Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Operserve
Încărcat de
An Ca ManDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Operserve
Încărcat de
An Ca ManDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
HELP OperServ commands: GLOBAL Syntax: /msg OperServ GLOBAL message Syntax: GLOBAL message Allows Administrators to send
messages to all users on the network. The message will be sent from the nick OperServ. STATS Syntax: /msg OperServ STATS [AKILL | ALL | RESET | MEMORY | UPLINK] Syntax: STATS [AKILL | ALL | RESET | MEMORY | UPLINK] Without any option, shows the current number of users and IRCops online (excluding Services), the highest number of users online since Services was started, and the length of time Services has been running. With the AKILL option, displays the current size of the AKILL list and the current default expiry time. The RESET option currently resets the maximum user count to the number of users currently present on the network. The MEMORY option displays information on the memory usage of Services. Using this option can freeze Services for a short period of time on large networks; don't overuse it! The UPLINK option displays information about the current server Anope uses as an uplink to the network. The ALL displays the user and uptime statistics, and everything you'd see with MEMORY and UPLINK options. UPTIME may be used as a synonym for STATS. OPER Syntax: /msg OperServ OPER ADD nick Syntax: OPER OPER OPER OPER ADD nick DEL {nick | entry-num | list} LIST [mask | list] CLEAR
Allows the Services Root Admins to add or remove nicknames to or from the Services operator list. A user whose nickname is on the Services operator list and who has identified to OperServ will be able to access Services operator commands. The OPER ADD command adds the given nickname to the Services operator list. The OPER DEL command removes the given nick from the Services operator list. If a list of entry numbers is given, those entries are deleted. (See the example for LIST below.) The OPER LIST command displays the Services operator list.
If a wildcard mask is given, only those entries matching the mask are displayed. If a list of entry numbers is given, only those entries are shown; for example: OPER LIST 2-5,7-9 Lists Services operator entries numbered 2 through 5 and 7 through 9. The OPER CLEAR command clears all entries of the Services operator list. Any IRC operator may use the OPER LIST form of the command. ADMIN Syntax: /msg OperServ ADMIN ADD nick Syntax: ADMIN ADMIN ADMIN ADMIN ADD nick DEL {nick | entry-num | list} LIST [mask | list] CLEAR
Allows the Services root to add or remove nicknames to or from the Services admin list. A user whose nickname is on the Services admin list and who has identified to OperServ will be able to access Services admin commands. The ADMIN ADD command adds the given nickname to the Services admin list. The ADMIN DEL command removes the given nick from the Services admin list. If a list of entry numbers is given, those entries are deleted. (See the example for LIST below.) The ADMIN LIST command displays the Services admin list. If a wildcard mask is given, only those entries matching the mask are displayed. If a list of entry numbers is given, only those entries are shown; for example: ADMIN LIST 2-5,7-9 Lists Services admin entries numbered 2 through 5 and 7 through 9. The ADMIN CLEAR command clears all entries of the Services admin list. Any IRC operator may use the ADMIN LIST form of the command. All other use limited to Services root. IGNORE Syntax: /msg OperServ IGNORE {ADD|DEL|LIST|CLEAR} [time] [nick | mask] Syntax: IGNORE {ADD|DEL|LIST|CLEAR} [time] [nick | mask] Allows Services Admins to make Services ignore a nick or mask for a certain time or until the next restart. The default time format is seconds. You can specify it by using units. Valid units are: s for seconds, m for minutes, h for hours and d for days. Combinations of these units are not permitted. To make Services permanently ignore the user, type 0 as time.
