Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Type of Incisions
Încărcat de
Chelzea ObarDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Type of Incisions
Încărcat de
Chelzea ObarDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
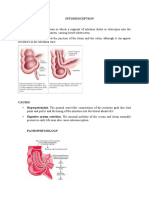
TYPE OF INCISIONS ABDOMINAL INCISIONS: Vertical incision : Midline incision Paramedian incision Transverse and oblique incisions : Kocher's
9;s subcostal Incision
INDICATION/OPERATIONS General access, exploratory laparotomy
Exposure of the upper part of the abdominal cavity, intraumbilical, lower abdomen and pelvis Biliary or hepatic procedures. May be extended across to a left subcostal incision to give useful access to the stomach and pancreas. In newborns and infants, this incision is preferred,because more abdominal exposure is gained per length of the incision than with vertical exposure because the infants abdomen has a longer transverse than vertical girth. This is also true of short, obese adults, in whom transverse incision often affords a better exposure Appendicectomy,cecostomy Access to sigmoid colon and pelvis, particularly if the midline is very scarred from previous surgery. Access to bladder, uterus, Fallopian tubes and ovaries. Good cosmetic result but gives no access outside the pelvis. To expose the lower end of esophagus. Ex:esophagogastric resection for carcinoma Wide exposure to of the upper abdomen and thorax used to expose the anterior cranial vault, the forehead, and the upper and middle regions of the facial skeleton.
Transverse Muscle dividing incision
Mc Burneys Grid iron or muscle spliting incision Oblique Muscle cutting incision Pfannenstiel incision Abdominothoracic incision
HEAD INCISIONS Bicoronal incision
INCISIONS OF THE EXTREMETIES: Smith Peterson approach. - Schaubel Modification
Provides exposure to hip joint,ileum Indications
open reduction of congenital hip dislocations, synovial biopsies, intra-articular fusions, excision of pelvis tumors, pelvic osteotomies
. Posterior Approach to the Acetabulum (KocherLangenbach)
Provides exposure to o posterior wall of acetabulum o posterior column of acetabulum Indications
posterior wall, posterior column , posterior wall and posterior column, simple transverse (patient prone)
Watson Jones approach
Provides exposure to acetabulum, proximal femur
Indications Hemiarthroplasty, ORIF of femoral neck fxs, synovial biopsy of hip, biopsy of femoral neck
INCISION OF THE SPINE: Anterior Approach to Cervical Spine
Exposes anterior vertebral bodies from C3 to T1 Indications excision of herniated discs, interbody fusion, removal of osteophytes from uncinate processes, excise tumors, debride osteomyelitis and drain abscesses
Retroperitoneal (Anterolateral) Approach to the Lumbar Spine
Can access L1 to sacrum o slightly more difficult to reach L5-S1 disk space than transperitoneal approach o bifurcation of great vessels occur at L4-5 Indications Psoas abscess drainage (without risk of postoperative ileitits), Spinal fusion, Biopsy or resection of vertebral body, Disc
replacement, Exposure of sympathetic chain (general surgery)
ABDOMINAL INCISIONS
http://www.orthonurse.org/portals/0/wound%20closure%20manual.pdf
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- EMC Design Guide For PCBDocument78 paginiEMC Design Guide For PCBFaruq AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Abdomen: - DefinitionDocument27 paginiAcute Abdomen: - DefinitionWorku KifleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case 1 History & PEDocument3 paginiCase 1 History & PEcbac1990Încă nu există evaluări
- Lecture Contents: Definitions Composition of Hernia Managment of HerniaDocument26 paginiLecture Contents: Definitions Composition of Hernia Managment of Herniaissam_1994Încă nu există evaluări
- Neoplastic Diseases of The OvaryDocument61 paginiNeoplastic Diseases of The Ovaryea013Încă nu există evaluări
