Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Interview Preparation - GSM Network Components & Functions
Încărcat de
Aashish VigDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Interview Preparation - GSM Network Components & Functions
Încărcat de
Aashish VigDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Interview Preparation Question & Answer
Summarize Frequency related Specification: System Frequencies: Uplink Downlink Wavelength Bandwidth Duplex Distance Carrier Separation Radio Channels Transmission Rate GSM -900 890 915 MHz 935 960 MHz 33 cm 25 MHz 45 MHz 200 kHz 125 270 kbits/s GSM- 1800 1710 1785 MHz 1805 - 1880 MHz 17 cm 75 MHz 95 MHz 200 kHz 375 270 kbits/s GSM- 1900 1850 1910 MHz 1930 - 1990 MHz 16 cm 60 MHz 80 MHz 200 kHz 300 270 kbits/s
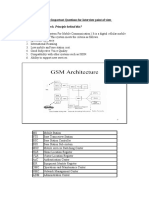
1. What are network components in GSM? The GSM network is divided into two systems. Each of these systems is comprised of a number of functional units which are individual components of the mobile network. Switching System (SS): It is responsible for performing call processing and subscribers related functions. MSC, GSMC, VLR, HLR, AUC & EIR. Base Station System (BSS): It performs all Radio related functions. BSC & BTS.
2. What is AUC? AUC means that Authentication Center. The main function of AUC is to authenticate the subscribers attempting to use a network. In this way, it is used to protect network operator against fraud. The AUC is database connected to HLR which provides it with the authentication parameters and ciphering keys used to ensure network security. 3. What is Basic unit of cellular system? A cell is the basic unit of cellular system and defined as the area of radio coverage given by one BS antenna system. Each cell is assigned a unique number called Cell Global Identity (CGI). 4. What are the states in MS (Mobile station)? IDLE : the MS is on but call is not in progress. BUSY: The MS is on but call in progress. DET : Detached, MS is switched OFF. IDET : Implicit detached, MS is out of coverage. 1/15
5. What is DTI? DTI means that Data Transmission Interface. The DTI is a hardware platform which implements the GSM-defined Inter working function (IWF). It performs data handling function such as data rate conversion. 6. What is TRC? TRC means that Transcoder Controller. The purpose of TRC is to multiplex network traffic channels from multiple BSCs onto one 64Kbits/s PCM channel which reduces network transmission cost. 7. What is MIN? MIN means that Mobile Intelligent Network nodes. Those can be added to basic GSM Network to provide Value-added services to subscribers. Service Switching Point (SSP) : SSP act as an interface between the call control functions of mobile network and the service control functions of a Service Control Point (SCP). Service Control Point (SCP) : SCP Contains the intelligence of a MIN Services. Service Data Point (SDP) : SDP manages the data which is used by an MIN services. 8. What is the formula for wavelength? Wavelength = Speed / Frequency 9. What is meaning of Simplex, Half Duplex & Full Duplex and which method is using for GSM? Simplex : One way only Half Duplex : Two way, only one at a time. Full Duplex : Two way, both at the same time. Full Duplex method is using in GSM. 10. What is Uplink & Downlink and why uplink frequency is always lower frequency? The direction from the MS to the network is referred to as Uplink. The direction from the network to the MS is referred to as Downlink. Lower frequency requires less power to transmit. This saves valuable battery power of the MSs. 11. What is ECP? ECP means that Echo Canceller Pool. Echo cancellers are used to minimize echo from PSTN.
