Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
LS4 Lec2 Final Exam Analysis
Încărcat de
Le DuongDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
LS4 Lec2 Final Exam Analysis
Încărcat de
Le DuongDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
LS4 Lec2 Final Exam 3/21/2002
____Key__________ Last name
_________________ First name
_________________ Student ID
________________ Disc. Section
1 ______________ 2 ______________ 3 ______________ 4 ______________ 5 ______________
6 ______________ 7 ______________ 8 ______________ 9 ______________ 10 _____________
11 _____________ 12 _____________ 13 _____________ 14 _____________ 15 _____________ Total
16 ______________ 17 ______________ 18 ______________ 19 ______________
__________________
Discussion
__________________
Midterm 1 ________
__________________
Midterm 2 ________
__________________
Midterm 3 ________
__________________
Quarter total score
__________________
Quarter grade Show All Your Work for Full Credit.
__________________
1. 15 pts A test cross of a tri-hybrid (the F1) gave these results (the F2): all wild type dumpy wings hooked bristles purple eyes dumpy wings & hooked bristles dumpy wings & purple eyes hooked bristles & purple eyes dumpy, hooked & purple 24 34 26 16 16 24 34 26 200
a. What were the genotypes of the purebred P generation parents that created the F1? Dp x hk pr
b. Determine the map of these traits and the distances that separate the markers. dp dp 41 m.u hk 41 m.u. pr + 24 16 16 26 82 c. What is the length of this linkage group? 82 m.u. 2. 10 pts. One in 10 males in the US has some form of X-linked recessive colorblindness. a. What is the colorblind allele frequency in the US population? 10% b. What is the expected proportion of females with normal color vision? 99% hk 26 16 16 24 82 pr + +
3. 15 pts. Flowers of a plant species can be scarlet, red, pink, coral or white. A series of crosses between plants produced the following results: Cross 1 2 a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. k. Parental phenotypes scarlet x red scarlet x scarlet red x red scarlet x pink scarlet x scarlet scarlet x red scarlet x red pink x pink scarlet x red coral x coral pink x white white x white scarlet x white Progeny all scarlet 76 scarlet, 25 pink 86 red, 29 pink 49 scarlet, 52 pink 69 scarlet, 22 red 50 scarlet, 51 red 54 scarlet, 26 red, 25 pink all pink 49 scarlet, 25 red, 23 coral 60 coral, 29 pink, 31 white all coral all white all scarlet 1
a. How many genes are involved in the inheritance of flower color in this plant? (S > r > p = w) b. Indicate all possible genotypes for the following phenotypes, scarletredpink coralwhiteSS, rr, pp pw ww Sr, rp, Sp, rw Sw
4. 10 pts. Gene X has three alleles X1 , X 2 and X3 with frequecies of 0.6, 0.3 and 0.1 in the population, respectively. Given random mating, calculate the combined frequency of all heterozygotes in the population. 1 - (0.6)2 - (0.3)2 - (0.1)2 = 1 - 0.36 - 0.09 - 0.01 = 0.54 or 2 x 0.6 x 0.3 + 2 x (0.6) x 0.1 + 2 x 0.3 x 0.1 = 0.36 + 0.12 + 0.06 = 0.54
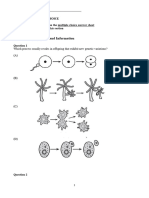
5. 15 pts. In the mushroom species kilumded, cap color is determined by four independently segregating alleles A, B, C, and D. Loss-of-function mutations in any of these genes result in the inability to synthesize pigment as diagramed below:
When both the red and blue pigments are produced, the mushroom caps are purple. Mushrooms with the genotype AaBbCcDd are crossed with those of genotype AaBbCcdd. a. What color are the caps of these parents? Purple, red b. For each phenotype below, determine what proportion of the progeny are expected to have each of the following cap colors: whiteyelloworangeredbluepurple1/4 3/16 9/128 27/128 9/128 27/128 (aa) (A - bb) (A - B - rrdd) (A - B - C - dd) (A - B - ccDd) (A - B - C - D -) (3/4 x 3/4 x 1/4 x 1/2) (3/4 x 3/4 x 3/4 x 1/2) (3/4 x 3/4 x 1/4 x 1/2) (3/4 x 3/4 x 3/4 x 1/2) 32/128 24 9 27 9 _ 27_____ 128
