Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Fallacy
Încărcat de
Aizad ShafeezDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Fallacy
Încărcat de
Aizad ShafeezDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
# 1
Fallacy
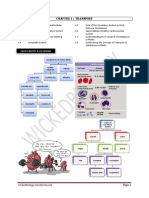
THE ANALOGICAL FALLACY
Definition
Concluding two things with several features in common must/probably share another feature. Changing the definition of a term used throughout the course of an argument to avoid refutation. Allowing an exception to a general rule but keeping the rule.
Problem
Some features are simply irrelevant to other features
Example
"These two people both have hair, eyes, a nose, and teeth. One of them has been to Ireland. Therefore, they probably both have been." God and the Ground of Being.
2 DEFINITIONAL RETREAT
3 THE EXCEPTION THAT PROVES THE RULE 4 ARGUMENTUM AD IGNORANTIAM (appeal to ignorance) 5 IGNORATIO ELENCHI
You wind up defending something different from that which you started defending If something really is a rule/law, then it has no exceptions.
The Johnsons' grandkids are all athletic. Sure, Billy couldn't hit a baseball to save his life, but he's the exception that proves the rule. "The Loch Ness Monster doesn't exist. We don't have any conclusive evidence that it does. So there!" "I should get McDonalds for dinner because my brother took out the trash." Just open Thank You For Arguing.
Claiming something is/isn't so just because it hasn't been disproved/proved. Using arguments irrelevant to your conclusion. Using humor that has no logical bearing on your arguments
This only works in certain epistemic situations. This should be obvious!
6 IRRELEVANT HUMOR
LOADED WORDS
Using vivid, valueladen terms to swing opinion.
The humor doesn't add any logical force to your arguments. At most it improves your ethos. Plays upon The abortion debate emotions.
# 8
Fallacy
ONE-SIDED ASSESSMENT
Definition
Only evaluating one side of a case. Casting a potential opponent in a bad light before they have a chance to speak. Refuting an example rather than the general idea behind the example.
Problem
Doesn't give the other side(s) a fair shot. Similar to an ad hominem
Example
Heinrichs on Intelligent Design (perhaps also guilty of A PRIORISM). "Only a moron would question my arguments." (Any takers?) God and theodicy.
POISONING THE WELL
10
11
12
13
14
Refuting one REFUTING THE example EXAMPLE usually doesn't refute an entire general thesis Moving the burden The person SHIFTING THE of proof to the making claims BURDEN OF wrong side. bears the PROOF burden of proof. Applying a double It uses a SPECIAL standard to double PLEADING elements of your standard. argument Making petty, Should be TRIVIAL forceless obvious! OBJECTIONS objections to an argument. Rejecting Perfection is UNOBTAINABLE something due to rarely PERFECTION possible failure to attainable. reach perfection. Using more explanatory entities than necessary OCKHAM'S RAZOR (violation) One should not posit unnecessary explanatory entities
"Aliens exist." "Why should I think that?" "Give me one reason you shouldn't." "Who made God?"
15
"I'd love to go to church more regularly, but what if the house burned down while I was gone?" "I'd like to go to Hawaii. But there's a 2% chance it'll rain at some point in our vacation. Therefore, I've decided not to go." "Sure, maybe only one person was involved in the murder. But I think there were five people: one from Australia, one with a gold tooth, one with shoes much too small for his feet, one who'd forgotten to brush his hair, and one with no middle name.
# 16
Fallacy
Definition
Problem
Should be obvious.
Example
"Ten reds in a row at roulette? Next one is bound to be black!" You only think that because your parents told you that." "Wouldn't It Be Nice" by The Beach Boys.
17
THE GAMBLER's Thinking FALLACY independent events are dependent or vice versa. GENETIC Denigrating an FALLACY argument based on its source. WISHFUL THINKING Thinking that, because something would be nice, it must be true.