2/15
12. What are the functionalities of MSC? Switching & Call Routing, Charging, Service provisioning, Communication with HLRs, Communication with VLR, Communication with other MSCs, Control of connected BSCs and communication with PSTN. 13. What are the functionalities of HLR? Subscription Database management, Communication with MSCs, Communication with GMSCs, Communication with AUC & VLR. 14. What is triplet and who is responsible for this? The primary function of AUC is to provide information which is then used by an MSC/VLR to perform subscriber authentication and to establish ciphering procedure on the radio link between the network and MSs. The information provided is called Triplet and consists of a non predictable Random number (RAND), a Signed RESponse (SRES), a ciphering key (Kc). 15. When can be authentication performed? Authentication can be preformed during each registration, each call setup attempt, location updating, before supplementary service activation and deactivation. 16. What are the functionalities of BSC? Radio network management, RBS management, TRC handling, Transmission network management, Internal BSC operation and maintenance & Handling of MS connection. 17. What are the hardware units in RBS? Distribution Switch Unit ( DXU), Transceiver Unit (TRU), Combining and Distribution Unit(CDU), Power supply unit (PSU), Energy control unit(ECU). 18. What is IMSI? International Mobile Subscribers Identity (IMSI) is a unique identity allocated to each subscribers which facilitates correct subscribers identification. It has 15 digits (3 MCC + 3 MNC + MSIN). 19. What is LAI? LAI Location Area Identity. It is a temporary network identity which is also required for routing. Paging, which is used to inform the MSC of the LA in which the MS is currently situated. Location updating of Mobile subscribers. It consists of MCC (Mobile Country Code) + MNC (Mobile Network Code) + LAC (Location Area Code). 20. What is BSIC? 3/15
BSIC Base Station Identity Code. It enables MSs to distinguish between different neighboring base stations. It consists of NCC (Network Color Code) + BCC (Base Station Color Code). NCC is used to distinguish between operators on each side of a border. BCC is used to distinguish between RBS using the same control frequencies. 21. What is MSRN? MSRN- Mobile Station Roaming Number. It is a temporary network identity which is assigned during the establishment of a call to a roaming number. It consists of CC (Country Code) + NDC (National Destination Code) + SN (Subscriber Number).
22. What is the use of MS purging? MS purging is used to inform the HLR that the VLR is about to remove a subscriber record from the VLR. The HLR then sets the MS purged flag and treats the subscribers as unreachable. This saves unnecessary network signaling and database lookup. 23. Which control channel is transmitting on SMS? Short messages are transmitted on the allocated signaling channel, SDCCH. 24. What is OSS?
4/15
Operation Support System provides an efficient and easy to use Operation and Maintenance system from remotely and centrally. OSS RC 1.1 & 9.1 25. Do you know about CHA? CHA is Command Handling. It enables an OSS user to send Man-Machine Language (MML) commands to NEs. CHA allows OSS to be connected directly to several NEs at the same time using multiple windows. 26. Do you know about OPS? An OPS is Operation Procedure Support. It is used to run the data transcript from OSS. 27. Do you know about CNA? CNA is Cellular Network Administration. It is used to plan and operate the cellular part of the GSM network, plan major future changes off-line & Implement new cells or new parameter values in the network. 28. If one subscriber is moving from one MSC to other MSC during Busy, which MSC is responsible for charging? Call Originating MSC. 29. How can we identify the prepaid subscribers from HLR subscription parameter? OICK Originating IN category Key. 30. What is location updating & what are the types of location updating? The mobile subscribers moves freely within GSM network, because the network knows the location of the mobile station, it is possible for the mobile subscribers to receive a call. To keep the system updated with the current subscriber location information, the mobile station must inform the system whenever it changes location area. There are four types of location updating, Normal, IMSI detach, IMIS attach & periodic registration.