6. 15 pts. yellow body males with bar eyes were crossed with females with normal body color and normal eye shape. Their progeny were normal body color daughters with bar eyes and sons with normal body color and normal eyes. Crosses of F1 brothers x sisters gave these results in the F2: 400 bar eye, normal body females 400 normal eye, normal body females 200 bar eye, normal body males 200 bar eye, yellow body males 200 normal eye, yellow body males 200 normal eye, normal body males
a. An X chromosome and an autosome are shown below. Females have a pair of each. Males have an X and Y chromosome plus a pair of autosomes. Mark the appropriate chromosome below with a location for the yellow gene. Label it. Do the same for the bar gene. Below the figure provide an explanation. If you put the genes on different chromosomes state how why and how you chose each chromosome. If you put the genes on the same chromosome state why and how far apart they are on the chromosome.
X chromosome Explanation:
Autosome
Yellow and Bar are X linked, but for enough apart to assort independently.
b. Propose allele symbols and show the genotypes of the P and F1. Draw the Punnet square for the F1 x F1 cross.
7. 15 pts. Androgen insensitivity in humans is a rare X-linked recessive trait that causes XY chromosome individuals to develop as females. Sparse facial hair is a rare but different X linked recessive trait that can only be detected in males. The interval separating the Sparse hair and androgen insensitivity markers is 12 cM. a. Jane, a woman whose father has sparse hair gives birth to an XY child who displays androgen insensitivity. Draw the pedigree for this family.
b. What is Janes mothers genotype? Heterozygous for androgen insensitive. c. What is the chance Jane's child has both the androgen insensitivity and the sparse hair traits? a + _______ + s
a + a +
+ s s +
0.44 0.44 0.06 0.06
as = ____0.6 _____ 0.44 + 0.06 = 12%
d What is the chance Janes next child will have sparse facial hair? 0.44 x 1/2 = 0.22
8. 15 pts. Three Hfr strains in E.ucla gave these gene orders: first transferred last transferred HfrA his HfrB pen HfrC lys gal cys thi lys bio bio thi thi cys bio lys pen cys gal his pen his gal
a. Draw the map of E.ucla.
b. You suspect pro is in the his to lys interval. Which Hfr strain is the best to map pro if it is in that location? Hfr A Design the genotype for your Hfr strain. Write the markers and the alleles you need for the Hfr strain in this cross. Include the marker for pro. his+ gal+ lys + pro+ pens c. Design the genotype of the F- strain. Write the markers and the alleles you need for the Fstrain in this cross. Include the marker for pro. His- gal- lys - pro- penr d. Design the media for your master plate. Glucose, added lysine, proline and penicillin e. Design the media for replica plates to determine the number of pro recombinants. Glucose, added lysine (withhold proline)
9. 15pts. Transduction mapping: compare the results of the 2 experiments to answer the questions. Arg a and arg b are allelic arg auxotrophs. Experiment 1. Donor arg a lac+ gal+ recipient arg b lac- gal-
select 100 transductants on minimal glucose media replica plate on lactose media: get 40 colonies replica plate on galactose media: get 6 colonies Experiment 2. Donor arg b lac+ gal+ recipient arg a lac- gal-
select 100 transductants on minimal glucose media replica plate on lactose media: get 4 colonies replica plate on galactose media: get 60 colonies a. what is the selected marker genotype for experiment 1? b. what is the order of the lac, gal, arg a and arg b mutants? arg+
c. which is closer to arg, lac or gal?
gal
10. 10 pts. The partial sequence of a messenger RNA below contains a nonsense mutation that prematurely terminates protein translation. Give the sequence of a mutation in the tRNATyr anticodon that would result in suppression of the bacterial mutation and determine the amino acid sequence of the suppressed peptide.