When adding a mask, it should be in the format user@host or nick!user@host, everything else will be considered a nick. Wildcards are permitted. Ignores will not be enforced on IRC Operators. MODE Syntax: /msg OperServ MODE channel modes Syntax: MODE channel modes Allows Services operators to set channel modes for any channel. Parameters are the same as for the standard /MODE command. UMODE Syntax: /msg OperServ UMODE user modes Syntax: UMODE user modes Allows Super Admins to set user modes for any user. Parameters are the same as for the standard /MODE command. OLINE Syntax: /msg OperServ OLINE user flags Syntax: OLINE user flags Allows Super Admins to give Operflags to any user. Flags have to be prefixed with a "+" or a "-". To remove all flags simply type a "-" instead of any flags. CLEARMODES Syntax: /msg OperServ CLEARMODES channel [ALL] Syntax: CLEARMODES channel [ALL] Clears all binary modes (i,k,l,m,n,p,s,t) and bans from a channel. If ALL is given, also clears all ops and voices (+o and +v modes) from the channel. KICK Syntax: /msg OperServ KICK channel user reason Syntax: KICK channel user reason Allows staff to kick a user from any channel. Parameters are the same as for the standard /KICK command. The kick message will have the nickname of the IRCop sending the KICK command prepended; for example: *** SpamMan has been kicked off channel #my_channel by OperServ (Alcan ( Flood)) AKILL Syntax: /msg OperServ AKILL ADD [+expiry] mask reason Syntax: AKILL ADD [+expiry] mask reason AKILL DEL {mask | entry-num | list}
AKILL LIST [mask | list] AKILL VIEW [mask | list] AKILL CLEAR Allows Services operators to manipulate the AKILL list. If a user matching an AKILL mask attempts to connect, Services will issue a KILL for that user and, on supported server types, will instruct all servers to add a ban (K-line) for the mask which the user matched. AKILL ADD adds the given user@host/ip mask to the AKILL list for the given reason (which must be given). expiry is specified as an integer followed by one of d (days), h (hours), or m (minutes). Combinations (such as 1h30m) are not permitted. If a unit specifier is not included, the default is days (so +30 by itself means 30 days). To add an AKILL which does not expire, use +0. If the usermask to be added starts with a +, an expiry time must be given, even if it is the same as the default. The current AKILL default expiry time can be found with the STATS AKILL command. The AKILL DEL command removes the given mask from the AKILL list if it is present. If a list of entry numbers is given, those entries are deleted. (See the example for LIST below.) The AKILL LIST command displays the AKILL list. If a wildcard mask is given, only those entries matching the mask are displayed. If a list of entry numbers is given, only those entries are shown; for example: AKILL LIST 2-5,7-9 Lists AKILL entries numbered 2 through 5 and 7 through 9. AKILL VIEW is a more verbose version of AKILL LIST, and will show who added an AKILL, the date it was added, and when it expires, as well as the user@host/ip mask and reason. AKILL CLEAR clears all entries of the AKILL list. SGLINE Syntax: /msg OperServ SGLINE ADD [+expiry] mask:reason Syntax: SGLINE SGLINE DEL SGLINE SGLINE SGLINE ADD [+expiry] mask:reason {mask | entry-num | list} LIST [mask | list] VIEW [mask | list] CLEAR
Allows Services operators to manipulate the SGLINE list. If a user with a realname matching an SGLINE mask attempts to connect, Services will not allow it to pursue his IRC session. SGLINE ADD adds the given realname mask to the SGLINE list for the given reason (which must be given). expiry is specified as an integer followed by one of d (days), h (hours), or m (minutes). Combinations (such as
1h30m) are not permitted. If a unit specifier is not included, the default is days (so +30 by itself means 30 days). To add an SGLINE which does not expire, use +0. If the realname mask to be added starts with a +, an expiry time must be given, even if it is the same as the default. The current SGLINE default expiry time can be found with the STATS AKILL command. Note: because the realname mask may contain spaces, the separator between it and the reason is a colon. The SGLINE DEL command removes the given mask from the SGLINE list if it is present. If a list of entry numbers is given, those entries are deleted. (See the example for LIST below.) The SGLINE LIST command displays the SGLINE list. If a wildcard mask is given, only those entries matching the mask are displayed. If a list of entry numbers is given, only those entries are shown; for example: SGLINE LIST 2-5,7-9 Lists SGLINE entries numbered 2 through 5 and 7 through 9. SGLINE VIEW is a more verbose version of SGLINE LIST, and will show who added an SGLINE, the date it was added, and when it expires, as well as the realname mask and reason. SGLINE CLEAR clears all entries of the SGLINE list. SQLINE Syntax: /msg OperServ SQLINE ADD [+expiry] mask reason Syntax: SQLINE SQLINE SQLINE SQLINE SQLINE ADD [+expiry] mask reason DEL {mask | entry-num | list} LIST [mask | list] VIEW [mask | list] CLEAR
Allows Services operators to manipulate the SQLINE list. If a user with a nick matching an SQLINE mask attempts to connect, Services will not allow it to pursue his IRC session. If the first character of the mask is #, services will prevent the use of matching channels (on IRCds that support it). SQLINE ADD adds the given mask to the SQLINE list for the given reason (which must be given). expiry is specified as an integer followed by one of d (days), h (hours), or m (minutes). Combinations (such as 1h30m) are not permitted. If a unit specifier is not included, the default is days (so +30 by itself means 30 days). To add an SQLINE which does not expire, use +0. If the mask to be added starts with a +, an expiry time must be given, even if it is the same as the default. The current SQLINE default expiry time can be found with the STATS AKILL command.