31. Explain Mobile Terminating call.
5/15
6/15
32. What are the types of Handover? Intra MSC Handover Both cells are belongs to same MSC. They are two types of intra MSC Handover, Intra BSC Handover Both cells belong to same BSC, in this case BSC manages most of the Handover. Inter BSC Handover two cells belong to different BSCs, but in same MSC. In this case MSC is involved in the signaling. Inter MSC Handover two cells belong to different MSCs. 33. What is the Emergency Number in GSM? 112 34. Which End of Selection Codes is using for Emergency Number? Emergency Call with SIM Card ES = 2290 Emergency Call with out SIM Card ES = 2577 35. What is EM? EM is an Extension Module; it is the smallest handling unit in the system. For Example ETC,ECP card. 36. How many EMs can we connected in an RPs pair? 16 EMs. 37. What is SNT & its use? SNT Switching Network Terminal. It is interface between GS (Group Switch) between EMs 38. What is Semi-permanent Connection and which command is used to check the status? It is not physical connection; it is a software connection and builds the path through the GS from a PCD-D device ( C7ST2C), to a two-way trunk devices EMs ( MALT-16,UPD-16). The Command is EXSCP. 39. Which command is used to find devices connected RP number? EXDRP 40. Which command is used to check the status of MTP routing? C7RSP 7/15
41. What are the commands to define Semi-permanent connection? EXSPI: NAME= EXSSI: DEV1= EXSSI: DEV2= EXSPE; EXSCI: NAME= 42. Which SSN ( Sub System Number) is used for HLR & VLR? SSN = 6 for HLR SSN = 7 for VLR SSN = 254 for BSC ( BSSAP) 43. Which command is used to find own VLR & HLR address? For VLR - MGCAP For HLR - HGCAP 44. Which command is used to check the status of SP & SSN? C7NCP : SP= , SSN=ALL;
45. Which command is used to get a number of calls at present for mobile originating & terminating & prepaid calls? ARLDP : APCLNK = ALL; 46. Which SAE is used to get a subscribers capacity in HLR? SAAEP : SAE = 261; 47. Which Command is used to get a subscribers capacity in VLR? MGSVP; 48. Which Command is used to get a prepaid subscribers capacity in VLR? SAAEP : SAE= 602, BLOCK= MTVIN ; (Mobile Telephony Visiting Subscriber intelligent Network Data Changeable Exchange Adaptation) 49. Which command is used to check the status of IOG & APG40 node? For IOG IMMCT : SPG = 0; IMCSP; END; For APG 40 APAMP; 8/15
50. Which command is used to get a related BLOCK for SAE? Or If Size alteration has been reported for GLOBAL, how can we find the corresponding SAE is related to which Block? SAACP:SAE ;
51. Which parameter is used to find subscriber has GPRS facility from HLR subscriber data? NAM - Network Access Mode NAM = 0 both GPRS & Non GPRS NAM = 1 Non GPRS NAM = 2 GPRS 52. If all devices are ABL for one route, but corresponding E1s are working fine, How to analysis the problem? To check the status of MTP Routing by command C7RSP , If Destination is inaccessible we have to analysis the C7 Link status. 53. Is possible to restrict a number of calls for particular B Number series & explain? Yes, by Call Gaping (TRD- Traffic Destination Code) ANCSI : BNC= b number series, TRD = ; NEDBC: BNC= b number series, CGSM= , ES= ;
54. What type of Interface we are using between MSC & BSC? A Interface, MALT ( MSC side E1 Name ) RALT ( BSC side E1 Name)
55. Which command is used to get CIC (Circuit Identity Code) for route device? EXDEP : DEV = ;
56. If one new site is integrated in BSC, What are the parameters to define in MSC side? CGI, BSC name, RO (Routing Origin), CO (Charging Origin) & EA (Emergency Area Code). 57. How can we check the roaming subscriber (other network subscriber) is registered or not in our VLR? By using the Command MGTRP : MSISDIN = --------; 58. What type of Interface we are using between BSC to BTS? 9/15
A Bis Interface 59. If you receive customer complaints- Subscribers tried to call to some destination, but call is going to different destination, what could be a possible problem in this scenario? The best Ans: CIC Mismatching 60. If subscribers have cross talk, what could be a possible problem in this scenario? E1s Cross connection or Jumbering connection may be wrongly connected to another E1 61. If Subscriber is moving from one MSC to another MSC during Busy condition, the call is dropped. How can we analysis the problem? Outer Cell is not defined in MSC. (MGOCI: CELL=----, CGI=------, MSC=----- ( Anchor MSC)) ( ii) . Subscriber is moving from one BTS to another BTS, the call is dropped. Neighboring cell is not defined in BSC.