AUGGUCAGAACUUAGGCCAGCUUCAUA Met Val Arg Ser Tyr Ala Ser Phe Ile
11. 10 pts. Two spontaneous Drosophila mutants with apricot colored eyes were identified independently and the mutant eyecolor genes were sequenced. Both mutants were found to carry a mutation at position 38 that changed the identity of the wild type Gly to either Arg or Glu. The mutants were mutagenized and their progeny screened for revertants to the wild-type eyecolor. Four revertants for mutant one and three revertants for mutant two were recovered and for each mutant, the eyecolor gene was sequenced. Based on the diagram below and using the attached genetic code, determine the sequence at codon 38 for each, mutant and revertant fly and the wild type sequence.
12. 10 pts. Eleven genomic clones, each containing DNA from chromosome 5 of C. elegans, were tested for cross hybridization in all pairwise combinations. Using the hybridization data below, determine how many contigs are defined by BAC clones A-K and draw a map of the contig(s) showing the order of overlapping clones within a given contig. In the table below, + = hybridization, - = no hybridization.
13. 15 pts. 6 auxotrophic Neurospora strains were crossed to each other to determine complementation and linkage relations. Growth of the heterokaryons on minimal media was recorded for each pair (+ or -). Then 1000 meiotic spores from each cross were germinated on minimal media. The number of spores that grew into colonies is shown in the table listing the crosses. proA proB proA ---50 (+) proB --proC proD proE proF proC 250 (+) 200 (+) --proD 100 (+) 50 (+) 150 (+) --proE 250 (+) 200 (+) 0 (-) 150 (+) --proF 50 (+) 0 (+) 200 (+) 50 (+) 200 (+) --5
a. How many genes are identified in this sample of mutants?
b. Determine the map locations of these genes. Show distances between the genes in map units.
c. 3 intermediate compounds (I, II, III) were tested to see if they support growth in the absence of proline. The results are that compound I supports growth for none the mutants, compound II supports growth only of strains A and D, and compound III supports growth only of strains A, B, D and F. What is the biosynthetic order of these compounds and proline? Assume they are all involved. Indicate which mutants block which steps.
d If you know that only 1 enzymatic activity separates compounds II and III, what is the minimum number of polypeptide chains forming the enzyme that catalyses the conversion of compound II to compound III? Explain. 2. Two genes (B, F) act at this step. Each produces a polypeptide chain. Likely protein is heterodimer or multiple. 10
14. 15 pts. Mutants at the trpA gene in 4 strains were examined for their effects on the polypeptide chain. The table lists what was found. Strain # 23 36 78 109 mutant change at the indicated amino acid position Gly to Arg at amino acid 211 Glu to Val at amino acid 49 Gly to Cys at amino acid 234 Lys to stop at amino acid 15 del 1 + + del 2 +
a. What is the map of the mutant changes in the trp A gene? Identify each mutant location by its strain number.