The SQLINE DEL command removes the given mask from the SQLINE list if it is present. If a list of entry numbers is given, those entries are deleted. (See the example for LIST below.) The SQLINE LIST command displays the SQLINE list. If a wildcard mask is given, only those entries matching the mask are displayed. If a list of entry numbers is given, only those entries are shown; for example: SQLINE LIST 2-5,7-9 Lists SQLINE entries numbered 2 through 5 and 7 through 9. SQLINE VIEW is a more verbose version of SQLINE LIST, and will show who added an SQLINE, the date it was added, and when it expires, as well as the mask and reason. SQLINE CLEAR clears all entries of the SQLINE list. SZLINE Syntax: /msg OperServ SZLINE ADD [+expiry] mask reason Syntax: SZLINE SZLINE SZLINE SZLINE SZLINE ADD [+expiry] mask reason DEL {mask | entry-num | list} LIST [mask | list] VIEW [mask | list] CLEAR
Allows Services operators to manipulate the SZLINE list. If a user with an IP matching an SZLINE mask attempts to connect, Services will not allow it to pursue his IRC session (and this, whether the IP has a PTR RR or not). SZLINE ADD adds the given IP mask to the SZLINE list for the given reason (which must be given). expiry is specified as an integer followed by one of d (days), h (hours), or m (minutes). Combinations (such as 1h30m) are not permitted. If a unit specifier is not included, the default is days (so +30 by itself means 30 days). To add an SZLINE which does not expire, use +0. If the realname mask to be added starts with a +, an expiry time must be given, even if it is the same as the default. The current SZLINE default expiry time can be found with the STATS AKILL command. The SZLINE DEL command removes the given mask from the SZLINE list if it is present. If a list of entry numbers is given, those entries are deleted. (See the example for LIST below.) The SZLINE LIST command displays the SZLINE list. If a wildcard mask is given, only those entries matching the mask are displayed. If a list of entry numbers is given, only those entries are shown; for example: SZLINE LIST 2-5,7-9 Lists SZLINE entries numbered 2 through 5 and 7 through 9.
SZLINE VIEW is a more verbose version of SZLINE LIST, and will show who added an SZLINE, the date it was added, and when it expires, as well as the IP mask and reason. SZLINE CLEAR clears all entries of the SZLINE list. SET Syntax: /msg OperServ SET option setting Syntax: SET option setting Sets various global Services options. Option names currently defined are: READONLY Set read-only or read-write mode LOGCHAN Report log messages to a channel DEBUG Activate or deactivate debug mode NOEXPIRE Activate or deactivate no expire mode SUPERADMIN Activate or deactivate super-admin mode SQL Activate or deactivate sql mode IGNORE Activate or deactivate ignore mode LIST List the options SET READONLY Syntax: /msg OperServ SET READONLY {ON | OFF} Syntax: SET READONLY {ON | OFF} Sets read-only mode on or off. In read-only mode, normal users will not be allowed to modify any Services data, including channel and nickname access lists, etc. IRCops with sufficient Services privileges will be able to modify Services' AKILL list and drop or forbid nicknames and channels, but any such changes will not be saved unless read-only mode is deactivated before Services is terminated or restarted. This option is equivalent to the command-line option -readonly. SET LOGCHAN Syntax: /msg OperServ SET LOGCHAN {ON | OFF} Syntax: SET LOGCHAN {ON | OFF} With this setting on, Services will send its logs to a specified channel as well as the log file. LogChannel must also be defined in the Services configuration file for this setting to be of any use. This option is equivalent to the command-line option -logchan. Note: This can have strong security implications if your log channel is not properly secured. SET DEBUG Syntax: /msg OperServ SET DEBUG {ON | OFF | num} Syntax: SET DEBUG {ON | OFF | num} Sets debug mode on or off. In debug mode, all data sent to
