Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
MG HL Syllabus
Încărcat de
이의선Descriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
MG HL Syllabus
Încărcat de
이의선Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
3.
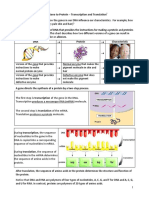
3 DNA structure
3.3.1 Outline DNA nucleotide structure in terms of sugar (deoxyribose), base and phosphate [2] 3.3.2 State the names of the four bases in DNA [1] 3.3.3 Outline how DNA nucleotides are linked together by covalent bonds into a single strand. [2] 3.3.4 Explain how a DNA double helix is formed using complementary base pairing and hydrogen bonds. [3] 3.3.5 Draw and label a simple diagram of the molecular structure of DNA [1]
3.4 DNA replication
3.4.1 Explain DNA replication in terms of unwinding the double helix and separation of the strands by helicase, followed by formation of the new complementary strands by DNA polymerase. [3] 3.4.2 Explain the significance of complementary base pairing in the conservation of the base sequence of DNA [3] 3.4.3 State that DNA replication is semi- conservative [1]
3.5 Transcription and translation
3.5.1 Compare the structure of RNA and DNA. [3] 3.5.2 Outline DNA transcription in terms of the formation of an RNA strand complementary to the DNA strand by RNA polymerase [2] 3.5.3 Describe the genetic code in terms of codons composed of triplets of bases. [2] 3.5.4 Explain the process of translation, leading to polypeptide formation. [3] 3.5.5 Discuss the relationship between one gene and one polypeptide. [3]
10.
Outline the production of a dipeptide by a condensation reaction. Include the structure of a generalized dipeptide in your answer. (Total 5 marks)
carboxyl / COOH group of one amino acid reacts with amine / NH2 group of another; water / H2O is eliminated; These steps can be shown diagrammatically peptide / covalent bond is produced; diagram of dipeptide, with peptide bond shown [2 max];
11.
Explain the process of translation.
(Total 9 marks)
consists of initiation, elongation and termination; mRNA translated in a 5' to 3' direction; binding of ribosome to mRNA; small sub-unit then large; first / initiator tRNA binds to start codon / to small subunit of ribosome; AUG is the start codon; second tRNA binds to ribosome; large subunit moves down mRNA after a second tRNA binds; amino acid / polypeptide on first tRNA is transferred / bonded to amino acid on second tRNA; peptide bonds between amino acids / peptidyl transferase; requires GTP; movement of ribosome / small subunit of ribosome down the mRNA; loss of tRNA and new tRNA binds; reach a stop codon / termination; polypeptide released; tRNA activating enzymes link correct amino acid to each tRNA; (activated) tRNA has an anticodon and the corresponding amino acid attached;
28. The structure of the DNA double helix was described by Watson and Crick in 1953. Explain the structure of the DNA double helix, including its subunits and the way in which they are bonded together. (Total 8 marks) subunits are nucleotides; one base, one deoxyribose and one phosphate in each nucleotide; description / diagram showing base linked to deoxyribose C1 and phosphate to C5; four different bases adenine, cytosine, guanine and thymine; nucleotides linked up with sugar-phosphate bonds; covalent / phosphodiester bonds; two strands (of nucleotides) linked together; base to base; A to T and G to C; hydrogen bonds between bases; antiparallel strands; double helix drawn or described; Accept any of the points above if clearly explained in a diagram. 29. Compare DNA transcription with translation.
(Total 4 marks)
both in 5' to 3' direction; both require ATP; DNA is transcribed and mRNA is translated; transcription produces RNA and translation produces polypeptides/protein; RNA polymerase for transcription and ribosomes for translation / ribosomes in translation only; transcription in the nucleus (of eukaryotes) and translation in the cytoplasm/at ER; tRNA needed for translation but not transcription;
30.
Outline the process of DNA profiling (genetic fingerprinting),
Including ways in which it can be used.