The chromosome map has the genes mal and pro nearby and on opposite sides of the trp gene. A large deletion (del 1) removes the mal gene and part of the trp gene, while another large deletion (del 2) removes the pro gene and part of the trp gene. Recombination tests with the mutant strains and deletions 1 and 2 were carried out with the results shown in the table above. + means some wild type recombinants formed, - means no recombinants formed. b. Show the locations of the mal and pro genes and the del 1 and del 2 deletions on your map above. c. Draw an arrow under your map above indicating the direction of transcription for the trp A gene. 15. 15 pts Below is the partial sequence of a yeast gene encoding a homodomain protein. The sequence is derived from the central portion of a single exon and contains an open reading frame. a. Indicate which DNA stand serves as the template strand during RNA synthesis. Top stand is template b. Determine the amino acid sequence encoded by the open reading frame, indicating the amino and carboxyl ends of the partial protein. c. What is the predicted function of the full length protein? Transcription factor, binds DNA 5'CAATGTGAGTAAGTTTACTTTCGACTAGTCCAGGGTTAGCAT3' 3'G,TTA,CAC,TCA,TTC,AAA,TGA,AAG,CTG,ATC,AGG,TCC,CAA,TCG,TA5' COOH Ile His Thr Leu Lys Ser Glu Val Leu Gly Pro Asn Ala - NH2 11
16. 15 pts One region of a chromosome has 5 possible restriction sites. Which sites are actually present determines the different alleles that are segregating in this family, as indicated by hybridization to a probe from part of the region.
a. How many different alleles can you find in this family?
b. Below is the map of the potential restriction sites. Draw a map for each of the alleles, showing which sites are present in that allele.
c. One of the possible restriction fragments is used as the probe. Which one is it? The 4 kb piece between R2 and R4 sites. 17. 10 pts In wild type C. elegans, low X-chromosome to autosome ratios result in high levels of Xol-1, the first component of the sex determination pathway. Using this information and the sex determination diagram below, predict the effects of expressing a transgene that results in high levels of Xol-1 on the activity of the tra-2 gene in hermaphrodites, and explain the how this expression will affect sex determination.
a. tra2 expression
__off __
b. sex determination __male_ differentiation 12
18. 15 pts. The probe G8 is 4 map units from the Huntington disease gene, a rare late onset neural degeneration disease. Shaded individuals have this disease. Southern blots with the G8 probe are shown for this family.
a. Is the Huntington disease dominant or recessive? Explain. Dominant, (rare) affected son has affected parent. b. Which children in generation III are at high risk (25% or greater) to get the Huntington disease gene? III1 & III3 c. What can you advise the youngest daughter (Sue) about her risk of getting the Huntington disease gene?
19. 10 pts pts Progeny resulting from the cross of a Class A mutant of Arabidopsis (aaBBCC) with a Class C mutant (AABBcc) are allowed to self fertilize. In what percent of the F2 progeny do you expect to see expression of Class C genes in whorls 1 and 2 of the flower?
13
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- A Detailed Introduction To String TheoryDocument567 paginiA Detailed Introduction To String TheoryLe Duong100% (3)
- Dihybrid Cross Problems 2013Document1 paginăDihybrid Cross Problems 2013kirancanada1Încă nu există evaluări
- Genetics Exam 1Document8 paginiGenetics Exam 1Tanweer Kumar100% (1)
- Genetics II QuizDocument8 paginiGenetics II QuizSchool Others0% (2)
- Cepheus AtomDocument49 paginiCepheus Atomlingshu8100% (1)
- Genetics Ch04 Test Bank PDFDocument10 paginiGenetics Ch04 Test Bank PDFejanlindsay50% (2)
- 2012 Bio 93 Final Exam Lecture D Version B KEYDocument11 pagini2012 Bio 93 Final Exam Lecture D Version B KEYHyds HshsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Review: DevitaDocument469 paginiReview: DevitaRabiya TahseenÎncă nu există evaluări