- Quiz 7. NCM 116 For StudentsDocument4 paginiQuiz 7. NCM 116 For StudentsZayne Lucas Gabrielle TadiamonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Operative Procedures: 1130 SRB's Manual of SurgeryDocument1 paginăOperative Procedures: 1130 SRB's Manual of SurgerymadhuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Essentials of Report Writing - Application in BusinessDocument28 paginiEssentials of Report Writing - Application in BusinessMahmudur Rahman75% (4)
- Urinary Tract InfectionsDocument44 paginiUrinary Tract Infectionstummalapalli venkateswara rao100% (2)
- Numerical Solution of Ordinary Differential EquationsDocument31 paginiNumerical Solution of Ordinary Differential Equationschandu3072002100% (1)
- 2015 Nutrition Diagnosis Terminologi 2015Document9 pagini2015 Nutrition Diagnosis Terminologi 2015Vivin Syamsul ArifinÎncă nu există evaluări
- TheSun 2008-11-04 Page16 Asian Stocks Rally Continues On Policy HopesDocument1 paginăTheSun 2008-11-04 Page16 Asian Stocks Rally Continues On Policy HopesImpulsive collectorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hirschprung DiseaseDocument9 paginiHirschprung DiseaseRajeev JhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 2-3 Part 1Document26 paginiWeek 2-3 Part 1EmpieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Audit AP TestsDocument3 paginiAudit AP TestsSweet Emme100% (1)
- Inguinal Hernias: CaseDocument6 paginiInguinal Hernias: Casechomz14Încă nu există evaluări
- Penetrating Abdominal Injury DiagnosisDocument3 paginiPenetrating Abdominal Injury DiagnosisRaquel ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fournier Gangrene Causes and AnatomyDocument16 paginiFournier Gangrene Causes and AnatomyAmirah Dahalan100% (1)
- Acute PeritonitisDocument4 paginiAcute PeritonitisSatrio Tri HadmokoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clinical Practice Guidelines: Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media in AdultsDocument28 paginiClinical Practice Guidelines: Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media in Adultsnanu-jenuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Incision Location Indications Advantages DisadvantagesDocument1 paginăIncision Location Indications Advantages Disadvantageskeish193Încă nu există evaluări
- Mamiek Dwi Putro Departemen / SMF Ilmu Bedah FK Unair / RSU DR Soetomo SurabayaDocument38 paginiMamiek Dwi Putro Departemen / SMF Ilmu Bedah FK Unair / RSU DR Soetomo SurabayamasmblinkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy and Physiology of Small and Large Intestines, Rectum and AnusDocument24 paginiAnatomy and Physiology of Small and Large Intestines, Rectum and AnusElmer PatrickÎncă nu există evaluări
- CholelitiasisDocument42 paginiCholelitiasisEdwin YosuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- History of Old ClientDocument33 paginiHistory of Old ClientMuhammad Aamir100% (1)
- Assisting: Venous Cut DownDocument4 paginiAssisting: Venous Cut DownJimnah Rhodrick BontilaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abdominal HerniaDocument19 paginiAbdominal HerniaDhanya MathewÎncă nu există evaluări
- Management of Patients With Gastric and Duodenal DisordersDocument7 paginiManagement of Patients With Gastric and Duodenal DisordersintotheunknownÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abdominal Incision TypesDocument36 paginiAbdominal Incision TypesMiftah AjiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fistula in AnoDocument21 paginiFistula in AnoHannah LeiÎncă nu există evaluări
- ORIF Radius and Ulna ProcedureDocument7 paginiORIF Radius and Ulna ProcedurealcojonicÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4-Conservative Treatment FX, CastingDocument53 pagini4-Conservative Treatment FX, CastingMuhammad TaqwaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pyogenic MeningitisDocument46 paginiPyogenic MeningitisShahnaaz ShahÎncă nu există evaluări
- OMCDocument37 paginiOMCyurie_ameliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydrocephalus and Spina Bifida: Pathophysiology, Clinical Presentation and ManagementDocument63 paginiHydrocephalus and Spina Bifida: Pathophysiology, Clinical Presentation and ManagementAjeng Aristiany Rahawarin100% (2)
- Total Abdominal HysterectomyDocument19 paginiTotal Abdominal HysterectomyMeidina Rachma Amanda100% (1)
