Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
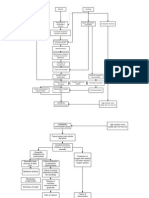
Pathophysiology of Stroke
Încărcat de
Joy Rachelle FerminDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Pathophysiology of Stroke
Încărcat de
Joy Rachelle FerminDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
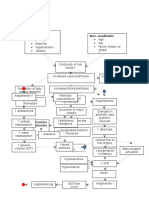
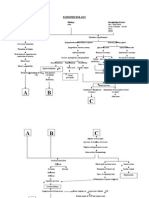
Modifiable Risk Factors *Age *Sex *Race *Heredity Atherothrombotic Disease lipid deposition formation of plaque narrowing of lumen
of blood vessel turbulent blood flow alteration in flow velocities intimal disruption or plaque rupture activation of clotting cascade activated platelets adhere to plaque surface fibrin clot
Partially Modifiable Risk Factors *Hypertension *Cardiac Impairments *Blood Lipid Abnormalities *Diabetes Mellitus Embolic Disease dislodged thrombi travel in the bloodstream Small vessel disease microaretromata or elevated BP occlusion of criface in the penetrating arteric endothelial injury
Modifiable Risk Factors *Smoking *Fat and Salt Intake *Obesity *Sedentary Lifestyle HPN chronic elevation of blood vessel Amyloid angiopathy deposition of beta amyloid sheets in the tunica media of blood vessel wall rigid, fragile and weak blood vessel
degeneration of formation of tunica media Chacot-Bauchad smooth muscle aneurysm in lipohyalinotic smooth muscle vessels is replaced with collagenous fibers unelastic blood vessel narrowing of lumen
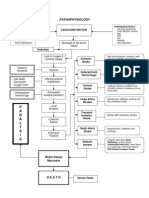
Occlusion Hypoperfusion
rupture
increased ICP
pain, dizziness
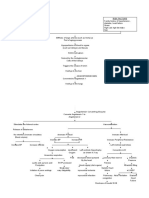
Compression of the different lobes of The brain systemic HPON reduces cerebral perfusion pressure Small arteries interruption of blood supply to the brain alteration in the functioning Constrict in of the different lobes activation of attempt to ischemia auto regulatory maintain distal tissue hypoperfusion FRONTAL LOBE: dysfunction in system pressure membrane the motor control of voluntary movements (e.g. speech) and hypoxia control of a variety of emotional expressions PARIETAL LOBE: dysfunction in the general senses of the body Tissue ischemia TEMPORAL LOBE: dysfunction in hearing and memory, disequilibrium OCCIPITAL LOBE: visual abnormalities Cell Death
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Coronary Artery Disease PathophysiologyDocument3 paginiCoronary Artery Disease PathophysiologyElmer Balgos Alinsog50% (4)
- Pathophysiology of CVADocument1 paginăPathophysiology of CVAChristine Joy Ilao PasnoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stroke PathophysiologyDocument2 paginiStroke PathophysiologyJaessa Feliciano100% (2)
- Pathophysiology CVADocument2 paginiPathophysiology CVASewyel Garburi100% (6)
- Stroke PathophysiologyDocument3 paginiStroke PathophysiologyMaureen Balagtas89% (9)
- Pathophysiology Diagram - StrokeDocument3 paginiPathophysiology Diagram - Strokemisstheatricality130100% (1)
- Pathophysiology CVA (Final2)Document10 paginiPathophysiology CVA (Final2)Jayselle Costes FelipeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cerebrovascular Accident PathophysiologyDocument1 paginăCerebrovascular Accident PathophysiologyBerde KangleonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of Ischemic Stroke FinalDocument3 paginiPathophysiology of Ischemic Stroke FinalAcohCChao67% (3)
- Pathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentDocument2 paginiPathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentJohn Michael FernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology CVADocument1 paginăPathophysiology CVANenette Aquino100% (2)
- Schematic Pathophysiology CVADocument10 paginiSchematic Pathophysiology CVAheiyu100% (5)
- Pathophysiology of CVADocument1 paginăPathophysiology of CVAYoussry JaranillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology CVDDocument1 paginăPathophysiology CVDPamela Shiermaine FilomenoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of StrokeDocument2 paginiPathophysiology of StrokeACe JAy100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of StrokeDocument3 paginiPathophysiology of StrokeAqeel Al-Mahdaly0% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Cva-Hpnii-Hemorrhagic StrokeDocument2 paginiPathophysiology of Cva-Hpnii-Hemorrhagic StrokeLarisse de Leon82% (11)
- Stroke PathophysiologyDocument5 paginiStroke Pathophysiologycinnabon_heart9100% (3)
- Pathophysiology of Cerebrovascular Disease: Predisposing Factors Etiology Precipitating FactorsDocument4 paginiPathophysiology of Cerebrovascular Disease: Predisposing Factors Etiology Precipitating FactorsLilot Antonio Rodriguez Vinarao100% (5)
- 3 PathophysiologyDocument4 pagini3 PathophysiologySherlyn KirisakiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of StrokeDocument4 paginiPathophysiology of StrokeACe JAyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of CVADocument7 paginiPathophysiology of CVAsarzlasco0967% (3)
- Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsDocument2 paginiPathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsJames John Galac88% (8)
- Stroke PathophysiologyDocument3 paginiStroke PathophysiologyMaureen EricaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentDocument3 paginiPathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentByron Paz Te100% (1)
- Pathophysiology CVD InfarctDocument1 paginăPathophysiology CVD InfarctElisa KerrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure III With Pleural EffusionDocument3 paginiPathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure III With Pleural EffusionKen100% (1)
- Pathophysiology Hemorrhagic StrokeDocument1 paginăPathophysiology Hemorrhagic StrokeJeffrey Dela CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Qtsoi Concept MapDocument5 paginiQtsoi Concept MapGenella BabantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of HCVD, DM2, CVD (Left Basal Ganglia)Document1 paginăPathophysiology of HCVD, DM2, CVD (Left Basal Ganglia)rexale ria100% (1)
- Group 4 - Hemorrhagic StrokeDocument60 paginiGroup 4 - Hemorrhagic StrokeKitz T AnasarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology CVADocument2 paginiPathophysiology CVATerence Valdehueza67% (3)
- Final patho-HCVDDocument2 paginiFinal patho-HCVDAlvin RamirezÎncă nu există evaluări
- CVA PathophysiologyDocument3 paginiCVA Pathophysiologyshmily_0810Încă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy and Physiology of CVADocument4 paginiAnatomy and Physiology of CVAKimsha ConcepcionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of StrokeDocument7 paginiPathophysiology of StrokeCHANDAN RAIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology CHFDocument2 paginiPathophysiology CHFPerry Oliver AlvarezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of Heart FailureDocument4 paginiPathophysiology of Heart FailureTiger Knee100% (2)
- Concept Map TBIDocument2 paginiConcept Map TBIraquel maniego67% (3)
- General Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsDocument2 paginiGeneral Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsIrish Nicole DCÎncă nu există evaluări
- Burn PathoDocument1 paginăBurn PathoArlan AbraganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of CVD InfarctDocument2 paginiPathophysiology of CVD InfarctIris Caberte86% (7)
- Bachelor of Nursing Science With HonoursDocument17 paginiBachelor of Nursing Science With HonoursMaryam HasanahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology HypertensionDocument1 paginăPathophysiology HypertensionAlinor Abubacar100% (3)
- Pathophysio Chronic GlomerulonephritisDocument1 paginăPathophysio Chronic GlomerulonephritisRan Ma100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentDocument3 paginiPathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentPaulo de Jesus86% (7)
- Pathophysiology of HCVD DM2 CVD Left Basal GangliaDocument1 paginăPathophysiology of HCVD DM2 CVD Left Basal GangliaJake Caballo100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureDocument3 paginiPathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failuretinayko100% (1)
- Atherosclerosis 2 2017 (Modified)Document64 paginiAtherosclerosis 2 2017 (Modified)Remo B AbyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hemodynamic Disorders: By: Dr. SL RasonableDocument59 paginiHemodynamic Disorders: By: Dr. SL RasonableJenneth Marquez JoloÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8-Cardiovascular Disorders-2Document16 pagini8-Cardiovascular Disorders-2ershauÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiovascular PathologyDocument182 paginiCardiovascular PathologyPavan chowdaryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Asinas Shairabsn3aDocument28 paginiAsinas Shairabsn3aJoshua ApolonioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bleeding DisordersDocument137 paginiBleeding DisordersJosiah BimabamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 30 - Pathology of AtherosclerosisDocument43 paginiLecture 30 - Pathology of Atherosclerosisapi-3703352100% (6)
- Liver Cirrhosis: Precipitating Factors: Predisposing FactorDocument22 paginiLiver Cirrhosis: Precipitating Factors: Predisposing FactorJorie RocoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liver Cirrhosis: (Alterations in Metabolic and Endocrine Functions)Document8 paginiLiver Cirrhosis: (Alterations in Metabolic and Endocrine Functions)Jorie RocoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Patologi Pembuluh DarahDocument77 paginiPatologi Pembuluh DarahDenise JohnsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Client-Based Pathophysiology CVADocument1 paginăClient-Based Pathophysiology CVAJeffrey Dela CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- AtherosclerosisDocument24 paginiAtherosclerosisnabilaÎncă nu există evaluări