- 12 Biology Genetics Exam Practise With AnswersDocument8 pagini12 Biology Genetics Exam Practise With AnswersBrooke GoodingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Testbank - Biology Quiz PDFDocument15 paginiTestbank - Biology Quiz PDFJoy FernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genetics Practice Exam 2Document3 paginiGenetics Practice Exam 2heyyyaleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Part A: Multiple Choice: Answer With The Best Choice. Make Sure That You Clearly Circle TheDocument8 paginiPart A: Multiple Choice: Answer With The Best Choice. Make Sure That You Clearly Circle TheQueng ElediaÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Insta Height FullDocument45 paginiA Insta Height Full6778HUN100% (2)
- Earth and Life Science - 2ndqtrexamDocument6 paginiEarth and Life Science - 2ndqtrexamMa. Lourdes LazaroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bio 140 Exam 4 ReviewDocument7 paginiBio 140 Exam 4 Reviewlp_blackoutÎncă nu există evaluări
- IGA 8 - e Chapter 4 PDFDocument73 paginiIGA 8 - e Chapter 4 PDFNandhiniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genetics Exam No AnswersDocument5 paginiGenetics Exam No AnswersLuminaFlux50% (2)
- Genetic ProblemsDocument20 paginiGenetic Problemsatik0% (2)
- IGCSE Biology 4325 Teacher S Guide UG013046Document58 paginiIGCSE Biology 4325 Teacher S Guide UG013046jassi-_22Încă nu există evaluări
- Genetics Exam 3 - KeyDocument6 paginiGenetics Exam 3 - KeyGestinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Mathematical Impossibility of EvolutionDocument4 paginiThe Mathematical Impossibility of EvolutionFlávio FilhoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Revision Exer.1Document4 paginiRevision Exer.1ravintheran kalimuthu0% (1)
- Review KeyDocument10 paginiReview KeybelovedaffectionÎncă nu există evaluări
- 221 Final 2012Document17 pagini221 Final 2012Gizem OsmanogluÎncă nu există evaluări
- Questions and Problems 3Document8 paginiQuestions and Problems 3Arnytha VebrianiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practice Prelim 3Document9 paginiPractice Prelim 3EricaÎncă nu există evaluări
- University of Texas BIO 325 ExamDocument6 paginiUniversity of Texas BIO 325 ExamGeetika InstaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assigned Problems - Solutions (Ch. 3)Document6 paginiAssigned Problems - Solutions (Ch. 3)aclarke0806Încă nu există evaluări
- Seminar 1 2018-19 SolutionsDocument4 paginiSeminar 1 2018-19 SolutionsAna Rodriguez PedrouzoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practice Prelim 2Document10 paginiPractice Prelim 2EricaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment For MSC Animal Breeding and Genetics Students Final 2020Document8 paginiAssignment For MSC Animal Breeding and Genetics Students Final 2020Hundeessaa OliiqaaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 9 ProtocolDocument7 paginiLab 9 ProtocolKareem HassanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genetics assignment probabilities ratios chi-squareDocument3 paginiGenetics assignment probabilities ratios chi-squareedomin00Încă nu există evaluări
- CH 03Document10 paginiCH 03Maiah Phylicia LatoyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2015C Exam3KEYDocument17 pagini2015C Exam3KEYGizem OsmanogluÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genetics WorkbookDocument57 paginiGenetics WorkbookLauren WinnettÎncă nu există evaluări
- PCB3063 Problem Set 1 Genetics Crosses and RatiosDocument3 paginiPCB3063 Problem Set 1 Genetics Crosses and RatiosSerene SheikhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exercise 1-3Document9 paginiExercise 1-3Patricia MedinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lingkages ProblemsDocument7 paginiLingkages ProblemsAnthony HugillÎncă nu există evaluări
- IGA 10e SM Chapter 04Document73 paginiIGA 10e SM Chapter 04duabgelor100% (4)
- Genetics Problem Set on Linkage, Inheritance PatternsDocument5 paginiGenetics Problem Set on Linkage, Inheritance PatternskristalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Past Years Jun 18Document9 paginiPast Years Jun 18Amirr4uddinÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2BIOL1018 Lunch Box Tutorial Questions 2023 FinalDocument4 pagini2BIOL1018 Lunch Box Tutorial Questions 2023 Finaldpkf6dj725Încă nu există evaluări
