Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Scheme Mid Year Exam f42012
Încărcat de
Faida HamidDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Scheme Mid Year Exam f42012
Încărcat de
Faida HamidDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
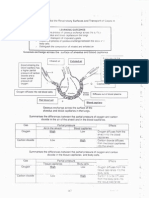
Question 1(a) (i) 1 ( a ) ( ii ) 1(a) ( iii ) 1(a) ( iv ) 1(a)(v ) 1(a) ( vi )
Description Bottom test tube touch the beaker Even /uniform heating 80C Solid and liquid At E kinetic energy is low , at F kinetic energy increase
Marks 1 1 1 1 1 2
60C Minimum 3 layers 1(b) No overlapping between atoms Process : diffusion Explanation: particles move randomly // freely
90C
1 1 1
From higher concentration region to lower concentration 2(a) (i) 2 ( a ) ( ii ) 2(a) ( iii ) 2(a) ( iv ) region Bromine and phenol Liquid Nickel
1 1 1 1
2(a)(v ) 2(b) (i)
Ion P : Liquid S: Solid
1 2
2 ( b ) ( ii )
2(b) ( iii ) 2(b) ( iv )
Particles of Q held together by weak intermolecular forces // A small / less amount of energy required to the forces
1 1
3(a) 3(b) (i) 3 ( b ) ( ii ) 3(c) (i) 3 ( c ) ( ii ) 3(d)
Proton , electron , neutron Total number of proton and neutron in the nucleus of an atom Reject : neutron numbers 17
24 12Y
1 1
1 1 1
3(e) (i) 3 ( e ) ( ii ) 3(f) 4(a)
Atoms of the same element which have same number of proton but different number of neutron // came proton number but different nucleon number W and X Group 16 , period 2 Volume = 0.06 dm3
0.06 = 0.0025 mol 24 No of molecules = 0.0025 6.02 10 23
1 2 1 1 1 1
No of moles = 4(b) (i) 4 ( b ) ( ii
= 1.505 10 21 molecules
4.515 10 21 atoms
) 4(c) (i) 4 ( c ) ( ii ) 4 ( c ) ( iii ) 4(d) 4(e) 5(a)
100 0.25 mol
48 100% = 48% 100
1 1 1 1 1 1
n=6 molecular formula = C6H12 Cu + 2 AgNO3 Cu(NO3)2 + 2 Ag Name of compound Lead (II) sulphate Aluminium oxide Calcium hydroxide 3 ( 2 marks ) 2 ( 1 marks ) Mg + 2 HNO3 Mg(NO3)2 + H2 Pb(NO3)2 + 2KI PbI2 + 2 KNO3 Chemical formula of compound PbSO4 Al2O3 Ca(OH)2
5(b) (i) 5 ( b ) ( ii ) 5(c)
1 1
5(d)
6(a)
W : Sulphuric acid // hydrochloric acid Y : Zinc // Magnesium // Aluminium Z : Anhydrous calcium chloride Collect the gas from the small hole in the test tube and put a burning wooden splinter in test tube No pop sound produced Copper : 1.16 g Oxygen : 0.29 g
1 1 1 1 1 1
6(b)
6(c) 6(d)
1 6(e) 6(f) Empirical formula = XO // CuO No reaction happened Cannot Magnesium is reactive metal SECTION B Question 7(a)(i) 7 ( a ) ( ii ) Description 18 and 20 respectively Similarities 1. having same proton number / number of electrons Differences 1. different in the number of neutron / nucleon number 2. different in physical properties Marks 1 1 1 [ free mark] 1 1
1 1
7(b)(i) 7 ( b ) ( ii )
2.having same valence electron / have same chemical proiperties Group 14 , period 2 Nucleus contains 6 proton and 6 neutron
1 1
Electrons move around the nucleus Two shells filled with electrons There are 6 valence electrons // electron arrangement 2.4 [accept any other suitable answers]
1 1 1 Max : 3
7 ( b ) ( iii ) Comparison Proton number Number of valence electron Chemical properties Number of neutron // nucleon number Physical properties Standard representation of element 7(c)(i) Diagram 7.2 6 4 similar 6 // 12 Different different S atom Any 4 6 4 Similar 7 // 13 Different different
7 ( c ) ( ii )
Substance X in both solid and liquid state Heat energy is released Kinetic energy of particles decreases They are closer to each other // attraction force between particles become stronger Number of mole in 16 g of oxygen = 16/32 // 0.05 mol Volume occupied by 16 g of oxygen = 0.05 24 // 12 dm3 Number of mole in 22g of CO2 = 22/44 // 0.05 mole Volume occupied by 22g of CO2 = 0.05 24 // 12 dm3 Able to determine empirical formula and molecular formula correctly Element Mass /g No of mole Simplest ratio no of mole C 0.48 0.48/12 //0.04 0.04/0. 01 //4 H 0.05 0.05/1 //0.05 0.05/0. 01 //5 N 0.28 0.28/14 //0.02 0.02/0. 01 //2 O 0.16 0.16/16 //0.01 0.01/0. 01 //1
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
8(a)
8(b)
