Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
16 XHTML Forms PR TM
Încărcat de
anitkumardasDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
16 XHTML Forms PR TM
Încărcat de
anitkumardasDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
www.netskills.ac.
uk
XHTML Forms
Web Pages: Behaviour
CSC1014
Topics
What are XHTML forms?
Form structure Form controls Form organisation and presentation Form submission
GET and POST methods for submitting form data Validation and processing principles
A simple example
Practicalities
JISC Netskills
CSC1014
What are XHTML forms?
XHTML form tags and attributes create an interface for user interaction Core purpose of a form is to collect user input and return it to a server
Instruct browser to create one or more form controls Provide a means to let user submit the form Specify how browser should include form data in request to server Specify where (URL) to send the input
JISC Netskills
CSC1014
XHTML form structure
Each form on page enclosed in <form> tags
wrapped around all controls for that form
Each <form> tag has method and action attributes
method (optional) specifies how form data will be packaged and sent to server. <form> tags enclose the whole form action (required) specifies the location (URL) that form data will be sent to
<body> <form method="get" action="http://a.server.com/script"> <p> Enter your name: <input type="text" name="username" /> </p> </form> </body>
JISC Netskills
CSC1014
Form controls
Form controls are replaced tags used to collect user input
The tag is replaced by the browser interface for that control type W3C provide guidelines for consistent user experience
Each form control will have a name attribute Most have an explicit value attribute or an implied value (based on the user action) On submission a successful form control will contain both a name and a value (Only) successful name/value pairs returned as a string to the server e.g.
username=Bob&age=35&email=bob@somewhere.com
JISC Netskills
CSC1014
Common form controls
One line text input Radio buttons Checkboxes Drop-down selections Multi-line line input Hidden fields Password fields Submit & reset buttons
JISC Netskills
CSC1014
One-line text input
The basic (default) form control created by <input> tag
Additional attributes to control basic behaviour e.g. Visible characters (width of box) with size e.g. size="25" Number of characters to accept with maxlength e.g. maxlength="8"
<form method="get" action="http://a.server.com/script"> <p> Enter your name: <input type="text" name="username" /> </p> </form>
username=Bob
JISC Netskills
CSC1014
Radio buttons
Create mutually exclusive controls user can only select one
<p>Choose ONE of the following: <input type="radio" name="choice" value="A" checked="checked" /> A <input type="radio" name="choice" value="B" /> B <input type="radio" name="choice" value="C" /> C </p> Same name attribute creates a single control Pre-selected option
Returns fixed name/value one option can (should?) be pre-selected
choice=A
JISC Netskills
CSC1014
Checkboxes
Create individual independent controls
Should return on if selected ( better to supply a value though!)
<p>Choose ONE of the following: <input type="checkbox" name="A" value="Yes" checked="checked" /> A <input type="checkbox" name="B" value="Yes" /> B <input type="checkbox" name="C" value="Yes" /> C </p> Different name attributes create independent controls Pre-selected option
A=Yes
JISC Netskills
CSC1014
Drop down menus
The <select> tag allows user to select from a list
Can pre-select a default with selected attribute
<p>Choose ONE of the following:<br /> <select name="drop_down"> <option value="None" selected="selected">No thanks</option> <option value="A">Choose A</option> <option value="B">Choose B</option> <option value="C">Choose C</option> </select> </p> Selected <option> returns a fixed value drop_down=A
JISC Netskills
CSC1014
Multi-line input
Collected using a <textarea> tag
Box contents (inc whitespace/newlines) returned as the value Requires rows and cols attributes to set the size
<p>Add some thoughts of your own... <br /> <textarea name="free_text" rows="4" cols="20"></textarea> </p> Initially displays 4 rows and 20 columns (chars) of text
Encoded newline characters free_text=Apples%0D%0ABanana
JISC Netskills
CSC1014
Password fields
Specific type of one-line text box which hides input from anyone looking at screen
Does not provide any other security or encryption!
<p> Care to give us a password? <input type="password" name="my_password" /> </p> password type tells browser to mask input (however that browser chooses to do it)
my_password=WhateverYouTypedIn!