- Practice Paper 2023 Task 1Document18 paginiPractice Paper 2023 Task 1Elissa ChanÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 03Document9 paginiCH 03SpringjesJiesiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prac Ex 01Document11 paginiPrac Ex 01Jinal PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Midterm GeneticsDocument12 paginiMidterm GeneticsĐức Huy NguyễnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assig III Fall 17.fimDocument3 paginiAssig III Fall 17.fimedomin00Încă nu există evaluări
- 2020 2014 Heredity Test 0Document6 pagini2020 2014 Heredity Test 0Giovanni TorresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practice Prelim 3 Answer KeyDocument10 paginiPractice Prelim 3 Answer KeyEricaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exercise 1-3Document9 paginiExercise 1-3Patricia MedinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Test Prep End of Course StudentDocument11 paginiBiology Test Prep End of Course StudentdanielleamyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Principles of Genetics Maximum Marks: 150 Time: 6 Hrs Section-A Answer All The Questions (20 1 20) Fill in The BlanksDocument5 paginiPrinciples of Genetics Maximum Marks: 150 Time: 6 Hrs Section-A Answer All The Questions (20 1 20) Fill in The BlanksRAJESHÎncă nu există evaluări
- LinkageMapping PresentationDocument25 paginiLinkageMapping PresentationAbaidullahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dihybrid Cross Problems 2015Document1 paginăDihybrid Cross Problems 2015api-233757247Încă nu există evaluări
- 2015C Exam3Document17 pagini2015C Exam3Jeff TongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genetics of Fruit Flies, Mice and YeastDocument9 paginiGenetics of Fruit Flies, Mice and YeastNurAlhudaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genetics Chapter Crossing OverDocument9 paginiGenetics Chapter Crossing OverNguyen Minh HoangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mendelian Genetics Practice QuestionsDocument10 paginiMendelian Genetics Practice QuestionsPouncingDeer1762Încă nu există evaluări
- LABORATORY ACTIVITY 6 - GENETIC LINKAGE AND RECOMBINATIONDocument3 paginiLABORATORY ACTIVITY 6 - GENETIC LINKAGE AND RECOMBINATIONNorsaidin TungkagÎncă nu există evaluări
- LK Gendas Sayed Munthazar 1905101050009Document18 paginiLK Gendas Sayed Munthazar 1905101050009Zuhra AmandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Which Response Describes The Behaviour of Chromosomes in Metaphase I and Anaphase II of Meiosis?Document6 paginiWhich Response Describes The Behaviour of Chromosomes in Metaphase I and Anaphase II of Meiosis?Alicia San JoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- UCB MCB 104 Midterm 1 Key 2015Document11 paginiUCB MCB 104 Midterm 1 Key 2015azgaray7Încă nu există evaluări
- lAP Biology Genetics Problem Set: in Peas, Seeds May Be Round (R) or Wrinkled (R)Document4 paginilAP Biology Genetics Problem Set: in Peas, Seeds May Be Round (R) or Wrinkled (R)Mary Rose CatalbasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genetics MCQ 1Document12 paginiGenetics MCQ 1Riya BÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2012exam2 With NotesDocument15 pagini2012exam2 With NotesLillyÎncă nu există evaluări
- c2 PDFDocument29 paginic2 PDFLe DuongÎncă nu există evaluări
- DraftSight 2015Document1 paginăDraftSight 2015Le DuongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Osteopathic Physician and Required CoursesDocument2 paginiOsteopathic Physician and Required CoursesLe DuongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Byzantine Generals Problem ExplainedDocument3 paginiByzantine Generals Problem ExplainedLe DuongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nano Magnetism PDFDocument38 paginiNano Magnetism PDFLe DuongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phys151 Syllabus Fall2018Document2 paginiPhys151 Syllabus Fall2018Le DuongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fact Sheet: Social Security and Supplemental Security Income (SSI) : What's The