- Conization of CervixDocument4 paginiConization of Cervixdrnareshkumar3281Încă nu există evaluări
- Gastric Outlet Obstruction: Its Surgical ManagementDocument40 paginiGastric Outlet Obstruction: Its Surgical ManagementGudeta shegerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intestinal Atresia and StenosisDocument7 paginiIntestinal Atresia and StenosisMichael NafarinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bartholin's Gland Cysts/Abscesses: Causes, Symptoms and Surgical TreatmentsDocument6 paginiBartholin's Gland Cysts/Abscesses: Causes, Symptoms and Surgical TreatmentsJane NathaniaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Common Surgical Instruments ModuleDocument5 paginiCommon Surgical Instruments ModuleAlokKumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- mhGAP Humanitarian Intervention Guide (mhGAP-HIG) - English VersionDocument68 paginimhGAP Humanitarian Intervention Guide (mhGAP-HIG) - English VersionПламен МинчевÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 PeritonitisDocument26 pagini1 PeritonitisGizachew AsimareÎncă nu există evaluări
- Preoperative Care Guide for SurgeonsDocument33 paginiPreoperative Care Guide for SurgeonsPrincewill SeiyefaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rare Kidney Cancer in ChildrenDocument12 paginiRare Kidney Cancer in ChildrenKath CamachoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ovarian CancerDocument15 paginiOvarian CancerAlmasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Etiology and Diagnosis of Bile Duct StonesDocument8 paginiEtiology and Diagnosis of Bile Duct Stoneskuncupcupu1368Încă nu există evaluări
- Hiatal Hernia: BY MR, Vinay KumarDocument27 paginiHiatal Hernia: BY MR, Vinay KumarVinay KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHOLELITHIASISDocument19 paginiCHOLELITHIASISAnil DasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gastric Outlet Obstruction (Stenosis) : Lior Shlomov 1852Document8 paginiGastric Outlet Obstruction (Stenosis) : Lior Shlomov 1852Lior ShlomovÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shock: Rose Ann J. Raquiza-Perante Post Graduate InternDocument53 paginiShock: Rose Ann J. Raquiza-Perante Post Graduate InternRose Ann RaquizaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dermatological History and Examination PDFDocument5 paginiDermatological History and Examination PDFHesbon MomanyiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2019 Hernia Kuliah FKDocument50 pagini2019 Hernia Kuliah FKKhairani NurhamidahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Omphalocelevsgastroschisis 160810122732Document23 paginiOmphalocelevsgastroschisis 160810122732LNICCOLAIO100% (1)
- CAJA, RENZO GABRIEL, BSN 2-1 NCM109-Midterm ModuleDocument14 paginiCAJA, RENZO GABRIEL, BSN 2-1 NCM109-Midterm ModuleRenzo GabrielÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comprehensive Guide to Obstetrics and Gynecology History and Physical ExamsDocument3 paginiComprehensive Guide to Obstetrics and Gynecology History and Physical ExamsAgus WijayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gastric Outlet Obstruction (Soltan Aiman NeazyDocument49 paginiGastric Outlet Obstruction (Soltan Aiman NeazyMohammed ElhashimiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Surgical Anatomy of the Stomach and DuodenumDocument75 paginiSurgical Anatomy of the Stomach and DuodenumMohamoud MohamedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chronic Suppurative Otitis MediaDocument6 paginiChronic Suppurative Otitis MediaSuhas IngaleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Procedural ReportDocument14 paginiProcedural ReportiamcharraeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gastrointestinal System: Miranda KhidesheliDocument155 paginiGastrointestinal System: Miranda KhidesheliTanmay NainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abdominal Trauma Signs, Symptoms and Nursing CareDocument24 paginiAbdominal Trauma Signs, Symptoms and Nursing CareSurgeryClassesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shaafi Medical College Obstetrics GuideDocument39 paginiShaafi Medical College Obstetrics Guidemustafe omarÎncă nu există evaluări