JISC Netskills
CSC1014
Hidden fields
Do not appear on screen! Used to return fixed values alongside user input
Values usually pre-populated e.g. time/date stamps Can be populated dynamically via client-side script e.g. returning calculated values alongside use input
<p> <input type="hidden" name="my_secret" value="hello" /> </p> Both name and value must be supplied. my_secret=hello
JISC Netskills
CSC1014
Form organisation
Tags/attributes for organising forms Uses <fieldset>, <legend>, <label>
Plus id attributes
Offers block-level structure
Reducing markup needed inside them e.g. <p>, <div> etc Logical blocks with descriptive names Associating labels with controls Increasing "hit area!" on small controls
Provides visual cues to users
Enhanced usability/accessibility
JISC Netskills
CSC1014
Using <fieldset> and <legend>
Block-level organisation used to group form controls together
Default visual appearance can be altered using CSS
<fieldset> groups block of controls
<legend> <fieldset> <legend>Your choices</legend> provides a label for Choose ONE of the following: <br /> group <input type="radio" name="choice" value="A" /> Apple <input type="radio" name="choice" value="B" /> Banana </fieldset>
JISC Netskills
CSC1014
Using labels and id
Allows text to be explicitly associated with a form control
Clicking on the label will activate the control
<label> can be explicitly linked to an id
<input type="radio" name="choice" value="A" id="A1" /> <label for="A1">Apple</label> <label> <input type="radio" name="choice" value="B" /> Banana </label>
<label> can also be wrapped around control & label content
JISC Netskills
CSC1014
Form buttons
3 types of form button control Submit most important Reset very useful!
Set by type attribute in <input> tag Invokes the browser's submit process and sends data to the server Clears user input and returns form to its initial state without reloading the page Can only be used if attached to client-side scripted actions or events
Button creates a generic button
Submit and Reset buttons do not require any programming or additional scripting to work
JISC Netskills
CSC1014
Submit button
Every good form should have one!
Can be a "regular" button (as drawn by the browser) or an image file Images not used as often now as buttons can be styled with CSS
<input type="submit" value="submit" /> type="submit" draws the browser's regular button value specifies the button text <input type="image" src="button.gif" alt="submit" /> type="image" tells the browser to use an image click to trigger form submission src and alt specifies the image and text alternative
JISC Netskills
CSC1014
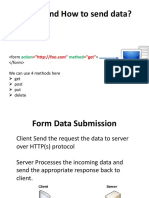
Submit process
Virtually every form should have one! Successful name/value pairs are attached to a request for the URL specified by the action attribute in the <form> tag The method attribute specifies the type of request made (and therefore how the data is attached)
On submission attach successful name/value pairs to an HTTP GET type request for this URL
<form method="get" action="http://a.server.com/script"> etc </form>
JISC Netskills
CSC1014
The GET method
When the user submits the form, browser makes an HTTP GET request for the processing URL
Successful form data is appended to the URL as a querystring The processing script will need to look in the querystring to extract data and use it
Querystring appended to URL
http:///formscript.php?inputbox=Arnold&choice=A
GET is the default method for all web requests (i.e. not actually restricted to use with forms)
Typed addresses in browser, links clicked in pages etc. Input data can be hard-coded directly in URLs/bookmarked e.g. http://www.google.com/search?hl=en&q=netskills
JISC Netskills
CSC1014
The POST method
Using method="post" browser makes an HTTP POST request for the processing URL
Specific method for carrying data to a server in the body of the request Form data sent in same format but in different part of request message The processing script will need to look in the querystring to extract data and use it
http:///formscript.php inputbox=Arnold&choice=A No querystring appended to URL Form data sent as name/value pairs in request body
POST needs to be specifically invoked usually via a form
Can be done programmatically using client-side scripting too
JISC Netskills
CSC1014
GET or POST for your form?
GET
Default method (used if no specific method supplied) Data submitted (including passwords!) visible in the querystring Results page can be bookmarked as data to rerun submission is stored in URL Refreshing a result page will repeat the submission with no warning Not suitable for large amount of data as URL is often truncated by browser Good for searches and simple applications where repeat submission not a problem
JISC Netskills
POST
Needs to be explicitly invoked via a form or script Submitted data not (easily) viewable as it sent in the request body Results pages cannot be bookmarked or returned to later as POST data is not stored User warned (by browser) before repeat action Can handle large amounts of data as post body can be any size Always use for login/password submissions
CSC1014
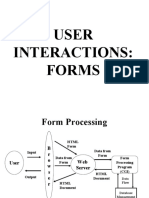
Handling form data
Once user has interacted with form, results must be processed Typically involves three stages: 1. Validation
Checking that the form has been completed and the correct type of data entered Extracting the submitted data and doing something useful with it (Optionally) returning something to the user
2. Processing 3. Feedback
JISC Netskills
CSC1014
Validation
Helps to ensure data submitted for processing is complete (required fields etc.) and consistent (format and type) Can be done client-side with JavaScript
Quick, efficient, better for usability Can be worked/disabled around by a malicious user Robust, potentially more powerful, can be slower Harder to work around if done correctly Specific database formats Eliminating malicious input etc.
