease; diabetes mellitus; hyperthyroidism; lactation.
Adverse effects Fear, anxiety, tenseness, restlessness, headache, light-headedness, dizziness, drowsiness, tremor, insomnia, hallucinations, psychological disturbances, convulsions, CNS depression, weakness, blurred vision, ocular irritation, tearing, photophobia, symptoms of paranoid schizophrenia Arrhythmias, hypertension resulting in intracranial hemorrhage, cardiovascular collapse with hypotension, palpitations, tachycardia,precordial pain in patients with ischemic heart disease Nausea, vomiting, anorexia Constriction of renal blood vessels and decreased urine formation (initialparenteral administration), dysuria, vesical sphincter spasm resulting in difficult and painful urination, urinary retention in males with prostatism Pallor, respiratory difficulty, orofacial dystonia, sweating
Headache, browache, blurred vision, photophobia, difficulty with night vision, pigmentary (adrenochrome) deposits in the cornea, conjunctiva, or lids with prolonged use Transitory stinging on initial instillation, eye pain or ache, conjunctivalhyperemia
Drug Interactions: Increased sympathomimetic effects with other TCAs (eg,imipramine) Excessive hypertension with propranolol, beta-blockers,furazolidone Decreased cardiostimulating and bronchodilating effects with beta-adrenergic blockers (eg, propranolol) Decreased vasopressor effects with chlorpromazine,phenothiazines Decreased antihypertensive effect of guanethidine, methyldopa
Nursing considerations Use extreme caution when calculating and preparing doses; epinephrine is a very potent drug; small errors in dosage can cause serious adverse effects. Double-check pediatric dosage. Use minimal doses for minimal periods of time; "epinephrine-fastness" (a form of drug tolerance) can occur with prolonged use. Protect drug solutions from light, extreme heat, and freezing; do not use pink or brown solutions. Drug solutions should be clear and colorless (does not apply to suspension for injection). Shake the suspension for injection well before withdrawing the dose. Rotate SC injection sites to prevent necrosis; monitor injection sites frequently. Maintain a rapidly acting alpha-adrenergic blocker (phentolamine) or a vasodilator (a nitrate) on standby in case of excessive hypertensive reaction.
Maintain an alpha-adrenergic blocker or facilities for intermittent positive pressure breathing on standby in case pulmonary edema occurs. Maintain a beta-adrenergic blocker (propranolol; a cardioselectivebeta-blocker, such as atenolol, should be used in patients with respiratory distress) on standby in case cardiac arrhythmias occur. Do not exceed recommended dosage of inhalation products; administer pressurized inhalation drug forms during second half of inspiration, because the airways are open wider and the aerosol distribution is more extensive. If a second inhalation is needed, administer at peak effect of previous dose, 35 min. Use topical nasal solutions only for acute states; do not use for longer than 35 days, and do not exceed recommended dosage. Rebound nasal congestion can occur after vasoconstriction subsides.
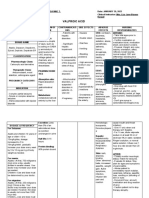
OXACILLIN Classification Penicillins Action A penicillinase resistant penicillin that inhibits cell-wall synthesis during microorganism multiplication; bacteria resists penicillins by producing penicilllinase enzymes that convert penicillins to inactivate penecillic acids. Oxacillin resists these enzymes. Indications Systemic infections caused by penicillinase-producing staphylococci Adverse reactions Common: Thrombophebitis Uncommon: Neuropathy, neuromuscular irritability, lethargy, hallucination, anxiety, confusion, agitation, depression, dizziness, fatigue, oral lesions, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, enterocolitis, interstitial nephritis, nephropathy, thrombocytopenia, hemolytic anemia, anemia, hypersensitivity reactions Nursing considerations Use cautiously in patients with other drug allergy, especially to cephalosporins. Obtain specimen for culture and sensitivity tests before first dose. To prevent vein irritation, avoid continuous infusions. Change site every 48 hours. Give 1-2 hours before or 2-3 hours after meals to prevent gastric irritation.