62. If a subscriber is trying to call some where, but call is suddenly quit what could be a problem? It may congestion in TRX signaling (SDCCH), or Congestion in TCH It may Call Gapping. 63. If subscribers have problem in MOC & MTC in particular MSC area What could be a problem? It may be MSC down ( ii) If MSC is working fine what could be problem ? MSC may be isolated from other nodes. (C7 Destination inaccessible, All RPs down in MSCs) 64. Which Number series is very important to route call for Mobile terminating call ( MTC)? MSRN Mobile station Roaming Number. 65. The Mobile subscribers are switched on the Mobile- what are the event happen? Location Updating: Network frequency & cell information is measured from BCCH. Performs Location update Mobile sends the IMSI number to system. IMSI analyzes in VLR - Command MGISI (Which command is using) System gets MGT (Mobile Global Title) 10/15
MGT analyzes by using of SCCP (Signaling Connection Control Point) to route to HLR. MAP version protocol is using. (Which protocol) C7GSI:TT=0,NA=4,NP=1,NS=VLRADD,GTRC=--; ( Which command) HLR verifies subscriber is roaming in authorized area HLR gives the permission to roam in the area by using SCCP VLR gives the permission to access the network. 66. If other network subscriber is trying to make location updating, but subscriber can not make location updating- What could be a possible problem in this scenario? Subscriber doesnt have roaming parameter. (OBR-1) (Which parameter in Subscriber data) If all the parameter is ok what could be a problem? SCCP problem It needs to check SCCP routing International Gateway exchanges.
67. If other network subscriber can make location updating, but he can not make outgoing call or receive call- what could be a problem? Subscriber doesnt have permission to make a call (OBO-1 & OBI-1, Operator determined barring of all outgoing calls & all incoming calls) (Which parameter in Subscriber data). It may be Subscriber activated the Supplementary services (BAOC-1, BAIC-1, BICRO-1-Barring of all outgoing calls, Barring of all incoming calls, Barring of incoming calls when roaming outside the Home PLMN country) (Which parameter or what is the use of this parameter?). It may be parameter mismatching between two operators. It may be congestion in SCCP routing in International Gateway exchange. 68. If own network subscribers can make location updating, but they can not make outgoing calls in a particular cell coverage area- How can you analyze the problem? Cell parameter (CGI, LAC, CO, RO-Charging Origin, Routing Origin) are not defined correctly in MSC. It may be value of RO & CO is defined as Zero. It may CGI or LAC mismatching between MSC and BSC. 69. Call has been intermittently dropped during the subscribers busy in a particular cell coverage area How can you analyze the problem? Site or Sector has been intermittently up and down due to E1s high bit error rate. 70. How can you analyze the problem during the site down? We have to analyze what are the alarms in the corresponding BSC. It may be site down due to Power problem. It may be site down due to indoor temperature out of normal condition. We can find the managed object fault code 2A 16 (RXMFP: MO=RXOCF-) (What type of alarm reported in the BSC, If indoor temperature out of normal condition?) 11/15
It may be DXU in local mode. E1 is not working, it may be transmission or microwave problem. (ii). There is no transmission or microwave problem but E1 down what could be a problem? It may be DXU down or loose connection in jumpering wire. (iii). There is no hardware fault & no power alarm what could be a problem? It may be circuit breaker tripped in the site or somebody switch off the power switch in RBS. (iv). How can we analyze the E1 down problem? From loop testing. 71. Who is generation the site power alarm? Or how is site power alarm reported in BSC? RBS is generating the power alarm; Power alarm (Commercial power failure) should be defined in RBS DXU. Power alarms are reported to BSC through Abis interface (E1). 