and from Services as well as a number of other debugging messages are written to the log file. If num is given, debug mode is activated, with the debugging level set to num. This option is equivalent to the command-line option -debug. SET LIST Syntax: /msg OperServ SET LIST Syntax: SET LIST Display the various OperServ settings SET NOEXPIRE Syntax: /msg OperServ SET NOEXPIRE {ON | OFF} Syntax: SET NOEXPIRE {ON | OFF} Sets no expire mode on or off. In no expire mode, nicks, channels, akills and exceptions won't expire until the option is unset. This option is equivalent to the command-line option -noexpire. SET SQL Syntax: /msg OperServ SET SQL {ON | OFF} Syntax: SET SQL {ON | OFF} Setting this will toggle Anope's usage of SQL, this should be used to disable and enable SQL should your SQL server go down while services are running. SET SUPERADMIN Syntax: /msg OperServ SET SUPERADMIN {ON | OFF} Syntax: SET SUPERADMIN {ON | OFF} Setting this will grant you extra privileges such as the ability to be "founder" on all channel's etc... This option is not persistent, and should only be used when needed, and set back to OFF when no longer needed. NOOP Syntax: /msg OperServ NOOP SET server Syntax: NOOP SET server NOOP REVOKE server NOOP SET remove all O:lines of the given server and kill all IRCops currently on it to prevent them from rehashing the server (because this would just cancel the effect). NOOP REVOKE makes all removed O:lines available again on the given server.
Note: The server is not checked at all by the Services. JUPE Syntax: /msg OperServ JUPE server [reason] Syntax: JUPE server [reason] Tells Services to jupiter a server -- that is, to create a fake "server" connected to Services which prevents the real server of that name from connecting. The jupe may be removed using a standard SQUIT. If a reason is given, it is placed in the server information field; otherwise, the server information field will contain the text "Juped by ", showing the nickname of the person who jupitered the server. RAW Syntax: /msg OperServ RAW text Syntax: RAW text Sends a string of text directly to the server to which Services is connected. This command has a very limited range of uses, and can wreak havoc on a network if used improperly. DO NOT USE THIS COMMAND unless you are absolutely certain you know what you are doing! UPDATE Syntax: /msg OperServ UPDATE Syntax: UPDATE Causes Services to update all database files as soon as you send the command. RELOAD Syntax: /msg OperServ RELOAD Syntax: RELOAD Causes Services to reload the configuration file. Note that some directives still need the restart of the Services to take effect (such as Services' nicknames, activation of the session limitation, etc.) QUIT Syntax: /msg OperServ QUIT Syntax: QUIT Causes Services to do an immediate shutdown; databases are not saved. This command should not be used unless damage to the in-memory copies of the databases is feared and they should not be saved. For normal shutdowns, use the SHUTDOWN command. SHUTDOWN Syntax: /msg OperServ SHUTDOWN
Syntax: SHUTDOWN Causes Services to save all databases and then shut down. RESTART Syntax: /msg OperServ RESTART Syntax: RESTART Causes Services to save all databases and then restart (i.e. exit and immediately re-run the executable). CHANLIST Syntax: /msg OperServ CHANLIST [{pattern | nick} [SECRET]] Syntax: CHANLIST [{pattern | nick} [SECRET]] Lists all channels currently in use on the IRC network, whether they are registered or not. If pattern is given, lists only channels that match it. If a nickname is given, lists only the channels the user using it is on. If SECRET is specified, lists only channels matching pattern that have the +s or +p mode. USERLIST Syntax: /msg OperServ USERLIST [{pattern | channel} [INVISIBLE]] Syntax: USERLIST [{pattern | channel} [INVISIBLE]] Lists all users currently online on the IRC network, whether their nick is registered or not. If pattern is given, lists only users that match it (it must be in the format nick!user@host). If channel is given, lists only users that are on the given channel. If INVISIBLE is specified, only users with the +i flag will be listed. EXCEPTION Syntax: /msg OperServ EXCEPTION ADD [+expiry] mask limit reason Syntax: EXCEPTION EXCEPTION EXCEPTION EXCEPTION EXCEPTION ADD [+expiry] mask limit reason DEL {mask | list} MOVE num position LIST [mask | list] VIEW [mask | list]
