Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Chest Pain Algorithm
Încărcat de
ascensiuneaininfernDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Chest Pain Algorithm
Încărcat de
ascensiuneaininfernDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
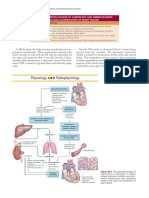
1 Chest discomfort suggestive of ischemia 2
EMS assessment and care and hospital preparation: Monitor, support ABCs. Be prepared to provide CPR and defibrillation Administer oxygen, Aspirin, Nitroglycerin, and Morphine if needed If available, obtain 12-lead ECG; if ST-elevation: - Notify receiving hospital with transmission or interpretation - Begin fibrinolytic checklist Notified hospital should mobilize hospital resources to respond to STEMI
2005 ECC Guidelines
3
Immediate ED assessment (<10 min) Check vital signs; evaluate oxygen saturation Establish IV access Obtain/review 12-lead ECG Perform brief, targeted history, physical exam Review/complete fibrinolytic checklist; check contraindications Obtain initial cardiac marker levels, initial electrolyte and coagulation studies Obtain portable chest x-ray (<30 min) Immediate ED general treatment Start oxygen at 4 L/min; maintain 02 sat >90% Aspirin 160 to 325 mg (if not given by EMS) Nitroglycerin sublingual, spray, or IV Morphine IV if pain not relieved by nitroglycerin
4
Review initial 12-lead ECG
5
ST elevation or new or presumably new LBBB; strongly suspicious for injury ST-Elevation MI (STEMI)
9
ST depression or dynamic T-wave inversion; strongly suspicious for ischemia High-Risk Unstable Angina/ Non-ST-Elevation MI (UA/NSTEMI)
13
Normal or nondiagnostic changes in ST segment or T wave Intermediate/Low Risk UA
6
Start adjunctive treatments as Indicated (see text for contraindications) Do not delay reperfusion -Adrenergic receptor blockers Clopidogrel Heparin (UFH or LMWH)
10
Start adjunctive treatments as Indicated (see text for contraindications) Nitroglycerin -Adrenergic receptor blockers Clopidogrel Heparin (UFH or LMWH) Glycoprotein llb/llla inhibitor
14 Yes
Develops high or intermediate risk criteria OR Troponin-positive?
15
No
7
Time from onset of symptoms <12 hours >12 hours
11
Admit to monitored bed Assess risk status
<12 hours
12
High-risk patient Refractory ischemic chest pain Recurrent/persistent ST deviation Ventricular Tachycardia Hemodynamic instability Signs of pump failure Early invasive strategy, including catheterization and revascularization for shock within 48 hours of an AMI Continue ASA, Heparin, and other therapies as indicated. ACE inhibitor/ARB HMG CoA reductase inhibitor (statin therapy) Not at high risk; cardiology to risk-stratify
Reperfusion strategy: Therapy defined by patient and center criteria Be aware of reperfusion goals - Door-to-balloon inflation (PCI) goal of 90 min - Door-to-needle (fibrinolysis) goal of 30 min Continue adjunctive therapies and: - ACE inhibitors/angiostensin receptor blocker (ARB) within 24 hours of symptom onset - HMG CoA reductase inhibitor (statin therapy)
Consider admission to ED chest pain unit or to monitored bed in ED Follow: Serial cardiac markers (including Troponin) Repeat ECG/continuous ST segment monitoring Consider stress test
16 Yes
Develops high or intermediate risk criteria OR Troponin-positive?
17
No
If no evidence of ischemia or infarction, can discharge with follow-up
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- Egg2Document432 paginiEgg2Marc TarcuÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- QC CardiologistDocument10 paginiQC CardiologistJefferson VelonzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test Bank ECGs Made Easy 5th Edition Barbara J AehlertDocument10 paginiTest Bank ECGs Made Easy 5th Edition Barbara J AehlertErnest67% (3)
- Brunner and Suddarth's Textbook of Medical-Surgical Nursing 12th Ed. (Dragged) 4Document1 paginăBrunner and Suddarth's Textbook of Medical-Surgical Nursing 12th Ed. (Dragged) 4jamie carpioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dysrhythmia Advance Content Outline A1 - 2020.1.2Document3 paginiDysrhythmia Advance Content Outline A1 - 2020.1.2Kimberly Whiteside50% (2)
- Physicians Directory PDFDocument126 paginiPhysicians Directory PDFThebestearldom0% (1)
- Congenital Heart Diseases: Non Cyanotic PlethoraDocument43 paginiCongenital Heart Diseases: Non Cyanotic PlethoraFauzi SatriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transesophageal EchocardiogramDocument3 paginiTransesophageal EchocardiogramsiddharthaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Facts About Sudden Cardiac ArrestDocument2 paginiFacts About Sudden Cardiac ArrestZeljko LekovicÎncă nu există evaluări
- VT Origin PDFDocument60 paginiVT Origin PDFNikita PratamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiology Curriculum LatestDocument31 paginiCardiology Curriculum LatestKrishÎncă nu există evaluări
- Common Valvular Heart Disease (At A Glance)Document1 paginăCommon Valvular Heart Disease (At A Glance)Tamim IshtiaqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- CCU AuditDocument75 paginiCCU AuditNica Reyes-Sindiong0% (1)
- Adobe Scan 07 Jul 2023Document15 paginiAdobe Scan 07 Jul 2023same.daweÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rate and RhythmDocument10 paginiRate and RhythmSamanta Luiza de AraujoÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECSI CAAlgorithm PDFDocument2 paginiECSI CAAlgorithm PDFCarlos ChiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heart Failure and Ejection FractionDocument1 paginăHeart Failure and Ejection FractionCecil-An DalanonÎncă nu există evaluări
- WP202208-HeartAssistTM For AdultDocument20 paginiWP202208-HeartAssistTM For AdultAlan BiÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Role of BB in Hypertensive Patients With SODocument12 paginiThe Role of BB in Hypertensive Patients With SOjimÎncă nu există evaluări
- 55-Article Text-102-1-10-20180320Document9 pagini55-Article Text-102-1-10-20180320Widya SafitriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aortic Root Dilatation As The Sole Cause of Atrial FibrillationDocument2 paginiAortic Root Dilatation As The Sole Cause of Atrial FibrillationNathania HoswandiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wolf's Down and Dirty Lists: News Journals Conferences Opinion Articles ForumsDocument2 paginiWolf's Down and Dirty Lists: News Journals Conferences Opinion Articles ForumsMohamed IbrahimÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9 CsaDocument34 pagini9 Csaمحمد بن الصادقÎncă nu există evaluări
- Surgery or General Medicine - A Study of The Reasons Underlying The Choice of Medical SpecialtyDocument6 paginiSurgery or General Medicine - A Study of The Reasons Underlying The Choice of Medical SpecialtyCarol BusseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Echocardiogram MayoDocument4 paginiEchocardiogram MayoMarta KitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Schedule D: List of Life Saveing or Life Sustaining Medical DevicesDocument5 paginiSchedule D: List of Life Saveing or Life Sustaining Medical DevicesAasma RehmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- BMJ 2022 074216.fullDocument20 paginiBMJ 2022 074216.fullArmando OrtegaÎncă nu există evaluări
- A. FlutterDocument8 paginiA. FlutterAdam ChungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pre-Excitation Syndromes in Children: Dr.K.MaheshDocument105 paginiPre-Excitation Syndromes in Children: Dr.K.MaheshNischal ShahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amedex 2023 - PagenoDocument1.943 paginiAmedex 2023 - PagenosajihanÎncă nu există evaluări