72. If site is down due to power problem but power alarms are not reported in BSC- what could be a problem? Power alarms are not defined in the RBS. 73. If site or sector is down but DXU or CF status is working what could be a problem? E1 has little bit error rate and TF (Timing Function) is not working due to timing synchronization mismatched between from one transmission media to another transmission media( like from Microwave to fiber or long distance transmission). 74. If site or sector is down DXU or CF working fine but TS (Time slot) is not working, we can not bring into operation- What could be a problem? IS Intermediate Switch is not working due to problem in DXU or loose connection in PCM cable at DXU. 75. Which command is used to check the GPRS is connected in BTS or not? RRGBP; 76. If sector is down DXU & E1 is working fine How can you analyze the problem? E1 is cascading from one sector to another sector. It needs to check cascading connection-PCM cable connection between one sector DXU to another sector DXU. 77. How can you verify the site or sector is connected by cascading and which parameter and value is defined in BSC&RBS? From TEI value RXMOP: MO=RXOCF-TGNo; & used devices are in the same E1. If TEI value is 62 The E1 is dropped in the first site or sector It TEI value is 61 The E1 is dropped in the second sector. 78. If C7 Links are down, E1 is working fine what could be a problem? 12/15
C7 links are deactivating from other end. If it is not deactivate what could be a problem? Corresponding RP fault RP is related to C7ST2C devices. 79. If no calls on the route or no call successful, but all devices are working fine during this condition, Should we receive any alarm? Yes NM ROUTE ASR SUPERVISION should be reported in AXE. (ASR Answer Ratio) 80. If software error is reported Which command is used to fine the corresponding Block name? LASLP:BN=INF1; 81. If billing files are not transfer What type of alarm we should receive in IOG20 & APG40? & how can you analyze the problem? IOG FILE PROCESS UTILITY AUTOMATIC TRANSFER FAILURE FILE=TTFILE00 APG40 BILLING, AP OUTPUT, CONNECTION TO EXTERNAL HOST LOST It needs to check any problem in IOG or APG, if there is no problem in IOG & APG, it needs Check the X25 link and BGW side. 82. Which command is used to find an APZ type and version? SAOSP; 83. Which command is used to check the status of Group Switch in AXE 10 & AXE 810? AXE 10 - GSSTP AXE 810 GDSTP 84. How can you find the IP address for the Remote connection (OSS) in IOG & APG? IOG IMLIT: SPG=0; ILACP: NTN=ALL; END; APG: APLOC; Ipconfig Exit
85. How the Emergency call for police & Ambulance is routed to based on particular coverage area?
13/15
Based on EA (Emergency Area Category) by using B number analysis call is routed & each cell should have EA code and should be defined in MSC during the CGI definition. 86. What is principle working RP-pair? Load Sharing. 87. How many RECCI you are giving when you are replacing MAU boards, and when? Two times, One is Power on the CP & 2nd when power on the MAU. 88. Which new hardware is implemented in the MSC in the core network of WCDMA system? TM line interface (ALI), Transcoder and Rate Adaptor (TRA) and High Speed signaling Links (HSL). 89. We can ask some question from the diagram:
90. If all the devices are blocked for inter MSC Route (Example MSC1 to MSC2) during this condition how can we find alternative route is their or not? We have to find the MSRNS (Mobile Station Roaming and Handover Number series) for the destination MSC (MSC2) (MGRSP: MSRNS=ALL). We have to find the RC (Routing Case) for the MSRNS in MSC1 (ANBSP:B=8-MSRNS) We can find alternative Route from ANRSP:RC=routing case No. 91. In a particular location area (LAC) is it possible to restrict for accessing a network to particular IMSI series? 14/15
Yes By using NRRG (National Roaming Restriction Group) in IMSI analysis 95. How can you find RPs are connected in Serial or Parallel? By using Command: DBTSP : TAB = RPSRPBSPOS; 92. If you are repairing or working in RPB S (RP bus Serial Type) What precaution should you take before changing RP bus serial? Otherwise what will happen? Before Changing we have to initiate SARPI command (RPB Maintenance work in Progress) During an RPB S branch change, there is always a risk of disturbance on the RPB S. To prevent a Maintenance Subsystem (MAS) from switching CP side. Otherwise System Restart will be happen, we can avoid the outage by using SARPI. 93. How can you define Roaming (Other Country or network Number for Roaming) in VLR? IMSIS Number Series Definition: MGIZI; MGICI; MGISI:IMSIS=404051010068786,M=5-919825,NA=4,ANRES=OBA-30&BO-33&MAPVER2&NRRG-0&PLMN-0&ERIS-2&NATMS&CBA-19&CBAZ-0; MGISP:IMSIS=404051,NOP; MGIAI;