GENERIC NAME: prednisone
BRAND NAME: Deltasone, Orasone, Prednicen-M, Liquid Pred DRUG CLASS AND MECHANISM: Prednisone is an oral, synthetic (man-made) corticosteroid used for suppressing the immune system and inflammation. It has effects similar to other corticosteroids such as triamcinolone (Kenacort), methylprednisolone (Medrol), prednisolone(Prelone) and dexamethasone (Decadron). These synthetic corticosteroids mimic the action of cortisol (hydrocortisone), the naturally-occurring corticosteroid produced in the body by the adrenal glands. Corticosteroids have many effects on the body, but they most often are used for their potent antiinflammatory effects, particularly in those conditions in which the immune system plays an important role. Such conditions include arthritis, colitis, asthma, bronchitis, certain skin rashes, and allergic or inflammatory conditions of the nose and eyes. Prednisone is inactive in the body and, in order to be effective, first must be converted to prednisolone by enzymes in the liver. Therefore, prednisone may not work as effectively in people with liver disease whose ability to convert prednisone to prednisolone is impaired PRESCRIPTION: yes GENERIC AVAILABLE: yes PREPARATIONS: Tablets of 2.5, 5, 10, 20, and 50 mg. Oral solution or syrup of 5mg/5ml STORAGE: Store at room temperature 20-25C (68-77F), and keep away from moisture. PRESCRIBED FOR: Prednisone is used in the management of inflammatory conditions or diseases in which the immune system plays an important role. Since prednisone is used in so many conditions, only the most common or established uses are mentioned here. Prednisone most often is used for treating several types of arthritis, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease,systemic lupus, allergic reactions, asthma and severe psoriasis. It also is used for treating leukemias, lymphomas, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura and autoimmune hemolytic anemia. Corticosteroids, including prednisone, are commonly used to suppress the immune system and prevent the body from rejecting transplanted organs. Prednisone is used as replacement therapy in patients whose adrenal glands are unable to produce sufficient amounts of cortisol. DOSING: The initial dose of prednisone varies depending on the condition being treated and the age of the patient. The starting dose may be from 5 to 60 mg per day and often is adjusted based on the response of the condition being treated. Corticosteroids typically do not produce immediate effects and must be used for several days before maximal effects are seen. It may take much longer before conditions respond to treatment. Prolonged therapy with prednisone causes the adrenal glands to atrophy
and stop producing cortisol. When prednisone is discontinued after a period of prolonged therapy, the dose of prednisone must be tapered (lowered gradually) to allow the adrenal glands time to recover. (See side effects.) It is recommended that prednisone be taken with food. DRUG INTERACTIONS: Prednisone may interact with estrogens andphenytoin (Dilantin). Estrogens may reduce the action of enzymes in the liver that break down (eliminate) the active form of prednisone, prednisolone. As a result, the levels of prednisolone in the body may increase and lead to more frequent side effects. Phenytoin increases the activity of enzymes in the liver that break down (eliminate) prednisone and thereby may reduce the effectiveness of prednisone. Thus, if phenytoin is being taken, an increased dose of prednisone may be required. PREGNANCY: Corticosteroids cross the placenta into the fetus. Compared to other corticosteroids, however, prednisone is less likely to cross the placenta. Chronic use of corticosteroids during the first trimester of pregnancy may cause cleft palate.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- DSM IIDocument136 paginiDSM IIfarleyknight100% (17)
- Endocrine NCLEX PN Pract & ANS Questions IIDocument13 paginiEndocrine NCLEX PN Pract & ANS Questions IIYA HOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study-Med WardDocument2 paginiDrug Study-Med WardErnest Brian FernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- School of Health and Allied Health Sciences Nursing Department Self-Directed Learning (Nur 146 - Clinical Area)Document3 paginiSchool of Health and Allied Health Sciences Nursing Department Self-Directed Learning (Nur 146 - Clinical Area)Milagros FloritaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study - CaseDocument9 paginiDrug Study - CaseMay EvelynÎncă nu există evaluări
- JM DrugDocument3 paginiJM DrugVerdie B. NgayanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nifedipine Drug StudyDocument2 paginiNifedipine Drug StudyMary Shane MoraldeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Name Dosa Ge Mechanis Mof Action Indicatio N Contraindic Ation Adverse/Side Effects Nursing InterventionsDocument14 paginiDrug Name Dosa Ge Mechanis Mof Action Indicatio N Contraindic Ation Adverse/Side Effects Nursing InterventionsVin LandichoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study OrthoDocument4 paginiDrug Study OrthoJhessa Curie Pitagan100% (1)