Allows Services admins to manipulate the list of hosts that have specific session limits - allowing certain machines, such as shell servers, to carry more than the default number of clients at a time. Once a host reaches it's session limit, all clients attempting to connect from that host will be killed. Before the user is killed, they are notified, via a /NOTICE from OperServ, of a source of help regarding session limiting. The content of this notice is a config setting. EXCEPTION ADD adds the given host mask to the exception list. Note that nick!user@host and user@host masks are invalid! Only real host masks, such as box.host.dom and *.host.dom,
are allowed because sessions limiting does not take nick or user names into account. limit must be a number greater than or equal to zero. This determines how many sessions this host may carry at a time. A value of zero means the host has an unlimited session limit. See the AKILL help for details about the format of the optional expiry parameter. EXCEPTION DEL removes the given mask from the exception list. EXCEPTION MOVE moves exception num to position. The exceptions inbetween will be shifted up or down to fill the gap. EXCEPTION LIST and EXCEPTION VIEW show all current exceptions; if the optional mask is given, the list is limited to those exceptions matching the mask. The difference is that EXCEPTION VIEW is more verbose, displaying the name of the person who added the exception, it's session limit, reason, host mask and the expiry date and time. Note that a connecting client will "use" the first exception their host matches. Large exception lists and widely matching exception masks are likely to degrade services' performance. SESSION Syntax: /msg OperServ SESSION LIST threshold Syntax: SESSION LIST threshold SESSION VIEW host Allows Services admins to view the session list. SESSION LIST lists hosts with at least threshold sessions. The threshold must be a number greater than 1. This is to prevent accidental listing of the large number of single session hosts. SESSION VIEW displays detailed information about a specific host - including the current session count and session limit. The host value may not include wildcards. See the EXCEPTION help for more information about session limiting and how to set session limits specific to certain hosts and groups thereof. CHANKILL Syntax: /msg OperServ CHANKILL [+expiry] channel reason Syntax: CHANKILL [+expiry] channel reason Puts an AKILL for every nick on the specified channel. It uses the entire and complete real ident@host for every nick, then enforces the AKILL. DEFCON Syntax: /msg OperServ DEFCON [1|2|3|4|5] Syntax: DEFCON [1|2|3|4|5] The defcon system can be used to implement a pre-defined set of restrictions to services useful during an attempted attack on the network. DEFCON AKILL NEW CLIENTS
* AKILL any new clients connecting DEFCON FORCE CHAN MODES * Force Chan Modes (OperServ) to be set on all channels DEFCON NO MLOCK CHANGE * No MLOCK changes DEFCON NO NEW CHANNELS * No new channel registrations DEFCON NO NEW CLIENTS * Kill any NEW clients connecting DEFCON NO NEW MEMOS * No new memos sent DEFCON NO NEW NICKS * No new nick registrations DEFCON ONLY * Ignore any non-opers with message DEFCON REDUCE SESSION * Use the reduced session limit of %d DEFCON SILENT ONLY * Silently ignore non-opers LOGGED Notice: All commands sent to OperServ are logged! MODINFO Syntax: /msg OperServ MODINFO FileName Syntax: MODINFO FileName This command lists information about the specified loaded module MODLIST Syntax: /msg OperServ MODLIST [Core|3rd|protocol|encryption|supported|qa tested] Syntax: MODLIST [Core|3rd|protocol|encryption|supported|qatested] Lists all currently loaded modules. MODLOAD Syntax: /msg OperServ MODLOAD FileName Syntax: MODLOAD FileName This command loads the module named FileName from the modules directory. MODUNLOAD Syntax: /msg OperServ MODUNLOAD FileName Syntax: MODUNLOAD FileName This command unloads the module named FileName from the modules directory. SVSNICK Syntax: /msg OperServ SVSNICK nick newnick Syntax: SVSNICK nick newnick Forcefully changes a user's nickname from nick to newnick.