Global Title Address definition for HLR Communication: C7TZI; C7TCI; C7GCI:GTRC=30,PSP=3-9422,PINTER,SSP=3-9421,SINTER; C7GSI:GTRC=30,NS=919825,TT=0,NP=7,NA=4; C7GSI:GTRC=30,NS=9825,TT=0,NP=7,NA=3; C7GSI:GTRC=30,NS=919825001001,TT=0,NP=1,NA=4; !VLR! C7GSI:GTRC=30,NS=919825001000,TT=0,NP=1,NA=4; !HLR! C7GSP:GTRC=30,NOP; C7TAI; For Integration by using 8th origin: ANBZI; ANBCI; ANBSI:B=8-919825,M=2-0,D=1-0,RC=1,BNT=3,CC=0,L=12; ANBSP:B=8-919825,NOP; ANBAI;
15/15
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Interview - QST Ans TelecomDocument19 paginiInterview - QST Ans TelecomSwarna Sekhar Dhar100% (1)
- Prepared By: Rady AbdelwahedDocument168 paginiPrepared By: Rady AbdelwahedAmr Sunhawy50% (2)
- GSM Architecture and InterfacesDocument25 paginiGSM Architecture and InterfacesTelebeansÎncă nu există evaluări
- GSM RF Quick Reference GuideDocument5 paginiGSM RF Quick Reference Guidesantoshkumar2711Încă nu există evaluări
- Network Access Technology Security FinDocument140 paginiNetwork Access Technology Security FinPARASPKKATHURIAÎncă nu există evaluări
- GSM questions on channels, quality, calls and dropsDocument11 paginiGSM questions on channels, quality, calls and dropsalonindÎncă nu există evaluări
- 01 Basic (CDMA)Document43 pagini01 Basic (CDMA)harish sÎncă nu există evaluări
- Global System For Mobile Communications (GSM) : Asad AliDocument66 paginiGlobal System For Mobile Communications (GSM) : Asad AliMuhammadwaqasnaseemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Knowledge For CDMA SystemDocument42 paginiBasic Knowledge For CDMA SystemSanjay GiriÎncă nu există evaluări
- GSM SMS and Call FlowDocument21 paginiGSM SMS and Call FlowLendry NormanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Global System For Mobile Communication (GSM)Document6 paginiGlobal System For Mobile Communication (GSM)RobertoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Telecom Interview Questions & AnswersDocument8 paginiTelecom Interview Questions & AnswersMd Saidur RahmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Second Generation (2G) Cellular Radio SystemsDocument40 paginiSecond Generation (2G) Cellular Radio SystemsMd. Golam Sarwar JoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mobile Wireless CommunicationDocument8 paginiMobile Wireless CommunicationTran Bao DuongÎncă nu există evaluări
- GSM LectureDocument26 paginiGSM Lecturesamy gomaaÎncă nu există evaluări
- GSM ArchitectureDocument8 paginiGSM ArchitectureAbhishek PandeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Knowledge About Radio Network: Viettel Networks Corporation - O0oDocument34 paginiBasic Knowledge About Radio Network: Viettel Networks Corporation - O0ovilaphong vongphachithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basics Communication Theory & Antenna TheoryDocument29 paginiBasics Communication Theory & Antenna TheoryRajesh SuwalkaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Global System For Mobile Communication (GSM) : DefinitionDocument9 paginiGlobal System For Mobile Communication (GSM) : DefinitionAnfal AslamÎncă nu există evaluări
- GSM SystemDocument13 paginiGSM Systemiamhridoy74Încă nu există evaluări
- Ussd Gateways Esme AND GSM ServicesDocument103 paginiUssd Gateways Esme AND GSM Services15octÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research Paper On GSM ArchitectureDocument7 paginiResearch Paper On GSM Architecturenodahydomut2100% (1)
- GSM Part TwoDocument14 paginiGSM Part TwosaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- GSM: Global System for Mobiles ExplainedDocument92 paginiGSM: Global System for Mobiles ExplainedmkbreaktherulesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 2. Telephone System InstallationsDocument25 paginiLecture 2. Telephone System InstallationsOpilaStephen100% (1)
- GSM Training on Radio Network PlanningDocument79 paginiGSM Training on Radio Network PlanningChee Leong100% (1)
