Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
List of Antibiotics
Încărcat de
desi_mDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
List of Antibiotics
Încărcat de
desi_mDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
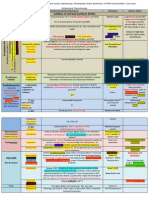
List of antibiotics
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Following is the list of antibiotics, sorted by class. The highest division is between bactericidal antibiotics and bacteriostatic antibiotics. Bactericidals kill bacteria directly where bacteriostatics prevent them from dividing. However, these classifications are based on laboratory behavior; in practice, both of these are capable of ending a bacterial infection.[1] See also pathogenic bacteria for a list of antibiotics sorted by target bacteria.
Antibiotics by class
Generic name
Brand names
Common uses[2]
Possible side effects[2]
Mechanism of action
Aminoglycosides Binding to the bacterial 30S ribosoma l subunit (some work by binding to the50S subunit), Hearing loss inhibiting the translocation of the Vertigo peptidyl-tRNA from the A-site to the P-site Kidney and also causing damage misreading of mRNA, leaving the bacterium unable to synthesize proteins vital to its growth.
Amikacin Gentamicin Kanamycin Neomycin Netilmicin Tobramycin
Amikin Garamycin Kantrex
[3]
Neo-Fradin
Netromycin Nebcin
Infections caused by Gramnegative bacteria, such as Escherichia coli and Klebsiellaparticularly Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Effective against Aerobic bacteria (not obligate/facultative anaerobes) and tularemia.
Paromomycin
Humatin
Ansamycins Geldanamycin Herbimycin Experimental, as antitumor antibiotics Carbacephem Loracarbef Lorabid Discontinued Carbapenems Ertapenem Doripenem Imipenem/Cilastatin Invanz Doribax Primaxin Bactericidal for both Gram positive and Gram-negative organisms and therefore useful Gastrointesti Inhibition of cell wall synthesis nal upset and prevents bacterial cell division by inhibiting cell wall synthesis.
for empiric broad-spectrum antibacterial coverage. (Note MRSA resistance to this class.) Meropenem Merrem
diarrhea Nausea Seizures Headache Rash and allergic reactions
Cephalosporins (First generation) Cefadroxil Cefazolin Duricef Ancef (discontinued) Good coverage against Gram positive infections. Gastrointesti nal upset and Same mode of action as other beta-lactam Nausea (if antibiotics: disrupt the synthesis of alcohol taken the peptidoglycan layer concurrently) of bacterial cell walls. diarrhea Allergic reactions Cephalosporins (Second generation) Cefaclor Cefamandole Cefoxitin Cefprozil Distaclor Mandol (discontinued) Mefoxin (discontinued) Cefzil Ceftin, Zinnat (UK) Less gram positive cover, improved gram negative cover. Gastrointesti nal upset and Same mode of action as other beta-lactam Nausea (if antibiotics: disrupt the synthesis of alcohol taken the peptidoglycan layer concurrently) of bacterial cell walls. diarrhea Allergic reactions Cephalosporins (Third generation) Cefixime Cefdinir Cefditoren Cefoperazone Cefotaxime Cefpodoxime Ceftazidime Suprax Omnicef, Cefdiel Spectracef Cefobid (discontinued) Claforan Vantin Fortaz Gastrointesti nal upset and Improved coverage of Gram negative organisms, except Pseudomonas. Reduced Gram positive cover. diarrhea Same mode of action as other beta-lactam antibiotics: disrupt the Nausea (if synthesis of alcohol taken the peptidoglycan layer of bacterial cell walls. concurrently) Allergic
Cefalotin or Cefalothi Keflin n (discontinued)
Cefalexin
Keflex
Cefuroxime
Ceftibuten Ceftizoxime Ceftriaxone
Cedax Cefizox (discontinued) Rocephin Cephalosporins (Fourth generation)
reactions
Gastrointesti nal upset and Same mode of action as other beta-lactam Nausea (if antibiotics: disrupt the synthesis of alcohol taken the peptidoglycan layer concurrently) of bacterial cell walls. diarrhea Allergic reactions
Cefepime
Maxipime
Covers pseudomonal infections.
Cephalosporins (Fifth generation) Gastrointesti Same mode of action nal upset and as other beta-lactam antibiotics: disrupt the diarrhea synthesis of the peptidoglycan layer Allergic of bacterial cell walls. reaction Gastrointesti nal upset and Same mode of action as other beta-lactam Nausea (if antibiotics: disrupt the synthesis of alcohol taken the peptidoglycan layer concurrently) of bacterial cell walls. diarrhea Ceftobiprole Zeftera Used to treat MRSA Allergic reactions Glycopeptides Teicoplanin Vancomycin Telavancin Targocid (UK) Vancocin Vibativ Lincosamides Clindamycin Lincomycin Cleocin Lincocin Serious staph-, pneumo-, and streptococcal infections in penicillin-allergic patients, also anaerobic infections; Possible C. difficilerelatedpseudome mbranous Bind to 50S subunit of bacterial ribosomal RNA thereb y inhibiting protein inhibiting peptidoglyca n synthesis
Ceftaroline fosamil
Teflaro
Used to treat MRSA
clindamycin topically foracne enterocolitis Lipopeptide
synthesis
Daptomycin
Cubicin
Gram-positive organisms
Bind to the membrane and cause rapid depolarization, resulting in a loss of membrane potential leading to inhibition of protein, DNA and RNA synthesis
Macrolides Azithromycin Clarithromycin Dirithromycin Erythromycin Roxithromycin Zithromax,Sum amed, Zitrocin Biaxin Dynabac (discontinued) Streptococcal Erythocin,Eryt infections, syphilis, upper hroped respiratory tract infections, lower respiratory tract infections, mycoplasmal infections, Lyme disease Tao (discontinued) Telithromycin Spectinomycin Spiramycin Ketek Trobicin Rovamycine Pneumonia Gonorrhea Mouth infections Monobactams Same mode of action as other beta-lactam antibiotics: disrupt the synthesis of the peptidoglycan layer of bacterial cell walls. Nitrofurans Furazolidone Furoxone Bacterial or protozoal diarrhea or enterit is Nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea (especially at higher doses) inhibition of bacterial protein Prolonged biosynthesis by QT interval binding reversibly to the subunit50S of the (especially bacterial ribosome, thereby inhibiting erythromycin translocation of ) peptidyl tRNA. Jaundice
Troleandomycin
Visual Disturbance, Liver Toxicity.[4]
Aztreonam
Azactam
Nitrofurantoin
Macrodantin,M Urinary tract infections acrobid Penicillins
Amoxicillin
Novamox,Amo Wide range of infections;
Gastrointesti
Same mode of action
xil Ampicillin Azlocillin Carbenicillin Cloxacillin Dicloxacillin Geocillin (discontinued) Tegopen (discontinued) Dynapen (discontinued) Floxapen(Sold to European generics Actavis Group) Mezlin (discontinued) Staphcillin (discontinued) Unipen (discontinued) Prostaphlin (discontinued) Pentids (discontinued) Veetids (PenVee-K) (discontinued) Pipracil (discontinued) Pfizerpen Negaban (UK) (discontinued) Ticar (discontinued) Principen (discontinued)
penicillin used forstreptococcal infections, syphilis, and Lyme disease
as other beta-lactam nal upset and antibiotics: disrupt the synthesis of diarrhea the peptidoglycan layer Allergy with of bacterial cell walls. seriousanaph ylactic reactions
Brain and kidney damage (rare)
Flucloxacillin
Mezlocillin Methicillin Nafcillin Oxacillin Penicillin G
Penicillin V
Piperacillin Penicillin G Temocillin Ticarcillin
Penicillin combinations Amoxicillin/clavulanat Augmentin e Ampicillin/sulbactam Piperacillin/tazobacta m Unasyn Zosyn
The second component prevents bacterial resistance to the first component
Ticarcillin/clavulanate Timentin Polypeptides Bacitracin Eye, ear or bladder infections; Kidney and nerve Inhibits isoprenyl usually applied directly to the damage (when pyrophosphate, a
Colistin
Coly-Mycin-S
eye or inhaled into the lungs; given by rarely given by injection, injection) although the use of intravenous colistin is experiencing a resurgence due to the emergence of multi drug resistantorganisms.
molecule that carries the building blocks of the peptidoglycan bact erial cell wall outside of the inner membrane [5] Interact with the gram negative bacterial outer membrane and cytopla smic membrane. It displaces bacterial counter ions, which destabilizes the outer membrane. They act like a detergent against the cytoplasmic membrane, which alters its permeability. Polymyxin B and E are bactericidal even in an isosmotic solution.
Polymyxin B
Quinolones Ciprofloxacin Enoxacin Gatifloxacin Levofloxacin Lomefloxacin Moxifloxacin Nalidixic acid Norfloxacin Ofloxacin Trovafloxacin Grepafloxacin Sparfloxacin Temafloxacin Cipro,Ciproxin, Ciprobay Penetrex Tequin Levaquin Maxaquin Avelox NegGram Noroxin Floxin, Ocuflox Trovan Raxar Zagam Omniflox Urinary tract infections, bacterial prostatitis, communityNausea (rare), acquired pneumonia, bacterial irreversible diarrhea, mycoplasmal damage to central infections, gonorrhea nervous system(uncommo n), tendinosis (rare) Withdrawn Withdrawn Withdrawn Withdrawn Sulfonamides Mafenide Sulfamylon Urinary tract infections (except sulfacetamide, used for eye infections, and mafenide and silver sulfadiazine, used topically for burns) Sulfonamidochrysoidi Prontosil ne(archaic) Sulfacetamide Sulfadiazine Silver sulfadiazine Sulamyd, Bleph-10 Micro-Sulfon Silvadene Folate synthesis inhibition. They are competitive vomiting, inhibitors of the and diarrhea enzymedihydropteroate Allergy(inclu synthetase, DHPS. DHPS catalyses the ding skin conversion of PABA Nausea,
inhibit the bacterial DNA gyrase or the topoisomerase IV enzyme, thereby inhibiting DNA replica tion and transcription.
Sulfamethizole Sulfamethoxazole Sulfanilimide (archaic) Sulfasalazine Sulfisoxazole
Thiosulfil Forte Gantanol
rashes) Crystals in urine Kidney failure Decrease inwhite
Azulfidine Gantrisin
Trimethoprim
Proloprim, Trimpex
blood cellcount Sensitivity to sunlight
(para-aminobenzoate) to dihydropteroate, a key step in folate synthesis. Folate is necessary for the cell to synthesize nucleic acids (nucleic acids are essential building blocks of DNA and RNA), and in its absence cells will be unable to divide.
TrimethoprimSulfamethoxazole(CoBactrim, Septra trimoxazole) (TMPSMX) Tetracyclines Demeclocycline Doxycycline Minocycline Oxytetracycline Declomycin Vibramycin Minocin Terramycin Gastrointesti nal upset Sensitivity to sunlight Potential toxicity to Syphilis, chlamydial infection s, Lyme disease,mycoplasmal infections, acne rickettsialinfections, *malaria *Note: Malaria is Sumycin,Achro caused by a protist and not a mycin bacterium. V, Steclin mother and fetus during pregnancy Enamel hypoplasia (staining of teeth; potentially permanent) transient depression of bone growth Drugs against mycobacteria inhibiting the binding of aminoacyl-tRNA to the mRNAribosome complex. They do so mainly by binding to the 30S ribosomal subunit in the mRNA translationcomplex.
Tetracycline
Clofazimine Dapsone Capreomycin Cycloserine Ethambutol Ethionamide Isoniazid Pyrazinamide
Lamprene Avlosulfon Capastat Seromycin Myambutol Trecator I.N.H. Aldinamide
Antileprotic Antileprotic Antituberculosis Antituberculosis, urinary tract infections Antituberculosis Antituberculosis Antituberculosis Antituberculosis mostly Grampositive and mycobacteria Mycobacterium avium complex Antituberculosis Antituberculosis Others Neurotoxicity,otot As oxicity other aminoglycosides Reddish-orange sweat, tears, and urine rash, discolored urine, GI symptoms Binds to the subunit of RNA polymerase to inhibit transcription Inhibits peptide synthesis
Rifampicin (Rifampin Rifadin, in US) Rimactane
Rifabutin Rifapentine Streptomycin
Mycobutin Priftin
Arsphenamine
Salvarsan
Spirochaetal infections (obsolete) Inhibits bacterial protein synthesis by binding to the 50S subunit of the ribosome Inactivates enolpyruvyl transferase, thereby blocking cell wall synthesis
Chloramphenicol
meningitis, MRSA, topical use, or for low cost internal treatment. Rarely: aplastic Chloromycetin Historic: typhus, cholera.gram anemia. negative, gram positive, anaerobes
Fosfomycin
Monurol
Acute cystitis in women
Fusidic acid Linezolid
Fucidin Zyvox VRSA Thrombocytopeni a
Metronidazole
Flagyl
Produces toxic free radicals which disrupt Discolored DNA and proteins. Infections caused by anaerobic urine,headache, m This non-specific bacteria; etallic mechanism is alsoamoebiasis, trichomoniasi taste, nausea ;alco responsible for its s, Giardiasis hol is activity against a contraindicated variety of bacteria, amoebae, and protozoa. Ointment for impetigo, cream
Mupirocin
Bactroban
for infected cuts Platensimycin Quinupristin/Dalfopris Synercid tin Rifaximin Xifaxan Traveler's diarrhea caused by E. coli A chloramphenicol analog. May inhibit bacterial protein synthesis by binding to the 50S subunit of the ribosome
Thiamphenicol
Gram-negative, Grampositive, anaerobes. widely used in veterinary medicine.
Lacks known anemic sideeffects.
Tigecycline Tinidazole
Tigacyl Tindamax Fasigyn Brand Names protozoan infections Common Uses[2] upset stomach, bitter taste, and itchiness Possible Side Effects[2] Mechanism of action
Generic Name
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Adult Infectious Disease Bulletpoints HandbookDe la EverandAdult Infectious Disease Bulletpoints HandbookEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (9)
- List of AntibioticsDocument8 paginiList of AntibioticsMiguel Angel Ortega100% (1)
- Antibiotics PDFDocument8 paginiAntibiotics PDFSarah JaneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmacology - Chapter 29Document5 paginiPharmacology - Chapter 29Ashley-Michelle LewisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gram Positive Bacteria: Antibacterial DrugsDocument4 paginiGram Positive Bacteria: Antibacterial DrugsMOHAMAD HASSOUNAÎncă nu există evaluări
- List of Antibiotics: Following Is The List Of, Sorted by Class. The Highest Division Is BetweenDocument11 paginiList of Antibiotics: Following Is The List Of, Sorted by Class. The Highest Division Is BetweenBhanuprakash PuthalapattuÎncă nu există evaluări
- AntibioticsDocument11 paginiAntibioticsSeshu Kelam100% (2)
- AntibioticsDocument9 paginiAntibioticsprince1500100% (1)
- Overview of AntibioticsDocument5 paginiOverview of AntibioticsakshahinbdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Generic Name Brand Names Common Uses Possible Side Effects Mechanism of ActionDocument13 paginiGeneric Name Brand Names Common Uses Possible Side Effects Mechanism of Actionangel3424Încă nu există evaluări
- List of AntibioticsDocument10 paginiList of AntibioticsAia JavierÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Effective: Antibiotics by ClassDocument4 paginiPseudomonas Aeruginosa. Effective: Antibiotics by ClassDocFrankÎncă nu există evaluări
- List of AntibioticsDocument11 paginiList of AntibioticsD. BarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing NotesDocument6 paginiNursing NotesLinguumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antibiotics by ClassDocument9 paginiAntibiotics by ClassHerlin Ajeng NurrahmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- AntibioticsDocument10 paginiAntibioticsStevhenson PortacioÎncă nu există evaluări
- List of Antibiotics - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument11 paginiList of Antibiotics - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaRamesh KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antibiotics by ClassVITEK-Bus-Module-1-Antibiotic-Classification-and-Modes-of-Action-1.pDocument6 paginiAntibiotics by ClassVITEK-Bus-Module-1-Antibiotic-Classification-and-Modes-of-Action-1.pJameston BostreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antimicrobials MD 3 GISDocument26 paginiAntimicrobials MD 3 GISmus zaharaÎncă nu există evaluări
- List of Antibiotics - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument13 paginiList of Antibiotics - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaAhsan Tanio DaulayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Protein Synthesis InhibitorsDocument28 paginiProtein Synthesis InhibitorsMaha JabeenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmacology-Antibiotic 2021Document52 paginiPharmacology-Antibiotic 2021Ngọc VânÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmacotherapy of ENT InfectionsDocument86 paginiPharmacotherapy of ENT InfectionsHoque Mohammed Newaz ShorifulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemotherapeutic DrugsDocument122 paginiChemotherapeutic Drugsdex7reme100% (1)
- A. Chemical StructureDocument34 paginiA. Chemical StructureAmit GaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing 3703 Pharmacology: Antimicrobials by Linda SelfDocument78 paginiNursing 3703 Pharmacology: Antimicrobials by Linda Selfdon yenÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.sulfonamide FinalDocument31 pagini1.sulfonamide FinalPrasad SangishettyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inhibitor of Cell Wall Synthesis (ICWS) : Proteus ComboDocument12 paginiInhibitor of Cell Wall Synthesis (ICWS) : Proteus Comboflomax23100% (1)
- Farmakologi AntiparasitDocument119 paginiFarmakologi AntiparasitFitri Sri WulandariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antibiotics: Microbial Control Antimicrobial AgentsDocument25 paginiAntibiotics: Microbial Control Antimicrobial AgentsMohammed Moutasim AyoubÎncă nu există evaluări
- AntibacterialsDocument8 paginiAntibacterialslisalynnleeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmacology AntibioticsDocument70 paginiPharmacology Antibioticsmaggie100% (1)
- Question 7 Mechanism of Action of Antibiotic Surgical Infection TBLDocument22 paginiQuestion 7 Mechanism of Action of Antibiotic Surgical Infection TBLKartik KumarasamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cephalosporins, Flouroquinolones and SulfonamidesDocument7 paginiCephalosporins, Flouroquinolones and SulfonamidesErum JanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aminoglycoside AntibioticsDocument36 paginiAminoglycoside AntibioticsGeneral InquiriesÎncă nu există evaluări
- DR - Vijay Nagdev H.O. Medical Unit-IDocument24 paginiDR - Vijay Nagdev H.O. Medical Unit-IVijai KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 AntibioticsDocument144 pagini1 AntibioticsRhomizal MazaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Beta Lactam AntibioticsDocument31 paginiIntroduction To Beta Lactam AntibioticsVishaal BhatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antimicrobial AgentsDocument3 paginiAntimicrobial AgentsErnie G. Bautista II, RN, MD100% (2)
- Antibiotics Antiviral Antifungal Antimalarial Antiseptic & Disinfectant Agents Antiinflammatory & AntirheumaticDocument69 paginiAntibiotics Antiviral Antifungal Antimalarial Antiseptic & Disinfectant Agents Antiinflammatory & AntirheumaticNop PiromÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Wall Inhibitors - Pharmacology 3 - Frank SsengoobaDocument16 paginiCell Wall Inhibitors - Pharmacology 3 - Frank SsengoobaVhugala AudreyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antibacterial Drugs: B.K. SatriyasaDocument56 paginiAntibacterial Drugs: B.K. SatriyasaVicÎncă nu există evaluări
- AntibioticsDocument4 paginiAntibioticsVladimir GurjanovÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clinical Pharmacology - Rationale Behind Antibiotics PrescriptionDocument12 paginiClinical Pharmacology - Rationale Behind Antibiotics PrescriptionhalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Top 10 List of Antibiotic ClassesDocument10 paginiTop 10 List of Antibiotic ClassesZubair khanÎncă nu există evaluări
- ChemotherapyDocument66 paginiChemotherapyElias HaimanotÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmacology: Fast and Dirty Board ReviewDocument7 paginiPharmacology: Fast and Dirty Board ReviewRochelleth7278Încă nu există evaluări
- Antibiotics EssayDocument5 paginiAntibiotics EssayIshwarya JonathanÎncă nu există evaluări
- First Generation Ciprofloxacin (Cipro) : Cell Wall SynthesisDocument17 paginiFirst Generation Ciprofloxacin (Cipro) : Cell Wall SynthesisVAnh NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemotherapy: BY Professor Dr. Ahmed KhalilDocument29 paginiChemotherapy: BY Professor Dr. Ahmed KhalilSAYED ZAKIÎncă nu există evaluări
- COTRIMOXAZOLE +FQsDocument62 paginiCOTRIMOXAZOLE +FQsHussein AlhaddadÎncă nu există evaluări
- PharChm2 - TetracyclinesDocument9 paginiPharChm2 - TetracyclinesEdrick RamoranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Hunt: Larr Sumalpong N22Document11 paginiDrug Hunt: Larr Sumalpong N22Larr SumalpongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharma-URO-CYCLIC LIPOEPETIDES (Vancomycin)Document6 paginiPharma-URO-CYCLIC LIPOEPETIDES (Vancomycin)Hussein AlhaddadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Metronidazole: Mechanism of Antibacterial Action Is Unclear, But NeedsDocument60 paginiMetronidazole: Mechanism of Antibacterial Action Is Unclear, But NeedsmmydungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cirilo Albert Hicban RN, RM LecturerDocument50 paginiCirilo Albert Hicban RN, RM Lecturerrongan008Încă nu există evaluări
- AntibioticsDocument6 paginiAntibioticsCyrus100% (1)
- Infectious DiseaseDocument31 paginiInfectious DiseasemirunahorgaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Farmakologi Obat Kusta Dan Antiparasit 2015Document84 paginiFarmakologi Obat Kusta Dan Antiparasit 2015Alex FerdinandÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antibiotics F MCP 1Document37 paginiAntibiotics F MCP 1Mohamed ElraiyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rifampicin-An Overview: Available Online atDocument5 paginiRifampicin-An Overview: Available Online atyeseniasaviraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cernadas-2013-Pediatric Allergy and ImmunologyDocument7 paginiCernadas-2013-Pediatric Allergy and ImmunologyMoisés PonceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multidrug Therapy (MDT) or Polychemotherapy: Dapsone, Rifampicin and Clofazimine Are CombinedDocument4 paginiMultidrug Therapy (MDT) or Polychemotherapy: Dapsone, Rifampicin and Clofazimine Are CombinedAnonymous Au0vHUÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Name Drug Interactions Nursing ConsiderationsDocument4 paginiDrug Name Drug Interactions Nursing ConsiderationsPagodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antituberculous Therapy in Special SituationsDocument8 paginiAntituberculous Therapy in Special SituationsMobeen Raza100% (1)
- TestBank Lewis Medical Surgical Nursing 11th 2020.pdf-282-305Document24 paginiTestBank Lewis Medical Surgical Nursing 11th 2020.pdf-282-305هدوء النسمةÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Food InteractionsDocument22 paginiDrug Food InteractionsPratiwi TiwiÎncă nu există evaluări
- TYRX BrochureDocument28 paginiTYRX Brochureleo chiuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microbiology, Infections, and Antibiotic Therapy: Elizabeth J. Rosen, MD Francis B. Quinn, MD March 22, 2000Document86 paginiMicrobiology, Infections, and Antibiotic Therapy: Elizabeth J. Rosen, MD Francis B. Quinn, MD March 22, 2000skmvicky1483Încă nu există evaluări
- LAMOTRIGINEDocument9 paginiLAMOTRIGINEDiffa RahmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antimycobacterials and AntiviralsDocument65 paginiAntimycobacterials and AntiviralsAndile MoloiÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Review of Current Practices in Periprosthetic Joint Infection Debridement and Revision ArthroplastyDocument12 paginiA Review of Current Practices in Periprosthetic Joint Infection Debridement and Revision ArthroplastyCleff FlowersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antituberculosis DrugsDocument31 paginiAntituberculosis DrugsF ParikhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Myrin P ForteDocument3 paginiMyrin P ForteJohn Zedric Villanueva ArciagaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Citing and Referencing Harvard StyleDocument34 paginiCiting and Referencing Harvard Stylekundayi shavaÎncă nu există evaluări
- National Leprosy Eradication Programme (Nlep)Document34 paginiNational Leprosy Eradication Programme (Nlep)Balaji KrishnanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data Pasien TB JuliDocument42 paginiData Pasien TB JuliTsubbatun NajahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Look For The Drug-Drug Interaction of The Following Drugs Given and Give Nursing Considerations As You Give The Drugs TogetherDocument2 paginiLook For The Drug-Drug Interaction of The Following Drugs Given and Give Nursing Considerations As You Give The Drugs TogetherLa CartaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Management of TB in Primary CareDocument49 paginiManagement of TB in Primary CareMonysyha AtriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of Tuberculosis: An Update Review: Pharmatutor January 2018Document8 paginiPathophysiology of Tuberculosis: An Update Review: Pharmatutor January 2018Michael HusainÎncă nu există evaluări
- NitrosaminesDocument31 paginiNitrosaminesJaya AbrahamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mycobacteria: Nocardia, Rhodococcus, Tsukamurella and GordoniaDocument7 paginiMycobacteria: Nocardia, Rhodococcus, Tsukamurella and Gordonia20C – Gorospe, Rhai Chezka V.Încă nu există evaluări
- MID 3 PHARMA Chemotherapeutic AgentsDocument85 paginiMID 3 PHARMA Chemotherapeutic AgentsMariah Angela PinedaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antimycobacterial DrugsDocument35 paginiAntimycobacterial DrugsJunah SeninaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2: Transmission and Pathogenesis of TuberculosisDocument26 paginiChapter 2: Transmission and Pathogenesis of TuberculosisMajd Ahmad Abdel RahimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Treatment of TB in Adults: by Dr. Irfhan Ali Hyder AliDocument45 paginiTreatment of TB in Adults: by Dr. Irfhan Ali Hyder AliInspireGutsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharm ReviewDocument14 paginiPharm ReviewangieswensonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antibiotics &anti-Infective AgentsDocument39 paginiAntibiotics &anti-Infective AgentsKC PalattaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- TB Hiv CoinfectionDocument29 paginiTB Hiv CoinfectionVinobhachowdary DondapatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Farmakologi Obat Kusta Dan Antiparasit 2015Document84 paginiFarmakologi Obat Kusta Dan Antiparasit 2015Alex FerdinandÎncă nu există evaluări