Limited to Super Admins.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (120)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- PSU Papers For Computer ScienceDocument2 paginiPSU Papers For Computer SciencemrinmoybasuÎncă nu există evaluări
- GrepDocument2 paginiGrepDayakar SirivatyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Getting Started With TEMPRO (Version 7.2)Document7 paginiGetting Started With TEMPRO (Version 7.2)Rustama RustamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mod 9 Introduction To CISCO IOS ICCNIOS003Document66 paginiMod 9 Introduction To CISCO IOS ICCNIOS003Mao BourichaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dhuha Rizky Ramadhan DBDDocument6 paginiDhuha Rizky Ramadhan DBDdhuharizkyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 0002089916Document1.037 pagini0002089916muthuÎncă nu există evaluări
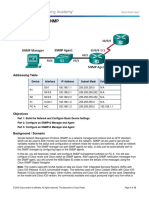
- Lab 5.2.2.6 - Configuring SNMPDocument12 paginiLab 5.2.2.6 - Configuring SNMPCarlos RedrovánÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sysbii File SharingDocument10 paginiSysbii File SharingDeepak KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fortinet: NSE7 - EFW-6.2Document7 paginiFortinet: NSE7 - EFW-6.2ivoÎncă nu există evaluări
- PowerISO PortableDocument3 paginiPowerISO PortableMuhammad NaeemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Personal Material Database - MaterealityDocument30 paginiPersonal Material Database - Materealitylobo1684Încă nu există evaluări
- Structured Programming CatDocument5 paginiStructured Programming Catpaul muthuriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Configure Remote SSL VPN in FortiGate With CLIDocument5 paginiConfigure Remote SSL VPN in FortiGate With CLIAynaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic On Terminal System of Switch: Huawei Technologies Co, LTDDocument18 paginiTopic On Terminal System of Switch: Huawei Technologies Co, LTDAbdullatifÎncă nu există evaluări
- X Way ForensicDocument4 paginiX Way ForensicZeljko TomicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Database PresentationDocument11 paginiAdvanced Database PresentationKingsleyphilanimafayo JereÎncă nu există evaluări
- Edmi Mk3 Dnp3 Profile A0 - 2Document14 paginiEdmi Mk3 Dnp3 Profile A0 - 2asela115Încă nu există evaluări
- Fetch and Open Cursor AnalysisDocument34 paginiFetch and Open Cursor Analysisruki100% (1)
- Java 3 Object Oriented Programming PDFDocument174 paginiJava 3 Object Oriented Programming PDFThe Underrated artistsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bliss: Blind Source Separation and ApplicationsDocument4 paginiBliss: Blind Source Separation and ApplicationspostscriptÎncă nu există evaluări
- BI Tools ComparisonDocument5 paginiBI Tools ComparisonscribdkeliyeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Database Operating ManualDocument21 paginiDatabase Operating ManualSharon PaulÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCSE 05 Implementing of A Network Infrastructure 05 TheoryDocument36 paginiMCSE 05 Implementing of A Network Infrastructure 05 Theorysivasankar015Încă nu există evaluări
- Parameterizable 8b/10b DecoderDocument20 paginiParameterizable 8b/10b DecoderRamesh ChandrakasanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 嵌入式系統 Introduction to Embedded System Design: Part 5: Serial Communication (UART)Document26 pagini嵌入式系統 Introduction to Embedded System Design: Part 5: Serial Communication (UART)N26094354鐘筠凱Încă nu există evaluări
- Simple Object Access ProtocolDocument27 paginiSimple Object Access ProtocolYaser essaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eplan Electric Handbook ContentsDocument9 paginiEplan Electric Handbook ContentsAkhilÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Oracle 9i DBA Fundamentals 1 Cram SheetDocument2 paginiThe Oracle 9i DBA Fundamentals 1 Cram SheetelibunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Network - CS610 Power Point Slides Lecture 01Document19 paginiComputer Network - CS610 Power Point Slides Lecture 01Ibrahim ChoudaryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample Resume For FreshersDocument3 paginiSample Resume For FreshersPranay PatilÎncă nu există evaluări