Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
K Chiteka Tutorials: Department of Industrial and Manufacturing Engineering
Încărcat de
KUDZANAYITitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
K Chiteka Tutorials: Department of Industrial and Manufacturing Engineering
Încărcat de
KUDZANAYIDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
K Chiteka Tutorials
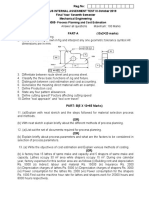
1. Outline, giving relevant examples, the characteristics of each of the following manufacturing generics; [explain in terms of; volume, machinery and investment, manpower, scheduling & routing, products] i) Project [5] ii) Jobbing [5] iii) Batch [5] iv) Line [5] v) Continuous [5]
2. Explain the business implications of the process choice ASPECTS Product type Product range Order size New prod. Intro. Process technology Process flexibility Volumes Investment R/Material inventory F/ Goods Inventory PROJECT JOBBING BATCH LINE CONTINUOUS
[15]
3. (a) Giving examples, briefly explain the Hybrid process (b) Describe the following batch related hybrids; i. ii. NC Machining centre
[5]
[5] [5]
Page 1
Department of Industrial and Manufacturing Engineering
iii. iv. v.
FMS GT Transfer lines
[5] [5] [5]
4. a) Outline the objectives of a good plant layout 1. Briefly explain the following layouts; i. Process layout ii. Product layout iii. Cellular layout iv. Fixed position layout v. Hybrid layout
[5] [5] [5] [5] [5] [5]
5.
The following data relates to an automotive repair shop. You are required to come up with an optimal plant layout that minimizes operational costs. Also fit-in the departments in a flow space of 5550m2.
The departments are as follows; A B C D E F G Receiving bay Workshop supervisor Materials store room Panel beating bay Spray booth Quality control Dispatch
Space Allocation Area Department (m2) A 1000
Department of Industrial and Manufacturing Engineering Page 2
B C D E F G
50 900 2000 400 200 1000
FROM-TO CHART A A B C D E F G B 100 C 500 D 50 400 E 50 900 1000 1000 1000 F G
[20]
6. It has been ascertained that the ideal cycle time, Tc of a particular product is 1.1 minutes. Breakdowns occur at a frequency, F = 0.13 per cycle. The average downtime per line stop is 4.3 minutes (Td =4.3 minutes). The scrape rate is 4.31%. The initial cost of the component is $.93 and it costs $53 per hour to operate the transfer line. Cutting tools cost 13c per work-part. a) Find; i. The production rate [1] ii. The number of hours required to meet a demand of 2351 units per week [1] iii. Line efficiency [1] iv. Cost per unit produced [2]
b) A nine-station transfer line has .03 as the probability that a workstation will breakdown. Determine; i. The frequency of line stops per cycle using the upper bound & lower bound approach. [2] ii. The production rate [3]
Department of Industrial and Manufacturing Engineering Page 3
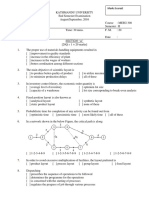
7. Below is a from-to chart showing the relative movemwnts between departments. The initial arrangement of departments is 1-2-3. To dept 1 1 2 3
from dept
2 10
3 5 20
Use the pair-wise exchange method to determine the optimal solution.
[10]