- Methyldopa, Losartan K, Ascorbic AcidDocument4 paginiMethyldopa, Losartan K, Ascorbic AcidRico Mae ValenciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dinoprostone and Metronidazole Drug StudyDocument3 paginiDinoprostone and Metronidazole Drug StudyMary Shane MoraldeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tramadol Drug StudyDocument4 paginiTramadol Drug StudyJust A Nsg StudentÎncă nu există evaluări
- TergecefDocument2 paginiTergecefianecunar100% (3)
- Generic Name: Acute Aspirin ToxicityDocument1 paginăGeneric Name: Acute Aspirin ToxicityShermayne Mallapre HernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study SARAHDocument2 paginiDrug Study SARAHirene Joy DigaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug AnalysisDocument3 paginiDrug AnalysisAbby BorabienÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study Ferrous SulfateDocument2 paginiDrug Study Ferrous SulfatePauline AnesÎncă nu există evaluări
- AztreonamDocument2 paginiAztreonamHannahShaeHayesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dexamethasone Drug StudyDocument2 paginiDexamethasone Drug StudyVIDMENTON PHÎncă nu există evaluări
- MethergineDocument2 paginiMetherginebdumaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- DS (Calcium + Vit. D)Document6 paginiDS (Calcium + Vit. D)Mary April MendezÎncă nu există evaluări
- MefenamicDocument1 paginăMefenamicChristian Clyde N. ApigoÎncă nu există evaluări
- TrimetazidineDocument2 paginiTrimetazidinemasheennavirgoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Altretamine: Drug DosageDocument16 paginiAltretamine: Drug DosagePrincess CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Duphaston PDFDocument4 paginiDuphaston PDFmarcusjanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Obat ObgynDocument8 paginiObat ObgynMuhammad Naqiuddin JalaluddinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Senokot-S (Senna Concentrate 8.6mg + Docusate Sodium 50mg)Document2 paginiSenokot-S (Senna Concentrate 8.6mg + Docusate Sodium 50mg)E100% (1)
- Manangan, Eugene B. - FDAR Boggy UterusDocument2 paginiManangan, Eugene B. - FDAR Boggy UterusGin MananganÎncă nu există evaluări
- KetorolacDocument5 paginiKetorolacMichelle Ann P. NacuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- BETAXOLOLDocument2 paginiBETAXOLOLjulieÎncă nu există evaluări
- SilgramDocument6 paginiSilgramJacqueline SweetÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Drug Study On MISOPROSTOLDocument6 paginiA Drug Study On MISOPROSTOLAlexandrea MayÎncă nu există evaluări
- P 398Document1 paginăP 398Arup Ratan PaulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study - CefradoxilDocument13 paginiDrug Study - CefradoxilJohara G'naid0% (1)
- Sal But AmolDocument2 paginiSal But AmolKay MirandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Urinalysis: Exam Normal Value Actual Value Interpretation Significance Nursing InterventionDocument9 paginiUrinalysis: Exam Normal Value Actual Value Interpretation Significance Nursing InterventionChaN.deDiosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study Omeprazole CompressDocument2 paginiDrug Study Omeprazole CompressAngelica TolledoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study FDocument3 paginiDrug Study FFatima Love Ariate-ArcasetasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument13 paginiDrug StudyAldrin Ian Oraza AlpeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Emergency Room Drug ListDocument28 paginiEmergency Room Drug Listiscariot02Încă nu există evaluări
- Cefoxitin Drug StudyDocument1 paginăCefoxitin Drug StudyArthur Christopher CorpuzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tetracycline Drug StudyDocument5 paginiTetracycline Drug StudyEmagra AzilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study - Magnesium SulfateDocument6 paginiDrug Study - Magnesium SulfatePrincess Alane MorenoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Name of The DrugDocument2 paginiName of The DrugSistine Rose LabajoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Seizure NCPDocument2 paginiSeizure NCPChristine Dela CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study: (Celecoxib)Document11 paginiDrug Study: (Celecoxib)Princess Brigitte R. PATE�AÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mucosta: Tablets 100mgDocument4 paginiMucosta: Tablets 100mgInukaicchi TakumichiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sas 11 Nur 145 - Wps OfficeDocument2 paginiSas 11 Nur 145 - Wps Officerica sebabillonesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ferrous Sulfate - Drug StudyDocument3 paginiFerrous Sulfate - Drug StudyElla Musk100% (1)