(Total 6 marks)
sample of DNA obtained / leucocytes / from mouthwash / hair / other named source; satellite DNA/repetitive sequences used for profiling; amplification of DNA by polymerase chain reaction / PCR; cutting DNA into fragments using restriction enzymes; separation of fragments of DNA (by electrophoresis); separation according to the length of the fragments; pattern of bands obtained / different pattern of bands with DNA from different individuals; used for criminal investigations / example of use in criminal investigation; used to check paternity / who is the father / mother / parent; used to check whether two organisms are clones; (Plus up to [2] for quality)
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- 12 Chem CH 10 MCQSDocument12 pagini12 Chem CH 10 MCQSSaran.kÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genescan™ Installation Standard Ds-33 6-Fam™, Vic, Ned™, Pet™ DyesDocument3 paginiGenescan™ Installation Standard Ds-33 6-Fam™, Vic, Ned™, Pet™ DyesbookmoonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Proteomics Final Exam 2014Document5 paginiProteomics Final Exam 2014AhmedSherifEdrisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Agarose Gel Electrophoresis: Genetics and Molecular Biology 3 Stage MLT DepartmentDocument26 paginiAgarose Gel Electrophoresis: Genetics and Molecular Biology 3 Stage MLT Departmentxelat bÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Prime Editing Compared With Wild Type CRISPRDocument3 paginiAdvantages and Disadvantages of Prime Editing Compared With Wild Type CRISPRCarlos Julio Nova LopezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nucleic Acids Rna World Biotech ProjectDocument18 paginiNucleic Acids Rna World Biotech ProjectSakshi SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transcription and Translation Worksheet 2Document2 paginiTranscription and Translation Worksheet 2n1n2n3n50% (2)
- Protein Synthesis Paper Lab InstructionsDocument11 paginiProtein Synthesis Paper Lab Instructionsapi-292473508Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter16 The CytoskeletonDocument83 paginiChapter16 The CytoskeletonRonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activity 19.1 Marking Scheme: Investigating The Primary Structure of RibonucleaseDocument3 paginiActivity 19.1 Marking Scheme: Investigating The Primary Structure of RibonucleaseMikeÎncă nu există evaluări
- AlphaDocument28 paginiAlphanandugulluÎncă nu există evaluări
- Platelet Function - Assessment, Diagnosis, and TreatmentDocument400 paginiPlatelet Function - Assessment, Diagnosis, and TreatmentethainkeroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Molecular Biology of The Cell 5th Edition Alberts Test BankDocument13 paginiMolecular Biology of The Cell 5th Edition Alberts Test Bankodettedieupmx23m100% (31)
- Molecular Biology of BacteriaDocument93 paginiMolecular Biology of BacteriaCamsy Wang100% (1)
- ETC Part Three Illustration AtfDocument1 paginăETC Part Three Illustration Atfpnsscsny29Încă nu există evaluări
- Amino Acids and ProteinsDocument9 paginiAmino Acids and ProteinsLeiÎncă nu există evaluări
- II. Cot AnalysisDocument32 paginiII. Cot AnalysisSuraj BhattaraiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oxford University Press - Online Resource Centre - Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument5 paginiOxford University Press - Online Resource Centre - Multiple Choice QuestionsHUAWEI HUAWEI50% (2)
- 2) Es Struttura ProteineDocument5 pagini2) Es Struttura ProteineAlbertoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alex - S Protein Folding For SCIENCE EPQ StuffDocument3 paginiAlex - S Protein Folding For SCIENCE EPQ StuffFunkymaleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 2 Dna Structure and Dna ExtractionDocument8 paginiLesson 2 Dna Structure and Dna ExtractionGreatel Elijah TorregosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fundamentals of Enzymology The Cell and Molecular Biology of Catalytic ProteinsDocument0 paginiFundamentals of Enzymology The Cell and Molecular Biology of Catalytic Proteinsmonica_elizabeth_35Încă nu există evaluări
- F - Gateway Cloning TechnologyDocument17 paginiF - Gateway Cloning TechnologyCarlos Alfredo Carmona GascaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biol 308 - Study QuestionsDocument47 paginiBiol 308 - Study QuestionsDivya100% (1)
- Nucleic Acid MetabolismDocument23 paginiNucleic Acid MetabolismMSc Biotech/MicroÎncă nu există evaluări
- LigationDocument5 paginiLigationHanumant SuryawanshiÎncă nu există evaluări
- DNA RNA and Protein Synthesis WS PPTDocument8 paginiDNA RNA and Protein Synthesis WS PPTAll about derreonnnÎncă nu există evaluări
- An acidic, thermostable exochitinase with β - N - acetylglucosaminidase activity from Paenibacillus barengoltzii converting chitin to N - acetyl glucosamineDocument11 paginiAn acidic, thermostable exochitinase with β - N - acetylglucosaminidase activity from Paenibacillus barengoltzii converting chitin to N - acetyl glucosamineAlonsoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hif2 PDFDocument12 paginiHif2 PDFArkipus PamuttuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quadruplex Nucleic Acids by Jonathon B Chairs and David GravesDocument285 paginiQuadruplex Nucleic Acids by Jonathon B Chairs and David Gravesm__rubelÎncă nu există evaluări