Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Abscess
Încărcat de
Sebastian ŁanowieckiDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Abscess
Încărcat de
Sebastian ŁanowieckiDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
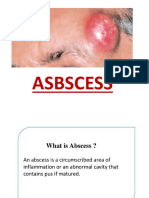
Abscess is the limited purulent dissolution of the soft tissues. The hypoderm in well expressed in children in MFA.
It has protective ammortisative functions, makes round counters of the face. But due to lack of the blood supply this hypoderm is involved into the inflammatory processes very often. As a result the cavity is formed and is filled in with the pus. Phlegmon is spreaded purulent dissolution of the soft tissues. This condition is an acute, diffuse inflammatory infiltration of the loose connective tissue found underneath the skin. It is believed today that cellulitis and phlegmon are interchangeable terms. The term cellulitis has prevailed and so the term phlegmon has just about been abandoned. Etiology: causative agent of abscesses and phlegmons are mixed microflora with dominating of Streptococcus and Staphylococcus in combination with Escherichia coli and other kinds of bacillus. Clinical Presentation. This disease is characterized by edema, headache, and reddish skin. The edema, whose margins are diffuse and not defined, may present in various areas of the face and its localization depends on the infected tooth responsible. For example, if the mandibular posterior teeth are involved, the edema presents as submandibular, and, inmore severe cases, spreads towards the cheek or the opposite side, leading to grave disfigurement of the face. When the infection originates in the maxillary anterior teeth, the edema involves the upper lip, which presentswith a characteristic protrusion. In the initial stage, cellulitis feels soft or doughy during palpation, without pus present, while in more advanced stages, a board-like induration appears, whichmay lead to suppuration. At this stage, the pus is localized in small focal sites in the deep tissue. Abscesses and phlegmons of odontogenic region appear as the result of infection spreading from the apical region due to exacerbation of chronic periapical inflammation of primary and permanent teeth, suppuration of the radical cysts. Osteomielitis can be accompanied with abscesses and phlegmons. They can be as a complication of periostitis. Peculiarities of the clinical course: 1. Soft tissues in children are characterized with the less tightness of fascias and aponeurosis which limit the anatomical space. 2. The hypoderm is more loosen. 3. Immaturity of the cellular barrier leads to the infection spreading on the new tissues. 4. Functional lymph system immaturity leads to lymph nodes involving in the inflammatory process more often. 5. Facial blood supply is better expressed in comparison with other areas and it has positive and negative (quick infection spreading) sides. 6. Significant pain reactions. 7. Rapid formation of the purulent process (2-3 days).
8. Superficial abscesses and phlegmones are accompanied with well expressed deformation of the face, and deep ones with disturbances of chewing, swallowing and speech. Classification: 1. Odontogenic, nonodontogenic 2. Superficial 3. Mental and submental area Canine fossa Buccal area Temporal area Zygomatical area Parotideomasseterica area Submandibular area Sublingual area Alveololingual groove Upper jaw Fossa canina (infraorbital area) Zygomatical area Orbital area Temporal fossa Subtemporal and pterygopalatinal fossae Hard and soft palate
Deep - Retroorbital cellular space - Subtemporal fossa - Pterygomandibular space - Bottom of the oral cavity - Peripharyngeal space - Temporal area
Lower jaw - mental and submental area - buccal - submandibular area - pterygomandibular area - peripharyngeal - parotideomasseterica area
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5795)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- Homeopathic Emergency Remedy List For DogsDocument19 paginiHomeopathic Emergency Remedy List For DogsnaZar100% (2)
- Tissue Salt Primer SchuesslerDocument36 paginiTissue Salt Primer SchuesslerYanka IlarionovaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wound AssessmentDocument19 paginiWound Assessmentdrsonuchawla100% (1)
- Surgical Infections 025203Document80 paginiSurgical Infections 025203Gracie KathyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presentation SSIDocument41 paginiPresentation SSIJawad Mustafa100% (1)
- Lecture 2 Boils and Carbucules - Ru.enDocument22 paginiLecture 2 Boils and Carbucules - Ru.enKandiwapa ShivuteÎncă nu există evaluări
- SurgeryDocument6 paginiSurgeryEthan HuntÎncă nu există evaluări
- OMCDocument37 paginiOMCyurie_ameliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wound DrainageDocument6 paginiWound DrainageNica LinsanganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Careplan Week2Document2 paginiCareplan Week2api-302138606Încă nu există evaluări
- The Zodiac and The Salts of SalvationDocument32 paginiThe Zodiac and The Salts of Salvationrogerfpa100% (1)
- Osteomyelitis Oral SurgeryDocument17 paginiOsteomyelitis Oral SurgeryFourthMolar.comÎncă nu există evaluări
- ABSCESSDocument35 paginiABSCESSlax prajapatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Full Download Test Bank For Comprehensive Radiographic Pathology 6th Edition by Eisenberg PDF Full ChapterDocument36 paginiFull Download Test Bank For Comprehensive Radiographic Pathology 6th Edition by Eisenberg PDF Full Chapterdiesnongolgothatsczx100% (15)
- Homeopath Divine RemedyDocument271 paginiHomeopath Divine RemedyAzad Ansari100% (6)
- OsteomyelitisDocument93 paginiOsteomyelitisRyan KurniawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tiger KingDocument23 paginiTiger KingRiddhima DasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diseases of Bone: Brig Shahid Jamal MBBS, Fcps (Pak), Frcpath (Uk) Professor of Histopathology Am College RawalpindiDocument27 paginiDiseases of Bone: Brig Shahid Jamal MBBS, Fcps (Pak), Frcpath (Uk) Professor of Histopathology Am College RawalpindiMuhammad IqbalÎncă nu există evaluări
- ParonikiaDocument5 paginiParonikiaNyimas Irina SilvaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathology Lecture 11 Scientific TeamDocument34 paginiPathology Lecture 11 Scientific TeammikiyaskayleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dictionary of Gael 02 Mac Lu of TDocument256 paginiDictionary of Gael 02 Mac Lu of TВерка Павловић0% (1)
- HONORARY New Article For 32-34Document3 paginiHONORARY New Article For 32-34Ramesh BeniwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Homoeophatic Therapeutics Samuel Lilienthal.04837 1Document6 paginiHomoeophatic Therapeutics Samuel Lilienthal.04837 1Haritha SivaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 4 PharmD 2022 Part IDocument15 paginiLecture 4 PharmD 2022 Part Iمنوعات عالميةÎncă nu există evaluări
- MODULE-1:: Introduction, History and Development of Veterinary Surgery, Classification and Surgical TerminologiesDocument160 paginiMODULE-1:: Introduction, History and Development of Veterinary Surgery, Classification and Surgical TerminologiesHarishKumar100% (1)
- Black S Medical Dictionary PDFDocument2.413 paginiBlack S Medical Dictionary PDFAlexandr Trotsky100% (1)
- CH 2 - Inflammation II Compatibility Mode PDFDocument19 paginiCH 2 - Inflammation II Compatibility Mode PDFHussam AL-AmirÎncă nu există evaluări
- DrainsDocument1 paginăDrainsMary Lou PeraltaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Therapeutics Lilienthal PDFDocument724 paginiTherapeutics Lilienthal PDFtohnas50% (2)
- Homeopathy 4 Cats DogsDocument25 paginiHomeopathy 4 Cats DogsatuguespÎncă nu există evaluări