- AmbroxolDocument1 paginăAmbroxolPrecious CarmelaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kremil S Drug StudyDocument1 paginăKremil S Drug StudyDivine LavaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study Ceftriaxone SodiumDocument3 paginiDrug Study Ceftriaxone SodiumPrincess Queenie OlarteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument21 paginiDrug StudyShyla Garnace JavillonarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument4 paginiDrug StudyLene ThereseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vitamin KDocument2 paginiVitamin KMuvs RazonÎncă nu există evaluări
- DP Discharge Plan@@@@@@@@Document6 paginiDP Discharge Plan@@@@@@@@Maemae SumalinogÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inbumin PDFDocument12 paginiInbumin PDFresa dianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dinoprostone GelDocument7 paginiDinoprostone GelSahil AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument2 paginiDrug StudyemmanuelmyagokayeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stugeron® TabletsDocument3 paginiStugeron® TabletsmahgadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Name of Drug Mechanism of Action Indications Contra-Indications Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument10 paginiName of Drug Mechanism of Action Indications Contra-Indications Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsmidskiescreamzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Suppurative Parotitis: Related SummariesDocument7 paginiAcute Suppurative Parotitis: Related SummariesFarida Dwi IrnawatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Normal Digestion / Absorption of FatDocument5 paginiNormal Digestion / Absorption of FatMarc Michael Dela CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Immunology and Immunochemistry PDFDocument8 paginiImmunology and Immunochemistry PDFboatcomÎncă nu există evaluări
- Option Com - Content&view Section&layout Blog&id 3 &itemid 60 FaqsDocument7 paginiOption Com - Content&view Section&layout Blog&id 3 &itemid 60 FaqsJig GamoloÎncă nu există evaluări
- ConjunctivitisDocument9 paginiConjunctivitisSaranya DeviÎncă nu există evaluări
- RosuvastatinDocument1 paginăRosuvastatinJoshua KellyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Appendix: Flow Charts and Treatment TablesDocument20 paginiAppendix: Flow Charts and Treatment TablesLeon LellaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PONR - Comprehensive Nursing Health History and Physical ExaminationDocument21 paginiPONR - Comprehensive Nursing Health History and Physical ExaminationDRJC100% (1)
- Anaemia in Pregnancy: Klinik Kesihatan Ibu Dan Anak Parit BuntarDocument10 paginiAnaemia in Pregnancy: Klinik Kesihatan Ibu Dan Anak Parit Buntarannurshah05Încă nu există evaluări
- ICD-10 TK Pedsos 2013Document10 paginiICD-10 TK Pedsos 2013Ludi Dhyani RahmartaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Depression and Diabetes Slides ENGDocument20 paginiDepression and Diabetes Slides ENGMaria Magdalena Dumitru100% (1)
- Full-Sentence Speech FinalDocument2 paginiFull-Sentence Speech Finalapi-363883917Încă nu există evaluări
- Life Is A Continous Process of AdjustmentDocument78 paginiLife Is A Continous Process of AdjustmentGulmoharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 7 Psychological DisorderDocument36 paginiUnit 7 Psychological DisorderAbel TayeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Personal Health Issues and ConcernDocument41 paginiPersonal Health Issues and Concernniña pinedaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brucellosis Brucellosis: Brucella Spp. Brucella SPPDocument24 paginiBrucellosis Brucellosis: Brucella Spp. Brucella SPPhussain AltaherÎncă nu există evaluări
- ICMR GuidelinesType2diabetes2018 0Document82 paginiICMR GuidelinesType2diabetes2018 0VISHWANATH MARSHIVANIKARÎncă nu există evaluări
- Valproic Acid DsDocument2 paginiValproic Acid DsCarissa Mae Tapec EstradaÎncă nu există evaluări
- DefibrillationDocument9 paginiDefibrillationJara Maris Moreno BudionganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture Schedule-3rd Year-Sem I-2023 & 2024Document2 paginiLecture Schedule-3rd Year-Sem I-2023 & 2024Jonathan AustinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Consensus Based Guidelines For The Recognition,.15Document13 paginiConsensus Based Guidelines For The Recognition,.15ms98alissaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adhd InfographicDocument1 paginăAdhd Infographicapi-666361680Încă nu există evaluări
- Digital Covid Questionnaire For Revival Approval FormatDocument2 paginiDigital Covid Questionnaire For Revival Approval Formatsouravdey3Încă nu există evaluări
- Celiac DiseaseDocument15 paginiCeliac DiseaseMarty AsisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Magic Surgery NotesDocument54 paginiMagic Surgery NotesChimwemwe TemboÎncă nu există evaluări
- Answers Mock Exam 1Document8 paginiAnswers Mock Exam 1Amin AzadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale Exchange: Prioritized Nursing Problem For Choanal AtresiaDocument9 paginiNursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale Exchange: Prioritized Nursing Problem For Choanal AtresiaJinaan MahmudÎncă nu există evaluări
- Patho AsthmaDocument1 paginăPatho AsthmaAyel JimenezÎncă nu există evaluări