Difference?Document2 paginiFact Sheet: Social Security and Supplemental Security Income (SSI) : What's The Difference?Le DuongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modifying Copper Phthalocyanine To Improve The Performance of OrgDocument125 paginiModifying Copper Phthalocyanine To Improve The Performance of OrgLe DuongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dilution Refrigirator Using Helium MixtureDocument15 paginiDilution Refrigirator Using Helium MixtureLe DuongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction to AC Magnetic MeasurementsDocument4 paginiIntroduction to AC Magnetic MeasurementsLe DuongÎncă nu există evaluări
- AMF Surface StructuresDocument30 paginiAMF Surface StructuresLe DuongÎncă nu există evaluări
- BIF101 Handouts PDF FULL BOOK UPDATED 2022 BY STUDENT INFO 5-1-1Document205 paginiBIF101 Handouts PDF FULL BOOK UPDATED 2022 BY STUDENT INFO 5-1-1Alishba khanÎncă nu există evaluări
- BTH 401 Bioprocessing EngineeringDocument211 paginiBTH 401 Bioprocessing EngineeringTigerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Seeds: Rajasthan State Corporation LTD.Document7 paginiSeeds: Rajasthan State Corporation LTD.Swatantra SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Childhood MedulloblastmaDocument17 paginiChildhood MedulloblastmaIrenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ebook Ebook PDF Principles of Genetics 7th Edition PDFDocument41 paginiEbook Ebook PDF Principles of Genetics 7th Edition PDFdonita.nichols650100% (32)
- Mapping GuideDocument28 paginiMapping GuideBekhiet AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology of Cancer - 971021 PDFDocument49 paginiBiology of Cancer - 971021 PDFgoniatite2002Încă nu există evaluări
- Pang Razi o 2012Document6 paginiPang Razi o 2012Patricio WernerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemosensation of Bacterial Secondary Metabolites Modulates Neuroendocrine Signaling and Behavior of C. ElegansDocument14 paginiChemosensation of Bacterial Secondary Metabolites Modulates Neuroendocrine Signaling and Behavior of C. ElegansGülsüm YıldırımÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intelligence Genes and Genomics Robert PlominDocument18 paginiIntelligence Genes and Genomics Robert PlominNemesterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nsaa s1 Specimen Explained AnswersDocument45 paginiNsaa s1 Specimen Explained AnswersKatia La PlacaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Towards An Evolution Model of Expressive Music Performance: Qijun Zhang Eduardo Reck MirandaDocument6 paginiTowards An Evolution Model of Expressive Music Performance: Qijun Zhang Eduardo Reck MirandaGracia MartínÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nature Magazine 7230 - 2009-02-05Document125 paginiNature Magazine 7230 - 2009-02-05jonathanwalker35Încă nu există evaluări
- United States Patent - 7794969Document47 paginiUnited States Patent - 7794969Sir TemplarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology Scripta PDFDocument243 paginiPathophysiology Scripta PDFMaor PichadzeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genetic EngineeringDocument2 paginiGenetic Engineeringapi-240404995Încă nu există evaluări
- Transposable Genetic ElementDocument60 paginiTransposable Genetic ElementabimubÎncă nu există evaluări
- Designer DNA ChallengeDocument11 paginiDesigner DNA ChallengeTimothy TwomeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zhang 2017Document8 paginiZhang 2017rr.almiralndwÎncă nu există evaluări
- DBT-JRF BET Part A Aptitude and General Biotechnology PDFDocument5 paginiDBT-JRF BET Part A Aptitude and General Biotechnology PDFambuÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Discussion On Theoretical Physics, Evolutionary Biology, Spirituality, and ChristianityDocument19 paginiA Discussion On Theoretical Physics, Evolutionary Biology, Spirituality, and ChristianityChristian PikeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction and Neoplasia - PathologyDocument20 paginiIntroduction and Neoplasia - PathologyjmosserÎncă nu există evaluări
- XenonDocument39 paginiXenonburningbrightÎncă nu există evaluări