- ProjectDocument37 paginiProjectSurina KondillyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mobile ComputingDocument102 paginiMobile Computingbhatt_chintan7Încă nu există evaluări
- Ik1330lab2 (KTH)Document7 paginiIk1330lab2 (KTH)Mehdi RabbaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Some Important Questions For Interview Point of View-1Document23 paginiSome Important Questions For Interview Point of View-1nileshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Telecom Questions and AnswersDocument20 paginiBasic Telecom Questions and AnswersKamranKhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- GSM 130921051638 Phpapp01Document23 paginiGSM 130921051638 Phpapp01andutokichoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Knowledge of CDMA: MSC Based WLLDocument46 paginiBasic Knowledge of CDMA: MSC Based WLLRanjit SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- GSM System Architecture: Mobile-Services Switching CenterDocument20 paginiGSM System Architecture: Mobile-Services Switching Centerpg5555Încă nu există evaluări
- 2G Network: Elecom EtworkDocument13 pagini2G Network: Elecom Etworkpg5555Încă nu există evaluări
- Figure 1. General Architecture of A GSM NetworkDocument15 paginiFigure 1. General Architecture of A GSM NetworkPiyush MalviyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mobile Computing5thDay5.08.2019Document61 paginiMobile Computing5thDay5.08.2019Kalyan DasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 4 - Mobile Communication - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument9 paginiUnit 4 - Mobile Communication - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inRohit kumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 4 - Mobile Communication - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument9 paginiUnit 4 - Mobile Communication - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inRohit kumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- GSM History And TechnologyDocument10 paginiGSM History And TechnologyAzeemuddin KhajaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Telecom Questions and AnswersDocument20 paginiBasic Telecom Questions and AnswersMuhammad Kashif84% (25)
- What is GSM? Understanding 2G Mobile TechnologyDocument8 paginiWhat is GSM? Understanding 2G Mobile TechnologyAvanish SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.GSM OverviewDocument46 pagini1.GSM OverviewAmit ThakurÎncă nu există evaluări
- GSM Network ArchitectureDocument72 paginiGSM Network ArchitectureAkash Kumar100% (1)
- GSM NetworkDocument23 paginiGSM NetworkLidiyaa WandeÎncă nu există evaluări
- GSM KT Session - MTN Iran PRS: Created By: Majid NaseriDocument137 paginiGSM KT Session - MTN Iran PRS: Created By: Majid NaseriSaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MOBILINK - Trainnig Workshop For Optimization GSM BASICDocument89 paginiMOBILINK - Trainnig Workshop For Optimization GSM BASICAli MurtazaÎncă nu există evaluări
- GSM Network Architecture: Mobile StationDocument6 paginiGSM Network Architecture: Mobile StationGurcan KavogluÎncă nu există evaluări
- Welcome All Trainees: Course No. 270 by Rajesh Suwalka Engineer (WMTDC)Document29 paginiWelcome All Trainees: Course No. 270 by Rajesh Suwalka Engineer (WMTDC)Rajesh Suwalka100% (1)
- Overview of GSMDocument15 paginiOverview of GSMtelecomnatcomÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.12 Questions (GSM) : Answers For Chapter 1 Answer - 1Document11 pagini1.12 Questions (GSM) : Answers For Chapter 1 Answer - 1edwinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mobile ComputingDocument17 paginiMobile ComputingPiyush SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- GSM and SS7 Overview: by Firoz AhmedDocument36 paginiGSM and SS7 Overview: by Firoz AhmedAhmed FerozeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Third Generation CDMA Systems for Enhanced Data ServicesDe la EverandThird Generation CDMA Systems for Enhanced Data ServicesEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Mobile Network Optimization: A Guide for 2G and 3G Mobile Network OptimizationDe la EverandMobile Network Optimization: A Guide for 2G and 3G Mobile Network OptimizationEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (3)