Empirical formula = C4H5N2O [C4H5N2O] = 194 [ 97 ]n = 194 N = 194/97 // 2 8(c) Molecular formula = C8H10H4O2 Able to calculate the molar mass and the percentage of nitrogen by mass in each of the three fertilisers and choose the best fertiliser 1. molar mass of ammonium sulphate = 132g/mol 2. percentage of nitrogen in ammonium sulphate = 21.2% 3. molar mass of urea = 60g/mol 4. Percentage of nitrogen in urea = 46.7% 5. molar mass of hydrazine = 32 g/mol 6. percentage of nitrogen in hydrazine = 87.5% 7. hydrazine has the richest source of nitrogen compares with other fertilisers. 9(a) 8. the farmer should choose hydrazine Process : freezing Particles of the compound arrange closer to each other // stronger forces of attraction formed among the particles This will release energy The energy released is equal to the heat energy lost to the 9(b)(i) 9 ( b ) ( ii ) temperature Arrangement of particles Movement of particles 80C Particles are orderly and closely packed together Vibrating and rotating about in their fixed positions The forces of strong 280C Particles are far apart Particles move randomly and rapidly in all directions Weak high 1 1 1 1 surrounding At 80C = Solid At 280C = Gas 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
9 ( b ) ( iii )
attraction Kinetic energy Low 1 mark for each comparison Able to describe the procedure correctly of 3 cm
1. a boiling tube is filled with powder of compound M to a depth 1 1
2. a thermometer is placed into powder of compound M in the boiling tube 3. a 500ml beaker is filled with coconut oil / palm oil until full 4. the beaker is then placed on a tripod stand 5. the boiling tube containing compound M is clamped onto a retort stand and immersed into the coconut oil / palm oil in the beaker 6. the coconut oil / palm oil is heated slowly and the stopwatch is started 7. the powder of compound M is stirred slowly with the thermometer 8. the temperature of the compound M is recorded at 30 seconds intervals until the compound M has melted completely Result : The temperature reading are recorded in a table as shown below.
1 1 1 1 1 1 Max : 6
The graph of temperature against time for the heating of compound M is plotted 1 1
Conclusion: Based on the graph, the temperature remains constant at TC (must indicate T in the graph) 10 ( a ) Therefore, the melting point of compound M is TC Molecular formula is a formula that shows the actual no of atom of each element in the compound
10 ( b )
10 ( c )
Procedure : 1. clean magnesium ribbon with sand paper 2. weigh crucible and its lid 3. put magnesium ribbon into the crucible and weigh the crucible with its lid 4. heat strongly the crucible without its lid 5. cover the crucible when the magnesium starts to burn and lift / raise the lid a little at intervals 6. remove the lid when the magnesium burnt completely 7. heat strongly the crucible for a few minutes 8. cool and weigh the crucible with its lid and the content 9. repeat the processes of heating , cooling and weighing until a constant mass is obtained 10 record all the mass 11. results :
Description Mass of crucible + lid Mass of crucible + lid + magnesium Mass of crucible + lid + magnesium oxide Mass (g) X Y z
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 1
12. calculations :
Element Mass (g) Number of mole of atoms Simplest ratio of moles / Mg yx yx 24 p O zy zy 16 q
1 1 Max : 12
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- Scheme Mid Year Exam f52012Document9 paginiScheme Mid Year Exam f52012Faida HamidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scheme Mid Year Exam f52012Document9 paginiScheme Mid Year Exam f52012Faida HamidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Module Chap 9Document21 paginiBiology Module Chap 9Faida HamidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Module Chap 8Document37 paginiBiology Module Chap 8Faida Hamid100% (4)
- Scheme Mid Year Exam f42012Document9 paginiScheme Mid Year Exam f42012Faida HamidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiration Chapter 7 Biology Form 4Document90 paginiRespiration Chapter 7 Biology Form 4Faida Hamid87% (23)
- Basic Formula For ChemistryDocument2 paginiBasic Formula For ChemistryFaida HamidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Module Chap 7Document14 paginiBiology Module Chap 7Faida Hamid100% (4)
- Biology Scheme Pertgh Penggal 2Document9 paginiBiology Scheme Pertgh Penggal 2Athirah Maestro100% (1)
- Biology Ques Pertgh Penggal 2Document7 paginiBiology Ques Pertgh Penggal 2Faida Hamid100% (2)
- Absorption of Digested FoodDocument18 paginiAbsorption of Digested FoodFaida HamidÎncă nu există evaluări
- MID-YEAR EXAMINATION (Chapter 1 To Chapter 6) : One Answer From The Options A, B, C and DDocument5 paginiMID-YEAR EXAMINATION (Chapter 1 To Chapter 6) : One Answer From The Options A, B, C and DFaida HamidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mind Map For Science Year 5Document43 paginiMind Map For Science Year 5usemyknow.blogspot.com100% (11)
- DC-DC Converter FundamentalsDocument63 paginiDC-DC Converter FundamentalsFaida HamidÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- TSP-408L-1 P/N 32441-002: ApplicationDocument2 paginiTSP-408L-1 P/N 32441-002: ApplicationSajjad ShamimÎncă nu există evaluări
- 11 5 Temperature and Pressure 4th EdDocument18 pagini11 5 Temperature and Pressure 4th Edapi-267245178Încă nu există evaluări
- Fabric Expansion JointsDocument28 paginiFabric Expansion Jointswarmachine269889Încă nu există evaluări
- Objective and Scope and Importance of Mineral Beneficiation With Special Reference To IndiaDocument4 paginiObjective and Scope and Importance of Mineral Beneficiation With Special Reference To IndiaVidya Sagar100% (1)
- Transfer Switching Equipment 100, 200, 260, 400A: Instr Uction ManualDocument32 paginiTransfer Switching Equipment 100, 200, 260, 400A: Instr Uction ManualMesseňger HệŢhốngÎncă nu există evaluări
- Operation Manual - WSRF-50Document175 paginiOperation Manual - WSRF-50eduardo100% (2)
- Euler-Ship Mast LocationDocument61 paginiEuler-Ship Mast LocationzeldaikÎncă nu există evaluări
- SMT - Kashibai Navale College of Engineering, Vadgaon Pune: Heat TransferDocument8 paginiSMT - Kashibai Navale College of Engineering, Vadgaon Pune: Heat TransferFS18ME046 MAYUR NikamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pressure MeasurementDocument19 paginiPressure MeasurementShadmanSakiefHridoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Design Considerations for Chemical Plant DesignDocument27 paginiGeneral Design Considerations for Chemical Plant DesignTeddy Ekubay GÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Properties of Materials Mod-1Document18 paginiElectrical Properties of Materials Mod-1Darshan rajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kalina Cycle and Cement IndustryDocument8 paginiKalina Cycle and Cement IndustryEhab SabryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bomba Electrica 1500gpm 300HP (Medidas)Document1 paginăBomba Electrica 1500gpm 300HP (Medidas)Fire ChileÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCQ 140Document14 paginiMCQ 140Aawez AkhterÎncă nu există evaluări
- KPSC/ KSEB/ SSC Electrical Score Academy: Questions: 75Document9 paginiKPSC/ KSEB/ SSC Electrical Score Academy: Questions: 75sreevasanthÎncă nu există evaluări
- Installation Instructions: Mico Basic 8.6Document2 paginiInstallation Instructions: Mico Basic 8.6Servizio TecnicoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Every Emergency.: C Safe Marine Generator SetsDocument4 paginiEvery Emergency.: C Safe Marine Generator SetsBrillyanÎncă nu există evaluări
- WM2077CW Service ManualDocument44 paginiWM2077CW Service ManualMichael David SharkeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rectification ProcessDocument5 paginiRectification ProcessDilnaz TegispayÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6ra 2620 6d v57 1a Z Simoreg d38035 Siemens Manual 02Document18 pagini6ra 2620 6d v57 1a Z Simoreg d38035 Siemens Manual 02Stefan IstratescuÎncă nu există evaluări
- High Efficiency Battery Charger Using DC-DC ConverterDocument4 paginiHigh Efficiency Battery Charger Using DC-DC ConvertersanilÎncă nu există evaluări
- R6.3 TR-XXL Parameter Settings ReleaseDocument493 paginiR6.3 TR-XXL Parameter Settings Releasemishu35Încă nu există evaluări
- Assessing The Impact of Industrial RobotsDocument14 paginiAssessing The Impact of Industrial RobotsKarthik SRSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fire Pump Installation GuideDocument3 paginiFire Pump Installation GuideJeff D. AgustinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rpdir-L12 Shielding WebDocument73 paginiRpdir-L12 Shielding WebWiie ArdiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genie GTH 4013Document202 paginiGenie GTH 4013Sam Manutenção100% (2)
- TERAO Presentation August 2022Document48 paginiTERAO Presentation August 2022LuatNguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sungris BrochureDocument8 paginiSungris Brochurechemasi123Încă nu există evaluări
- Specialist Water Supply Systems PP-R pipe system Ensure reliabilityDocument16 paginiSpecialist Water Supply Systems PP-R pipe system Ensure reliabilitymabj68Încă nu există evaluări
- Damper mechanism details for Atlas Copco rock drills under 40 charactersDocument27 paginiDamper mechanism details for Atlas Copco rock drills under 40 characterssalvador341100% (2)