Can be done server-side by web server application Is best done at both ends for data-sensitive applications
JISC Netskills
CSC1014
Processing (server side)
Submitted data typically passed through web server to a serverside scripting application
Typically via CGI (Common Gateway Interface) PHP, Perl, Python ASP and/or .NET Java etc.
Scripting application could be one of many
Application may carry out some validation (previous slide) then functionality depends on the task in hand
JISC Netskills
CSC1014
A simple form
<form method="get" action="http://a.server.com/formscript.php"> <fieldset><legend>About You</legend> Your name: <input type="text" name="username" /> <input type="submit" value="Submit Info" /> </fieldset> </form>
JISC Netskills
CSC1014
with some (very) simple client-side validation
<script type="text/javascript"> function validate() { if (document.forms[0].username.value == ""){ alert("Please fill in your name"); return false; } } </script> validate() runs and alerts user if box is empty then returns false stopping submit process and allowing user to correct error without reloading the page
<form method="get" action="http://a.server.com/formscript.php" onsubmit="return validate();"> <fieldset><legend>About You</legend> An event handler in the form Your name: <input type="text" name="username" /> forces a JavaScript function called validate() to run <input type="submit" value="Submit Info" /> when submit button pressed </fieldset> but before data is sent to </form> server
JISC Netskills
CSC1014
and then some (very) simple server-side processing (PHP)
http://a.server.com/formscript.php?username=Arnold Incoming request (with querystring) <?php if (isset($_GET["username"];)){ $NAME = $_GET["username"]; } ?> <html> <head> <title>My Form Results</title></head> <body> <h1>Form results</h1> <p>Your name is: <?=$NAME ?></p> </body> </html>
JISC Netskills
Simple server-side validation checks that querystring contains correct item (username) If it does then value is extracted and used in results page (feedback to user)
Form results
Your name is: Arnold
CSC1014
Practicalities
Creating a form-based user interface is very easy but Adding the functionality for validation and processing will involve some (often complex) programming Creating your own client-side validation using JavaScript is usually easier (and under your control) In practice you may find that your host/organisation provides some standard server-based form processing/validating scripts
Usually tailored to the server systems they run May not be possible to tailor, but may well be all you need
JISC Netskills
CSC1014
Reference URLs
W3Schools tutorial
http://www.w3schools.com/html/html_forms.asp http://www.webstandards.org/learn/tutorials/accessibleforms/beginner/ There are also intermediate and advance linked from the same place http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/interact/forms.html
Web Standards Project guide to accessible forms
W3C HTML forms specifications
JISC Netskills
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Developing Microsoft Dynamics GP Business ApplicationsDe la EverandDeveloping Microsoft Dynamics GP Business ApplicationsÎncă nu există evaluări
- HTML-Forms: Form's Information Your Web PageDocument10 paginiHTML-Forms: Form's Information Your Web PagevinsunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Creating Web Page Form: Faculty of Computer Science & EngineeringDocument32 paginiCreating Web Page Form: Faculty of Computer Science & EngineeringTrình PhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3Document90 paginiChapter 3aditya thoteÎncă nu există evaluări
- HTML Search Forms and CGI Programs GuideDocument27 paginiHTML Search Forms and CGI Programs GuideGautham LogarajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ip Slide NotesDocument7 paginiIp Slide Notesabumansoor52Încă nu există evaluări
- 6 - FormsDocument26 pagini6 - FormsNighat Ghafor GhaznawiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Conquer Forms With HTML5 and CSS3Document96 paginiConquer Forms With HTML5 and CSS3vaishali khairnarÎncă nu există evaluări
- WT-Program ManualDocument61 paginiWT-Program ManualNARENDRA YADAVÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Manual 03Document19 paginiLab Manual 03anjiya aliÎncă nu există evaluări
- HTML Forms: Course Instructor: Saadia ShehryarDocument35 paginiHTML Forms: Course Instructor: Saadia ShehryarSara MahmoodÎncă nu există evaluări
- HTML Forms With PHPDocument19 paginiHTML Forms With PHPRitik 2.0Încă nu există evaluări
- Internet and Web Programing Cse3002 E1Document7 paginiInternet and Web Programing Cse3002 E1Akshat SwaminathÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Sheet 03Document11 paginiLab Sheet 03tariqshah457Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit 2 FormsDocument34 paginiUnit 2 FormsAnjali KasaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- User Interactions: Form ProcessingDocument21 paginiUser Interactions: Form ProcessingAhmed AbedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 6 ModifiedDocument11 paginiLesson 6 ModifiedchathurangamadushanjayathilakaÎncă nu există evaluări
- HTML5 Forms GuideDocument56 paginiHTML5 Forms GuideBrandon StarkÎncă nu există evaluări
- WEEK 5. Introduction To Web ApplicationDocument17 paginiWEEK 5. Introduction To Web ApplicationsecretÎncă nu există evaluări
- ZongDocument56 paginiZongمحمد وقاص سعیدÎncă nu există evaluări
- It8078 Web Design and ManagementDocument60 paginiIt8078 Web Design and ManagementLokithÎncă nu există evaluări
- HtmlformsDocument21 paginiHtmlformscahcet eduÎncă nu există evaluări
- ASP SheetDocument59 paginiASP Sheetrachitapatel449Încă nu există evaluări
- Htmlforms-Lecture 3Document65 paginiHtmlforms-Lecture 3pharuna199Încă nu există evaluări
- HTML Forms and Css - Chapter 7 Topic - 1 Forms Objective Type QuestionsDocument22 paginiHTML Forms and Css - Chapter 7 Topic - 1 Forms Objective Type QuestionsVikas ShuklaÎncă nu există evaluări
- HTML Forms: East West UniversityDocument50 paginiHTML Forms: East West UniversityFaysal AhsanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Where and How To Send Data?: Action MethodDocument14 paginiWhere and How To Send Data?: Action MethodMuhammad HammadÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is CGI?: Gateway Interface Is A Standard For InterfacingDocument33 paginiWhat Is CGI?: Gateway Interface Is A Standard For InterfacingUmang Bhatt100% (1)
- DHTML EventsDocument14 paginiDHTML EventsRitesh Kumar 75Încă nu există evaluări
- PW1 05-Form+IntroPHP PDFDocument30 paginiPW1 05-Form+IntroPHP PDFThomas DelongeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Web Programming Unit-1 NotesDocument85 paginiWeb Programming Unit-1 NotesKadasi AbishekÎncă nu există evaluări
- HTML & CSS: Basic Web Dev LessonsDocument51 paginiHTML & CSS: Basic Web Dev LessonsBe Len DaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Web Designing and Web Technologies-IiDocument39 paginiWeb Designing and Web Technologies-IiSai SurveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 2 - Chapter 04 - Working With FormsDocument24 paginiUnit 2 - Chapter 04 - Working With FormsSnr Berel ShepherdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Other Technologies: Indian Institute of Technology KharagpurDocument21 paginiOther Technologies: Indian Institute of Technology KharagpurAbdul Ghani KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intro To Forms: HTML Forms Are Used To Gather A Form Can Contain Elements Like RadioDocument21 paginiIntro To Forms: HTML Forms Are Used To Gather A Form Can Contain Elements Like RadioAshutosh TrivediÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basics: Request Yields Input From The Browser GET or POSTDocument22 paginiBasics: Request Yields Input From The Browser GET or POSTjasbamraÎncă nu există evaluări
- It Is Intimated That Following Lectures Will Not Be Repeated and Would Be Part of Mid-Term& Final Exam As WellDocument17 paginiIt Is Intimated That Following Lectures Will Not Be Repeated and Would Be Part of Mid-Term& Final Exam As WellAdnan5035Încă nu există evaluări
- User Interactions: FormsDocument18 paginiUser Interactions: FormsSanthanakumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- FormsDocument11 paginiFormsSridhar TalariÎncă nu există evaluări
- WE LAB 1 - 2k18 (Part 2) - 2Document11 paginiWE LAB 1 - 2k18 (Part 2) - 2Muhammad AhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Web Technology Lab RCS-554: N.H. 58, Delhi-Roorkee Highway, Baghpat Road Bypass Crossing, Meerut-250005Document32 paginiWeb Technology Lab RCS-554: N.H. 58, Delhi-Roorkee Highway, Baghpat Road Bypass Crossing, Meerut-250005paras pandeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Codigo GS & HTML Trabajando Din ControlDocument5 paginiCodigo GS & HTML Trabajando Din ControljaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Common Gateway Interface) .: ObjectivesDocument50 pagini(Common Gateway Interface) .: ObjectivesAlfred AmponsahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 6Document32 paginiLecture 6kmani11811Încă nu există evaluări