- From GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G: An Introduction to Mobile Networks and Mobile BroadbandDe la EverandFrom GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G: An Introduction to Mobile Networks and Mobile BroadbandÎncă nu există evaluări
- Networked Control System: Fundamentals and ApplicationsDe la EverandNetworked Control System: Fundamentals and ApplicationsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Client Needs and Software Requirements V2.2Document43 paginiClient Needs and Software Requirements V2.2Mehmet DemirezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To CPHQDocument24 paginiIntroduction To CPHQmonir61Încă nu există evaluări
- MS 2400 1 2010 P-TocDocument7 paginiMS 2400 1 2010 P-Tocfauzirohani0% (1)
- ASME Piping Standards and Material Selection GuideDocument36 paginiASME Piping Standards and Material Selection Guideتدریس زبان ESLÎncă nu există evaluări
- 300G IM SettingsSheets 20160122Document27 pagini300G IM SettingsSheets 20160122zeljkoradaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bip 0072-2014 PDFDocument94 paginiBip 0072-2014 PDFgrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steel Design DocumentDocument198 paginiSteel Design Documentpudumai100% (5)
- BLACK+DECKER Guidelines PDFDocument62 paginiBLACK+DECKER Guidelines PDFAnupam GanguliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pundit Transducers - Operating Instructions - English - HighDocument8 paginiPundit Transducers - Operating Instructions - English - HighAayush JoshiÎncă nu există evaluări
- HP Warranty Order Format (WOF) repair parts documentDocument1 paginăHP Warranty Order Format (WOF) repair parts documentAnonymous BH8FLrUebÎncă nu există evaluări
- API 620 Vs API 650 Steel Oil Storage TanksDocument2 paginiAPI 620 Vs API 650 Steel Oil Storage TanksBogdan ChivulescuÎncă nu există evaluări
- LightWave 3D 8 TexturingDocument505 paginiLightWave 3D 8 Texturingmanjeethlal80% (5)
- MagazineDocument34 paginiMagazineAhmed Khalil100% (1)
- First Law of ThermodynamicsDocument21 paginiFirst Law of ThermodynamicsMariam50% (2)
- Glossary of Heat Exchanger TerminologyDocument2 paginiGlossary of Heat Exchanger Terminologypvwander100% (1)
- Netsh Wlan Start HostednetworkDocument3 paginiNetsh Wlan Start HostednetworkM Nanda KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kotler Mm15e Inppt 22Document28 paginiKotler Mm15e Inppt 22SHAKTI KARÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kohler Tt1584PIMDocument20 paginiKohler Tt1584PIMJohn ElyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vietnam ProjosDocument271 paginiVietnam Projosjbart252Încă nu există evaluări
- Bhawesh BajajDocument2 paginiBhawesh BajajJacob PruittÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fonestar 4x40w Ver Dap AudioDocument14 paginiFonestar 4x40w Ver Dap AudioAntonio LopezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project ReportDocument10 paginiProject ReportKaljayee singhÎncă nu există evaluări
- BEIT16 AbhishekgokheDocument3 paginiBEIT16 AbhishekgokheSEIT02 Abhishek GokheÎncă nu există evaluări
- Caracterización Y Zonificación Edáfica Y Climática de La Región de Coquimbo, ChileDocument23 paginiCaracterización Y Zonificación Edáfica Y Climática de La Región de Coquimbo, ChileSantos DamasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project ScopeDocument2 paginiProject ScopeRahul SinhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Law of NationsDocument667 paginiThe Law of NationsJo Jo100% (1)
- Hydraulic Cylinder Joints: Understanding Loads and DesignDocument16 paginiHydraulic Cylinder Joints: Understanding Loads and DesignVinaySeebaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem Based Task Dfc2043Document3 paginiProblem Based Task Dfc2043player6675100% (1)
- Training Estimator by VladarDocument10 paginiTraining Estimator by VladarMohamad SyukhairiÎncă nu există evaluări
- ATAL FDP On The Role of Materials in Electric Vehicles Workshop - ReportDocument12 paginiATAL FDP On The Role of Materials in Electric Vehicles Workshop - ReportPuneet Mohan SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări