Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
CT Assignment I
Încărcat de
mosesalvinDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
CT Assignment I
Încărcat de
mosesalvinDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Dept of Electrical &Electronics Engineering Assignment I I Year EE
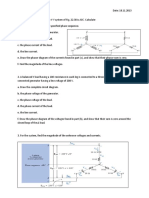
KRICHOFFS LAW
OHMS LAW 1). For the network of Fig 1 a. Find the currents I and I6. b. Find the voltages V1 and V5. c. Find the power delivered to the 6 k resistor
4). Using branch-current analysis, find the current through each resistor for the networks of Fig. 4. The resistors are all standard values
2). For the series-parallel network of Fig. 2 a. Find the current I. b. Find the currents I3 and I9. c. Find the current I8. d. Find the voltage Vab
5). For the networks of Fig.5, determine the current I2 using branch-current analysis, and then find the voltage Vab.
3). For the network of Fig. 3 a. Determine the current I1. b. Calculate the currents I2 and I3. c. Determine the voltage levels Va and Vb.
6). For the networks of Fig.5, determine the current I2 using branch-current analysis, and then find the current through 5 resistor
Figure 3 MESH CURRENT ANALYSIS
networks of Fig. 7). Write the mesh equations for each of the networks of Fig.6 solve for the loop currents in each network. Use clockwise mesh currents
8). Write the mesh equations for each of the networks of Fig.6 solve for the loop currents in each network. Use clockwise mesh currents
12). Determine the nodal voltages for the networks of Fig.
STAR-DELTA TRANSFORMATION 9). For the networks of Fig., determine the current I2 using mesh-current analysis, and then find the voltage across 5 resistor 13).Using STAR-DELTA transformation, find the current I
NODE VOLTAGE ANALYSIS 10). Determine the nodal voltages for the networks of Fig.
11). Determine the nodal voltages for the
THEVENINS THEOREM AND NORTONS THEOREM 15, Using Thevenins Theorem and Nortons theorem, find its equivalent circuit to find the current passing through the load resistance
SUPER POSITION THEOREM 14). Using the principle of superposition, find the current I2 through the 12-k resistor of Fig.
16, Using Thevenins Theorem and Nortons theorem, find the current through 6 resistor
17, Using Thevenins Theorem and Nortons theorem, find its equivalent circuit
MAXIMUM POWER TRANSFER THEOREM 18, Find the unknown value of resistance R if maximum power is transferred. What is the maximum power/
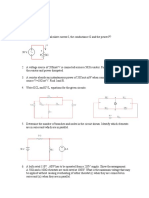
TWO MARK QUESTIONS 1. State Ohms law. 2. State Kirchhoffs voltage law. 3. State Kirchhoffs Current law. 4. Mention the limitations of Ohms Law. 5. Give two applications of both series and parallel combination. 6. State two salient points of a series combination of resistance. 7. State two salient points of a parallel combination of resistance. 8. Explain how voltage source with a source resistance can be converted into an equivalent current source. 9. Define an ideal voltage source. 10. Define an ideal current source. 11. Name the four different types of dependent sources in electric circuits. 12. What is meant by Unilateral and bilateral element? 13. What is meant by linear and nonlinear elements? 14. What is meant by active and Passive elements? 15. State Superposition theorem. 16. State Thevenins theorem. 17. State Nortons theorem. 18. State Maximum power transfer theorem. 19. State reciprocity theorem. 20. Three resistors Rab, Rbc and Rca are connected in STAR. Write the expression for resistors in equivalent DELTA. 21. Three resistors Rab, Rbc and Rca are connected in delta. Write the expression for resistors in equivalent star. 22. Give the limitations of using Superposition theorem. 23. Write some applications of Maximum power transfer theorem. 24. Define the current division rule. 25. Write the voltage division rule.
RECIPROCITY THEOREM 19, Verify the Reciprocity Theorem for the given circuits/
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Dynamics 13esi Solutions Manual c19 PDFDocument57 paginiDynamics 13esi Solutions Manual c19 PDFNkoshiEpaphrasShoopalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- A History of Network Synthesis and Filter Theory For Circuits Composed of Resistors, Tors and CapacitorsDocument10 paginiA History of Network Synthesis and Filter Theory For Circuits Composed of Resistors, Tors and Capacitorsdadado98Încă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Numerical Electrostatics Using MATLABDocument2 paginiIntroduction To Numerical Electrostatics Using MATLABrxavierva0% (1)
- Noise Generation in Dynamic Wireless Power TransferDocument4 paginiNoise Generation in Dynamic Wireless Power TransferChristian DavidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pages From (Monson Hayes) Schaum S Outline of Digital SignalDocument7 paginiPages From (Monson Hayes) Schaum S Outline of Digital SignalMhmdÁbdóÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 1,2,3,4 ControlDocument23 paginiLab 1,2,3,4 ControlKathlyn Yanguez100% (1)
- Polyphase System QUESTIONDocument5 paginiPolyphase System QUESTIONmaruf048Încă nu există evaluări
- Modelling and Control of A Gas Pressure Reduction SystemDocument339 paginiModelling and Control of A Gas Pressure Reduction SystemErick Renzo Hidalgo OrtegaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab1 VHDLDocument9 paginiLab1 VHDLGautam GowdaÎncă nu există evaluări
- POWER ELECTRONICS DEVICES AND CIRCUITSDocument111 paginiPOWER ELECTRONICS DEVICES AND CIRCUITSnazibÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Twisting Tennis RacketDocument19 paginiThe Twisting Tennis RacketCarlos Daniel ArmentaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cap 13 PDFDocument140 paginiCap 13 PDFRicardo LimaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fourier Transform PairsDocument5 paginiFourier Transform PairsSwati100% (1)
- Magnetically Coupled Circuits PDFDocument21 paginiMagnetically Coupled Circuits PDFOrlando100% (1)
- Important PhasorsDocument22 paginiImportant PhasorsRaturi DeepankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mathmetical Problem Series-ParallelDocument5 paginiMathmetical Problem Series-ParallelKamrul HassanÎncă nu există evaluări
- ET Tut2 Ans AUT2016-17Document6 paginiET Tut2 Ans AUT2016-17Tirumala Rao Yalla100% (1)
- Solution Sheet 2 Electronic CircuitsDocument15 paginiSolution Sheet 2 Electronic CircuitsWajdi BELLILÎncă nu există evaluări
- Boletín Cepre Uni 2020-Ii (Aritmética) PDFDocument41 paginiBoletín Cepre Uni 2020-Ii (Aritmética) PDFdavidÎncă nu există evaluări
- LCR Lab ReportDocument5 paginiLCR Lab ReportBen BrownÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assigment EPSD Lab PDFDocument5 paginiAssigment EPSD Lab PDFArjit AgarwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- UlabyISMCh08Document55 paginiUlabyISMCh08Filipe GalizaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ucd: Physics 9C - Electricity and Magnetism: Tom WeidemanDocument173 paginiUcd: Physics 9C - Electricity and Magnetism: Tom WeidemanEuler Portilla CarrascoÎncă nu există evaluări
- FM 3e SM Chap06Document96 paginiFM 3e SM Chap06raees ahmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- 15A04403 Electromagnetic Theory & Transmission LinesDocument2 pagini15A04403 Electromagnetic Theory & Transmission LinesRadhika MahankaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Newman FormulaDocument6 paginiNewman Formulaearla10050% (1)
- Numerical Methods Final Requirements ShshsiwzbDocument10 paginiNumerical Methods Final Requirements ShshsiwzbIñigo Carlos AquinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Fiolhais, M.C.N. Et Al.) A Variational Proof of Thomson's TheoremDocument3 pagini(Fiolhais, M.C.N. Et Al.) A Variational Proof of Thomson's Theoremlev76Încă nu există evaluări
- DC Motor Transfer Functions ExplainedDocument4 paginiDC Motor Transfer Functions ExplainedKareem AbouelwafaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Newton 2nd law method (work and energy equation) RectilinearDocument9 paginiNewton 2nd law method (work and energy equation) Rectilineardaniel hambissaÎncă nu există evaluări
- BÀI TẬP VẬT LÝ 3Document13 paginiBÀI TẬP VẬT LÝ 3Trung NamÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE3251 Electric Circuit Analysis Lesson PlanDocument6 paginiEE3251 Electric Circuit Analysis Lesson PlanrajalakshmiÎncă nu există evaluări
- LCA - Mesh & Nodal Analysis ProblemsDocument5 paginiLCA - Mesh & Nodal Analysis ProblemsMaaz SaleemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cap 14 PDFDocument182 paginiCap 14 PDFRicardo Lima100% (1)
- CHAN Chhenghong (E20150030) PDFDocument5 paginiCHAN Chhenghong (E20150030) PDFCHAN ChhenghongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electric Power Engineering Lecture NotesDocument209 paginiElectric Power Engineering Lecture NotesRaj Boda0% (1)
- 250 WATT Power Inverter: Power Small Appliances From Your Car or Any Other 12-Volt Source With Our 250-Watt InverterDocument3 pagini250 WATT Power Inverter: Power Small Appliances From Your Car or Any Other 12-Volt Source With Our 250-Watt Invertertaner56Încă nu există evaluări
- Control Systems Assignment: Steady-State Error, Sensitivity & ResponseDocument3 paginiControl Systems Assignment: Steady-State Error, Sensitivity & Responseritesh sunithaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment # 1: P-N Junction Diode: TheoryDocument9 paginiExperiment # 1: P-N Junction Diode: Theorypoonginithi040% (1)
- Hall Effect PDFDocument32 paginiHall Effect PDFFachni RosyadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- TTL Ic 7448Document3 paginiTTL Ic 7448haseeb ahmad ch.0% (1)
- Course Code Course Name Course Structure Ececc05 Signal and Systems 3-1-0 L-T-PDocument2 paginiCourse Code Course Name Course Structure Ececc05 Signal and Systems 3-1-0 L-T-PSuvdeep NayakÎncă nu există evaluări
- BJT Equivalent Circuit ModelsDocument6 paginiBJT Equivalent Circuit ModelshasnaintoahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ec6303 - Ss QB (Part - A & B) 2Document10 paginiEc6303 - Ss QB (Part - A & B) 2Maheshwaran MahiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mini-Quiz Documents on Oscillations and WavesDocument11 paginiMini-Quiz Documents on Oscillations and WavescmegmhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solved: Find Vo in Fig. E8.21 using mesh analysisDocument5 paginiSolved: Find Vo in Fig. E8.21 using mesh analysis20280110Încă nu există evaluări
- Fast Calculation of A Voltage Stability IndexDocument11 paginiFast Calculation of A Voltage Stability IndexphieuxuatkhoÎncă nu există evaluări
- LM7805 Voltage RegulatorDocument5 paginiLM7805 Voltage RegulatorDeepak SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Proposed 15 Numerical Problems For PresentationDocument8 paginiProposed 15 Numerical Problems For PresentationalexÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE201 Electric Circuit Analysis Question BankDocument14 paginiEE201 Electric Circuit Analysis Question BankFLOWERÎncă nu există evaluări
- Question Bank Basic Electrical & Electronics Engineering ElectricalDocument9 paginiQuestion Bank Basic Electrical & Electronics Engineering Electricalcsvtu notesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Question Bank BeeDocument25 paginiQuestion Bank Beedhruv goraiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Question Bank On Unit IDocument4 paginiQuestion Bank On Unit IanupamÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE 1151 Circuit Theory Question BankDocument19 paginiEE 1151 Circuit Theory Question BankVIVEK AHLAWATÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iae 1 Important QuestionsDocument4 paginiIae 1 Important Questionssuresh270Încă nu există evaluări
- Ee6201 CT U1 5 QBDocument10 paginiEe6201 CT U1 5 QBsakilakumaresanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 1 For CircuitsDocument4 paginiAssignment 1 For CircuitsAmir EyniÎncă nu există evaluări
- BEE New Important QuestionsDocument9 paginiBEE New Important Questionsaraq3501Încă nu există evaluări
- Na Question BankDocument13 paginiNa Question BankkrishmkeeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eca QB Mid 1Document5 paginiEca QB Mid 1Dr. ARUNA BHARATHI M GCETÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aptitude QuestionsDocument9 paginiAptitude QuestionsmosesalvinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Candidate CodeDocument5 paginiCandidate CodemosesalvinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maths Q ODocument4 paginiMaths Q OmosesalvinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aptitude QuestionsDocument9 paginiAptitude QuestionsmosesalvinÎncă nu există evaluări
- EC 46, Control System Unit IV - Assignment Stability AnalysisDocument2 paginiEC 46, Control System Unit IV - Assignment Stability AnalysismosesalvinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power ElectronicsDocument31 paginiPower ElectronicsmosesalvinÎncă nu există evaluări
- 127639-231211-AC Lap Single FullDocument9 pagini127639-231211-AC Lap Single FullmosesalvinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Emergency CallDocument6 paginiEmergency CallNugrohoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Variable Frequency Drive Using IR215xDocument7 paginiVariable Frequency Drive Using IR215xartyomÎncă nu există evaluări
- Novajet Refference GuideDocument74 paginiNovajet Refference GuideoralbnetworkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mktech Is1-19Hd & Receptor: Receptor PVR de Satelit Si Semnal Terestru Raport de TestareDocument7 paginiMktech Is1-19Hd & Receptor: Receptor PVR de Satelit Si Semnal Terestru Raport de TestareAlexander WieseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ball MillsDocument8 paginiBall MillsBoy Alfredo PangaribuanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Narayana 10 01 24 SR Star Co Scmodel A, B&C Jee Main GTM 12n Key&sDocument10 paginiNarayana 10 01 24 SR Star Co Scmodel A, B&C Jee Main GTM 12n Key&sReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- CRSP ManualDocument140 paginiCRSP ManualCarlos Andrés Buenahora BallesterosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cat 120H, 12H, 140H, 143H, 160H, 163H TransmisiónDocument8 paginiCat 120H, 12H, 140H, 143H, 160H, 163H TransmisiónJefferson Maldonado.Încă nu există evaluări
- Verilog Interview Questions & AnswersDocument6 paginiVerilog Interview Questions & AnswersKrishna Saroja SankaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Emp2 Box Pressure TransmitterDocument8 paginiEmp2 Box Pressure TransmitterAsif HameedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced clutter options for radio propagation modelingDocument40 paginiAdvanced clutter options for radio propagation modelingLaura VillarrealÎncă nu există evaluări
- Baja Parts Catalog PX250S Motorcycle VIN Prefix LUAHDocument20 paginiBaja Parts Catalog PX250S Motorcycle VIN Prefix LUAHholycostÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evaporative Pre CoolerDocument46 paginiEvaporative Pre CoolerLizbeth Ramirez AlanyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CNA09016 SGDocument8 paginiCNA09016 SGSatyarth SampathÎncă nu există evaluări
- 06 - 1 Cutting Tools - 2013 - LRDocument17 pagini06 - 1 Cutting Tools - 2013 - LRBaggerkingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zimbabwe Engineer ITDG Small Scale Production of Fired Clay BricksDocument8 paginiZimbabwe Engineer ITDG Small Scale Production of Fired Clay BricksdkataleÎncă nu există evaluări
- MET312 Non Destructive Testing SyllabusDocument8 paginiMET312 Non Destructive Testing SyllabusHARI KRISHNANÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digital Logic DesignDocument4 paginiDigital Logic DesignkiranÎncă nu există evaluări
- d-Copia3500MF 4500MF 5500MFsmY113351-4Document1.051 paginid-Copia3500MF 4500MF 5500MFsmY113351-4ctecisbÎncă nu există evaluări
- SPINTRONICSDocument33 paginiSPINTRONICSSyam Pradeep ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- DESIGN II - ChemTran General Reference GuideDocument332 paginiDESIGN II - ChemTran General Reference GuideDebabrata MitraÎncă nu există evaluări
- NOX Reduction EPADocument399 paginiNOX Reduction EPApartha6789Încă nu există evaluări
- SANTO 72358 KA3: Electronic RefrigeratorDocument32 paginiSANTO 72358 KA3: Electronic RefrigeratorSakthipriya JeganathanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Troubleshoot Microlab 600 DiluterDocument3 paginiTroubleshoot Microlab 600 DiluterAkmal RakhmadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Axle, Front - Differential and Carrier - Jee0123251Document3 paginiAxle, Front - Differential and Carrier - Jee0123251Husi NihaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brandt M FR Btd500blnDocument74 paginiBrandt M FR Btd500blnStéphane JoussetÎncă nu există evaluări
- Environmental Quality Control of Emission From Diesel Engines Regulations 1996 - P.U.a 429-96Document22 paginiEnvironmental Quality Control of Emission From Diesel Engines Regulations 1996 - P.U.a 429-96scribdledeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Online Quiz System DocumentationDocument92 paginiOnline Quiz System DocumentationSultan Aiman100% (1)
- Multi-disciplinary profile of IS/IT outsourcing researchDocument47 paginiMulti-disciplinary profile of IS/IT outsourcing researchIsabel MirandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ASTM E92-17 Standard Test Methods For Vickers Hardness and Knoop Hardness of Metallic MaterialsDocument27 paginiASTM E92-17 Standard Test Methods For Vickers Hardness and Knoop Hardness of Metallic MaterialsCarlos Pinto Pradilla88% (8)