- Web Design Programming Individual AssignmentDocument16 paginiWeb Design Programming Individual Assignmentsmengesha838Încă nu există evaluări
- Building Websites FormsDocument25 paginiBuilding Websites FormsHoàng ThịnhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reviewer in Computer 10Document7 paginiReviewer in Computer 10Krizzlyn FontelarÎncă nu există evaluări
- HTML5 Reference Poster PDFDocument1 paginăHTML5 Reference Poster PDFaryienneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Source Codes of Examples Practiced in ClassDocument21 paginiSource Codes of Examples Practiced in Classminchuu2330Încă nu există evaluări
- Lab 1 - HTML - GOOGLE FIREBASEDocument17 paginiLab 1 - HTML - GOOGLE FIREBASEHuy HuyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comp 6 Ms. Tumasis Soliman, Ma. Cristina B. Ab4EaDocument7 paginiComp 6 Ms. Tumasis Soliman, Ma. Cristina B. Ab4EaChuck SolimanÎncă nu există evaluări
- CS8661 - Ip ManualDocument89 paginiCS8661 - Ip ManualLOKESH V [34]Încă nu există evaluări
- Practical No:01: AIM: Develop Simple Servlet Question Answer Application To Demonstrate Use of Index - HTMLDocument53 paginiPractical No:01: AIM: Develop Simple Servlet Question Answer Application To Demonstrate Use of Index - HTMLAdeeb MehmoodÎncă nu există evaluări
- MVC 8 ValidationDocument11 paginiMVC 8 ValidationZain Alabeeden AlarejiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Web ADI - Oracle Custom WEB ADI Setups and Process For AP Invoice InterfaceDocument43 paginiWeb ADI - Oracle Custom WEB ADI Setups and Process For AP Invoice InterfaceHari HariÎncă nu există evaluări
- It Is Intimated That Following Lectures Will Not Be Repeated and Would Be Part of Mid-Term& Final Exam As WellDocument15 paginiIt Is Intimated That Following Lectures Will Not Be Repeated and Would Be Part of Mid-Term& Final Exam As WellAdnan5035Încă nu există evaluări
- Lab Task1 AwdDocument12 paginiLab Task1 Awd2023103475Încă nu există evaluări
- Web 4 UtpalDocument17 paginiWeb 4 UtpalSONU_KUMARÎncă nu există evaluări
- HTML Forms: © Krupa ShahDocument79 paginiHTML Forms: © Krupa ShahBCASEM517HIMALAYÎncă nu există evaluări
- 21 Regular Expressions PR TMDocument14 pagini21 Regular Expressions PR TManitkumardasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 11 CSS Box Model - PR - TMDocument16 pagini11 CSS Box Model - PR - TManitkumardasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 22 Practical Scripting PR TMDocument8 pagini22 Practical Scripting PR TManitkumardasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 20 Form Validation PR TMDocument6 pagini20 Form Validation PR TManitkumardasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 09 XHTML Standards & Validation - PR - TMDocument15 pagini09 XHTML Standards & Validation - PR - TManitkumardasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 14 CSS Browser Support - PR - TMDocument5 pagini14 CSS Browser Support - PR - TManitkumardasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 18 Javascript & XHTML Dom - PR - TMDocument12 pagini18 Javascript & XHTML Dom - PR - TManitkumardasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 19 DOM Event Handling - PR - TMDocument6 pagini19 DOM Event Handling - PR - TManitkumardasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 17 Javascript PR TMDocument16 pagini17 Javascript PR TManitkumardasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 12 CSS Positioning PR TMDocument19 pagini12 CSS Positioning PR TManitkumardasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 15 CSS Validation PR TMDocument2 pagini15 CSS Validation PR TManitkumardasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 04 Web Content Creation - PR - TMDocument9 pagini04 Web Content Creation - PR - TManitkumardasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10 CSS Essentials PR TMDocument23 pagini10 CSS Essentials PR TManitkumardasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 08 XHTML Tables PR TMDocument8 pagini08 XHTML Tables PR TManitkumardasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 07 XHTML Images & Multimedia - PR - TMDocument17 pagini07 XHTML Images & Multimedia - PR - TManitkumardasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 06 XHTML Tags & Attributes - PR - TMDocument29 pagini06 XHTML Tags & Attributes - PR - TManitkumardasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 02 How The Internet Works - PR - TMDocument13 pagini02 How The Internet Works - PR - TManitkumardasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 05 HTML & XHTML - PR - TMDocument18 pagini05 HTML & XHTML - PR - TManitkumardasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 01 What Is The Web - PR - TMDocument9 pagini01 What Is The Web - PR - TManitkumardasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 03 Web Architecture & HTTP - PR - TMDocument17 pagini03 Web Architecture & HTTP - PR - TManitkumardasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Source CodeDocument14 paginiSource Codeemmannuuell100% (1)
- Onsen Ui DumpDocument3 paginiOnsen Ui DumpMahesh VPÎncă nu există evaluări
- Math Omir ManualDocument83 paginiMath Omir ManualInex PlicávelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Web Easy v8Document96 paginiWeb Easy v8x01001932Încă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To AutoCADDocument11 paginiIntroduction To AutoCADJiji MacasoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Beginning Excel 2019Document387 paginiBeginning Excel 2019Tinashe MurindagomoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 50 AutoCAD TipsDocument18 pagini50 AutoCAD TipsAleksandar Stefanovic100% (1)
- ShinobiDocument5 paginiShinobiVika VigneshvikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Free Proxy Lists - HTTP Proxy Servers (IP Address, Port)Document2 paginiFree Proxy Lists - HTTP Proxy Servers (IP Address, Port)mojiee25% (8)
- OCTOPUS6 user guideDocument81 paginiOCTOPUS6 user guideAnuraag Srivastava100% (4)
- Android Windows7 Installation InstructionsDocument3 paginiAndroid Windows7 Installation Instructionsanaksebelah100% (1)
- MacOffice 1985Document350 paginiMacOffice 1985KoWunnaKoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Python GUI Examples (Tkinter Tutorial)Document18 paginiPython GUI Examples (Tkinter Tutorial)LeonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test Case For Google Web PageDocument12 paginiTest Case For Google Web PageDhiraj Chaudhari 137 CoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Codename One Developers GuideDocument212 paginiCodename One Developers GuidemenhoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jquery mCustomScrollbarDocument10 paginiJquery mCustomScrollbarPatrick Jullian Rodriguez MejiasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scribd Premium CookieDocument6 paginiScribd Premium CookieZnerskiscribdtrialÎncă nu există evaluări
- LISTING PROGRAM DoneDocument41 paginiLISTING PROGRAM DoneDarmawan HanifÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 3 Part 2 MS ExcelDocument17 paginiModule 3 Part 2 MS ExcelADITYA KUMARÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aalan Sason Singarayan A: Sri Ambal Vidhyalaya (Cbse), Vilathikulam-Srm University, Ramapuram - BtechDocument1 paginăAalan Sason Singarayan A: Sri Ambal Vidhyalaya (Cbse), Vilathikulam-Srm University, Ramapuram - BtechAalan sason Singarayan AÎncă nu există evaluări
- MS Word 2010 EssentialsDocument12 paginiMS Word 2010 EssentialsKimberly Quin CanasÎncă nu există evaluări
- SAP Business One Web Browser Access LimitationsDocument4 paginiSAP Business One Web Browser Access Limitationsvictor odtohanÎncă nu există evaluări
- SAP Navigation Training2Document68 paginiSAP Navigation Training2ladystarrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Essential Windows UI ElementsDocument7 paginiEssential Windows UI ElementsMangalmay ChannelÎncă nu există evaluări
- ASSA GAMING PAD 22881 - Advancedmanuals - VA - 1-1Document78 paginiASSA GAMING PAD 22881 - Advancedmanuals - VA - 1-1eliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toolbox Log SnapshotDocument11 paginiToolbox Log Snapshotpe causaÎncă nu există evaluări
- GB Assessment Test (Gbat) : #Covid-19. Stay Safe, Stay EducatedDocument9 paginiGB Assessment Test (Gbat) : #Covid-19. Stay Safe, Stay EducatedJASON50% (2)
- User Interface 1: Swing ComponentsDocument6 paginiUser Interface 1: Swing ComponentsCliezl Bautista NguhoÎncă nu există evaluări
- H 1305 GDocument376 paginiH 1305 GdavilimaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Form Sys Time LimitDocument7 paginiForm Sys Time LimitPhạm Minh KhôiÎncă nu există evaluări