18
Attacks source, not necessarily argument Not all things which would be nice are in fact true.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (120)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- LAW OF ContractDocument1 paginăLAW OF ContractKhurshid Manzoor Malik50% (2)
- Crime Scene Drawing January Incident 10501-10600Document100 paginiCrime Scene Drawing January Incident 10501-10600columbinefamilyrequest100% (2)
- Christianity and Mental Health WEB VERSIONDocument64 paginiChristianity and Mental Health WEB VERSIONWorld Religion NewsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alcatraz Analysis (With Explanations)Document16 paginiAlcatraz Analysis (With Explanations)Raul Dolo Quinones100% (1)
- GDPDocument12 paginiGDPAizad ShafeezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Perfect Score Module WebsitesDocument106 paginiPerfect Score Module Websites林雯Încă nu există evaluări
- CH 11 EducationDocument6 paginiCH 11 EducationAizad ShafeezÎncă nu există evaluări
- BudgetDocument1 paginăBudgetAizad ShafeezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Part A: Multiple-Choice Questions (Please Circle The Correct Answer) (6Document3 paginiPart A: Multiple-Choice Questions (Please Circle The Correct Answer) (6Aizad ShafeezÎncă nu există evaluări
- CIFP IB2002 - Assignment OnlineDocument2 paginiCIFP IB2002 - Assignment OnlineAizad ShafeezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ramadan Employee Guide English 2012Document12 paginiRamadan Employee Guide English 2012Aizad ShafeezÎncă nu există evaluări
- I B 2003 Course Plan January Semester 2014Document8 paginiI B 2003 Course Plan January Semester 2014Aizad ShafeezÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Escaped Prisoner 2014Document2 paginiThe Escaped Prisoner 2014Aizad ShafeezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interm Lab Aug 24Document1 paginăInterm Lab Aug 24Aizad ShafeezÎncă nu există evaluări
- 06e104 Study GuideDocument54 pagini06e104 Study GuideAizad ShafeezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Untitled DocumentDocument1 paginăUntitled DocumentAizad ShafeezÎncă nu există evaluări
- 123456Document4 pagini123456Lance EsquivarÎncă nu există evaluări
- SQ1 Mogas95Document1 paginăSQ1 Mogas95Basant Kumar SaxenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Recent Cases On Minority RightsDocument10 paginiRecent Cases On Minority RightsHarsh DixitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pre T&C Checklist (3 Language) - Updated - 2022 DavidDocument1 paginăPre T&C Checklist (3 Language) - Updated - 2022 Davidmuhammad farisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Syllabus Biomekanika Kerja 2012 1Document2 paginiSyllabus Biomekanika Kerja 2012 1Lukman HakimÎncă nu există evaluări
- First Aid General PathologyDocument8 paginiFirst Aid General PathologyHamza AshrafÎncă nu există evaluări
- GE 110HP DC Trolley MotorDocument10 paginiGE 110HP DC Trolley MotorAnthony PetersÎncă nu există evaluări
- LIM Gr7 Q4W3Document9 paginiLIM Gr7 Q4W3Eto YoshimuraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alice (Alice's Adventures in Wonderland)Document11 paginiAlice (Alice's Adventures in Wonderland)Oğuz KarayemişÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tour Guiding and Escort Services - 301Document95 paginiTour Guiding and Escort Services - 301Zane 19531Încă nu există evaluări
- Feuerhahn Funeral Bullet 17 March 2015Document12 paginiFeuerhahn Funeral Bullet 17 March 2015brandy99Încă nu există evaluări
- International Gustav-Bumcke-Competition Berlin / July 25th - August 1st 2021Document5 paginiInternational Gustav-Bumcke-Competition Berlin / July 25th - August 1st 2021Raul CuarteroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Q & A Set 2 PDFDocument18 paginiQ & A Set 2 PDFBharathiraja MoorthyÎncă nu există evaluări
- W2-Prepares Feasible and Practical BudgetDocument15 paginiW2-Prepares Feasible and Practical Budgetalfredo pintoÎncă nu există evaluări
- PEG Catalog Siemens PDFDocument419 paginiPEG Catalog Siemens PDFrukmagoudÎncă nu există evaluări
- ISIS Wood Product Solutions Selects Cloud-Hosting Partner Real Cloud Solutions LLCDocument2 paginiISIS Wood Product Solutions Selects Cloud-Hosting Partner Real Cloud Solutions LLCdevaprÎncă nu există evaluări
- Skype OptionsDocument2 paginiSkype OptionsacidwillÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5e - Crafting - GM BinderDocument37 pagini5e - Crafting - GM BinderadadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- StatisticsAllTopicsDocument315 paginiStatisticsAllTopicsHoda HosnyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessment NCM 101Document1 paginăAssessment NCM 101Lorainne Angel U. MolinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ListeningDocument2 paginiListeningAndresharo23Încă nu există evaluări
- Group 4 - Regional and Social DialectDocument12 paginiGroup 4 - Regional and Social DialectazizaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Module in Human BehaviorDocument60 paginiFinal Module in Human BehaviorNarag Krizza50% (2)
- Research Report On Energy Sector in GujaratDocument48 paginiResearch Report On Energy Sector in Gujaratratilal12Încă nu există evaluări
- Name: Kartikeya Thadani Reg No.: 19bma0029Document4 paginiName: Kartikeya Thadani Reg No.: 19bma0029Kartikeya ThadaniÎncă nu există evaluări
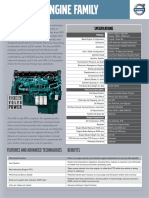
- Volvo D16 Engine Family: SpecificationsDocument3 paginiVolvo D16 Engine Family: SpecificationsJicheng PiaoÎncă nu există evaluări