8. Table Q6.1 below provides the data relating to work elements, individual cycle times, and precedence constraints.
Work element 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Tej 0.15 0.21 0.72 0.13 0.3 0.11 0.63 0.51 0.33 0.31
Preceded by 1 2 3 3 3,4 5,6 5 7,8 9
Assuming a cycle time of .89 minutes, determine the minimum number of workstations required. i. ii. Using the Largest candidate rule Using the Ranked Positional weight method
Department of Industrial and Manufacturing Engineering Page 4
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Production and Maintenance Optimization Problems: Logistic Constraints and Leasing Warranty ServicesDe la EverandProduction and Maintenance Optimization Problems: Logistic Constraints and Leasing Warranty ServicesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Production Automation Paper Final Term Fall 2014Document2 paginiProduction Automation Paper Final Term Fall 2014Shaukat Ali ShahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Operation Management and Information SystemDocument32 paginiOperation Management and Information SystemaanandlÎncă nu există evaluări
- 15P701Document4 pagini15P701rajakrishnanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced ManufacturingDocument5 paginiAdvanced Manufacturingmukesh3021Încă nu există evaluări
- End Term Examination: Fifth Semester (Mca) December-2009Document4 paginiEnd Term Examination: Fifth Semester (Mca) December-2009Pratiksha TiwariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Layout: Critical Thinking ExercisesDocument9 paginiLayout: Critical Thinking ExercisesJennysanÎncă nu există evaluări
- MBA22 - Production & Operations ManagementDocument2 paginiMBA22 - Production & Operations ManagementNayan KanthÎncă nu există evaluări
- MENG448 MDTRM1 Spring 16 SolutionDocument4 paginiMENG448 MDTRM1 Spring 16 SolutionSara AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paper-9 Dec-12 ICWAI Group 1 InterDocument20 paginiPaper-9 Dec-12 ICWAI Group 1 InterVelayudham ThiyagarajanÎncă nu există evaluări
- B.E. (Mech. S/W) (2003 Course) (402065) : Production Management (Elective - Iii)Document82 paginiB.E. (Mech. S/W) (2003 Course) (402065) : Production Management (Elective - Iii)Rameez BedekarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2014 MFE2201 Advanced Manufacturing SystemsDocument5 pagini2014 MFE2201 Advanced Manufacturing SystemsBernice JohnsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guidelines-Facility Industrial DesignDocument3 paginiGuidelines-Facility Industrial Designkhanh123ctmÎncă nu există evaluări
- Time: 3 Hours Answer All Questions Maximum: 100 MarksDocument3 paginiTime: 3 Hours Answer All Questions Maximum: 100 MarksAnonymous ZB6qyhD6Încă nu există evaluări
- Sample Mid Term ExamDocument12 paginiSample Mid Term ExamDevanshi ShahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Model Test Paper - 1 CMA Inter Group-II Paper - 9 Operations Management & Strategic Management Section - A (Operations Management) 1Document17 paginiModel Test Paper - 1 CMA Inter Group-II Paper - 9 Operations Management & Strategic Management Section - A (Operations Management) 1Rajesh ShuklaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Emt 2512 Manufacturing Process PlanningDocument4 paginiEmt 2512 Manufacturing Process PlanningAlvin KiruiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test Series: 1 Manufacturing System Design (MEL 361) Time: 50 Min Max. Marks: 20Document2 paginiTest Series: 1 Manufacturing System Design (MEL 361) Time: 50 Min Max. Marks: 20Soubhav ChamanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Question 1Document5 paginiQuestion 1Ramesh ShresthaÎncă nu există evaluări
- B eDocument651 paginiB eRohit GaikwadÎncă nu există evaluări
- P-9 Operation Management and Information SystemDE211Document20 paginiP-9 Operation Management and Information SystemDE211sam_kale007Încă nu există evaluări
- Quan 2204Document6 paginiQuan 2204Sanjay VaryaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Code - No: 07A6EC04Document4 paginiCode - No: 07A6EC04ideepujÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessment 2Document7 paginiAssessment 2achumakotishiniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iem 102Document4 paginiIem 102Aparna DuggiralaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ASSIGNMENT #2 Manual Assembly Lines: KNP 4073: Advanced Manufacturing SystemDocument1 paginăASSIGNMENT #2 Manual Assembly Lines: KNP 4073: Advanced Manufacturing SystemKevin VinodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Universiti Teknologi Mara Final Examination: Confidential EM/APR 2010/MEM575/KJP585/450Document8 paginiUniversiti Teknologi Mara Final Examination: Confidential EM/APR 2010/MEM575/KJP585/450Pierce EpoiÎncă nu există evaluări
- B.E. (2003 Patt.)Document517 paginiB.E. (2003 Patt.)Aniket SankpalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Automation in ManufacturingDocument8 paginiAutomation in ManufacturingPradeepkumarKatgiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Assessment Test (FAT) - May 2017: Course: - Class NBR(S) : Slot: Time: Three Hours Max. Marks: 100Document4 paginiFinal Assessment Test (FAT) - May 2017: Course: - Class NBR(S) : Slot: Time: Three Hours Max. Marks: 100ak164746Încă nu există evaluări
- Seventh Semester B.Tech. Degree Examination, June 2009 03.705 Elective - V: OPERATIONS RESEARCH (H) (2003 Admission)Document6 paginiSeventh Semester B.Tech. Degree Examination, June 2009 03.705 Elective - V: OPERATIONS RESEARCH (H) (2003 Admission)loopycrowÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 3 & 5 Product Design For Manufacture & AssemblyDocument15 paginiCH 3 & 5 Product Design For Manufacture & Assemblywellwisher01Încă nu există evaluări
- Afin317 FPD 1 2020 1Document8 paginiAfin317 FPD 1 2020 1Daniel Daka100% (1)
- 15P701Document3 pagini15P701rajakrishnanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assembly Line BalancingDocument13 paginiAssembly Line BalancingAnurag SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- BTME 2nd Year AssignmentDocument15 paginiBTME 2nd Year AssignmentshishunalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Facilities LayoutDocument116 paginiFacilities Layoutishan1880% (1)
- Course Code: MET 406 Gths/Rs - 19 / 7659 Eighth Semester B. E. (Mechanical Engineering) ExaminationDocument3 paginiCourse Code: MET 406 Gths/Rs - 19 / 7659 Eighth Semester B. E. (Mechanical Engineering) ExaminationMubarika SabirÎncă nu există evaluări
- De Thi QT 1 Sang Thứ 7Document2 paginiDe Thi QT 1 Sang Thứ 7Kim Can NguyễnÎncă nu există evaluări
- AFIN317 2015 Semester 2 Final ExamDocument9 paginiAFIN317 2015 Semester 2 Final ExamSandra K JereÎncă nu există evaluări
- 20180204-Test01 (Chap01 Automats in Chap02) - With AnswersDocument10 pagini20180204-Test01 (Chap01 Automats in Chap02) - With AnswersdeepakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dba 1651 Sem IIDocument11 paginiDba 1651 Sem IIthamiztÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ford Capacity Analysis ReportDocument7 paginiFord Capacity Analysis Reportss2mrattriÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.2.3 Building Material Selection: Example 2.5Document51 pagini2.2.3 Building Material Selection: Example 2.5raandkadeewanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 10 Machining Economics: StructureDocument22 paginiUnit 10 Machining Economics: StructureTapas BanerjeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Minggu III-IV PTLFDocument53 paginiMinggu III-IV PTLF1C - FAWAIQOTUL HIMMAÎncă nu există evaluări
- TIE6111201508 Design, Analysis and Control of Manufacturing SystemsDocument5 paginiTIE6111201508 Design, Analysis and Control of Manufacturing Systemstafara mundereÎncă nu există evaluări
- SRM Institute of Science and Technology: Ramapuram CampusDocument4 paginiSRM Institute of Science and Technology: Ramapuram CampusManikandan NÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optimization of CNC MachiningDocument3 paginiOptimization of CNC MachiningVIVA-TECH IJRIÎncă nu există evaluări
- PPC Model QPDocument2 paginiPPC Model QPS Deva PrasadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment No - 1: Department of Mechanical Engineering, J.S.S.A.T.E, BangaloreDocument9 paginiAssignment No - 1: Department of Mechanical Engineering, J.S.S.A.T.E, BangalorejtsrinivasdownÎncă nu există evaluări
- PRODUCTION PLANNING AND CONTROL May 2017Document7 paginiPRODUCTION PLANNING AND CONTROL May 2017srinivasÎncă nu există evaluări
- M.B.A (2019 Pattern) (1) (2) - 36-37Document2 paginiM.B.A (2019 Pattern) (1) (2) - 36-37Sandeep ChaudharyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Course Code: INT 207 Itsj/Rw - 17 / 1325 Fourth Semester B. E. (Industrial Engineering) ExaminationDocument3 paginiCourse Code: INT 207 Itsj/Rw - 17 / 1325 Fourth Semester B. E. (Industrial Engineering) ExaminationMithileshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cpim Eco QuestionDocument21 paginiCpim Eco QuestionEwa WasilukÎncă nu există evaluări
- SCM-210 Assignment 2 Student VersionDocument5 paginiSCM-210 Assignment 2 Student VersionEvelyn PattÎncă nu există evaluări
- FinalDocument26 paginiFinalRitesh KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Energy Efficient Manufacturing: Theory and ApplicationsDe la EverandEnergy Efficient Manufacturing: Theory and ApplicationsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Friction Stir Welding of Steels AReview Paper PDFDocument5 paginiFriction Stir Welding of Steels AReview Paper PDFKUDZANAYIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Friction Stir Welding of Steels AReview Paper PDFDocument5 paginiFriction Stir Welding of Steels AReview Paper PDFKUDZANAYIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Friction Stir WeldingDocument13 paginiFriction Stir WeldingKUDZANAYIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrochemical Machining, Advanced Machining Processes, Non Traditional Manufacturing Processes, Precision Manufacturing, Manufacturing ProcessesDocument23 paginiElectrochemical Machining, Advanced Machining Processes, Non Traditional Manufacturing Processes, Precision Manufacturing, Manufacturing ProcessesKUDZANAYI100% (1)
- Mechanics of GrindingDocument19 paginiMechanics of GrindingKUDZANAYIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Materials Management Packaging: by Kudzanayi ChitekaDocument18 paginiMaterials Management Packaging: by Kudzanayi ChitekaKUDZANAYIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Theory of Metal CuttingDocument10 paginiTheory of Metal CuttingKUDZANAYIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engineering Economic AnalysisDocument3 paginiEngineering Economic AnalysisKUDZANAYIÎncă nu există evaluări
- An107 - Implementing 16-Bit PWM Using The PCADocument18 paginiAn107 - Implementing 16-Bit PWM Using The PCAMot. Schutzen '90Încă nu există evaluări
- GP4000 Series Installation Guide: NVE32340 - 02 - ENDocument36 paginiGP4000 Series Installation Guide: NVE32340 - 02 - ENalex140979Încă nu există evaluări
- Gardner Denver Rotary Screw Compressors: History, Stability, & DependabilityDocument4 paginiGardner Denver Rotary Screw Compressors: History, Stability, & DependabilitySpark ElectricÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manual Book Frenic MiniDocument263 paginiManual Book Frenic Miniabdul rahmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pre-K Scope and Sequence PDFDocument9 paginiPre-K Scope and Sequence PDFXiaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mausam: Project Proposal OnDocument14 paginiMausam: Project Proposal OnHyy NepalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of ComputerDocument41 paginiTypes of ComputerAngelita CapagalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anna University Tiruchirappalli Tiruchirappalli - 620 024: Regulations 2007 Curriculum M.E. Software EngineeringDocument31 paginiAnna University Tiruchirappalli Tiruchirappalli - 620 024: Regulations 2007 Curriculum M.E. Software EngineeringRevathy GmÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abb ActuatorDocument160 paginiAbb ActuatorSayak GhoshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abb GCDocument105 paginiAbb GCMarthen TangkeÎncă nu există evaluări
- NNDL LabDocument33 paginiNNDL LabPrince KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Weighing The Move To An OpenStack Cloud in GovernmentDocument21 paginiWeighing The Move To An OpenStack Cloud in GovernmentScoop News GroupÎncă nu există evaluări
- SME - Metal Enclosed SwitchgearsDocument4 paginiSME - Metal Enclosed SwitchgearsViorel BorsÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE 466/586 VLSI Design: School of EECS Washington State University Pande@eecs - Wsu.eduDocument32 paginiEE 466/586 VLSI Design: School of EECS Washington State University Pande@eecs - Wsu.eduPhạm Đức ThuậnÎncă nu există evaluări
- C++ Programming MCQ (Multiple Choice Questions) : Here Are 1000 Mcqs On C++ (Chapterwise)Document4 paginiC++ Programming MCQ (Multiple Choice Questions) : Here Are 1000 Mcqs On C++ (Chapterwise)aiml HemaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Telecom Billing PDFDocument33 paginiTelecom Billing PDFOzioma IhekwoabaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NASA - Management.a.continuing - Bibliography.with - Indexes.19800014705 1980014705Document175 paginiNASA - Management.a.continuing - Bibliography.with - Indexes.19800014705 1980014705mac9papÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dfccil 2023Document3 paginiDfccil 2023T TiwariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fibre Raceway WebDocument12 paginiFibre Raceway WebKaja YusufÎncă nu există evaluări
- 360 Modena ECU Error CodesDocument21 pagini360 Modena ECU Error CodesDamien Jorgensen100% (2)
- SBO Solution BriefDocument4 paginiSBO Solution BriefroyshahanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 661FX-M (1.0)Document60 pagini661FX-M (1.0)sarokihÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manual Bomba Injetora 4d56 COVEC - FDocument55 paginiManual Bomba Injetora 4d56 COVEC - Fpanhead659370100% (1)
- Estatement-202310 20240118082918Document3 paginiEstatement-202310 20240118082918jooamir70Încă nu există evaluări
- Ceic3006 Lecture 5Document88 paginiCeic3006 Lecture 5sarahÎncă nu există evaluări
- OTME OXE Datasheet EN PDFDocument9 paginiOTME OXE Datasheet EN PDFMegresAmirÎncă nu există evaluări
- 120scmapi PDFDocument1.680 pagini120scmapi PDFSasidhar Bhagavan SunkaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- SRDF Solutions PDFDocument192 paginiSRDF Solutions PDFJimmy UkoboÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2012 Rotary Cutoff ValveDocument4 pagini2012 Rotary Cutoff ValveZikriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cisco Nexus 3548-X, 3524-X, 3548-XL, and 3524-XL SwitchesDocument16 paginiCisco Nexus 3548-X, 3524-X, 3548-XL, and 3524-XL Switchesbonsai todayÎncă nu există evaluări