- INTUSSUSCEPTIONDocument3 paginiINTUSSUSCEPTIONS GÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zollinger EllisonDocument2 paginiZollinger EllisonFrama Intan MiguelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tissue Handling and Wound Closure IIDocument12 paginiTissue Handling and Wound Closure IIChelzea ObarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transpo Case DigestsDocument5 paginiTranspo Case DigestsChelzea ObarÎncă nu există evaluări
- IPL Digest Del RosarioDocument2 paginiIPL Digest Del RosarioChelzea ObarÎncă nu există evaluări
- IPL Digest Del RosarioDocument2 paginiIPL Digest Del RosarioChelzea ObarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Proforma Invoice: DescriptionDocument3 paginiProforma Invoice: Descriptionanon-690278Încă nu există evaluări
- Or Medallist Results WorldSkills Scale and 100 ScaleDocument39 paginiOr Medallist Results WorldSkills Scale and 100 ScaleJoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adjectives Weekly Plan1Document10 paginiAdjectives Weekly Plan1RItta MariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Canary TreatmentDocument117 paginiCanary TreatmentRam KLÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alarm Management Second Ed - Hollifield Habibi - IntroductionDocument6 paginiAlarm Management Second Ed - Hollifield Habibi - IntroductionDavid DuranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3-The Hospitality & Travel Marketing SystemDocument14 paginiChapter 3-The Hospitality & Travel Marketing SystemCharis AbadÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2004 Canon Bino BrochureDocument6 pagini2004 Canon Bino BrochureCraig ThompsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Arsh Final Project ReportDocument65 paginiArsh Final Project Report720 Manvir SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nigerian Romance ScamDocument10 paginiNigerian Romance ScamAnonymous Pb39klJÎncă nu există evaluări
- CM - Scope of ServicesDocument3 paginiCM - Scope of ServicesMelvin MagbanuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Laptop repair messageDocument3 paginiLaptop repair messagePonpes Manbaul MaarifÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cases 39 45 PDFDocument11 paginiCases 39 45 PDFYvette Marie VillaverÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eurapipe ABS Pipe - Fittings ManualDocument52 paginiEurapipe ABS Pipe - Fittings ManualLê Minh ĐứcÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test Engleza 8Document6 paginiTest Engleza 8Adriana SanduÎncă nu există evaluări
- Product 243: Technical Data SheetDocument3 paginiProduct 243: Technical Data SheetRuiÎncă nu există evaluări
- User Manual - Rev3Document31 paginiUser Manual - Rev3SyahdiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lehman BrothersDocument10 paginiLehman BrothersJaikishin RuprajÎncă nu există evaluări
- BS en 1044-1999 - Brazing Filler MetalsDocument26 paginiBS en 1044-1999 - Brazing Filler MetalsBorn ToSinÎncă nu există evaluări
- A-00 IndexDocument10 paginiA-00 IndexNizarHamrouniÎncă nu există evaluări
- 45 - Altivar 61 Plus Variable Speed DrivesDocument130 pagini45 - Altivar 61 Plus Variable Speed Drivesabdul aziz alfiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Audi A3 Audi A3 Audi A3 Audi A3 No. 2 / 1 No. 2 / 1 No. 2 / 1 No. 2 / 1Document18 paginiAudi A3 Audi A3 Audi A3 Audi A3 No. 2 / 1 No. 2 / 1 No. 2 / 1 No. 2 / 1Crisedu VasriÎncă nu există evaluări
- On-Chip ESD Protection Design For IcsDocument14 paginiOn-Chip ESD Protection Design For IcsMK BricksÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nidhi Investment Consultant: Magic Mix Illustration For Mr. AB Prafulbhai (Age 18)Document2 paginiNidhi Investment Consultant: Magic Mix Illustration For Mr. AB Prafulbhai (Age 18)jdchandrapal4980Încă nu există evaluări
- Compliance Risks and Controls: Speaker: Dott. Fabio AccardiDocument14 paginiCompliance Risks and Controls: Speaker: Dott. Fabio AccardiJefferson WidodoÎncă nu există evaluări